Important components of immunity include lymphocytes, which are a separate subgroup of lymphocytes. They are produced in the bone marrow; the main task of the elements is to identify foreign pathogens and formulate an immune system response to them. An increase in the number of lymphocytes is associated with pathologies that need to be determined to select the correct therapy.
Lymphocytes - what are they, what are they?
Lymphocytes are one of the components of white blood cells; a complete blood test for lymphocytes . They play an important role in the formation of immune responses. Their function is to recognize pathogens and mutated own cells. After identifying a foreign object, lymphocytes destroy it in one way or another: phagocytosis, production of special antigens. To destroy their own cells that have degenerated into cancer or have undergone other changes, lymphocytes send a special chemical signal that causes such a cell to start the process of self-destruction. In addition to a general blood test for lymphocytes, a biochemical blood test is performed at the MedArt Medical Center.
There are three types of these cells:
- T lymphocytes. They mature in the thymus. They play an important role in the fight against foreign bodies and infections. Some T-lymphocytes perform regulatory functions and are responsible for the duration and strength of the immune response. It is these cells that are affected when infected with HIV.
- B lymphocytes. Their main task is to produce antibodies against viruses and other infectious agents. In addition, they are able to retain information about past diseases, thereby creating permanent immunity.
- NK – cells. Their main function is to detect and eliminate body cells that have degenerated into malignant ones.
Lymphocytes are formed in the red bone marrow; their young, immature forms are called lymphoblasts. Maturation occurs in several stages, occurring not only in the bone marrow, but also in the lymphoid nodes and other organs of the lymphatic system.
The appearance of an increased number of lymphocytes can serve as a marker of bone marrow pathologies and the development of tumor processes in it. An increase in the level of lymphoblasts is also recorded during prolonged infectious processes. In this case, this serves as a sign of depletion of the body's defenses. The immune system does not have time to prepare a sufficient number of lymphocytes to fight the pathogen, and this becomes the reason for the appearance of a large number of lymphoblasts in the blood.
Features of lymphocytosis
The term indicates disturbances in the functioning of the female body, the activity of the immune system to combat intrusions:
- bacteria, viruses;
- protozoa, parasites.
Other reasons for an increased concentration of lymphocytes include their damage or death due to:
- burn disease;
- tissue necrosis;
- inflammatory processes;
- allergies;
- autoimmune diseases;
- oncological pathologies.
Cells reach problem areas, but with further progression of the disease they begin to die en masse.
The chronic form of lymphocytosis is the result of diseases of the blood or hematopoietic system, lymphatic department. Taurus do not fully mature and cannot fully perform the functions assigned to them. To normalize the balance, the bone marrow produces even more lymphocytes, but the benefits from the increased work are minimal.
The accumulation of protective cells may be due to problems with their utilization in the spleen. Doctors believe that it is not deviations in tests that are of greatest importance, but the sources of their occurrence. Dysfunction of the immune system leads to the development of chronic infections, autoimmune diseases with attacks on one’s own cells, the formation and further proliferation of atypical structural units.
Indications for analysis
A general blood test for lymphocytes is prescribed if there is a suspicion of an increase or decrease in their number. The analysis can be prescribed for other reasons; it allows you to obtain a lot of valuable data about the state of the blood and the whole body. The main indications include:
- Detection of the immune response to the presence of pathogenic microorganisms.
- The state of human immunity.
- Physical and chemical composition of blood.
- Preventive analysis - to detect hidden changes in the blood formula that do not manifest themselves with specific symptoms.
Why are lymphocytes needed?
A detailed blood test is a unique picture that can reveal even the most insignificant health data.
Blood consists of three groups
components:
- red blood cells
involved in the transport of oxygen; - platelets
, which initiate blood clotting; - leukocytes (“white blood”)
– the “parents” of immunity.
They are formed from five subgroups
: neutrophils; - lymphocytes;
- monocytes;
- basophils;
- eosinophils.
Each of the subgroups performs its assigned protective function.
