In this article we will study an important characteristic of the heart - its pulse with a frequency of 80 beats per minute.
The pulse is a mirror reflection of the work of the heart itself. That is, this is the frequency of narrowing of the artery walls in response to heart contractions or beats. Each age and sex group has its own normal indicators. Therefore, a pulse of 80 beats cannot specifically indicate increased or increased indicators, because everyone has their own standards, which largely depend on lifestyle. The number of strokes of 80 is the maximum medical limit. But is it really dangerous and what to do in this case, we will find out in this article.
Heart rate indicators
The first thing every person should know is that a rapid pulse is how many beats there are in one minute, as well as what the normal limits are.
It is known that medicine calls an absolutely normal pulse of 60-80 beats in 60 seconds. And what’s interesting is that the younger a person is, the more often he experiences such a rhythm.
Depending on age, the pulse should show the following numbers:
For reference! In newborn infants, the normal heart rate is 140 beats per minute; in children aged 3 years and older, it is 100 beats per minute. Accordingly, in adulthood, for example, at 45 years old, the norm will be 70 strokes.
Normal and increased heart rate
Normal pulse is 60-80 beats per minute. In older people it is about 60 beats, in young people the heart beats faster. In some cases, a pulse of more than 100 beats is considered normal. An elevated pulse occurs due to congenital physiological characteristics of the body.
The indicators for children also differ: 140 beats in newborns, and in young children it is at least 100 beats. Teenagers can experience rapid heartbeat when the body undergoes restructuring.
Indicators of normal heartbeat
Tachycardia can last from 15 minutes to several days. If the cause is overwork (mental or physical) or some other factors, then after they are eliminated, the work of the heart will stabilize. In this case, there is no danger for the development of cardiac pathologies.
However, a pulse of 130 beats per minute over a long period of time indicates the presence of serious heart problems. In severe situations, it is a harbinger of myocardial infarction. Therefore, if the heart activity increases, it is advisable to visit a cardiologist and assess all the risks associated with the pathological condition.
Causes of tachycardia
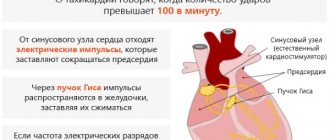
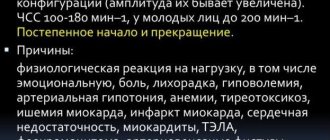
Tachycardia is an increased heart rate that occurs regularly . Moreover, the situation when in a person it is higher than 100-120 beats per minute can be observed from 15 minutes to several days in a row.
And the first thing to begin with the examination and treatment of such patients is to determine the reasons and factors why the pulse and heartbeat increase.
There are different reasons:
Physiological - a more harmless situation, which can be corrected in alternative ways.
It could be:
- excessive smoking of tobacco products;
- taking drugs;
- excessive coffee consumption;
- physical and nervous overstrain;
- intellectual loads;
- insomnia;
- temperature increase;
- taking drugs of a certain group;
- hot weather.
Pathological is a dangerous situation that can only be corrected by a medical specialist and competent treatment. It could be:
- vascular and heart diseases;
- blood diseases;
- presence of oncological tumors;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- endocrine disorders;
- severe infectious diseases.
Important! Diuretics, hormones, hypotensive drugs, nitrates, caffeine-containing or vagolytic agents, as well as sympathomimetics can provoke the development of tachycardia.
Reasons for violation
The causes of high heart rate in medicine are divided into physiological and pathological. Physiological is recognized as tachycardia, which occurs for a short time for subjective reasons and disappears after their elimination.
A physiological increase in heart rate begins as a result of:
smoking;- taking narcotic substances;
- drinking alcohol;
- coffee abuse;
- nervous or physical stress;
- mental overload;
- elevated temperature;
- insomnia;
- taking certain medications;
- too hot weather.
When the pulse is constantly significantly higher than normal, then we can talk about pathological processes in the heart. Usually its increase to 130 beats indicates the development of:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- blood diseases;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- oncology;
- endocrine problems;
- infectious diseases.
Satellites of tachycardia include weakness, a feeling of pulsation in large vessels, a strong heartbeat, and ringing in the ears. When the heart is overloaded, the vision begins to darken, and the body is covered in cold, sticky sweat. If treatment is not promptly applied, the following may develop:
- stroke;
- acute ventricular failure;
- cardiac asthma;
- arrhythmic shock.
Consequences of increased heart rate
A pulse of 130 beats or more - is this normal or is it still dangerous?
