Thoracic osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease of the thoracic spinal column, in which literally “premature aging”, “wear and tear” of intervertebral discs, joints, and the vertebrae themselves occurs. The disease does not occur as often as cervical or lumbar osteochondrosis, due to the structural features of the thoracic spinal column:
- The thoracic vertebrae are firmly fixed, as they are connected to the ribs, and through them to the sternum, forming a single structure - the chest. This part of the spine has less mobility compared to the lumbar or cervical spine.
- In the thoracic region, the spine has a physiological bend - kyphosis. This is an arc whose apex faces backward. The spine is curved forward, so the highest mechanical loads occur on the anterior and lateral parts of the vertebrae; the degenerative process predominantly develops in the anterior part.
- Osteophytes - bone growths on the vertebral bodies - in thoracic osteochondrosis are mainly located in the anterior part, due to this the symptoms of the disease are weakly expressed and may be absent for a long time.
What happens in the vertebrae during osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine?
With osteochondrosis of this part of the spinal column, the degenerative process begins with the intervertebral disc. Changes occur in it at the biochemical level, due to this the disc swells for a while, then its height decreases. He ceases to cope with his function normally.
Then, tears and cracks appear in the peripheral part of the intervertebral disc - the fibrous ring. This predisposes to the subsequent development of intervertebral hernia.
The degenerative process also develops in the intervertebral and spinal-costal joints (spondyloarthrosis). This leads to narrowing of the intervertebral foramina through which the spinal cord roots exit, pinching, irritation and dysfunction of the latter.
Due to dysfunction of the intervertebral discs, the load on the vertebrae increases. A compensatory mechanism is activated - bone growths - osteophytes - appear along the edges of the vertebral bodies. This condition is called spondylosis.
If the first symptoms of the disease occur, visit the neurological center of the multidisciplinary international clinic Medica24. You will be examined by an experienced specialist and examined using modern diagnostic equipment.
Forecast
If you ignore the first manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis and, without sparing the spine, continue to lead the same lifestyle, the disease can progress2, causing various disorders. Among them are vertebral artery syndrome2.
The vertebral arteries pass through openings in the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae and provide blood supply to the brain5. With osteochondrosis, the vertebral artery may become pinched in its orifice; sometimes it spasms in response to irritation, which often impairs cerebral circulation2,5.
A typical manifestation of vertebral artery syndrome is a burning, throbbing headache2 that:
- is felt in the back of the head and “gives” to the temporal, frontal and parietal regions5;
- usually occurs or worsens when turning the head or throwing it back5;
- accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms - redness or pallor of the face, nausea, dizziness and tinnitus5.
to come back to the beginning
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine according to modern standards
The disease occurs in the form of alternating exacerbations, when all the symptoms clearly manifest themselves, and remissions - periods of improvement.
During exacerbation of osteochondrosis, spinal traction is used. The patient is placed on a bed with a raised head and secured with special rings by the armpits, so that traction occurs due to the weight of his own body. Underwater traction can also be used. The patient is in a vertical position in the pool, a special float is attached to his neck, and a load of a certain weight is suspended from his legs.
Pain syndrome due to thoracic osteochondrosis is combated with the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. The doctor may use a paravertebral block, when an anesthetic solution is injected into the area of the affected nerve roots. According to indications, sedatives are prescribed to help relieve stress and nervous tension caused by the disease.
Physiotherapeutic procedures include ultrasound treatment, electrophoresis with novocaine, diadynamic currents, and UHF therapy. To unload the spine, a neurologist may prescribe wearing a corset.
During remission, treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis includes massage, physical therapy, physiotherapy, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
The need for surgical treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region occurs very rarely.
Do not self-medicate - it may not only be useless, but also cause harm. In order to receive effective therapy for thoracic osteochondrosis, you need to undergo an examination, understand the causes of the problem, the pathological processes that occur in the body. Make an appointment with a specialist at the medical center International Clinic Medica24 - this can be done at any time of the day by calling.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The main symptom of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is pain. It is characterized by some features:
- By nature, she is most often stupid. Burning, aching pain is less common.
