Tachycardia is one of the most common heart rhythm disorders. The main mechanism for the development of pathology is to increase the automaticity of the sinus node. In this case, the heart rate increases to more than 90 beats per minute. Tachycardia may not have subjective manifestations. Most often it is felt as increased heartbeat. In the presence of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, this type of arrhythmia can worsen the general condition and provoke the development of complications. Therefore, treatment of tachycardia should be prescribed and strictly monitored by a specialist.
Causes of tachycardia
An increased or increased heart rate does not always mean there are problems with the cardiovascular system. For example, in preschool age it is considered normal and does not require special help. Symptoms of cardiac tachycardia can also appear in practically healthy people as a result of activation of physiological compensatory mechanisms, that is, as the body’s response to the influence of one or another external factor. The reaction of the nervous and cardiovascular systems, accompanied by the release of adrenaline into the blood, causes increased heart rate. The occurrence of tachycardia can be provoked by the following factors:
- stress, physical activity and emotional arousal;
- increase in ambient temperature;
- consumption of caffeinated drinks, alcohol, and certain medications;
- sudden change in body position, etc.
When the action of the provoking factor ceases, the heart rhythm gradually returns to normal.
However, tachycardia often accompanies the presence of certain pathological conditions. It can be a manifestation of various cardiovascular diseases - arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction, heart disease (rheumatic or congenital), cardiosclerosis, etc. In addition, tachycardia can be neurogenic in nature, that is, associated with disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system and brain. Other causes include fever that develops against the background of an infectious-inflammatory process (pneumonia, tonsillitis, etc.).
Main reasons
A rapid pulse with low blood pressure is not always a dangerous condition and requires urgent medical intervention. The need for treatment and the effectiveness of therapy depend on why the heart rate has increased, as well as on the inverse relationship. That is, does the pressure drop due to an increase in heart rate or does the opposite happen? First, blood pressure decreases, and the heart rate increases.
Both conditions can be caused by different reasons. But more often, tachycardia becomes a secondary factor, manifesting itself as a compensatory reaction of the body to a sharp drop in blood pressure. A condition where a relatively healthy person’s pulse increases with reduced blood pressure is accompanied by hypovolemia. This means that there has been a decrease in the volume of blood circulating throughout the body.
There are two types of pathology:
- True. It manifests itself with blood loss, dehydration or release of blood plasma into the intercellular space - this reduces the amount of blood in the cavity of the vascular bed.
- Relative. It is characterized by pathological vasodilation, in which the blood volume is no longer sufficient to maintain blood pressure levels in a stable state.
In response to insufficient blood volume and a drop in pressure, the heart reacts by increasing the number of contractions to maintain the blood supply to important organs and systems - this is how a condition develops when the pressure is low and the pulse is fast. In this case, both the upper (systolic) and lower (diastolic) pressure drops immediately.
Dehydration
Losing a large amount of fluid from the body often leads to a decrease in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate. Dehydration occurs as a result of diarrhea (poisoning, infectious diseases, enterocolitis and irritable bowel syndrome). The body also loses a lot of fluid due to vomiting, excessive sweating, and after drinking large amounts of alcohol.
In an elderly person, a drop in blood pressure and increased heart rate are often the result of dehydration due to diabetes and the use of diuretics. Diuretics are prescribed to elderly patients to treat hypertension, which occurs in half of patients over 50–60 years of age; they remove excess fluid from the body. And with diabetes, glucose levels in the blood rise, causing the kidneys to produce more urine.
Blood loss
Blood loss is the most common reason why blood pressure drops during tachycardia. A person can lose blood as a result of injuries and inflammatory diseases, such as gastric and duodenal ulcers, hemophilia, malignant neoplasms of the intestine, esophageal varices, and cirrhosis of the liver.
Release of blood plasma into the intercellular space
Circulating blood volume decreases simultaneously with a drop in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate in the case of certain types of diseases. This happens with inflammatory pathologies of the kidneys, heart failure, liver and biliary tract diseases. Blood effusion also occurs after severe burns to the body and a decrease in protein levels in the blood.
Why can blood pressure decrease with tachycardia?