Lymphocytes, along with other components, are responsible for the immune response to pathogenic bacteria and form “immune memory”. Only unlike monocytes and neutrophils, which destroy third-party bacteriological components that enter the blood, leukocytes fight their own diseased cells
. These include areas affected by viruses, mutations and tumor formation.
Appearing in the blood, lymphocytes remain “clean” only for several days. After this, different glands (lymph nodes) differentiate them into types, assigning each their own functions.
| Type of lymphocyte | Blood percentage | Functions |
| B lymphocytes | 10-15% | The most important cells are form a “memory” of the immune system . Every time B lymphocytes encounter pathogenic cells, they adapt to them and “record” this condition in “immune memory”. Advertising: Thanks to them, vaccination becomes effective, and throughout life the body develops immunity and remains resistant to previous diseases. |
| T lymphocytes | 80% | They are engaged in suppressing pathogenic viruses, bacteria, and fungi. |
| NK lymphocytes | 5-10% |
They are responsible for the destruction of their own cells, on the surface of which a marker of infection is detected. With their help, the body itself can overcome virus-infected and tumor cells. |
Preparing for analysis
The analysis for lymphocytes is included in the general blood test, the rules for their conduct are the same. That is, such an examination does not require special preparation. There are only two conditions that must be met:
- Blood is taken in the morning.
- 8-12 hours before blood sampling you need to abstain from food.
You should also not smoke 2-3 hours before the procedure. Components of tobacco smoke can cause serious temporary changes in white blood cell levels. You should avoid drinking alcohol 2-3 days before taking the test, as alcohol can also affect the reliability of the results obtained.
If these requirements are not met, the accuracy of the examination may deteriorate, which will lead to the doctor receiving unreliable information and possible errors in diagnosis or re-prescribing the examination.
Assessment of cellular immunity indicators
The first study is always a leukocyte count (see chapter “Hematological studies”). Both relative and absolute values of the number of peripheral blood cells are assessed.
Determination of the main populations (T-cells, B-cells, natural killer cells) and subpopulations of T-lymphocytes (T-helpers, T-CTLs). For the initial study of immune status and identification of severe immune system disorders
WHO recommended determination of CD3, CD4, CD8, CD19, CD16+56, CD4/CD8 ratio. The study allows you to determine the relative and absolute number of the main populations of lymphocytes: T cells - CD3, B cells - CD19, natural killer (NK) cells - CD3- CD16++56+, subpopulations of T lymphocytes (T helper cells CD3+ CD4+, T-cytotoxic CD3+ CD8+ and their ratio).
Research method
Immunophenotyping of lymphocytes is carried out using monoclonal antibodies to superficial differentiation tonsillitis on cells of the immune system, using flow laser cytofluorometry on flow cytometers.
The selection of the lymphocyte analysis zone is made based on the additional marker CD45, which is present on the surface of all leukocytes.
Conditions for taking and storing samples
Venous blood taken from the ulnar vein in the morning, strictly on an empty stomach, into a vacuum system to the mark indicated on the tube. K2EDTA is used as an anticoagulant. After collection, the sample tube is slowly inverted 8-10 times to mix the blood with the anticoagulant. Storage and transportation strictly at 18–23°C in an upright position for no more than 24 hours.
Failure to meet these conditions leads to incorrect results.
Interpretation of results
T lymphocytes (CD3+ cells).
An increased amount indicates hyperactivity of the immune system, observed in acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. An increase in the relative indicator occurs with some viral and bacterial infections at the onset of the disease and exacerbations of chronic diseases.
A decrease in the absolute number of T-lymphocytes indicates a failure of cellular immunity, namely a failure of the cellular-effector component of immunity. It is detected in inflammation of various etiologies, malignant neoplasms, after injury, surgery, heart attack, smoking, and taking cytostatics. An increase in their number in the dynamics of the disease is a clinically favorable sign.
B lymphocytes (CD19+ cells)
A decrease is observed with physiological and congenital hypogammaglobulinemia and agammaglobulinemia, with neoplasms of the immune system, treatment with immunosuppressants, acute viral and chronic bacterial infections, and the condition after removal of the spleen.
