- Physiological and pathological bradycardia
- What happens in the body when the heart rate slows down?
- Varieties
- Why do different types of bradycardia develop?
- Low heart rate in children: causes and consequences
- Manifestations
- Diagnostic procedures
- Treatment for low heart rate
- Surgical treatment
A condition in which the heart rate slows down is called bradycardia. They talk about it if the frequency of beats per minute is reduced to 60 or less. In some cases, this is caused by physiological reasons, but most often low pulse occurs in people with various pathologies. Heart rate (heart rate) decreases in cardiac diseases, poisoning, central nervous system diseases, and overdose of certain medications.
Physiological and pathological bradycardia
Low heart rate as a physiological phenomenon is typical for professional athletes. Due to constant intense training, the body gets used to increased stress, which affects autonomic regulation. The heart rate naturally slows down in a sleeping person. When the body is at rest, the pulse becomes low and blood pressure decreases. This is the norm. After waking up, when a person begins to engage in vigorous activity, the heart rate increases.
If there is a slowing of the heart rate while awake for unknown reasons, this condition requires the attention of specialists. Most often it is caused by diseases of the cardiovascular or nervous system, endocrine disorders, and injuries. Low heart rate occurs in both adults and children.
Symptoms
If the pulse decreases significantly, the person experiences:
- weakness of the body as a whole;
- headache of varying strength;
- numbness in the limbs and a decrease in their temperature;
- problems with vision, attention, concentration.
Once again, it is worth emphasizing that symptoms are not always immediately visible, so it is worth, especially in old age, to measure your pulse immediately after waking up.
What happens in the body when the heart rate slows down?
Heart rate decreases due to malfunction of the sinus node. It is responsible for the production of electrical impulses, due to which the heart contracts at a physiological frequency. If the sinus node is malfunctioning, the signals are distributed incorrectly along the pathways. This primarily concerns the conduction of electrical impulses between the sinus node and the components of the heart muscle.
With a moderately low heart rate, a person does not notice a pronounced deterioration in well-being. If the heart rate continues to slow down, negative symptoms appear. They are caused by impaired blood supply to tissues. Together with the blood, nutrients and oxygen are supplied to the tissues, therefore, with a prolonged state of low heart rate, a person develops oxygen starvation. Oxygen starvation manifests itself as weakness, lethargy, and other signs of deterioration in health.
A pulse less than 40 beats indicates severe bradycardia. This condition is dangerous for the body due to severe circulatory disorders. The patient is advised to take medication, but in severe cases, drug therapy is not enough, and surgery is performed to install a pacemaker.
First aid for bradycardia
The selection of medications for the correction of pathological changes is carried out by the attending physician, taking into account the etiological factor of the condition. If the relationship between pulse and pressure is abnormal, it is contraindicated to take drugs from the group of beta blockers and calcium antagonists, as they cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure and inhibition of the activity of the sinus node. The drugs of choice are drugs from the class of ACE inhibitors, which have a smooth mechanism of action. However, if there is a sharp deterioration in the condition, every hypertensive patient should know what to do at home to stabilize the indicators.
During an attack, the following measures should be taken:
- Take a horizontal position on your back, while your torso should be slightly raised.
- Wrap the lower limbs in a blanket, apply a heating pad or mustard plasters to the feet.
- Take medicine (Losartan, Lasix, Amlodipine, Captopress).
In cases where an increase in blood pressure occurs even with a slight decrease in heart rate, but is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in condition, it is necessary to call an ambulance or transport the patient to a hospital.
Varieties
Low heart rate can be acute or chronic. The classification of bradycardia depending on the cause includes four types of disease:
- neurogenic;
- organic;
- medicinal;
- toxic.
Sometimes doctors do not have an exact answer to the question of why a person has a low pulse. In this case, we are talking about idiopathic bradycardia - a disease of unknown etiology. Mature and elderly people are susceptible to pathology. Experts are confident that a low heart rate may be associated with the physiological processes of aging.
Dependence of pulse on pressure
Heart contractions create pulsation in the vessels when another volume of blood is released into the circulatory system during the period of the pulse impulse. Therefore, pulse rate is a reflection of the functional state of the myocardium, as well as an integral diagnostic parameter of arterial hypertension.
In hypertension, when blood pressure levels increase, activation of a compensatory mechanism is observed, in which intracranial pressure increases, provoking the activity of the vagus nerve. The protective mechanism is aimed at suppressing cardiac activity to prevent damage to brain tissue. After blood pressure normalizes, the activity of the vagus nerve is inhibited and the heart rate returns to physiological normal.
