Tachycardia is a pathology in which the number of heart contractions (HR) increases relative to the norm - 60-80 beats per minute.
An attack of tachycardia can be a completely physiological phenomenon, for example, after active physical exertion. In this case, it goes away on its own and does not require any intervention, but pathological forms must be treated under medical supervision.
Usually the attack begins suddenly, the contraction of the heart accelerates (up to 120-150 beats per minute), weakness, stabbing pain in the heart, and a feeling of fear may occur. Provoking factors can be stress, large meals, drinking alcohol or caffeine, an allergic reaction, bloating, hot flashes during menopause in women.
What factors affect heart rate?
The most common non-infectious pathology in all countries of the world is diseases of the circulatory system. Based on the results of epidemiological studies dating back to the late 90s of the 20th century, WHO experts came to the conclusion that an increase in heart rate (HR) at rest is one of the risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases in healthy people.
According to the national recommendations of the All-Russian Scientific Society of Cardiology, the resting heart rate of a healthy adult should be no more than 80-85 beats per minute and correspond to the pulse rate. The optimal heart rate for an adult at rest is from 60 to 80 beats per minute, while the specific heart rate is individual for each person and depends on a number of factors.
The first is gender. Women have higher normal heart rates than men. This is explained by the specific characteristics of hormonal and emotional backgrounds.
The second is age. In adults, the normal heart rate increases with age: at the age of up to 50 years, the average normal value is 70 beats per minute, at the age of 50-60 years - 74 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute in people over 60 years of age.
In addition, heart rate depends on lifestyle, including physical activity: trained people have a lower heart rate than those leading a sedentary lifestyle. Bad habits also have an impact - smoking, alcohol abuse.
And finally, this indicator correlates with external factors: heart rate increases with lack of sleep, nervous tension, after a heavy meal, increased ambient temperature, etc.
How to treat tachycardia in the hospital and at home?
Tachycardia is considered a general concept in the practice of a cardiologist, which combines any disturbance of heart rhythm, accompanied by an increase in the number of contractions of the atria or ventricles. Due to the fact that this is a fairly large group of diseases, approaches to eliminating this pathological condition also vary significantly. Tachycardia can be treated independently or with the help of a doctor. In the latter case, there is the possibility of drug treatment or surgical intervention.
Drug groups
- beta blockers, which help slow down the conduction of the excitatory signal through the heart and are effective for all types of tachycardia;
- calcium channel blockers reduce the concentration of this ion inside striated muscle cells, which reduces the frequency and strength of contractions during tachycardia;
- sodium blockers affect the action potential and are also effective for arrhythmia;
- Cordarone is placed in a separate group, but this drug is rarely used for tachycardia, mainly in its ventricular form.
Medicines for tachycardia include not only antiarrhythmics.
Drugs with a different mechanism of action that are used in the treatment of patients with high heart rate include:
- Sedatives that reduce the excitability of the sympathetic nervous system, thereby eliminating its increased effect on the conduction system of the heart. These drugs are especially effective in patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, panic attacks and other mental disorders. It is advisable to take them after meals.
- Metabolic drugs that improve the nutrition of myocardial cells and nerve fibers of the cardiac conduction system. These include Mildronate, Mexicor, Preductal and some others. These drugs are practically harmless and have no contraindications. They are prescribed in tablets for oral administration after meals.
- Asparkam (magnerot) is a medicine that contains potassium and magnesium salts. As a result of their intake after meals, the level of these electrolytes in the muscle cells of the heart, as well as in the intercellular space, is normalized.
In addition to specific therapy, in the treatment of rapid pulse (especially of sinus origin), medications for tachycardia that do not have a direct effect on the heart can be used. In this case, these drugs affect the cause of the disease. For example, for anemia, iron supplements are used, for thyrotoxicosis - Mercazolil, etc. Take them after meals.
It is important to remember that for tachycardia, treatment should be selected strictly individually, since the sensitivity of patients to one drug can be completely different.
Surgical operations
Surgery for cardiac arrhythmia cannot be performed after eating, since various complications can occur during anesthesia, including aspiration pneumonia. Since most operations are performed as planned, the patient is not recommended to eat in the evening.