- The pain intensifies during sudden movements, turns of the body, during a deep breath, after prolonged stress on the back, sleep (especially on an uncomfortable mattress or pillow).
- Most often, pain is localized between the shoulder blades, but can be of a girdling nature.
- At night, there may be sensations that many patients describe as: “as if the back was being squeezed by iron pincers.”
In addition to pain, thoracic osteochondrosis may cause other symptoms caused by compression of the nerve roots.
First aid
If the heart rhythm is abnormal, it is necessary to lay the person down and calm him down. In most cases, arrhythmia with osteochondrosis disappears within half an hour. Taking any sedative, preferably one that does not contain alcohol, will help you feel better. This is a weak water infusion of St. John's wort, motherwort or tea with oregano, lemon balm, and thyme. If blood pressure is slightly elevated, then it is best to give the patient a tablet of Novo-Passit, Tenoten, Persen.
If the readings are very high, you need to invite a doctor and take an antihypertensive drug, for example, Enalapril.
Other symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
Pain leads to spasm of blood vessels. This manifests itself in the form of chilliness in the legs, peeling of the skin, and increased brittleness of the nails.
Symptoms of the disease can mimic disorders of the internal organs. If the degenerative process affects the upper part of the thoracic spine, so-called pseudocardiac syndrome may occur. There is a sharp pain in the chest, sometimes it radiates under the shoulder blade, into the arm and jaw. The person gets scared, freezes, is afraid to move or take a deep breath, as this increases the pain. In such cases, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis between osteochondrosis and angina pectoris.
Sometimes pain occurs in the pit of the stomach, under the right rib - in this case, the manifestations of the disease resemble pathologies of the stomach, liver, and gall bladder.
Sometimes there are disorders of the digestive organs, urination disorders, and in the genital area.
Understanding the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis is not always easy. Often, to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor has to prescribe an additional examination to rule out disorders of the cardiovascular system and digestive organs. Contact the experienced specialists of the international clinic Medica24.
Additional symptoms
Patients with thoracic osteochondrosis often complain to doctors of pain in the heart, reminiscent of an angina attack. They are localized behind the sternum or slightly to the left. The pain can be squeezing, pressing, burning or cutting, pulling. The severity of discomfort also varies. In one case, the pain is quite tolerable, in the other it is so intense that the person begins to moan loudly. Unlike angina, with osteochondrosis it cannot be eliminated by taking medications, for example, Nitroglycerin.
The clinical picture of cervical pathology is more varied and is caused by compression of the vertebral artery. The following clinical manifestations are observed:
- migraine-like headaches;
- dizziness, loss of coordination of movements;
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air when inhaling;
- decreased visual and hearing acuity, tinnitus, double vision of objects before the eyes;
- sore throat, dry non-productive cough.
With osteochondrosis affecting the lumbar intervertebral discs, symptoms of lumbago, or “lumbago,” occur. When moving awkwardly, such acute pain appears that the person freezes in one position, afraid to straighten up and get to the bed to lie down.
What causes the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine?
Manifestations of the disease are caused by a number of pathological processes occurring in the spinal column:
- Reduced height of the intervertebral disc: as a result, the diameter of the intervertebral foramen through which the nerve roots pass decreases.
- Compression of nerve roots by pathologically altered intervertebral joints.
- Compression of the roots by osteophytes - bony outgrowths on the vertebrae.
- The formation of intervertebral hernias - in the thoracic spine they are much less common than in the lumbar and cervical spine.
Advantages and disadvantages of cervical ultrasound
Each medical procedure has its own pros and cons. Fortunately, ultrasound examination of the cervical spine has more benefits. Let's look at some of them:
- 100% safety of the method. Clinical studies have shown that ultrasound does not harm the body. Even when compared with radiography or computed tomography, ultrasound has a significant advantage.
- Duration of the procedure. An ultrasound examination of the cervical spine is performed in less than half an hour.
- Study protocol. The necessary indicators are recorded, then deciphered by the ultrasound doctor and printed out. Immediately after the procedure, the patient receives information about the state of his health.