The doctor will definitely notify him of the consequences of this condition.
Prolonged tachycardia can lead to the development of complex diseases, such as:
- arrhythmic shock;
- stroke;
- cerebral ischemia;
- thromboembolism;
- cardiac asthma;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- decreased immunity;
- acute ventricular failure.
An accelerated heart rate of 130 beats indicates certain risks, such as heart overload.
Which will sooner or later lead to its wear. The condition is accompanied by insufficient blood circulation and oxygen starvation, which will cause other organs and the brain to suffer.
Risks and consequences of tachycardia
A pulse of 130 creates the danger of rapid wear and tear of the heart, which is working under overload. This leads to the development of serious diseases of the cardiac and vascular systems.
Insufficient blood circulation, which occurs over a long period of time, leads to diseases of other organs. This happens because the oxygen in the blood does not reach the body's systems in sufficient quantities.
As a result, the brain and other organs suffer. Cerebral ischemia, various disorders in the endocrine system and other diseases develop that rapidly develop and lead to death.
As a result of impaired blood flow, red blood cells sometimes begin to break down and the ability of blood to clot is impaired. As a result, clots form that clog the blood vessels. Thromboembolism develops. Blood clots are localized in different areas. The cells of the body suffer from hypoxia. The combination of thromboembolism with an increased pulse is an explosive mixture. Trophic ulcers, stroke, and cardiac arrest may develop.
If the pulse rate increases during coronary artery disease, the myocardial muscle consumes oxygen in huge doses. The cardiac output is disrupted and hypoxia develops. Oxygen starvation provokes tissue death in the myocardium, which leads to stroke.
Ischemic stroke
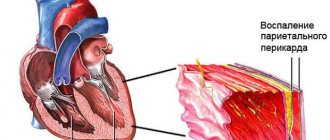
With prolonged tachycardia, insufficiency develops in the ventricles of the heart, resulting in a disturbance in the large blood vessels of the valves. Blood does not enter the general circulation. Blood pressure begins to drop sharply, leading to cardiac shock, which carries a risk of death.
As a result of lack of oxygen, pulmonary edema and fibrillation sometimes develop, which can also cause death. The patient constantly loses consciousness, resulting in injuries.
A constant lack of oxygen in the blood provokes a disruption of metabolic processes in the body and a decline in immunity. The patient easily picks up any infections, which, in turn, aggravate the situation.
Pathological tachycardia is an extremely dangerous sign. It indicates that a person has a serious heart condition.
If attacks occur periodically, this indicates that the disease is developing in the initial stage. Don't delay visiting a cardiologist.
The main consequences of tachycardia are:
- development of heart failure;
- cardiac conduction disturbance;
- ischemic stroke;
- rapid wear and tear of the heart muscles;
- persistent oxygen starvation of the whole body;
- cardiac asthma;
- the onset of death.
Clinical picture of tachycordia
In order to promptly diagnose an attack of tachycardia, it is important to know the first and characteristic signs of this condition.
They are the following manifestations:
- darkness in the eyes;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- prostration;
- lightheadedness or fainting.
Prevention of tachycordia
If tachycardia regularly makes itself felt, you should resort to a number of manipulations to stop the attack. In some cases, it will be necessary to provide primary medical care to the patient to stabilize the heart.
If an increase in heart rate occurs during physiological tachycardia, it is possible, by taking certain preventive measures, to stop the attack and thereby alleviate the patient’s condition.
Doctors recommend lying down for a while and trying to relax. The heart will calm down and the signs of tachycardia will disappear.
If this doesn't help, you should try this exercise:
- Inhale, tense your muscles, hold your breath, exhale and relax.
- Repeat several times until your heart calms down.
The purpose of the exercise is to activate the parasympathetic system. Its main carrier is the vagus nerve. By straining it, we stabilize the pulse.
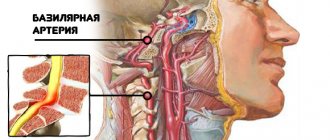
Massaging the carotid artery helps a patient stop an incipient attack of tachycardia. It is necessary to apply light pressure with your fingertips on the neck area under the lower jaw. If you inadvertently put more pressure on the artery, you may faint.
Cold water will also help prevent an attack of tachycardia. You need to put it in a basin and immerse your face in water for one minute. Cold will help relax the heart and stabilize its functioning.
How to quickly reduce your heart rate to 80 beats at home?