In many patients, the appearance of a rapid pulse causes a sharp decrease in blood pressure levels, that is, an inverse relationship can be traced. With an increased heart rate, the heart ejects less blood because it does not have time to be fully filled with it, which causes the blood pressure level to decrease.
However, this type of tachycardia, when the pulse affects the pressure, is relatively rare. This phenomenon is diagnosed in patients with signs of ischemia or in adolescents with additional congenital pathways of the cardiac conduction system. However, the pressure does not drop when the temperature rises, after physical activity, fear or pain.
Additional reasons
The following pathological conditions of the body may additionally lower blood pressure and increase heart rate:
- iron deficiency anemia, when the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood is reduced;
- panic attacks - attacks of uncontrollable anxiety, fear, panic;
- alcohol abuse and addiction to drugs;
- postprandial hypertension (when blood pressure drops sharply after eating food) and orthostatic hypertension (a jump in blood pressure downward with a sharp change in body position in space, mainly when getting up from a sitting or lying position);
- hypoglycemia – insufficient amount of glucose in the blood plasma;
- arterial valve stenosis;
- ingestion of toxic substances into the body (mercury vapor, lead, cyanide);
- thyrotoxicosis is dysfunction of the thyroid gland when it produces a large amount of hormones.
Often, low blood pressure readings are observed during exacerbation of allergies during grass flowering seasons. A person with a tendency to sensitization may feel weakness, shortness of breath, runny nose, lacrimation, his blood pressure drops, and his pulse quickens due to nervous excitement and swelling of the mucous membranes.
Symptoms of the disease
Tachycardia, which is a sign of a disease, is characterized by the following symptoms.
- A feeling of interruptions and/or “failures” in the functioning of the heart is the most common manifestation.
- Shortness of breath (lack of air), which occurs with little physical activity or even at rest.
- Pain in the heart (accompanies an attack of tachycardia in vegetative-vascular dystonia and some other diseases).
- Dizziness and darkening of the eyes, lightheadedness and even fainting (this is due to impaired blood supply to the brain).
In general, the manifestation of clinical symptoms of tachycardia depends on the nature of the underlying disease, as well as on the severity and duration of the arrhythmia itself.
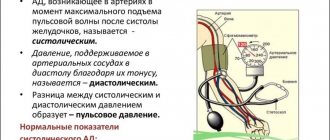
Norms of pulse and pressure
First of all, if signs of tachycardia appear against the background of low blood pressure, before going to the doctor you need to make sure that the pulse and blood pressure are measured correctly. Often people violate the required measurement algorithm, which is why they get incorrect results and panic ahead of time.
Pulse measurement should be carried out only on the wrist, during complete rest, without talking or laughing. Why shouldn’t you put your fingers on your neck, although heartbeats can be felt better there? In the area of the carotid artery, the vessels have a large diameter, and when exposed to and pressed on them, the heart rate (heart rate) indicators change and become unreliable.
Blood pressure should also be measured at rest, 40–50 minutes after eating, and you should not speak or move during the procedure. The measurement is carried out on both hands with an interval of 5 minutes, twice. In this case, the cuff should correspond to the volume of the arm, be worn 2–3 cm above the elbow and inflated 30–40 units more than the expected blood pressure level.
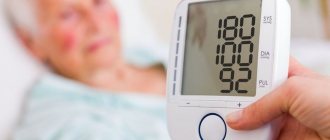
Blood pressure norms for different ages are:
- 17–20 years – 100/70, 120/80 mmHg. Art.;
- 20–45 years – 120/70, 130/80 mmHg. Art.;
- 50–60 years – 140/90 mm Hg. Art.;
- people over 60 years old – 150/90 mmHg. Art.
A high pulse with low pressure is most often recorded in people with signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia, as well as after prolonged or excessive physical exertion. Normally, after 30–60 minutes of physical activity, the heartbeat rhythm should recover on its own within 5–10 minutes. If this does not happen, especially if low blood pressure is recorded at the same time, initial signs of heart failure can be suspected.
Another reason for an increase in heart rate due to a decrease in blood pressure is considered to be chronic fatigue. When a person does not sleep the required 7–8 hours a day in a row, regularly suffers from stress and increased nervous excitability, the body gradually wears out, including the heart muscle.
