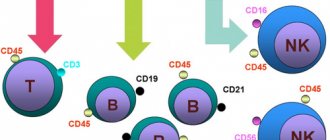
A general blood test makes it possible to confirm a superficial diagnosis of adverse changes in the human body. If, during such a diagnosis, the ratio of several different types of leukocytes is established, which is called leukogram or leukocyte formula, the specialist can determine the state of the immune system and give a very likely assumption about the progression of the infection (bacterial or viral in nature). So, this article will consider an example of a case in which decreased lymphocytes and increased neutrophils were found.
First you need to find out what their concepts are. Both types of cellular structures are types of white blood cells (as well as monocytes, eosinophils and basophils), but their functions and purposes in the human body differ significantly.
Decreased neutrophils – neutropenia
Neutropenia is a reduced concentration of neutrophils and other granulocytes in the blood. It can be physiological and pathological. Physiological neutropenia occurs during excessive physical exertion, during pregnancy, after eating or stress. This condition is caused by the influence of various exogenous factors:
- radiation radiation,
- toxic substances - poisons and chemicals,
- some medications - antibiotics, immunosuppressants, hormones, cytostatics.
Physiological neutropenia does not pose a threat to human life and goes away on its own after the provoking influence is eliminated.
The cause of the pathological form is always a disease . Such neutropenia requires additional examination to identify the cause of the disorder.
Diseases in which the level of neutrophils in the blood decreases:
- viral infections - ARVI, chicken pox, hepatitis, rubella, measles, HIV;
- generalized fungal infection;
- chronic inflammation;
- radiation sickness;
- hematological disorders - agranulocytosis, anemia;
- hereditary forms of cyclic and severe congenital neutropenia;
- helminthiasis and parasitosis;
- malignant bone marrow tumors;
- allergic reactions - anaphylactic shock.
As a result of these pathologies, the bone marrow produces fewer neutrophils. A long-term inflammatory process depletes the human body and disrupts its functions. Blood cells are actively dying, the neutrophil series does not have time to be replenished with new forms. Some medications have a direct inhibitory effect on myelopoiesis, the process of neutrophil formation.
Neutropenia is a polyetiological condition. When making a diagnosis, this indicator is rarely assessed in isolation. In the hemogram, the ratio of various leukocyte fractions plays a key role.
Table: the combination of different leukocytes is normal
Increased lymphocytes – lymphocytosis
Lymphocytosis is a condition in which the absolute number of lymphocytes in the blood exceeds 3.6x109. In this case, the level of neutrophils is reduced, and the level of monocytes is increased.
Lymphocytes perform a protective function, destroying viruses, atypical cells, and pathogenic fungi. When the body is attacked by these foreign agents, lymphocytosis occurs. There are other processes in which the concentration of these immune cells in the blood increases. An increased level of lymphocytes indicates the onset of inflammation in the body. The doctor, analyzing the accompanying manifestations, determines the location of the lesion.
Pathologies in which the concentration of lymphocytes in the blood increases:
- viral infections - chickenpox, measles and rubella in a child, influenza and ARVI in an adult;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- specific bacterial infection - tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis, diphtheria;
- acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemia;
- lymphosarcoma;
- hyperthyroidism;
- autoimmune disorders.
These diseases are manifested by lymphocytosis and neutropenia. As a result of hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue, hypersecretion of lymphocytes occurs, which intensively enter the blood. This is observed when the process is chronic, long-term recurrent course of the disease and when inflammation subsides.
Lymphocytosis with an increase in neutrophils is observed with purulent inflammation - sepsis, peritonitis, tonsillitis, pyelonephritis; necrotic processes - stroke, frostbite, gangrene, extensive burns; lead or alcohol intoxication; oncopathology.
Lymphocytosis is sometimes observed in completely healthy people. The physiological form occurs when:
- pregnancy,
- menses,
- poor nutrition,
- prolonged fasting,
- alcohol abuse,
- smoking,
- high physical activity,
- hard work
- chronic stress,
- general exhaustion,
- violation of blood donation rules.
An increased level of lymphocytes in the blood is considered a temporary phenomenon. Lymphocytosis occurs after any operation. It is always found in individuals who have undergone splenectomy.
Causes of low lymphocytes and increased neutrophils
Typically, low lymphocytes and high neutrophils are caused by various pathologies and viruses. It is understood that in both the first and second cases the factors of deviation from the norm will be different.