Radical methods for treating arrhythmia and tachycardia include:
- catheter ablation;
- valve replacement;
- installation of a pacemaker
- stenting or bypass surgery of the coronary arteries;
- implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator;
- removal of hormone-producing tumors;
- heart transplant.
All of these interventions for arrhythmia are aimed at eliminating the source of tachycardia. After normal myocardial function is restored, the rhythm disturbance also disappears.
Home therapy
Treatment of tachycardia at home can be done with herbs, exercises, diet, and various techniques that slow down the conduction of nerve impulses in the heart. Medication treatment at home is also possible, but it must be agreed with your doctor.
Uncontrolled use of antiarrhythmic drugs can cause the development of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias and even death of the patient.
Phytotherapy
Herbal treatment at home is perhaps the most common and quite effective method of treatment for arrhythmia and rapid pulse.
The following drugs are effective for treating tachycardia:
- You can reduce your heart rate during arrhythmia by taking turnip decoction. To do this, pour 200 ml of liquid into two large spoons of chopped root vegetables and cook for 15 minutes. Then strain and drink after meals.
- For uneven pulse and tachycardia, you can prepare a decoction of peppermint. To do this, brew a small spoonful of dried leaves of the plant with boiling water. You can also drink this medicine instead of regular tea after meals.
Physical training
A simple set of exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the body and heart can be performed by almost every patient. This does not require special equipment, and gymnastics can be done at home. Physical exercise should not be done after meals, since with a full stomach these activities do more harm than good. The optimal time for gymnastics is early morning.
Diet
The diet is not only possible, but also must be followed at home.
If arrhythmia and increased heart rate occur in a patient after eating, then most likely the mechanism of its development is associated with irritation of the diaphragm by a full stomach. In this case, a diet in which food is taken frequently, but in small portions, will help cope with tachycardia. This will reduce the load on the heart, and the patient’s condition will improve significantly.
The same can be said about overweight people. They have a relationship between body weight and the load on the myocardium. In this case, by reducing excess weight, the patient will reduce not only the load on the heart, but also the risk of developing arrhythmia. Any low-calorie diet will do to achieve this.
The cause of a rapid pulse may be a lack of certain vitamins and other nutrients, so nutrition for such arrhythmias should be balanced.
How to correctly calculate your pulse?
For self-counting, the most common method is palpation (palpation) of the radial artery of the wrist. You need to count your pulse at rest, no earlier than 2 hours after eating, bathing, or massage. The accuracy of the result depends on the correct counting technique.
First, you need to take a watch or stopwatch. Sit down with your hand on a horizontal surface, palm up. Place the index, middle and ring fingers of the opposite hand on the wrist approximately 3 centimeters from the base of the thumb;
When you feel the pulsation, you need to lightly press the artery to the inside of the radius. There is no need to press with force, as the pulse wave may disappear under pressure.
Then you need to count the number of blood pulses within 1 minute. Pulse waves should follow each other at regular intervals; then count the pulse on the second hand.
An increase in heart rate at rest greater than 90 beats per minute is considered tachycardia.
Breathing exercises for tachycardia
It is often easier to prevent tachycardia than to deal with attacks. And special breathing exercises can help you in this matter. It improves the filling of the heart with blood, trains the heart muscle, saturates the blood with oxygen, enhances gas exchange and stabilizes the pulse. In addition, it relieves emotional stress and calms the nervous system. Many methods of correct breathing for tachycardia have been developed, but the most popular and effective gymnastics are Buteyko, Strelnikova and qigong.
Breathing exercises according to Buteyko
These exercises, which help the heart, are known all over the world and are practiced by people in many countries. Initially, the complex was developed for patients with asthma, but later its creator realized that it could also be effective for people suffering from tachycardia. It is based on diaphragm training, and the complex itself consists of seven exercises.
- Inhale through your nose (for 5 seconds), leaving your stomach at rest, stop breathing for a few seconds and exhale. Perform 10 approaches.
- Inhale for 9 seconds, filling the diaphragm with air first and then the chest. Exhale slowly, rest for a few seconds. Take 11 similar breaths.
- Massage the bridge of your nose during rest breaks.
- Breathe alternately through your left and right nostrils (close one with your finger). Take 10 breaths into each nostril.