If a pulse of 80 beats is not considered normal for you and arose spontaneously, then you should perform a number of certain actions:
- Stop temporarily physical or any other work
- Unbutton your collar or loosen your clothing at the neck area
- Take a comfortable position and try to relax
- Take a soothing drink or an hour with chamomile, lemon balm, mint and honey, as well as black currant
- If you feel that your general condition is worsening, then you should call a doctor. Emergency situations include symptoms such as chest pain, severe dizziness, numbness in the fingers and panic.
A pulse of 80 beats is not a critical limit for taking medications!
If necessary, your doctor may prescribe medications to lower your heart rate. Beta blockers and calcium antagonists are commonly used. They act differently in the blood vessels and heart, thereby helping to reduce heart rate and blood pressure.
As a rule, they are used primarily in patients with arterial hypertension and concomitant high pulse. In people with high blood pressure and a normal heart rate, these drugs may cause your heart rate to drop sharply. Drugs of both groups are rarely prescribed only to reduce heart rate.
Facilities
Treatment for high heart rate
A rapid pulse in men and women above 100 beats per minute can develop at any time of the day. This can happen day or night, during nervous shocks or at rest.
What this means can only be determined by the attending physician. First, you can provide first aid to the victim.
It is as follows:
- providing the patient with bed rest and rest;
- deep breaths for patients, holding their breath, generally measured deep breathing;
- performing simple breathing exercises, which consists of taking deep breaths and quick exhalations for 10 minutes.
For short-term attacks of tachycardia, homeopathic medications are first taken. For example, tincture of valerian or motherwort.
You can also take Valocordin or Corvalol on your own.
If the patient requires complex medical treatment, the following drugs are used:
- beta-blockers (for example, Metoprolol, Atenolol, Timolol, etc.);
- antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, Diltiazem);
- sodium or calcium channel blockers (for example, Verapamil or Novocainamide);
- thyreostatic agents (for example, Mercazolil);
- sedative sedatives (for example, Persen, Valerian, etc.);
- tranquilizers in advanced cases (for example, Phenazepam, Alprazolam, etc.).
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine will tell you what to take when your heart rate is elevated to normalize your readings.
The following plant substances are recognized as the best stabilizers of the heart, blood vessels, and blood pressure:
- Melissa;
- linden blossoms;
- chamomile flowers;
- stinging nettle;
- Birch buds;
- lavender blossoms;
- lemongrass;
- green parts of mistletoe;
- mistletoe.
Advice! Traditional medicine can be used in practice in parallel with basic drug treatment. The main thing is that the chosen means are approved by the attending cardiologist.
According to the standard recipe:
- take a couple of glasses of boiling water
- dissolve 2 tablespoons of any plant material in it
- after which the mixture boils in a water bath for about 10-15 minutes.
It is also important to ensure that the body receives the full amount of magnesium. It helps to reduce tissue permeability, as a result of which potassium cannot enter the blood in unlimited quantities.
It is recommended to eat more of:
- soy;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- bran;
- dark green vegetables;
- crayfish and shrimp;
- chocolate;
- cocoa.
Proper nutrition during tachycardia does not independently reduce the pulse, but creates conditions for the action of drugs and prevents an increase in rhythm.
Necessary:
- give up alcohol, coffee and caffeinated drinks, reduce cocoa and chocolate consumption;
- take food in fractional quantities, avoid overeating;
- drink enough water;
- exclude spicy and hot foods from the diet;
- Foods high in potassium and magnesium are beneficial: legumes, peaches, bananas, melon, nuts.
If the cause of a frequent rhythm is neurocirculatory dystonia, then non-drug methods are successfully used:
- baths: pine, with essential oils (geranium, sage, rose);
- relaxing massage;
- reflexology (acupuncture, acupressure);
- electrosleep.
Good effectiveness in slowing heart rate was noted for dosed physical activity. At a low level of training, walking, therapeutic and breathing exercises, and yoga are used.
Exercises should not cause discomfort.
What deviations can be considered pathology?
Measuring your pulse helps determine if something is wrong with your health. Indicators can be measured on the arm, on the temples, on the carotid artery. Let's take a closer look at how to do this:
To measure the pulse on your hand, you need to position your left hand comfortably. Using the index and middle fingers of your right hand, press on the artery on the inside of your wrist.- To measure at your temples, you need to take a sitting position and try to relax. Place the fingers of your left hand on your left temple and begin counting the blows.