So, an increase in neutrophils usually occurs due to the following factors:
- acute infections caused by bacteria, which are accompanied by a purulent-inflammatory process:
- localized _ Observed with moderate neutrophilia with certain manifestations (abscesses, infections of the ENT organs, appendicitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, acute tonsillitis, diseases of the genitourinary organs and others);
- generalized. For severe neutrophilia (sepsis, peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), infectious diseases such as cholera or scarlet fever).
- necrosis and necrotic lesions (myocardial infarction, stroke, gangrene, severe burns);
- recent vaccination;
- effects on the bone marrow of toxic substances (alcohol, lead);
- bacterial toxicosis without infection directly by bacteria (for example, when there were unbroken botulinum toxins in the food, and the bacteria themselves had already become inactive);
- the disintegration of a malignant neoplasm is a process in which damaged cells stop growing and begin to be excreted naturally.
In turn, a decrease in lymphocytes most often indicates the following problems.
- Miliary tuberculosis (hematogenous, usually generalized form of tuberculosis, accompanied by a dense rash of small tuberculous tubercles in the lungs).
- Tuberculosis of the bronchial glands.
- Hematological diseases of lymphatic tissue (lymphoma, lymphosarcoma).
- Exposure of the body to different types of ionizing radiation. Severe health effects, such as skin burns or radiation sickness, can occur when the radiation dose crosses certain limits.
- Multiple myeloma is a malignant neoplasm of plasma cells, which is mainly localized in the bone marrow.
- Aplastic anemia is a disease of the hematopoietic system. With this disease, the bone marrow basically stops producing different types of blood cells, including red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells in the required quantities.
- The use of glucocorticoids are steroid hormones from the subclass of corticosteroids produced by the adrenal glands.
- AIDS, a condition that progresses due to HIV infection and is characterized by a decrease in T-lymphocytes and multiple opportunistic diseases.
- Renal failure is a dysfunction of the kidneys. The decrease can occur in both acute and chronic forms of renal failure.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus is a serious illness during which the human immune system mistakes its own cells for foreign agents and begins to fight them.
- Lymphogranulomatosis is a malignant disease of lymphatic tissue, accompanied by the presence of huge Reed-Berezovsky-Sternberg cellular structures, which are identified during a microscopic examination of the affected lymph nodes.
Based on the reasons described above, if the levels of segmented neutrophils are increased and lymphocytes are decreased, this most likely indicates the presence of a viral infection or the development of inflammation. In this case, you need to immediately consult a doctor and undergo treatment.
Decreased neutrophils and increased lymphocytes at the same time
The leukocyte formula is important when making a diagnosis. It is in the leukogram that changes most often occur. However, the total number of leukocytes remains normal.
- Viral infections are characterized by an increase in lymphocytes and a decrease in neutrophils. The absolute level of leukocytes in the blood does not exceed normal limits. Such leukogram data indicate the body’s active fight against viruses. They are often obtained at the incubation stage, when there are no symptoms of the disease, and the microbes have already entered the body and begun their life activity. Neutropenia and lymphocytosis are observed in persons who have recently had acute respiratory viral infections. Lymphocytes migrate to the site of inflammation, multiply and differentiate to provide reliable antimicrobial protection. It takes some time for blood counts to normalize. When recovery occurs, the concentration of leukocytes is restored.
- Cancers are characterized by an imbalance of immune cells that form and mature in the bone marrow. Tumors of an organ disrupt its functioning. At the same time, the level of lymphocytes increases and the number of neutrophils in the blood decreases. Aplastic anemia is manifested by pallor, impotence, dizziness, and bleeding. In the absence of timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the disease develops into leukemia. The most common oncohematological diseases include chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. B lymphocytes accumulate in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and liver. These oncopathologies are characterized by a slow course and specific symptoms.
- Neutropenia with lymphocytosis is also observed in allergic reactions . Such research results allow doctors to determine the presence of a tendency to allergies. At the same time, along with lymphocytes, eosinophils are also increased.
- Many lymphocytes in the blood are found not only during respiratory infections , but also during tuberculosis, brucellosis, typhoid fever, systemic lupus erythematosus, lymphogranulomatosis, and renal pathology.
- Purulent-destructive and vascular diseases also require a hemotest, which can be used to detect lymphocytosis and neutropenia. These include: abscesses, phlegmons, boils, gangrene, heart attack, stroke.
