What factors affect heart rate?
The most common non-infectious pathology in all countries of the world is diseases of the circulatory system. Based on the results of epidemiological studies dating back to the late 90s of the 20th century, WHO experts came to the conclusion that an increase in heart rate (HR) at rest is one of the risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases in healthy people.
According to the national recommendations of the All-Russian Scientific Society of Cardiology, the resting heart rate of a healthy adult should be no more than 80-85 beats per minute and correspond to the pulse rate. The optimal heart rate for an adult at rest is from 60 to 80 beats per minute, while the specific heart rate is individual for each person and depends on a number of factors.
The first is gender. Women have higher normal heart rates than men. This is explained by the specific characteristics of hormonal and emotional backgrounds.
The second is age. In adults, the normal heart rate increases with age: at the age of up to 50 years, the average normal value is 70 beats per minute, at the age of 50-60 years - 74 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute in people over 60 years of age.
In addition, heart rate depends on lifestyle, including physical activity: trained people have a lower heart rate than those leading a sedentary lifestyle. Bad habits also have an impact - smoking, alcohol abuse.
And finally, this indicator correlates with external factors: heart rate increases with lack of sleep, nervous tension, after a heavy meal, increased ambient temperature, etc.
Who is at risk
Pathological forms of tachycardia, not associated with stress or physiological characteristics, most often occur in an already unhealthy body. The risk group includes patients with diseases of the nervous, endocrine, respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Women are more prone to certain types of tachyarrhythmias - for example, chronic inappropriate sinus tachycardia
In addition, there are behavioral risk factors for the development of arrhythmias. They are practically no different from those for any pathology of the circulatory system. These include excessive nervousness, excessive consumption of caffeinated drinks, lack of sleep and a sedentary lifestyle.
How to correctly calculate your pulse?
For self-counting, the most common method is palpation (palpation) of the radial artery of the wrist. You need to count your pulse at rest, no earlier than 2 hours after eating, bathing, or massage. The accuracy of the result depends on the correct counting technique.
First, you need to take a watch or stopwatch. Sit down with your hand on a horizontal surface, palm up. Place the index, middle and ring fingers of the opposite hand on the wrist approximately 3 centimeters from the base of the thumb;
When you feel the pulsation, you need to lightly press the artery to the inside of the radius. There is no need to press with force, as the pulse wave may disappear under pressure.
Then you need to count the number of blood pulses within 1 minute. Pulse waves should follow each other at regular intervals; then count the pulse on the second hand.
An increase in heart rate at rest greater than 90 beats per minute is considered tachycardia.
Folk remedies
Photo: evrikak.ru
There are traditional medicines that can slow down the heart rate. However, it is worth noting that in no case should you self-medicate; you must carefully follow all the recommendations of your doctor. Before using any folk remedy based on medicinal herbs, you should consult your doctor. We offer you the following recipes:
- Pre-grind the valerian root and dry it. Take 1 tablespoon of the resulting raw material and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let it brew for 1 – 2 hours, after which the infusion is ready for use. It is recommended to take 1/3 cup 3 times a day. The average course of treatment is 3 weeks;
- take 1 tablespoon of pre-prepared motherwort and pour 200 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 10 - 20 minutes. It is recommended to drink a glass of the resulting infusion throughout the day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks;
- take lemon balm and valerian root. Mix the listed collection components in equal proportions. Then a small amount of yarrow is added to the resulting collection. One tablespoon of the collection is poured into a glass of cold water and infused for 3 hours, after which the infusion is simmered in a water bath for 20 - 30 minutes. The finished broth should be carefully strained to prevent the ingress of small parts of raw materials. It is recommended to take 2-3 sips throughout the day. The course of treatment is 2 – 3 weeks;
- take 1 tablespoon of dried hawthorn leaves and flowers, pour 1 glass of boiling water, let it brew for 2 - 3 hours. After carefully filtering through a strainer, the infusion becomes ready for use. It is recommended to take 2 tablespoons 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 2 – 3 weeks;
- Grate the turnips on a fine grater, take 2 tablespoons of the resulting mass and pour a glass of boiling water. Place on the fire and simmer over low heat for 15 - 20 minutes. Let the broth cool, after which it should be strained. It is recommended to take ½ glass 2 times a day after meals;
- Take 1 tablespoon of dried rose hips and rinse them thoroughly under running water. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over the dried berries and let it brew for 6 hours, after which the finished infusion should be strained. It is recommended to drink half a glass 3 times a day.
It is important to emphasize once again that before using traditional medicine, you should consult with a qualified specialist. In addition, the use of folk remedies without medications is allowed only for mild tachycardia, when there are no hemodynamic disturbances.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Physiological and pathological tachycardia
Depending on the causes of occurrence, physiological and pathological tachycardia are distinguished.
Physiological tachycardia occurs during emotional, physical stress, high temperature and humidity, being in hot and stuffy rooms, abuse of tonic drinks - strong tea, coffee, energy drinks, taking certain medications, smoking or drinking alcohol.
In healthy people, physiological tachycardia is an adaptive mechanism and, when the external stimulus is removed, the heart rate returns to normal within 5 minutes.