An increase is observed in autoimmune diseases, chronic liver diseases, cirrhosis, cystic fibrosis, bronchial asthma, parasitic and fungal infections. Typically during the period of convalescence after acute and chronic viral and bacterial infections. A pronounced increase is observed in chronic B-lymphocytic leukemia.
NK lymphocytes with the CD3-CD16++56+ phenotype
Natural killer cells (NK cells) are a population of large granular lymphocytes. They are capable of lysing target cells infected with viruses and other intracellular antigens, tumor cells, as well as other cells of allogeneic and xenogeneic origin.
An increase in the number of NK cells is associated with activation of anti-transplant immunity, in some cases observed in bronchial asthma, occurs in viral diseases, increases in malignant neoplasms and leukemia, and in the period of convalescence.
A decrease is observed with congenital immunodeficiencies, parasitic infections, autoimmune diseases, radiation, treatment with cytostatics and corticosteroids, stress, and zinc deficiency.
Helper T-lymphocytes with the CD3+CD4+ phenotype
An increase in absolute and relative amounts is observed in autoimmune diseases, possibly in allergic reactions, and in some infectious diseases. This increase indicates stimulation of the immune system to the antigen and serves as confirmation of hyperreactive syndromes.
A decrease in the absolute and relative number of T cells indicates a hyporeactive syndrome with a violation of the regulatory component of immunity and is a pathognomic sign for HIV infection; occurs in chronic diseases (bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.), solid tumors.
T-cytotoxic lymphocytes with the CD3+ CD8+ phenotype
An increase is detected in almost all chronic infections, viral, bacterial, protozoal infections. Is characteristic of HIV infection. A decrease is observed in viral hepatitis, herpes, and autoimmune diseases.
CD4+/CD8+ ratio
The study of the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (CD3, CD4, CD8, CD4/CD8) is recommended only for monitoring HIV infection and monitoring the effectiveness of ARV therapy. Allows you to determine the absolute and relative number of T-lymphocytes, subpopulations of T-helpers, CTLs and their ratio.
The range of values is 1.2–2.6. A decrease is observed with congenital immunodeficiencies (DiGeorge, Nezelof, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome), with viral and bacterial infections, chronic processes, exposure to radiation and toxic chemicals, multiple myeloma, stress, decreases with age, with endocrine diseases, solid tumors. It is a pathognomic sign for HIV infection (less than 0.7).
An increase in value of more than 3 – in autoimmune diseases, acute T-lymphoblastic leukemia, thymoma, chronic T-leukemia.
The change in ratio may be related to the number of helpers and CTLs in a given patient. For example, a decrease in the number of CD4+ T cells in acute pneumonia at the onset of the disease leads to a decrease in the index, but CTL may not change.
For additional research and identification of changes in the immune system in pathologies
requiring assessment of the presence of an acute or chronic inflammatory process and the degree of its activity, it is recommended to include a count of the number of activated T-lymphocytes with the CD3+HLA-DR+ phenotype and TNK cells with the CD3+CD16++56+ phenotype.
T-activated lymphocytes with the CD3+HLA-DR+ phenotype
A marker of late activation, an indicator of immune hyperreactivity. The expression of this marker can be used to judge the severity and strength of the immune response. Appears on T-lymphocytes after the 3rd day of acute illness. With a favorable course of the disease, it decreases to normal. Increased expression on T lymphocytes can occur in many diseases associated with chronic inflammation. Its increase was noted in patients with hepatitis C, pneumonia, HIV infection, solid tumors, and autoimmune diseases.
TNK lymphocytes with the CD3+CD16++CD56+ phenotype
T-lymphocytes carrying CD16++ CD 56+ markers on their surface. These cells have properties of both T and NK cells. The study is recommended as an additional marker for acute and chronic diseases.
A decrease in them in the peripheral blood can be observed in various organ-specific diseases and systemic autoimmune processes. An increase was noted in inflammatory diseases of various etiologies and tumor processes.