Decreased neutrophils and increased lymphocytes in the blood are a common sign of a bacterial or viral infection. Extensive infection is accompanied by the release of an infectious agent into the bloodstream. Neutrophils quickly die after interacting with the pathogen, and the bone marrow does not have time to produce them in sufficient quantities. Patients experience the main symptoms of the pathology: fever, chills, lethargy, rapid heartbeat, hyperhidrosis, tachypnea, hypotension. If signs of intoxication syndrome appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. To make a correct diagnosis and avoid mistakes, it is necessary to evaluate the quantitative indicators of blood cells not in isolation, but in the totality.
In children, low neutrophils and high lymphocytes are normal. This crossover is due to an incompletely formed immune system. A common reason for deviation is vaccination. In response to foreign invasion, the body reacts by producing antibodies - lymphocytes. In this case, granulocytes are not produced in full.
Indicators of two forms of neutrophils
When a neutrophil develops in the red bone marrow, it forms into a band.
It enters the plasma in certain quantities and after a certain period of time is divided into segments. So it becomes segmented, that is, fully formed, and after a few hours it penetrates the membranes of the capillaries of various organs. It is in those areas that it resists foreign agents. The concentration of segmented cells is written as a percentage in the leukocyte formula. With its help, it is possible to assess the condition of the blood, and therefore the body. However, before this, the norm of these cells in the blood should be determined. As already mentioned, in an adult healthy person the norm of segmented bodies ranges from 47% to 72%, and in band bodies it corresponds to 1–5%.
The analysis can also show changes in the leukocyte formula. Typically, two shifts are specified, either left or right. A shift of the formula to the left indicates the presence of bodies that are not yet fully formed, which, in accordance with the norm, should be exclusively in the bone marrow, but not in the blood. And a shift of the formula to the right means that the content of segmented cells is increased, and the number of nuclear segments becomes more than five.
Therefore, when deciphering a clinical analysis, it is necessary to pay close attention to the indicators of both forms, since deviations can warn of serious changes in the body.
If you promptly see the discrepancy between these bodies and the required number, there is a chance of avoiding many of the ensuing consequences that are associated with the development of the inflammatory process.
Diagnostics
Lymphocytes and neutrophils are blood cells that perform vital functions and can tell a lot about the patient’s condition. In order not to miss the development of serious diseases, it is necessary to take a general blood test annually. Leukocytes are determined according to special standard standards. The identified discrepancy characterizes the high activity of blood cells and signals the beginning of the development of pathological processes. Based on the results of the study, even hidden, asymptomatic diseases can be detected.
The analysis requires capillary blood from the patient. They take it in the morning, strictly on an empty stomach, having eliminated smoking and alcohol for several days. You should inform your doctor in advance about taking vital medications. The patient should be as calm as possible physically and psychologically before collecting the material. Only a specialist can correctly decipher the results of the study. He evaluates all hemotest indicators in aggregate. The leukocyte formula deserves special attention, reflecting the ratio of individual types of leukocytes in percentages and numbers. Leukocyte calculation allows you to determine the number of white blood cells per unit volume. The content of some fractions changes due to an increase or decrease in others.
An extended blood test with leukocyte count is required for patients with:
- acute infectious and inflammatory diseases,
- immunodeficiency conditions,
- frequent relapses of bacterial and fungal infections,
- pregnant women.
By analyzing a high or low percentage of white blood cells, the doctor may suspect a patient has a rare autoimmune disorder, hematological disease, or immunodeficiency. Based on the leukocyte formula, one can draw a conclusion about the development of complications, the course of the pathological process and the prognosis of the disease. Using leukogram results, doctors differentiate between viral and bacterial infections.
- Viral damage is characterized by an increase in lymphocytes and a decrease in neutrophils.
- Infectious diseases caused by bacteria are manifested by a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left - an increase in neutrophilic leukocytes and a relatively low content of lymphocytes.
Laboratory indicators do not allow making a final diagnosis of the existing pathology. To do this, it is necessary to conduct a more detailed examination of the patient, including clinical signs, anamnestic data, instrumental methods and a whole list of analyzes of biological material.
To determine the cause of the disorder, the doctor needs to find out:
- patient complaints,
- objective signs,
- anamnesis,
- heredity.
Taking certain medications can affect the number of certain fractions of leukocytes in the blood . These include antibiotics, antihistamines, diuretics, corticosteroids, anticoagulants, and muscle relaxants. It is necessary to inform the doctor about the treatment performed. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy also cause an increase in the proportion of white cells in the blood. A prolonged decrease in neutrophils and an increase in lymphocytes require additional examinations - blood tests for tumor markers, tomographic, radiographic and ultrasound examinations of internal organs.
After receiving the results of tests and tests, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and draws up a treatment plan.