- Non-invasive. Ultrasound is absolutely painless; it does not cause a person physical or moral discomfort.
- No special training required. Before a spinal examination, the patient does not need to follow a diet or other preparatory measures.
- The only disadvantages that can be noted are the need for additional research if any abnormalities are detected in the patient.
Effective treatment of symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
You can often cope with the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis at home. Many people “save” themselves, without doctors, with over-the-counter painkillers and painkillers, and by applying heat.
However, self-medication is only a temporary reduction in symptoms, and if done incorrectly, the problem can only worsen. During an exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, gymnastics and massage are contraindicated. On the contrary, at this time you should try to unload the spinal muscles as much as possible.
An experienced neurologist will correctly assess your condition and prescribe treatment that will help. The symptoms described in this article do not always indicate thoracic osteochondrosis; competent differential diagnosis is often necessary.
Visit a specialist. The neurological center of the multidisciplinary international clinic Medica24 employs experienced neurologists, uses modern diagnostic equipment, and treats diseases in accordance with the principles of evidence-based medicine. Clinic administrators are on duty at the telephone around the clock, call at any time.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The causes of thoracic osteochondrosis are not fully understood, and in general, this disease raises a large number of questions for many doctors. Some even argue that such a disease does not actually exist, and its manifestations are usually caused by completely different pathologies. By the way, in English-speaking medicine this term refers to completely different diseases.
Complications
It is impossible to independently determine what caused the rapid heartbeat. It is necessary to contact a cardiologist for a thorough examination. If osteochondrosis, protrusion, or hernia are detected, the patient will be referred for further treatment to a neurologist or vertebrologist.
If a patient with arrhythmia or extrasystole does not seek medical help, then he may soon be diagnosed with chronic myocardial hypoxia. The situation is aggravated by feelings of anxiety and lack of air. If left untreated, radicular syndrome and discogenic myelopathy may develop.
Possible causes of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis
It is currently believed that the disease can be caused by one of the following reasons, or a combination of them:
- Autoimmune disorders in the body. The immune system begins to work incorrectly and attack the body’s own connective tissue, ligaments, and cartilage.
- Injuries suffered. For example, a subluxation or compression fracture of a vertebra in the thoracic region increases the risk of osteochondrosis in the future.
- Age. Many people over 40 years old experience degenerative changes in their spines. But not everyone gets sick.
- Permanent spinal injury. Most often this occurs in people who constantly work sitting or standing in the same position and make the same type of movements.
- Congenital malformations of the vertebrae. Because of them, the functioning of the spinal column is disrupted, the load on the vertebrae and intervertebral discs is distributed incorrectly. This contributes to the development of the degenerative process.
Understanding the causes of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is not always easy. We invite you to undergo an examination by a specialist doctor and examination using modern equipment at the medical center International Clinic Medica24.
When to see a cardiologist
In most cases, arrhythmia appears simultaneously with other signs of osteochondrosis at the 2nd radiographic stage. Therefore, pathology is indicated by both heart rhythm disturbances and back pain, limitation of movements, crunching in the spine when bending or turning. Any of these symptoms should be a signal to consult a doctor for medical help.
What reasons can lead to exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine?
The disease proceeds in waves - an exacerbation occurs, the symptoms of osteochondrosis become pronounced, then they subside - remission occurs. Factors that can provoke another exacerbation:
- In more than half of the cases, this occurs after sudden movements, prolonged stay in a monotonous position (static loads on the spine), intense physical activity, or heavy lifting.
- Hypothermia - both general and directly in the thoracic spine.
- Nervous tension, stress.
- Spinal injuries - acute (bruise), chronic (with prolonged and intense loads on the spinal column).
- Various infections.
Sometimes (in 15-20% of cases) exacerbation of thoracic osteochondrosis occurs for no apparent reason.
Treatment errors
The most common mistake patients make is taking antiarrhythmic drugs to normalize the heart rate. Such drugs do not improve well-being due to the specific pharmacological action. It is useless to eliminate heart pain or arrhythmia with Corvalol or Valocordin. The slight relaxing effect after taking them is due to the ethanol included in the composition.