Study of early and late markers of T-lymphocyte activation (CD3+CD25+, CD3-CD56+, CD95, CD8+CD38+)
additionally prescribed to assess changes in IS in acute and chronic diseases, for diagnosis, prognosis, monitoring the course of the disease and therapy.
T-activated lymphocytes with the CD3+CD25+ phenotype, IL2 receptor
CD25+ is a marker of early activation. The functional state of T-lymphocytes (CD3+) is indicated by the number of receptors expressing IL2 (CD25+). In hyperactive syndromes, the number of these cells increases (acute and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, thymoma, transplant rejection), in addition, their increase may indicate an early stage of the inflammatory process. In peripheral blood they can be detected in the first three days of illness. A decrease in the number of these cells can be observed with congenital immunodeficiencies, autoimmune processes, HIV infection, fungal and bacterial infections, ionizing radiation, aging, and heavy metal poisoning.
T-cytotoxic lymphocytes with the CD8+CD38+ phenotype
The presence of CD38+ on CTL lymphocytes was noted in patients with various diseases. An informative indicator for HIV infection and burn disease. An increase in the number of CTLs with the CD8+CD38+ phenotype is observed in chronic inflammatory processes, cancer and some endocrine diseases. During therapy, the indicator decreases.
Subpopulation of natural killer cells with the CD3- CD56+ phenotype
The CD56 molecule is an adhesion molecule widely present in nervous tissue. In addition to natural killer cells, it is expressed on many types of cells, including T-lymphocytes.
An increase in this indicator indicates an expansion of the activity of a specific clone of killer cells, which have less cytolytic activity than NK cells with the CD3- CD16+ phenotype. The number of this population increases in hematological tumors (NK-cell or T-cell lymphoma, plasma cell myeloma, aplastic large cell lymphoma), chronic diseases, and some viral infections.
A decrease is observed with primary immunodeficiencies, viral infections, systemic chronic diseases, stress, treatment with cytostatics and corticosteroids.
CD95+ receptor
– one of the apoptosis receptors. Apoptosis is a complex biological process necessary to remove damaged, old and infected cells from the body. The CD95 receptor is expressed on all cells of the immune system. It plays an important role in controlling the functioning of the immune system, as it is one of the receptors for apoptosis. Its expression on cells determines the cells' readiness for apoptosis.
A decrease in the proportion of CD95+ lymphocytes in the blood of patients indicates a violation of the effectiveness of the last stage of culling defective and infected own cells, which can lead to relapse of the disease, chronicization of the pathological process, the development of autoimmune diseases and an increase in the likelihood of tumor transformation (for example, cervical cancer with papillomatous infection ). Determination of CD95 expression has prognostic significance in myelo- and lymphoproliferative diseases.
An increase in the intensity of apoptosis is observed in viral diseases, septic conditions, and drug use.
Activated lymphocytes CD3+CDHLA-DR+, CD8+CD38+, CD3+CD25+, CD95.
The test reflects the functional state of T-lymphocytes and is recommended for monitoring the course of the disease and monitoring immunotherapy for inflammatory diseases of various etiologies.
Research method
Material for analysis of lymphocytes is collected from a vein using a conventional syringe or a special vacuum system. The traditional technique of taking an analysis using a conventional syringe is currently outdated and can lead to the following difficulties:
- Blood clotting in a needle.
- Destruction of some blood cells.
- Long manipulation time.
- Contact of blood with the environment
- It is difficult to maintain the correct ratio of blood and reagents. In addition, the traditional technique does not exclude contact of medical personnel with the patient’s biomaterial, which can pose a health hazard. Therefore, many clinics use modern vacuum containers for blood collection.
Blood enters it due to the vacuum in the test tube; all parameters of the vacutainer are selected at the production stage in order to reduce the time for blood collection and ensure the correct ratio of the amount of reagent and blood.
Advantages of vacuum systems:
- A standardized blood collection process that takes minimal time.
- Contact of medical staff with the patient’s blood is completely excluded.
- Simple labeling and identification of samples, eliminating confusion with tubes.
- Almost painless procedure.
You can take blood for a general analysis from a finger, but at the moment this procedure is used much less frequently.