The situation is aggravated for patients with signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia; their high pulse as a result of stress or overexertion is accompanied by weakness, fainting, sweating and dizziness. It often happens in hypotensive patients that the pulse jumps during visible weather changes and magnetic storms. Then they experience irritation, nervous excitement, the pulse rises, and the blood pressure level drops.
Consequences of tachycardia
Physiological tachycardia, which occurs in healthy people even in the presence of pronounced subjective manifestations, is not life-threatening and has a good prognosis. For patients suffering from heart disease, the consequences can be quite serious. The main and severe complications are the development of heart failure, states of loss of consciousness and even sudden death. In addition, the presence of tachycardia increases the risk of blood clots, which in turn leads to frequent heart attacks and stroke. Therefore, timely provision of assistance for tachycardia is so important.
Diagnosis of tachycardia
Electrocardiography
The ECG plays a leading role in the differential diagnosis of tachycardia and in helping to identify its causes. This method allows you to determine the type of pathology, as well as the rhythm and heart rate. If the severity of symptoms of cardiac tachycardia increases, it is advisable to conduct daily Holter ECG monitoring. This method is highly informative. It allows you to identify and analyze any heart rhythm disturbances within 24 hours. Holter monitoring helps detect ischemic changes during normal physical activity.
Echocardiography
It is a standard examination method to exclude heart pathology in case of any rhythm disturbances. Thanks to echocardiography, the doctor receives data on the size of the heart chambers, the thickness of the myocardial walls, and changes in the valve apparatus. This examination allows you to identify violations of local contractility.
Electrophysiological study
This is an invasive method of examining patients with cardiac pathology. Electrophysiological testing is used when appropriate before surgery to treat arrhythmia. Used to diagnose different types of tachycardia in a limited number of patients. This method boils down to determining the nature of the propagation of an electrical impulse throughout the myocardium, making it possible to determine the mechanisms of tachycardia or cardiac conduction disorders.
Additional examinations
Additional research methods are used to identify the causes of cardiac pathology. The specialist may prescribe a blood test (general and thyroid hormone tests) and electroencephalography. In rare cases, an MRI of the heart is performed, usually to detect congenital abnormalities.
Low pressure. High heart rate!
08/17/2021 | Category Hypertension
We treat people, we treat them, but they keep getting sick and sick, and we can’t cure them. Things are especially bad for those doctors who practice pills; this is of no use. I also heal people, and they heal from me. But more people still get sick than recover. Now all diseases are rejuvenated. The youth and children, all sick, went. Because it’s not clear what they eat: Coca-Cola, McDonald’s, candy bars, all sorts of Snickers, a lot of other things, very “healthy”, in quotes. What it is? How will they be healthy? What will happen to them by the age of 20-30?
I feel sorry for people who suffer from various heart problems, which is why I treat hypertension. Very often I hear complaints about low blood pressure and high pulse. What's happened? What is the reason? What to do? There can be many reasons. For example, there was an overdose of drugs for hypertension. When a person comes to see me and I tell him: “Do you understand that you are poisoned if you take these medications? You are drinking toxins, poison, poison,” he does not believe. And when the pressure jumps, out of fear he takes not one, as expected, but two or three pills. And the pressure drops because he poisoned his heart, swallowed pills that contain a substance that blocks cardiac activity. Or his blood vessels opened because he poisoned them all, and this caused his blood pressure to drop. Then an ambulance arrives and they begin to infuse a pressure-raising solution so that the person does not die from lack of oxygen in the brain.
Pressure can be reduced by cardiac or vascular means. When a person overdid it with vascular drugs, his blood vessels relaxed and his blood pressure dropped. What should the heart do in this case? How can he saturate his brain with oxygen? The brain demands food, begins to worry, demands: faster, faster, in order to at least get oxygen due to the speed of blood flow. At the same time, the heart overworks, becomes overloaded, and may not even have time to supply itself with blood through the coronary arteries. And then it is possible that a heart attack may occur due to a functional lack of oxygen in the heart muscle. In general, there is little good.