If you have arrhythmias, it is strictly forbidden to visit baths, saunas, lift weights, or engage in active sports. Even minor physical activity can cause a serious deterioration in well-being.
What diseases can cause symptoms resembling thoracic osteochondrosis?
The diagnosis of “osteochondrosis” is not always made justifiably; even the doctor cannot always figure out what is happening to the patient. Back pain often occurs due to other diseases:
- Myofascial pain syndrome. A common condition in which pain occurs as a result of constant spasm of the back muscles.
- Herniated intervertebral discs. They are rare in the thoracic region, but can also be the main cause of pain between the shoulder blades and neurological disorders.
- Injuries. If the injury was relatively mild - for example, a soft tissue bruise, a muscle strain - the symptoms of “osteochondrosis” bother you for some time and then go away on their own, even if no treatment has been carried out. Pain can also be caused by more serious injuries - for example, a compression fracture, vertebral subluxation.
In order to correctly understand the causes of back problems, the patient must be examined by an experienced doctor and a full examination must be carried out. All this can be done at the medical center International Clinic Medica24. In our clinic, high-quality medical care is available around the clock; you can contact the administrator at any time, including holidays and weekends, by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
When the manifestations of “osteochondrosis” begin to bother you, you need to carry out a correct, comprehensive diagnosis and understand the true causes of the symptoms that have arisen. They are not always located in the spine itself. This helps to prescribe the appropriate treatment and deal with the problem as quickly and effectively as possible.
At the Medica24 international clinic, you will be examined by an experienced neurologist, and you will be prescribed all the necessary diagnostic methods.
If you want to have a healthy heart, treat your spine
- home
- Articles
- My spine is my health
- If you want to have a healthy heart, treat your spine
20.11.2017
It has been proven that problems with the spine provoke the development of heart and vascular diseases. Cardiologists know this, but everyone needs to know about it in order to preserve the heart and blood vessels from a young age.
Back pain is a fairly common occurrence in the lives of each of us. But the statistics of visits to the doctor regarding osteochondrosis are small - only up to 20 percent of potential patients. As a rule, they come when it becomes completely unbearable, although 85 percent of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis translated from Greek osteon means “bone”, hondros – “cartilage”, and the ending “oz” indicates the dystrophic nature of the changes in these structures. The result is a disease of the bone and cartilage. The scientific definition of spinal osteochondrosis is as follows: spinal osteochondrosis is degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc and adjacent vertebral bodies. In other words, osteochondrosis is changes caused by disruption of metabolic processes in the disc, that is, nutrition and dehydration. Osteochondrosis is not a disease, but a sign of aging - the same as wrinkles, baldness and gray hair. With osteochondrosis, intervertebral discs - special cartilaginous structures that provide our spine with flexibility and mobility - become defective. This is where it all begins.
There are many theories for the development of osteochondrosis, in each of which the main factor is one or another reason, such as hereditary predisposition, mechanical trauma, metabolic disorders, etc. It is especially difficult to determine the cause of osteochondrosis due to the fact that this disease occurs in both elderly and young people, and at the same time in well-built people, and vice versa.
What are the prerequisites for the development of osteochondrosis?
- Disruption of normal relationships in the musculoskeletal system (congenital and acquired postural disorders, spinal curvatures such as scoliosis and kyphosis, flat feet, pelvic obliquity, different lengths of limbs, craniovertebral anomalies, etc.).
- Violation of water-electrolyte balance and mineral metabolism in the body, which negatively affects the elasticity of cartilage tissue and the strength of bone tissue, reduces their resistance to static and dynamic loads.
- The development of osteochondrosis in obesity, when excess weight puts additional pressure on the spine. Against the background of excess weight, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine most often occurs, and then pathology occurs in those internal organs that are innervated from this section.
- A very important reason why osteochondrosis occurs is a general disorder of metabolic processes in the body.