What affects the level of lymphocytes
When lymphocytes in the blood increase in women, there may be many reasons that provoked the phenomenon.
Advertising:
The concentration of lymphocytes is influenced by such basic factors
:
- unbalanced diet, prolonged fasting;
- lifestyle, bad habits (especially smoking), stress;
- hormonal changes, including those due to the menstrual cycle and pregnancy;
- blood loss as a result of various injuries always causes a decrease in the level;
- previous surgical intervention;
- individual physiological characteristics;
- Frequent use of medications, in particular the use of contraception.
Under the influence of the above reasons, the indicator may have slight fluctuations even in an absolutely healthy woman.
If the lymphocyte count is out of range and shows too high a level, this phenomenon is called lymphocytosis. Most often it occurs due to the development of a focus of inflammation in some part of the body.
It is important to understand that lymphocytosis does not occur as a separate disease: it is already a consequence, the source of which is a previously occurring disease.
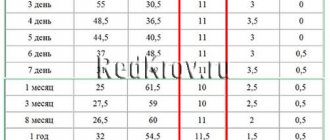
Norms
The normal level of lymphocytes in the blood depends on the age of the patient. In children, the number of lymphocytes is higher; over time, this figure gradually decreases. The number of these cells is influenced by the gender of the patient; in women the indicator is relatively higher. This is due to the greater activity and adaptive capacity of the lymphatic system of the female body.
| Person's age | Absolute content | Ratio in % |
| In a child under one year old | 2-12 | 45-71 |
| In a one-year-old child | 4-10 | 38-61 |
| 2-4 years | 3-9 | 34-50 |
| 4-10 years | 1,6-6,7 | 31-51 |
| 10-18 years | 1,3-5,3 | 31-43 |
| Over 18 years old, adults | 1-4,9 | 20-40 |
| Cancer risk for women: | 265 | 368 |
Lymphocyte norms in women
The number of lymphocytes in women is affected by hormonal changes, menstrual cycle disruptions, and pregnancy
To determine the number of lymphocytes (LYM) in the blood, they are counted during a blood test; the result is compared with the established norm. The number of these cells should be approximately the same in men and women, but for the latter some deviation from the standard values is allowed.
The level of LYM in the body is determined based on two types of values: relative and absolute. The relative amount is indicated based on the percentage of the total level of cells in a given group, and the absolute amount is indicated in units per 1 liter of blood.
The LYM norm for women ranges from 22 to 37% in relative terms, and 1-4.7 units in absolute terms.
Active production of T-lymphocytes by the immune system is a normal reaction to the introduction of bacterial or viral infectious agents into the body. Based on this, we can conclude that their increased level signals inflammatory processes that occur against the background of the vital activity of foreign bodies.
The norm of lymphocytes for women is established taking into account the age and condition of the body (pregnancy, phase of the menstrual cycle or menopause). Their maximum number is typical for girls under 1 year of age and amounts to up to 75% in relative terms. This ratio is determined by the active functioning of the immune system at this stage of child development.
Then the LYM rate gradually decreases. Thus, the following indicators have been established:
- up to 55% – girls under 10 years old;
- 30-45% – puberty;
- from 20 to 37% – from 16 years of age.
In medicine, there are significant and insignificant increases in this criterion (the latter is not significant and does not affect the diagnosis).
If the established norm is exceeded by 10 units, but no other changes in laboratory criteria are observed, then this can be considered as a physiological feature.
For example, if the analysis results in a LYM percentage of 43-45%, the patient will be given a repeat blood test after 3 days. Such indicators may be the result of daily fluctuations or improper preparation for collecting biomaterial. However, if the first analysis showed a lymphocyte count of more than 50%, then with a high probability the doctor will prescribe additional diagnostic methods.
Lymphocytes are increased
The reason why lymphocytes are elevated is often a variety of viral infections. This increase is called lymphocytosis, and is most often recorded in diseases caused by viruses:
- Epstein-Barr.
- Adenovirus.
- Herpes.
- Childhood infections (rubella, measles, mumps).