- Take one deep breath, while drawing in your stomach and hold your breath for 8 seconds.
- Take 12 breaths over the course of a minute (each should last at least two seconds).
- Normalize your breathing.
This breathing exercise has some contraindications: age under four years, developmental delay or mental retardation, period of viral diseases, severe bleeding or chronic tonsillitis. In these conditions, exercise can make you feel worse.
Complex of breathing exercises according to Strelnikova
These breathing exercises for tachycardia help fill the blood with oxygen. They should be performed twice a day (ideally before breakfast and before bed) for 25-30 minutes. In this case, you can gradually increase the load every day. Strelnikova’s gymnastics is also called paradoxical, because breaths in it are always combined with any movements that complicate this phase of breathing. The technique involves a short and noisy inhalation through the nose and a calm, smooth, voluntary exhalation (through the mouth or nose). It is important not to take in too much air when inhaling and not to interfere with exhalation; let all the air come out completely.
At first, you can take 4 breaths, and then double them, gradually reaching 32 breaths in a row.
The complex includes a large number of breathing exercises; we will give only a few of the main ones.
- In a standing position, bend your elbows and place them in front of you (as if for a game of “Ladushki”), then take a short and noisy breath in through your nose and at the same time clench your hands into fists (only the palms move, the hands are motionless). Exhale smoothly and calmly, while unclenching your fists. For the first time, take 8 breaths, then you can gradually increase their number.
- While standing, take a few small breaths and then start walking (1 breath per step). For the first time, take 8 breaths, then you can increase their number.
- In a standing position, lower your arms down and clench your fists for each inhalation, and unclench them for each exhalation. Repeat 6 times with a 25 second rest.
- In a standing position, keep your hands on your belt, while inhaling, lower your hands down, strongly unclenching your fingers, and as you exhale, return them to their previous position. Perform 12 times with a rest of 5-7 seconds.
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart, while inhaling, bend over and place your arms to the sides, and as you exhale, return to the starting position. Repeat 12-13 times with short rest breaks.
- Tilt your head left and right, take a sharp breath at the end point of the tilt.
- Perform springy bends of the torso forward and at the same time take a sharp, noisy breath at the lowest point. It is not necessary to bend very low and straighten your back completely.
- Bend your arms at the elbows and raise them to shoulder level. Bring your arms together in front of your chest (at this moment the upper part of your lungs is compressed) and take a noisy, active breath at this moment.
- Stay in the starting position, perform springy bends back and bring your arms in front of your chest. Inhale at the extreme point of the inclination.
- Perform spring squats in a half-lunge (one leg in front, the other behind) and bring your arms down. Inhale at the extreme point of the squat at the moment when you bring your arms together.
- Bend forward and backward like a pendulum. Inhale at the extreme point of the tilt; when bending back, bring your arms together in front of your chest.
Contraindications to performing this complex are: myopia, glaucoma, high blood pressure. Also, you should not combine Strelnikova’s exercises with other breathing techniques.
A set of qigong exercises
For arrhythmia and tachycardia of the heart, Tibetan qigong gymnastics is also effective. It is performed 2 hours after eating. It is important to monitor your pulse so that it does not exceed 120 beats per minute. If you experience shortness of breath or pain in the heart area during exercise, stop exercising and consult your doctor.
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart and lower your arms down. Wiggle your arms, then bend them at the elbows, lift them up and throw them down sharply. Relax and rest for a few minutes.
- Standing in one place, raise your legs one at a time. As you lift your leg, throw your opposite arm up. This exercise usually results in intense sweating.
- Standing straight, spread your arms to the sides and raise them with your palms up. Bending your back a little, take a slow breath, lean forward and, lowering your clenched fists, exhale.
- Standing straight, raise your arms at chest level and bend them slightly at the elbows (fingers should point up). As you inhale, smoothly spread your arms out to the sides as far as possible, squeezing your chest forward. As you exhale, return to the starting position. Continue the exercise until a feeling of warmth appears in your chest; it normalizes the functioning of the heart very well.
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart, raise your arms to chest level and connect them together. Make small circular movements with your hands; it is important to inhale and exhale in one circle.