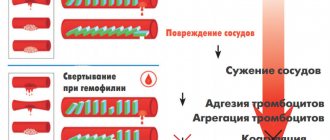
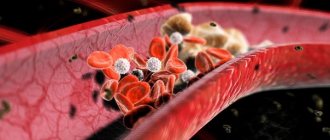
This process provokes the development of heart and vascular diseases and has a very simple physical nature. In diseases of the spine accompanied by degenerative changes, the vertebral (vertebral) artery running along the spinal column is pinched. The vessel is compressed by bone osteophytes (growths of bone tissue) or spasmodic muscles, which provokes an increase in intravascular pressure.
Due to pinching of the vertebral artery and compression of the nerve roots going to the heart, it begins to hurt. This is not yet a heart disease, the pain is of a so-called radicular nature, but the innervation is disrupted, which contributes to the development of heart disease itself.
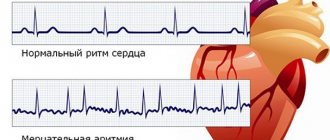
Against the background of a pathological condition of the spine, tachycardia (palpitations) develops. “Pumping” blood through a compressed vessel requires more effort from the body. For this reason, the heart rate increases. Palpitations are an external manifestation of increased load on the heart with osteochondrosis.
With osteochondrosis, tachycardia has some features:
- it is observed constantly, including in a state of complete rest;
- becomes more pronounced when changing a position to a more uncomfortable one or increasing the load on the spine;
- the correct heart rhythm is maintained: there are no interruptions in the work of the heart, beats follow at equal intervals between them;
- tachycardia is reduced as a result of measures aimed at treating the underlying disease - osteochondrosis.
In cases where the heart muscle cannot cope with a significant load, arrhythmia (heart rhythm disturbances) and extrasystole (so-called interruptions in heart function) develop. In case of prolonged manifestation of the symptom, the risk of developing chronic hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the myocardium increases.
With osteochondrosis, extrasystole initially appears only after physical exertion. In this case, the heart muscle does not have enough oxygen to push blood, and there is a need for additional contractions. With heavy physical activity, sudden movements, bending, turning, the nerve root is pinched. When a nerve in the thoracic spine is compressed, the functioning of the heart can be impaired.
Manifestations of cardiac dysfunction in osteochondrosis are:
- heartbeat;
- increased tension in the interscapular area;
- feeling of lack of air;
- frequent development of pre-fainting states;
- fever, increased sweating;
- feeling of internal discomfort;
- increased pulse with periodically occurring strong waves.
Osteochondrosis is often accompanied by increased blood pressure. The reason for this phenomenon is still the same - compression of the vertebral (vertebral) artery running along the spinal column. It is often compressed as a result of muscle spasm, swelling of soft tissues or displacement of the intervertebral disc. And since the vertebral vessel is responsible for blood circulation in the brain, the narrowing of its lumen leads to insufficient nutrition of the brain (30% of the brain is supplied precisely by the vertebral artery). The natural reaction to this event is an increase in blood pressure. Due to high blood pressure, the body tries to increase blood flow to the brain. At the same time, the heart rate increases, which also leads to increased blood pressure.
These factors explain pressure surges during cervical osteochondrosis and its exacerbation. In such extreme conditions, the body takes measures to eliminate disturbances and normal nutrition of brain cells. Thus, with a significant narrowing of the lumen of the artery, in order for a sufficient volume of blood to pass through, it is necessary to increase the speed of blood flow. For this reason, the body begins to release substances that increase blood pressure. This is the only way to restore normal nutrition to brain tissue. In the chronic form of the disease, high blood pressure is always observed.
As a result of scientific research, it has also been proven that if a person has previously had high blood pressure, then osteochondrosis in the cervical and thoracic region aggravates the course of hypertension, since it increases the resistance (immunity) of the body to the ongoing antihypertensive therapy. With cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, pain in the heart often occurs, which patients sometimes mistake for angina. This is explained by the fact that the heart and spine are connected through nerve cells through the spinal cord. Find connections between the seventh cervical and fifth thoracic vertebrae.
Thus, cervicothoracic osteochondrosis contributes to the appearance of heart rhythm disturbances, increased blood pressure and, indirectly, the development of myocardial ischemia.