The number of lymphocytes may increase with some bacterial infections, such as syphilis, whooping cough, or tuberculosis. Diseases caused by protozoa, such as malaria and toxoplasmosis, can lead to lymphocytosis. Often, an increase in lymphocytes is caused by helminthic infestations.
Lymphocytes may be elevated for reasons unrelated to infection. These include:
- Hypersensitivity reactions.
- Stress lymphocytosis.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Disorders of the endocrine organs, especially the thyroid gland.
- Development of tumors and pretumor processes.
The most striking signs of an increase in the number of lymphocytes include:
- Enlarged liver, spleen and lymph nodes.
- General malaise, manifestations of respiratory infections, redness and swelling of the mucous membranes.
- A sharp increase or decrease in temperature, accompanied by chills.
- Dyspeptic symptoms - vomiting, stool disorders, nausea.
- Nervous system disorders due to elevated temperature.
It should be borne in mind that lymphocytosis does not always manifest itself through severe symptoms. Often, elevated levels of these cells are discovered by chance. Only a doctor can accurately determine the reason why a change in the blood formula occurred; this often requires additional tests.
To eliminate lymphocytosis, you need to cure the disease that led to an increased immune response. It is important to understand that the hematopoietic system responds to recovery with a certain delay. Even after complete recovery, lymphocytosis can persist for up to several months.
What is the danger of increased lymphocytes?
Blood cancer is the most terrible diagnosis when there is an increase in lymphocytes in the blood
An increase in lymphocytes in itself is not dangerous: the diseases that caused such a change may pose a danger.
Let's consider the most common diseases in which a laboratory sign occurs:
- Infectious mononucleosis occurs when infected with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a member of the herpes virus family. Typical manifestations: difficulty breathing through the nose without discharge, sore throat, sudden enlargement of lymph nodes, weakness, rise in temperature. As the disease progresses, symptoms of damage to internal organs appear: rashes on the body, yellowing of the skin and sclera, darkening of urine and discolored feces.
Cells infected with EBV become almost immortal and prone to degeneration into malignant ones. It is possible that the Epstein-Barr virus is the cause of lymphogranulomatosis and nasopharyngeal carcinomas (cancerous tumors).
- Herpes virus infection begins with severe weakness, drowsiness, fatigue, lymph nodes become enlarged, and vesicular rashes appear on days 2-3. The localization of the bubbles is different: lips, nasal mucosa, genitals, torso. Shingles is one of the manifestations of herpes infection and is a very serious disease.
- Lymphocytosis can be the first sign of HIV infection, so when doctors have an increase in lymphocytes, they first prescribe a blood test for HIV and hepatitis B and C. The immunodeficiency virus can circulate in the body for up to 10 years after infection without causing clinical symptoms. Frequent herpetic rashes, colds, weakness and drowsiness may cause slight concern. During the period of the first manifestations, the temperature rises, the lymph nodes enlarge, a sore throat develops, diarrhea and headache appear. A person may mistake the symptoms for a common cold, treat it with medication, and forget about the incident. Subsequently, the patient gradually loses weight, has a prolonged fever, suffers from bowel movements, white masses appear in the mouth (fungal infection), and the red border of the lips often becomes inflamed (cheilitis).
- Blood cancer - leukemia, lymphoma - the most terrible diagnosis when the number of lymphocytes increases. The main symptoms are identical for any leukemia: pronounced enlargement of lymph nodes, night sweats, weakness, fever, fatigue, shortness of breath and cough.
Lymphocytes are low
A decrease in lymphocytes is called lymphopenia. This condition is typical for the following diseases:
- AIDS.
- Long-term, severe infections.
- Bone marrow pathologies.
- Tumors of lymphatic tissues.
- Exposure to radiation.
- Taking certain groups of drugs, such as cytostatics.
- Pregnancy.
In most cases, a decrease in the level of lymphocytes indicates a depleted immune system, when the body, for various reasons, is unable to maintain the required level of these cells in the blood.
Lymphopenia rarely presents with characteristic symptoms. The most common signs of this condition include:
- Reduction or complete absence of tonsils and other peripheral lymph nodes.