- To measure the pulse on the carotid artery, lightly press the fingers of your right hand into the space under the lower jaw, next to the trachea.
The number of beats should be counted for at least a minute. Otherwise the indicators will be incorrect. Any significant deviations from the norm when measuring the pulse at rest indicate the possibility of pathology.
Increased frequency
Knowing the pulse rate helps to determine with great accuracy whether the increased rhythm is a natural cause or indicates signs of pathological tachycardia. It is also necessary to take into account the physical condition of the person. If he feels well, there is no reason to worry.
Signs of pathological conditions are:
disorientation, even fainting;- pain in the sternum;
- visual hallucinations;
- manifestation of shortness of breath;
- protruding cold sweat;
- weakness and lethargy.
With a more detailed diagnosis, the doctor may reveal:
- heart pathologies;
- changes in the vascular system;
- chemical poisoning;
- pulmonary diseases;
- hypokalemia;
- endocrine problems;
- nervous diseases;
- oncology;
- inflammatory processes;
- infectious diseases.
It is generally accepted that the heart rate and pulse rate are the same. However, situations are possible when the heart beats much faster. This indicates heart damage as a result of electric shock, intoxication with cardiac glycosides, sympathomimetics, myocardial infarction.
Do not assume that elevated readings are a sign of high blood pressure. Various options are possible:
- Increased heart rate and normal blood pressure. The causes may be an attack of vegetative-vascular dystonia, poisoning, or elevated body temperature. If the underlying causes are eliminated, the pulse will stabilize on its own. It is enough to take the appropriate medications, relieve intoxication, and lower the temperature.
- Increased heart rate and high blood pressure. May indicate physiological and pathological conditions: severe physical strain, stress, emotional exhaustion, development of diseases of the cardiovascular system. The doctor must pay great attention to correct diagnosis.
- Increased heart rate and low blood pressure. May indicate the development of cardiogenic or hemorrhagic shock. In the first case, the pathology manifests itself against the background of severe heart disease. In the second - due to severe blood loss. In both situations, it is impossible to help the patient at home. We urgently need to call an ambulance.
Slowdown
A decrease in heart rate in people who practice regular physical activity is considered normal. At rest their heart rate can be up to 40 beats per minute. A similar picture is observed in any person when he is in a state of deep sleep. This condition is recognized as physiological bradycardia.
A completely different attitude should be taken when an ordinary person has a reduced heart rate. We are talking about pathological bradycardia. It manifests itself as a result:
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Hormonal disorders due to thyroid disease.
- Changes in the functioning of the sinus node due to oxygen starvation.
- Sick sinus syndrome.
- Atrioventricular blockades.
- Myocardial infarction.
Is running safe with a heart rate of 120-130?
Running with a heart rate of 120-130 beats per minute is safe for the heart in the absence of diseases and for people under 55 years of age.
This load belongs to the recovery mode and helps:
- adapt the heart to the increased need for oxygen;
- open reserve capillaries;
- improve overall endurance;
- reduce the amount of fat in the body;
- strengthen muscles.
When training, trained athletes have a pulse of up to 150-160 beats. This rhythm leads to a gradual slowdown in resting heart rate if the training plan is correctly constructed.
If you are sick, you cannot rely on such numbers. It is necessary to choose a load that does not cause a deterioration in the nutrition of the heart; most often, a heart rate of 115-120 beats per minute is considered the limit.
Recommendations from experts
To prevent the development of pathological tachycardia, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle:
- spend more time in the fresh air,
- quit smoking,
- drink less alcohol.
It is necessary to sleep enough hours, try not to overload yourself physically, and avoid stress.
You can find out how to lower your heart rate when your heart rate is 130 beats per minute or higher by consulting a doctor.
- In severe cases, you need to call an ambulance and provide first aid to the patient. And then undergo a course of treatment with medications of different groups.
- The folk remedies indicated in the article are suitable for the prevention of tachycardia and further stabilization of the condition after the main treatment.
Causes of pulse fluctuations in a healthy person
You can learn more about how heart rate depends on a person’s age by looking at this table (Table 1).
Table 1 - Pulse rates by age
Depending on a number of factors, these indicators may vary. The activity of the human heart is influenced by the following factors:
- smoking;
- taking narcotic substances;
- alcohol abuse;
- food consumption;
- weather.
If your heart rate deviates by only 3-4 units at rest, this is normal. It’s another matter when a strong heartbeat is constantly present. Then we are talking about a serious pathology.