How can you avoid the development of osteochondrosis and related diseases of the vascular system? And if they are present, how to reduce symptoms and prevent complications?
Unfortunately, neither powerful anti-inflammatory drugs, nor physical therapy, nor other external influences cure osteochondrosis, they only relieve or reduce its exacerbation, and after a while the disease will make itself felt again.
What's the solution? It exists and has been known for a long time .
Osteochondrosis is a disease that is “afraid” of preventive procedures. If you reconsider your lifestyle and change it as much as possible, then with a high degree of probability you will be able to prevent the development of the disease or stop its progression. There are simple rules for this:
- Drink at least two liters of water a day (the spine is afraid of dehydration!).
- Provide your body with maximum mobility.
- Play sports. The most ideal option is swimming.
- Review your diet, bringing it closer to “alkaline” (you can read about alkalizing foods on many pages on social networks).
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Every morning, perform exercises from the physical therapy complex (or others - as you wish, but with mandatory stretching elements!)
- Don't overexert your muscles.
- Get a simple relaxing massage to relieve stress after a hard day at work.
- Walk and move more.
But we need to talk specifically about the features of the diet in the twenty-first century. One of the main commandments of Hippocrates: “Eliminate the cause - the disease will go away!” forgotten by modern medicine.
We forget that not only movement is important for the health of our spine. It, like other parts of our body, needs water, oxygen and proper nutrition. It’s no secret that athletes who move and train a lot often develop severe, disabling forms of osteochondrosis. Hippocrates said: “Food must be your medicine, otherwise medicine will be your food.”
Complete natural food has always been and will be the basis for the formation of health, treatment of diseases and their prevention, and there is nothing else left to do but to look for a way to transform modern half-empty food into complete food.
The only question is how to do this in modern conditions, when the condition of the soil, the technology of growing vegetables and grains, the technology of industrial food preparation, and the technology of keeping animals do not contribute to obtaining nutritious food. Not only does it lack protein and vitamins, it does not contain the set of minerals necessary for normal metabolism in the body, without which neither vitamins nor proteins, other things being equal, will be absorbed.
Even scientists who for many years “held a perimeter defense” against the use of biologically active additives (dietary supplements) now agree that in the current conditions it is impossible to ensure a healthy diet without them.
What nutrition does our spine need to keep it healthy?
First of all, a large complex of minerals that are needed for the construction and normal functioning of bones, ligaments, cartilage, synovium and synovial fluid and intervertebral discs. This, of course, is calcium, phosphorus, silicon, magnesium, zinc, selenium and many other equally important ones. How to provide the body with exactly those substances (minerals) that are lacking today, right now? How not to “overdo it” with the dosage and course of administration? How to ensure the absorption of these important elements in the body?
This requires a natural, harmless, easily digestible and multi-component source. And we have been using it in our wellness practice for more than twenty years. This is lithovit, created on the basis of the natural mineral zeolite, which contains about eighty minerals in an easily digestible form. “Litovit-M” (pure zeolite) never causes allergic reactions (and, moreover, is successfully used for all types of allergies, including psoriasis and bronchial asthma), is harmless when used correctly and can be used from the first years of life.
The regimen for taking Litovit-M is very simple: adults take it 2.5-3 grams twice a day with a glass of clean water, or even better, Sabelnik drink concentrate, which contains components that improve the nutrition of the tissues of the spinal joints and relieve them inflammation. The course of treatment is a month, after which it is recommended to “feed” our elastic structures of the spine with a source of organic silicon in the form of the Optisorb dietary supplement, two sachets (2.5 g) twice a day. The course of admission is one month.
If the treatment is preventive, it can be done twice a year, preferably in autumn and spring. If osteochondrosis is already manifesting, then these products should be taken regularly for at least three weeks a month. It is worth recalling that since both dietary supplements are sorbents, they should be taken an hour to an hour and a half before taking medications.