- Skin diseases - eczema, pyoderma.
- Common signs of blood diseases are ulcers of the oral mucosa, petechiae, pallor, and jaundice.
- Enlarged liver and spleen.
As in the case of lymphocytosis, to normalize the level of these cells, it is necessary to eliminate the cause that led to the pathological condition. You need to see a doctor who can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment regimen.
In the case of lymphopenia in pregnant women, with a moderate decrease in the level of lymphocytes, there is no need to take special measures. Enhanced monitoring of your health status and regular completion of all necessary examinations is sufficient. If there is a sharp drop in lymphocytes, you should seek medical help for additional diagnostics.
Reasons for increased lymphocytes in women
All causes of lymphocytosis are divided into three types. In accordance with this, the reasons for the increase in lymphocytes in the blood in women are also identified.
Relative lymphocytosis
With an infectious disease, there is an increase in lymphocytes in the blood
If the levels of other body cells are normal, then elevated lymphocytes in the blood may indicate:
- Acute viral infection. Lymphocytes are the first barrier when the body encounters pathogenic viruses. Therefore, in diseases at the acute stage, the number of T-LYM increases earlier than the level of other blood cells.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. This disease is characterized by damage to connective tissue both at the local and systemic levels. The causes and mechanism of arthritis are not yet fully understood. Some researchers are inclined to believe that the etiology of the disease is bacterial in nature, since about 25 different species of bacteria have been identified that take part in the process.
- Elevated levels of certain thyroid hormones. Problems with the thyroid gland are often accompanied by autoimmune disorders, when the body cannot adequately recognize “its own” and “foreign” cells. In this case, the immune system activates defense mechanisms with double force, which is accompanied by increased production of lymphocytes.
- Chronic adrenal insufficiency. The disease is secondary and occurs due to bacterial infection (tuberculosis, for example) or after intoxication with particularly dangerous chemical compounds.
- Abnormal enlargement of the spleen. Here the level of lymphocytes will depend on the severity of the pathology. For example, in infectious diseases and autoimmune disorders the increase is weak, but in malaria it is strong.
- Typhoid fever. This infectious disease has a characteristic clinical picture, and therefore the doctor will quickly determine the cause of the increase in lymphocytes in the blood.
LYM may increase as a side effect of certain medications.
Absolute lymphocytosis
Absolute lymphocytosis in women can be observed for the following reasons:
- Viral infection. It is especially acute in hepatitis, cytomegalovirus infection, and mononucleosis.
- Whooping cough. “Childhood” infection, accompanied by a long, painful cough.
- Pathologies of the lymphatic system that develop into malignant neoplasms. They are characterized by excessive accumulation of T-lymphocytes in the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
- Toxoplasmosis. If infected during pregnancy, there is a high probability that the child will die at birth. Those who survived suffer from severe pathologies (central nervous system diseases, mental retardation, etc.).
- Tuberculosis. Modern medicine can easily diagnose this disease. The sooner the patient undergoes a full diagnosis, the greater the likelihood that the disease can be quickly overcome.
Lymphocytosis during pregnancy
A pregnant girl may not be aware of an abnormally high level of lymphocytes in her blood, so often this fact is revealed only after a detailed examination and testing.
During pregnancy, a decrease in the number of lymphocytes is observed in the female body, which is normal. This is a tactic of the body developed over thousands of years at the genetic level, thanks to which the fetus is protected from the mother’s immune system. Otherwise, the immune system would activate all defense mechanisms to overcome the father’s foreign biomaterial. Every pregnant woman should know about this and understand that the norm of lymphocytes will be different for her.
Here, any deviations from the proper level of lymphocytes may indicate any disturbances in the mother’s body, which may also affect the development of the fetus. Therefore, pregnant women should donate blood regularly to promptly identify any possible problems.
Types of lymphocytosis, reasons for their appearance
Depending on the root cause that causes the growth of lymphocytes and the rate of their increase, different types of this phenomenon are distinguished.