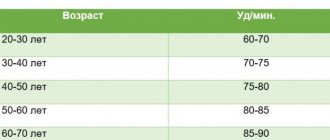
Physiological indicators of blood pressure depending on age category
Bradycardia is considered to be a decrease in the contractile activity of the heart less than 60 beats/min. due to a disruption in the formation of electrical impulses in the atrio-sinus node or due to a failure in the conduction system. Manifestations of the pathological condition in hypertension depend on the stage of both diseases.
Normal heart rate depending on age
In some clinical cases, patients with hypertension are diagnosed with bradycardia, which is difficult to treat, since most antihypertensive drugs contain substances that slow down the heart rate, which is already weak.
Why do different types of bradycardia develop?
- Diseases of the central nervous system. A decrease in heart rate often occurs in patients with VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia), increased intracranial pressure, neoplasms and brain contusions. People with such diseases suffer from chronic neurogenic bradycardia. It also occurs against the background of neuroses with autonomic disorders. If a person wears clothing that compresses the neck, the carotid sinus is disrupted and the pulse slows down.
- Endocrine pathologies, gastrointestinal diseases. People with stomach and duodenal ulcers often suffer from a slow pulse. When the production of thyroid hormones decreases, metabolic processes are disrupted and the heart rate decreases. With the development of myxedema, which is expressed by an acute lack of thyroid hormones, bradycardia worsens and begins to threaten human life. The same thing happens with diabetic ketoacidosis, a decrease in adrenaline production by the adrenal glands.
- Cardiological pathologies. Bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia and is most often associated with heart disease. Low pulse is one of the symptoms of myocardial infarction or inflammation, cardiosclerosis, and a number of other pathologies. The reason is changes in the tissues of the sinus node and myocardium. The process of generating electrical impulses is disrupted, and tissue conductivity deteriorates. The most severe complication is dysfunction of automatism, in which the production of impulses stops. If the pathology affects the myocardium, the generation of impulses is preserved, but there are difficulties with their transmission to the ventricles. Only a certain proportion of the signals reach the target, so the heart rate becomes slow.
- Incorrect medication intake. Some types of drugs cause drug-induced bradycardia. It is caused by incorrectly selected dosage or hypersensitivity to the components of cardiac glycosides, anti-arrhythmic drugs, adrenergic blockers, and morphine-based drugs.
- Poisoning, intoxication in diseases. Slowing of the pulse occurs in people with impaired water and electrolyte balance, as well as with severe infectious lesions of the body. In severe forms of hepatitis, liver failure develops and, as a result, intoxication. The same happens with sepsis and typhoid fever. Heart rate slows down with excessive intake of calcium and potassium into the body, and poisoning with organophosphorus substances.
Why does the heart rate decrease?
The most dangerous condition is that the pulse is thirty to forty beats per minute, and does not increase after training. The causes of the problem are conventionally divided into subcategories.
Physiology
Here we are talking about the following:
- unfavorable night's sleep - in sleep, as you know, all processes go slower. Stale air, excessively cold or hot, taking sleeping pills are the reasons why the heartbeat after sleep may not recover to normal levels;
- low temperatures - the lower the temperature, the lower the heart rate. The body uses protection laid down at the genetic level: mass accumulates, and in winter a layer of fat is created. But in this situation, a decrease in heart rate is relatively normal and generally does not threaten health;
- professional sports - sometimes athletes naturally have a heart rate of no more than fifty beats per minute due to well-pumped muscles. Theoretically, it is less dangerous, but can still lead to oxygen starvation. However, older people rarely engage in professional sports, and this is most often not about them.
Cardiology
A weak heart is the key cause of pulse problems, then the following occur:
- ischemia – blood circulation in the heart or other organs weakens, metabolic processes become abnormal;
- myocardial infarction – the heart muscle is completely or partially damaged and a blood clot forms there. Symptoms: chest pain, weakness, heavy sweating;
- general heart failure - sometimes it can go unnoticed for many years, which is why it is necessary to check the pulse in order to detect such a disease in time. The heart pump gradually works worse and worse and theoretically can stop completely;
- cardiomyopathy - a list of diseases that combine changes in the structure of heart tissue: blood vessels, muscles, valves and aorta;
- myocarditis – inflammation in the heart due to infections, problems with the immune system, severe allergies;
- congenital or emerging heart defects.