Pathological tachycardia occurs in cardiovascular, endocrine, acute infectious, oncological and other diseases and accompanying conditions - dehydration, large blood loss, shock conditions, pain syndrome, etc. - or when the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted.
Thus, tachycardia at rest is most often a symptom of some disease and requires medical examination.
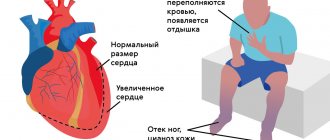
With tachycardia, the heart works under increased load and does not have time to fill with blood in the required volume, the blood supply to all organs deteriorates, and oxygen starvation develops.
The kidneys, organs of vision and gastrointestinal tract, central and peripheral nervous systems suffer, and the course of existing diseases is complicated.
The heart muscle gradually wears out, which can result in heart failure. In addition, there is a life-threatening type of tachycardia, so a visit to the doctor cannot be postponed.
Prevention of tachycardia
Since tachycardia itself is not a disease, there is no specific prevention for this condition. Primary preventive measures consist of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, daily routine and proper rest - that is, the same as for the prevention of any heart failure.
Secondary preventive measures that should be followed in case of already established heart pathology imply more serious lifestyle adjustments, drug therapy prescribed by a doctor (if necessary, surgical interventions), as well as regular medical examinations.
When should you see a doctor?
Alarming symptoms include constant heartbeat at rest with a heart rate of more than 80 beats per minute, different time intervals between pulse beats when counting the pulse, different pulse values on the left and right arms.
You should also consult a doctor in case of fainting, episodes of loss of consciousness, chest pain, a feeling of “interruptions” in the heart, tachycardia after blood loss, vomiting, diarrhea, when tachycardia is combined with shortness of breath, dizziness, insomnia, frequent headaches, increased blood pressure. pressure, increased sweating, trembling hands.
In addition, it is important to inform your doctor if tachycardia occurs even with minor physical activity and does not go away within 5 minutes, as well as if an attack of tachycardia begins suddenly or there are repeated attacks.
An attack of tachycardia is manifested by the following symptoms: within a few minutes, the heart rate increases sharply and can reach 150-200 beats per minute, accompanied by sweating, weakness, and a feeling of fear.
Atrial and atrioventricular varieties
The atrial type of tachycardia is rarely detected. It occurs in a small area, appears irregularly, but can last for several days or even months. In patients with severe heart failure and the elderly, there may be several lesions, but most often the condition is harmless, asymptomatic or with mild manifestations. This may include dizziness, shortness of breath, and chest pain. This condition is treated with standard medications: quinidine and other depressants, antiarrhythmic drugs, anesthetics. In difficult cases, surgical catheter ablation is performed.
The atrioventricular type is divided into two types: nodal and with additional pathways. Tachycardia is quite common (especially in women), attacks are rare, begin suddenly, last from several minutes to a day or more. Among the symptoms:
- pulsation in the cervical area characteristic of a tachycardic attack;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- anginal pain;
- suffocation and loss of consciousness.
The frequency and severity of paroxysms are successfully reduced with medication and physiotherapy. The cardiologist determines the treatment method, focusing on the origin of the pathology, existing complications, and the course of paroxysms.
How to relieve an attack of tachycardia?
Unbutton your clothing collar, open a window or balcony, inhale deeply and exhale very slowly; breathe like this for 5-10 minutes. Then hold your breath and, as it were, “push” the air into the lower abdomen - this stimulates the vagus nerve, as a result of which the heartbeat will slow down;
Take Corvalol or Valocordin: dissolve 15-20 drops of the drug in half a glass of water at room temperature;
Wash your face with cold water, lie down on a high pillow, place a towel soaked in cold water on your forehead, try to relax;
Close your eyes and simultaneously press on your eyeballs for 2-3 minutes: press for 10 seconds, break for 10 seconds;
Find the right carotid artery (immediately under the jaw, at this point it connects to the cervical artery) and gently, without pressure, massage it. This technique also stimulates the vagus nerve and slows the heart rate.
If the condition does not improve, the heart rate does not decrease, dizziness appears, a feeling of shortness of breath, darkened vision, call an ambulance.
Diagnostics
Only a cardiologist can determine how to treat cardiac tachycardia. It is useless to treat tachycardia itself as a symptom. The only effective way to combat heart palpitations is to eliminate its root cause.
- Available: doctor’s appointment from 1500 rubles
- Convenient: open daily from 8:00 to 21:00
- Quickly: we will carry out all the diagnostics at the first appointment
- Complete: has all the necessary equipment
But first of all, the root cause must be correctly identified. For this purpose, experienced cardiologists prescribe comprehensive diagnostics to medical patients. A set of laboratory and hardware examinations may include:
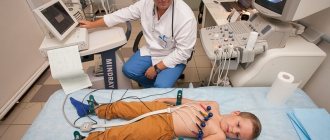
- Electrocardiogram is standard.
- Daily ECG monitoring according to Holter, 2-3 days monitoring).
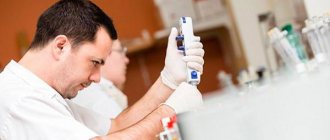
- General and detailed blood tests.
- Analysis of urine.
- Blood test for thyroid hormones.
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart.
- Echocardiography.