- Standing straight, clasp your hands together and raise them to chest level. As you inhale, raise one elbow and lower the other. As you exhale, smoothly change your elbows, slightly bending your spine. Exercise stimulates the functioning of the heart and lungs well.
In general, any breathing exercise helps not only the heart, it relaxes the entire body, improves blood circulation, fills the blood with oxygen and relieves nervous tension well.
Physiological and pathological tachycardia
Depending on the causes of occurrence, physiological and pathological tachycardia are distinguished.
Physiological tachycardia occurs during emotional, physical stress, high temperature and humidity, being in hot and stuffy rooms, abuse of tonic drinks - strong tea, coffee, energy drinks, taking certain medications, smoking or drinking alcohol.
In healthy people, physiological tachycardia is an adaptive mechanism and, when the external stimulus is removed, the heart rate returns to normal within 5 minutes.
Pathological tachycardia occurs in cardiovascular, endocrine, acute infectious, oncological and other diseases and accompanying conditions - dehydration, large blood loss, shock conditions, pain syndrome, etc. - or when the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted.
Thus, tachycardia at rest is most often a symptom of some disease and requires medical examination.
With tachycardia, the heart works under increased load and does not have time to fill with blood in the required volume, the blood supply to all organs deteriorates, and oxygen starvation develops.
The kidneys, organs of vision and gastrointestinal tract, central and peripheral nervous systems suffer, and the course of existing diseases is complicated.
The heart muscle gradually wears out, which can result in heart failure. In addition, there is a life-threatening type of tachycardia, so a visit to the doctor cannot be postponed.
When should you see a doctor?
Alarming symptoms include constant heartbeat at rest with a heart rate of more than 80 beats per minute, different time intervals between pulse beats when counting the pulse, different pulse values on the left and right arms.
You should also consult a doctor in case of fainting, episodes of loss of consciousness, chest pain, a feeling of “interruptions” in the heart, tachycardia after blood loss, vomiting, diarrhea, when tachycardia is combined with shortness of breath, dizziness, insomnia, frequent headaches, increased blood pressure. pressure, increased sweating, trembling hands.
In addition, it is important to inform your doctor if tachycardia occurs even with minor physical activity and does not go away within 5 minutes, as well as if an attack of tachycardia begins suddenly or there are repeated attacks.
An attack of tachycardia is manifested by the following symptoms: within a few minutes, the heart rate increases sharply and can reach 150-200 beats per minute, accompanied by sweating, weakness, and a feeling of fear.
Heart arythmy. Symptoms, treatment methods
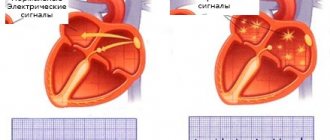
Cardiac arrhythmia is a disturbance in the frequency, rhythm and sequence of excitation and contraction of the heart. Arrhythmia is widespread and its causes can be any heart disease, as well as the influence of autonomic, endocrine and other metabolic disorders. Electrolyte disorders are especially important, in particular deviations in the content of potassium and calcium in cells. Arrhythmias are possible with intoxication and certain drug exposures; they may be associated with congenital characteristics of the conduction system. Arrhythmia is based on disturbances in the electrophysiological properties of the conduction system and contractile myocardium. Arrhythmias are diagnosed mainly by ECG.
TYPES AND SYMPTOMS OF ARRHYTHMIA
Sinus tachycardia - increased heart rate to 120-150 beats per minute. In healthy people, it occurs during physical and emotional stress. But after them, the heart rate returns to normal. A persistent increase in sinus rhythm up to 100-140 beats per minute is observed in heart failure, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, anemia, and diseases of the nervous system. In this condition, the patient experiences increased heartbeat with unpleasant sensations in the heart area.
The cause of such tachycardia can be household, toxic and medicinal effects. Their elimination leads to normalization of the condition without the additional prescription of any special drugs.
Paroxysmal tachycardia is a sudden increase in heart rate at rest to 140-200 beats per minute. The patient should be in a horizontal position during an attack; it is better to call a cardiac team.
Bradycardia is a drop in heart rate to 60-40 or less beats per minute. It is more common in neuroses and pathologies of the digestive system. No special therapy is required, exercise therapy (physical therapy) and massage are useful, it is recommended to take Zelenin drops, ginseng, and chamomile tea.