Equally important is a balanced diet of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and phospholipids (lecithin). And such an opportunity also exists; NPF “Nov” has developed and produced, in accordance with GOST requirements, the protein mixture “NovoProtein”. By drinking one glass of cocktail (1-2 tablespoons per 150-200 ml of warm water) per day, you can be sure that the minimum necessary nutrition for cell growth and division will be provided.
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease, so for a lasting effect you need to be patient and persistently repeat courses of taking Litovit-M, Optisorb, the drink Sabelnik, NovoProtein, and follow all the above recommendations. But if you consider how many problems of the heart and blood vessels (and many other organs too) can be avoided, “the game is worth the candle”!
And when starting to take care of the health of your spine, you should always remember the wise saying - the one who walks can master the road!
What diagnostic methods are used for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine?
For thoracic osteochondrosis, the doctor prescribes an examination, which may include the following diagnostic methods:
- Radiography. Usually photographs are taken in two projections: full face and profile. Based on the images in the photographs, you can evaluate the condition of the bodies and arches, articulations of the vertebrae, the height of the intervertebral discs, and the width of the spinal canal.
- X-ray contrast studies. Discography (images after the injection of a contrast solution into the intervertebral disc) and myelography (injection of a contrast solution into the space surrounding the spinal cord) help to detect at what level the spinal cord and its roots are compressed by the deformed intervertebral disc. Recently, these studies are practically not used, as more accurate diagnostic methods have appeared - CT and MRI.
- Computed tomography for thoracic osteochondrosis helps to detect the affected intervertebral disc, assess its size, the degree of “wear”, compression of the spinal cord and its roots.
- Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to examine the spinal cord and its roots, the degree of their damage, detect intervertebral hernia, and narrowing of the lumen of the spinal canal.
An important principle of the Medica24 international clinic is that we always have the interests of the patient as a priority. Our doctors never try to prescribe as many tests as possible. The scope of the diagnosis is exactly such that the neurologist can obtain all the necessary information, establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe the optimal treatment.
Diagnostics
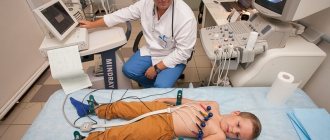
The primary diagnosis is made based on a study of the patient's medical history and complaints. During an external examination, characteristic signs of osteochondrosis and its developed complications can be detected - deformation of the vertebral structures during palpation, spasm of the muscles of the affected part of the spine. To identify the cause of heart rhythm disturbances, a number of instrumental studies are carried out:
- electrocardiography is an electrophysiological method for recording the biopotentials of the heart. Allows you to determine the frequency and regularity of heart contractions or the loss of individual contractions - arrhythmias;
- Electromyography is a research method that allows you to assess the degree of muscle damage, localization and extent of pathology. Used to exclude peripheral neuropathy, often masquerading as angina.
Multiple coracoid osteophytes on x-ray.
Radiography is used to diagnose osteochondrosis. MRI or CT is performed to detect protrusions and hernias that cause compression of the vertebral artery.
CT scan of the lumbar spine for osteochondrosis.
How difficult is it to diagnose osteochondrosis in the thoracic spine?
The main manifestation of thoracic osteochondrosis is pain in the back and chest. This symptom can occur with a variety of different diseases. Moreover, they are not always associated with the spine.
For example, pain from myofascial pain syndrome is the result of chronic spasm of the back muscles. Often the disease must be differentiated from pathologies of the heart, stomach, liver, and other internal organs.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine always requires a careful approach from the doctor; it is important not to miss other possible pathologies.
With us you will receive a reliable diagnosis and correct treatment, thanks to the fact that the international clinic Medica24 employs neurologists with extensive experience and uses high-precision modern diagnostic equipment. Call at any time of the day, any day of the week.
What therapy is carried out for arrhythmia and osteochondrosis
Pain in the heart area of a vertebrogenic nature is often not as pronounced as in the primary pathology, therefore antiarrhythmic drugs are not used in such cases. As a rule, they are limited to physiotherapy and various methods of traditional medicine.
- Deep acupressure has a fairly strong effect on heart pain and back discomfort. Helps to relax the muscles in the spine area, which are about 6-4 cm deep, and therefore cannot be affected by a traditional type of massage.