Toxicology
The cause is toxins when:
- severe intoxication due to poisoning;
- improper, chaotic use of medications, such as stimulants;
- incorrect amounts of potassium, sodium, magnesium in the body;
- wrong diets;
- smoking, drinking alcohol or, worse, drugs.
Other diseases
Other heart diseases:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- anemia;
- increased pressure inside the skull;
- meningitis;
- hepatitis;
- diphtheria;
- typhoid fever;
- diabetes.
Finally, natural aging may also be the cause in very old age.
Low heart rate in children: causes and consequences
A pulse below normal is detected in approximately 3.5% of children. As a rule, the pathology is caused by congenital heart defects or insufficiency of the sinus node. In children without heart disease, problems may occur due to a bacterial or viral infection. Pathogenic microbes release waste products that cause a response from the immune system and disrupt the functioning of the heart.
Some people have a low heart rate from birth, and this becomes evident at an early age. This phenomenon is called constitutional-familial bradycardia, which is hereditary.
In children and adolescents, the development of various types of arrhythmia can be triggered by excessive psycho-emotional stress and an unfavorable family environment.
Folk remedies for low heart rate
To increase your heart rate without drugs and health risks, alternative medicine has some effective recipes.
Some of them are accepted and even recommended by official medicine, for example:
Lemon - citrus strengthens the vascular wall, cleanses blood vessels of toxins and toxins, improves immunity, so for such problems you should regularly consume fresh lemon, add it to tea, take fresh juice and season dishes with it.
Walnuts – due to the content of Omega-3 fatty acids, blood pressure and the functioning of the cardiovascular system as a whole are normalized. Nuts should also be consumed regularly in small portions.
Dried apricots – this dried fruit cleanses blood vessels and prevents their blockage, and also lowers blood pressure, so you need to get into the habit of eating dried apricots regularly.
Radish juice with honey – the core of the black radish needs to be removed from the vegetable, and a little honey should be put inside. After a day, juice will appear there, which you need to drink several times a day, 20 grams each.
Pine tincture - young pine shoots are washed, crushed, then a tablespoon of raw material is diluted in a glass of alcohol. The mixture must be kept for 10 days in a dark place, after which take 20 drops 1-2 times every day.
Lemon and garlic - squeeze the juice out of five lemons into a glass container, and add 5 squeezed heads of garlic there. The mixture is infused and 20 grams of the product are drunk before each meal for a month.
Red wine - you need to boil a homemade drink, add cumin, cinnamon and honey, mix the composition thoroughly and drink 30-50 grams daily.
Yarrow decoction - the herb in the amount of 1-2 spoons is brewed with a cup of boiling water, infused under a lid and filtered to remove sediment. You need to take a cup of decoction in several parts per day.
Rose hips - a decoction must be prepared from the fruits of the plant in the standard way. Next, grind any sour berries, add to the broth and sweeten with natural fresh honey.
Herbal collection - in the same proportions combine coffin, calendula, valerian, sedum, wormwood, and Echinaceae. A couple of tablespoons of the mixture are brewed in 500 ml of boiling water and simmered a little in a water bath. The strained broth is taken in 100 g doses. a couple of times a day.
An alternative way to speed up the heartbeat and pulse is to apply mustard plaster to the area to the right of the heart.
You need to keep it for no longer than 3 minutes, so as not to overdo it and cause a skin burn.
You can start using home remedies, even the most harmless ones, only with the permission of your doctor. There are many proven recipes to increase tone. But if the reasons for the decrease in heart rate are unknown and there was no consultation with specialists, folk remedies cannot be used.
Another contraindication to any home methods is the period of pregnancy. It is not recommended to use even proven remedies on your own during pregnancy.
Manifestations
With a slight reduction in heart rate, the disease is asymptomatic and is detected by measuring the pulse. More pronounced bradycardia manifests itself as symptoms of circulatory disorders:
- weakness, fatigue, dizziness;
- pallor and bluish tint of the skin;
- slowdown in intellectual and physical development in childhood;
- irritability;
- excessive sweating;
- fainting;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- chest pain.
If the heart rate drops critically, the patient requires emergency medical care.
Weak pulse: clinical picture
In order to timely determine a decrease in heart rate, as well as understand it, every person should know the main symptoms of this condition.