Extrasystole is a premature contraction of the heart or its parts. It can be asymptomatic; in some cases, the patient feels a “push” in the chest, “stopping” of the heart or pulsation in the epigastric region. For neuroses and reflex extrasystoles in people with diseases of internal organs, the most important is the correction of nutrition and lifestyle, as well as the treatment of the underlying and concomitant pathologies.
Atrial fibrillation - heart contractions, most often irregular, erratic, from 50 to 480 beats per minute.
Palpitations - a feeling of rapid or increased contractions of the heart. In healthy people, the appearance of palpitations is facilitated by changes in the excitability of the nervous system that regulates the activity of the heart, under the influence of heavy physical activity, excitement, high air temperature, abuse of tobacco, alcohol, strong tea, and coffee. Palpitations also occur in diseases of the cardiovascular system, in diseases occurring with fever. Sometimes this condition occurs even with slight physical stress or even at rest, and may be accompanied by a feeling of fear.
TRADITIONAL METHODS FOR TREATING CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA
When choosing a treatment method for arrhythmia, it is imperative to establish the cause and determine the type of arrhythmia. Identifying the underlying disease is one of the important tasks of complex treatment of such conditions. Another important task is to eliminate the arrhythmia itself.
It is necessary to begin treating the disease that caused the arrhythmia as early as possible. of medications (cardiac, anti-inflammatory, hormonal, etc.) depends on the correct diagnosis But treatment of these diseases alone is not always sufficient to normalize the conductivity of the heart muscle. In many cases, special medications are prescribed - antiarrhythmics. There are several groups of antiarrhythmic drugs. Some of them reduce cardiac conductivity, others, on the contrary, increase it. Some of them also relieve heart pain. Mineral and vitamin complexes are widely used in treatment.
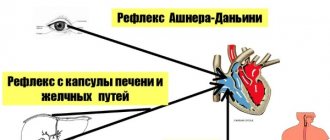
There are several reflex effects . with the help of which the heart rate decreases during paroxysmal and sinus tachycardia. This is a technique of pressing on the eyeballs for several minutes, massaging the sides of the neck on both sides (not used in older people). Pressure on the abdominals, deep breathing, and inducing a gag reflex have the same effect. These effects are not used in patients in the acute period of myocardial infarction, in severe stages of angina pectoris, or in cerebral atherosclerosis. The effect of these techniques is based on reducing the stimulating influence on the heart from the nervous system.
In addition to drug therapy and reflex techniques, pacemakers . which help the myocardium restore rhythm.
Physiotherapeutic treatment for arrhythmias is prescribed very selectively. For extrasystoles, it is possible to use electric sleep, a low-frequency magnetic field, carbon dioxide and radon baths. If attacks of atrial fibrillation occur no more than 1-2 times a month, carbon dioxide water and dry baths, as well as four-chamber baths, can be included in the treatment. For blockades and other forms of arrhythmias, except for atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal tachycardia, physiotherapeutic methods are not used.
Leave a comment or two
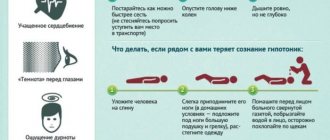
How to relieve an attack of tachycardia?
Unbutton your clothing collar, open a window or balcony, inhale deeply and exhale very slowly; breathe like this for 5-10 minutes. Then hold your breath and, as it were, “push” the air into the lower abdomen - this stimulates the vagus nerve, as a result of which the heartbeat will slow down;
Take Corvalol or Valocordin: dissolve 15-20 drops of the drug in half a glass of water at room temperature;
Wash your face with cold water, lie down on a high pillow, place a towel soaked in cold water on your forehead, try to relax;
Close your eyes and simultaneously press on your eyeballs for 2-3 minutes: press for 10 seconds, break for 10 seconds;
Find the right carotid artery (immediately under the jaw, at this point it connects to the cervical artery) and gently, without pressure, massage it. This technique also stimulates the vagus nerve and slows the heart rate.
If the condition does not improve, the heart rate does not decrease, dizziness appears, a feeling of shortness of breath, darkened vision, call an ambulance.