I described an acute situation, but there is also a chronic situation, if a person constantly takes blood pressure medications for years. His heart function is getting worse and worse, because the pressure has not gone away, and he can no longer live without pills. He became addicted to the drugs, he toxically poisoned himself and, above all, the heart muscle. The heart weakens and can only maintain pressure through the pulse. Heart failure occurs. This is a chronic case.
Low blood pressure and high pulse occur even in young people with a normal heart and normal blood vessels. A vertebra in the neck is displaced, which sharply reduces blood flow to the control center of the heart and blood vessels. With such a violation, a person develops panic syndrome. Panic arises due to a sharp lack of oxygen in the head. The disruption of blood flow in the vascular center is so strong that it simply does not work, as if it is turned off. And then, in order to maintain vital activity, the heart autonomously raises pressure. Although usually at the level of cardiac regulation, the heart can only increase or decrease the pulse rate. The pressure is controlled by the central apparatus. In any case, low blood pressure and high pulse are very bad signs. And if this happens to you, then you need to understand the reasons in detail and get qualified help. It's not worth tolerating. However, drugs that reduce pulse and increase blood pressure should not be used either.
Imagine that the specific cause of the violation is not yet clear to you. But its symptoms are removed, but the cause, for example, disruption of blood flow to the brain stem, where the vascular center is located, is left. The pulse was lowered with one drug, the pressure was increased with another. And then the blood flow was restored, and the control center started working. He did the same thing as the medications: he lowered the pulse and raised the blood pressure. The result was a double effect. In this case, hypertensive crisis and bradycardia (low pulse) are inevitable. This is a very bad combination, because the heart works at maximum load, it puts a lot of pressure, and the pulse is rare. Blood passes through the coronary arteries that supply the heart with difficulty, and all this with a powerful load on the heart. In such a situation, you can get a heart attack. Here we need to understand it clinically. The question is quite serious. I hope I explained everything clearly.
Watch more in the video:
____________
Follow Dr. Shishonin on Instagram and get more useful health tips:
https://www.instagram.com/shishonin_official/ @shishonin_official
Treatment of tachycardia
Medicinal
To treat tachycardia, drugs belonging to the following groups are used.
- Antiarrhythmic. These are drugs with different mechanisms of action. Only the attending physician can prescribe them, based on clinical data. Self-medication is dangerous, since the same medications can be effective for one type of tachycardia and contraindicated for another.
- Sedatives. Most often these are synthetic drugs or herbal products. They are prescribed for the treatment of tachycardia associated with vegetative-vascular dystonia. Such drugs help normalize the functioning of the nervous system and, as a result, reduce the frequency of arrhythmia attacks.
If tachycardia is accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, pressor amines are usually prescribed to increase it to a level of 100-110 mmHg. Art.
Surgical
Common radical methods of treating tachycardia include minimally invasive surgery. It is performed under local anesthesia. This could be radiofrequency catheter ablation, installation of an artificial pacemaker, etc. Among the main reasons requiring serious surgical care are the following.
- Hormonal disorders. Common causes of tachycardia are thyrotoxicosis (excess thyroid hormones) and pheochromocytoma (a hormonally active tumor in the kidney or adrenal gland). In such cases, surgical removal of the tumor or part of the gland that produces excess hormones is usually recommended.
- Structural and functional changes. Cardiac surgery is performed in the presence of severe congenital heart defects, severe circulatory disorders (IBC), to eliminate the consequences of rheumatism, etc.
In some cases, arrhythmia does not require special treatment if it is a symptom of anemia, is caused by the presence of a malignant blood disease (for example, leukemia), occurs against the background of fever, etc. For tachycardia caused by such causes, treatment is the elimination of the underlying disease.
Treatment
Treatment of tachycardia with hypotension depends on the reasons that provoked the pathological changes. Typically, drugs that slow your heart rate also lower your blood pressure. Therefore, the therapy of the pathology is complex and consists of a whole range of means. Taking any medications on your own is strictly prohibited.
The patient must not only take the prescribed medications, but also follow the doctor’s recommendations. You need to follow a daily routine and a special diet, and avoid stress. You should stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Experienced specialists at the medical center in Lyublino treat tachycardia due to hypotension. Doctors have extensive experience and successfully cope with pathology. To make an appointment and for more information, please call.
All articles
5% discount Print coupon from our website
Ask your question on the website Get professional advice!