- Ointments with bee or snake venom, as well as various analgesic components, help increase heat generation and dilation of blood vessels at a depth of 2 cm. This allows you to relax the muscles, which thereby relieves pressure from the nerve roots, and therefore reduces pain and manifestations of arrhythmia.
- The most commonly used medications are vasodilators, anti-inflammatory and diuretics.
For severe cardialgia, an analgesic may be prescribed, but this is a symptomatic treatment that does not give a long-term effect, so the main thing is to eliminate the underlying cause, that is, osteochondrosis.
4.17 Aug. rating ( 83 % score) – 12 votes – ratings
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
It is impossible to get rid of osteochondrosis of the spine that has already occurred, but it is quite possible to slow down its development and prevent the onset of pain if you pay close attention to your health2:
- balance nutrition2;
- do not overeat, normalize body weight2 so as not to overload the spine5;
- exclude hypothermia, trying to avoid staying in a draft or damp room5;
- maintain physical activity2;
- play sports, swimming is especially useful5;
- organize the workplace correctly6;
- when working for a long time in a forced position, regularly change position and stretch your neck6;
- choose a comfortable pillow and mattress for a comfortable sleep2.
In advanced cases, osteochondrosis can not only reduce the quality of life, but also deprive a person of his ability to work2. Therefore, try to notice in time the factors that can lead to the destruction of intervertebral discs, and, if possible, eliminate or reduce their harmful effects on the spine. If you are concerned about neck pain, be sure to consult your doctor. Only a specialist can determine the stage of the disease, select painkillers and prescribe a course of physical therapy or physiotherapy.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist
Literature
- Treatment and prevention of osteochondrosis A.A. Pilipovich// General Medicine 2. 2015 - pp. 15-22
- Spinal osteochondrosis // Clinical recommendations / All-Russian public organization Association of Traumatologists and Orthopedists of Russia (ATOR) - 2021.
- Voronyanskaya L.K., Evsyutina V.B. Physical rehabilitation of patients with cervical osteochondrosis // Problems of physical education and sports / No. 9. - 2010. - pp. 19-21
- Sklyarenko O. V., Sorokovikov V. A., Koshkareva Z. V. Some aspects of the pathogenesis and diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (literature review). Acta biomedica scientifica. 2019; 4(6): 47-53. doi: 10.29413/ABS.2019-4.6.7.
- Bezrukova, O. V. Therapeutic exercise for spinal osteochondrosis: a textbook // O. V. Bezrukova, G. I. Bulnaeva; GBOU VPO IGMU of the Ministry of Health of Russia. – Irkutsk: IGMU, 2013. – 58 p.
- Isaikin A.I. Pain in the cervical spine // Difficult patient / No. 7. - VOLUME 10. - 2012. - P. 36-41.
- Chekhonatsky A. A, Komleva N. E, Chekhonatsky V. A. Some features of the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of radiculo- and myelopathic syndromes of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (review) // Saratov. scientific and medical journal / 2021. - T. 16, No. 1. — P. 64-68.
- Instructions for medical use of the drug Motrin® / Reg. number PN002874/01 / ,
- Childress MA, Becker BA. Nonoperative Management of Cervical Radiculopathy. American Family Physician. 2021 May 1;93(9):746-54. PMID: 27175952. 746-754
- Cervical Spondylosis (Arthritis of the Neck). from the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. Reviewed by Thomas Ward Throckmorton, MD, FAAOS. 2021 https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases—conditions/cervical-spondylosis-arthritis-of-the-neck
- Grishan M.A. “Physiological consequences of physical inactivity for the human body” Medical and pharmaceutical journal “Pulse”, vol. 20, no. 12, 2021, pp. 70-73.
- Svetoslav Nikolaev Stoev, Stanislav Radoslavov Gueоrguiev, Vasil Georgiev Madzharov, Hristina Viktorova Lebanova (2021). “Naproxen in Pain and Inflammation – A Review”, International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Phytopharmacological Research, 11(1), pp.142-148.