Advertising:
| Type of lymphocytosis | The reason why it occurs |
| Reactive | Diseases that cause disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. These include infectious mononucleosis, vitamin deficiency, AIDS, and exhaustion of the body for various reasons. Of the bacterial infections, only two can cause lymphocytosis: tuberculosis of various forms and syphilis. To normalize the level of lymphocytes, you only need to get rid of the infection. |
| Malignant | Oncological neoplasms of a malignant nature. Depending on the stage of development of the pathology, lymphocytosis can occur in acute or chronic form. In the latter case, it becomes very difficult to find the disease that caused the growth of lymphocytes. |
| Post-infectious | Previously suffered acute diseases of infectious origin. Most often, lymphocytosis is provoked by influenza, rubella, chicken pox, various forms of hepatitis, measles and scarlet fever. |
Causes of lymphocytosis
Elevated lymphocytes in the blood of women against the background of normal levels of other immune cells may be a sign of:
- acute form of viral infection
. Lymphocytes are the first defense mechanism that is activated when encountering foreign antigens. At the acute stage of the disease, the number of lymphocytes reaches its maximum, while other immune cells are not yet activated; - rheumatic diseases
. A sign of pathology is damage to connective tissue of a local or systemic nature. The nature of rheumatic diseases still remains a controversial issue. Some scientists are inclined to bacterial etiology. For example, the causative agents of rheumatoid arthritis include more than 25 species of bacteria. Among them, in addition to pathogenic species, there are also representatives of the normal microflora of the human body; - excess levels of thyroid hormones, which is often accompanied by various autoimmune pathologies
. In this case, there is a failure in the process of recognizing “self” and “foreign” cells. At the same time, the immune system activates protective mechanisms against its own cells; - chronic adrenal insufficiency
. As a rule, the disease is of a secondary nature and occurs as a result of a bacterial infection (for example, tuberculosis) or intoxication with chemicals; - abnormal enlargement of the spleen
. The severity of the pathology depends on the root cause as a result of which it arose. Thus, a slight increase is typical for infectious and autoimmune diseases. A pronounced form of pathology is observed in malaria
How to lower the level of lymphocytes
It is important to remember that it is not lymphocytosis itself that needs to be treated, but its root – the disease that triggered the development.
Having gotten rid of pathogenic bacteria and viruses, the number of cells will normalize on its own over time.
The only exception is the appearance of physiological lymphocytosis. In such cases, doctors prescribe personalized medication regimens to restore the balance of blood components. The dosage and mechanism of taking drugs are prescribed individually, after a detailed medical diagnosis.
Diagnosis of lymphocytosis
It is impossible to accurately diagnose pathology only by the number of lymphocytes. Checking the blood condition is based on a detailed blood test.
Most often these indicators are compared
:
- Leukocytes and lymphocytes
. Their mutual increase may indicate blood cancer. With tuberculosis and some other viral infections, a low leukocyte count and a high lymphocyte count are shown; - Platelets and lymphocytes
. An increase in two indicators is observed in autoimmune diseases; - Red blood cells and lymphocytes
. The synchronous growth of these bodies occurs during infection.
Symptoms of lymphocytosis
In the initial stages of increasing the level of lymphocytes in a person, no special changes or symptoms are observed.
Lymphocytosis is not a disease, but a current state of the blood, which is formed as a result of the development of pathology and indicates the work of the body’s defense system, therefore it has no specific symptoms
.
Any accompanying changes or external signs correspond to the disease that caused lymphocytosis.
Advertising:
It is usually accompanied by the following symptoms
:
- enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits, neck, behind the ears, and in the groin area;
- when palpated, you feel their lumpiness, the place of pressure begins to hurt, and turns red;
- temperature rises;
- some women experience increased sweating;
- severe migraines;
- you feel constant fatigue, even with moderate exercise;
- the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, constipation or diarrhea, nausea often occur;
- appetite worsens, weight loss.
To correctly find out what the growth of lymphocytes indicates, you need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis from a doctor and pass all the prescribed tests. Untimely treatment and prolonged presence of lymphocytes outside normal limits can cause complications.