It is quite difficult to detect bradycardia at its very beginning, and visible signs appear when the consequences of this condition appear.
The clinical picture may be as follows:
- impaired human orientation in space;
- sudden loss of strength;
- pain in the temples and forehead;
- urge to vomit;
- increased fatigue;
- Frequent lightheadedness or fainting.
Over time, an insufficient pulse provokes the development of hypoxia (oxygen starvation of the brain). Accordingly, dysfunction of the brain, fatal arrhythmia, dysfunction of the sinus node.
Treatment for low heart rate
To cure a decreased heart rate, you need to know exactly its cause. If the condition is caused by hormonal pathology or water-electrolyte imbalance, therapy is selected after conducting the necessary tests for hormones and electrolytes. Taking medications replenishes the lack of necessary substances and thereby normalizes heart rhythm.
If bradycardia is due to drug overdose, other drugs should be selected or daily doses reduced.
A low pulse during intoxication is a side effect caused by the underlying disease, so it is this that needs to be treated.
If the decrease in heart rate is due to cardiac pathology, the cardiologist selects the appropriate treatment for the given clinical case. Even in the absence of symptoms, people with bradycardia need to undergo regular medical examinations to monitor changes in heart function.
For a chronic decrease in heart rate, the following is prescribed:
- cardioprotectors;
- drugs to improve metabolic processes in myocardial tissues;
- antioxidants;
- drugs with anabolic effects.
Duration of treatment is 3-6 months. The doctor selects a combination of medications and monitors the progress of treatment. Complex therapy may include herbal preparations that have a tonic effect. Basically, extracts of ginseng and eleutherococcus are prescribed - natural stimulants.
In severe conditions, it is important to normalize the pulse rate as soon as possible to avoid tissue hypoxia. The patient is hospitalized and parenteral drugs are used to improve myocardial function.
How to restore your pulse
The simplest methods of stabilization:
- thermoregulation – wear warm clothes in cold weather and try to avoid overheating in hot weather;
- healthy sleep at the right time of day;
- walk more.
Among the slightly less easy to use, but very useful methods:
- drinking tonic drinks – green and black tea, coffee. But make sure that the pressure does not jump because of them;
- spicy and sweet foods, like bitter dark chocolate or black pepper. But this should not be used for diabetes and stomach diseases;
- hot showers and baths are among the most pleasant and least dangerous methods. If you want to improve the water, you can add sea salt or essential oils, and the nervous system will feel better;
- light massage – older people should massage their temples, ears, feet, and back of the head. This will not cause harm, but will improve the heartbeat;
- alcohol - yes, under certain circumstances it can be useful, but only with careful adherence to the measure and dosage, and also in the absence of contraindications. Increase your pulse with fifty ml of wine or twenty-five ml of good cognac.
Surgical treatment
The reason for surgical intervention for bradycardia is the patient’s serious condition, which has developed in connection with heart defects or acquired diseases. Operations are performed for children and adults. For children with congenital pathologies, epicardial stimulators or endocardial electrodes are installed.
Young and older people are advised to have a pacemaker installed. It takes over the production of electrical impulses that are generated at a physiological frequency. This allows you to ensure a normal heart rate and prevent negative consequences.
Intraventricular conduction disorders
There are isolated blockades of the branches of the His bundle, bi- and trifascicular blockades. Isolated bundle branch blockade: right bundle branch block, left anterior bundle branch block, left posterior bundle branch block. Bifascicular blockades: a combination of 2 isolated blockades. Trifascicular blocks: a combination of a bifascicular block with 1-2 degree AV block or alternating two types of bifascicular blocks, for example, LBBB and RBBB. If intraventricular conduction disturbances are detected, dynamic observation is required to determine the indications for pacemaker implantation: trifascicular blocks (alternating or bifascicular in combination with 2nd degree AV block).
Is it possible to avoid the development of the disease?
A slow heartbeat can be determined by counting the pulse, but an electrocardiogram will help make the correct diagnosis. An echocardiogram and a series of tests may also be needed for a more accurate diagnosis.
Prevention and maintaining a healthy lifestyle play a big role in preventing heart disease. This is facilitated by:
- eliminating bad habits from your life, especially smoking;
- monitoring the amount of glucose in the blood;
- physical activity;
- monitoring your own weight;
- resistance to stress;
- healthy diet.
Drug treatment prescribed by a doctor and physical therapy exercises will also help reduce the risk of developing bradycardia.