Published: 03/30/2021 17:00:00 Updated: 03/30/2021
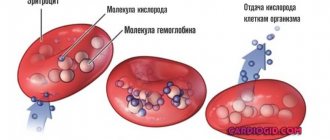
Erythrocytes are red blood cells, the most numerous blood cells. Formally, they are not cells, since during the process of maturation they lose many of the structures necessary for cells. For example, they lack nuclei and do not synthesize any protein molecules, unlike other cells in the body. So the name “cell” in this case is used for convenience. Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow and constantly circulate in the body, performing the most important function of maintaining life - they carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs and remove carbon dioxide.
In addition to red blood cells, blood contains plasma, platelets, and leukocytes. However, the number of red blood cells is so large that just a couple of drops of blood contains about one billion of these cells. They make up about 40% of the total blood volume. Actually, it is red blood cells that give our blood its characteristic red color due to its hemoglobin content.
Red blood cells do not last forever, they wear out over time and eventually die. The average life cycle of a red blood cell is approximately 120 days—a total of four months. However, do not worry, the bone marrow is constantly producing new cells and maintaining the required level of red blood cells. Various unfavorable circumstances can reduce or, conversely, increase their reproduction rate and affect their life expectancy - thus, the balance of blood composition is disrupted. An increase or decrease in red blood cells is associated with various pathological conditions. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
How to insure yourself against hemolysis when taking tests?
Unfortunately, when taking tests, practically nothing depends on the patient.
However, it is important to make the right choice of clinic. It is worth choosing a medical institution that has a good reputation and where qualified doctors work
In principle, even if hemolysis occurs during the test, it’s okay. Of course, it’s a pity to waste your time and money (in some cases) on a repeat visit to the clinic. The situation is worse with children. Usually a blood test is very frightening for a small child (especially if the blood is taken from a vein) and getting him to come to the laboratory is quite an event. And what mother would want her child to have a vein injected several times?
To prevent such situations, do not be afraid to ask nurses and laboratory technicians about the specifics of their work. You can ask under what conditions the material will be stored and what will be done with it later. In most cases, health workers at private clinics are quite friendly and will not be annoyed by such questions.
If you have to take a blood test, make sure you have sterile equipment in advance. It is worth bringing gloves, a syringe and possibly a test tube. It would be nice if the preservative solution was poured into your test tube right in front of you. This will make it possible to ensure that the container is clean and sterile.
If you plan to take tests in a private clinic, you should first read reviews about it. It happens that people complain of constant blood clotting after the test - and this happens in the same clinic. Thus, most likely, the management of the medical institution makes money from repeated tests, which are again paid for out of the patients’ pockets. In these cases, you should demand your money back and retake the test elsewhere.
Causes and types of pathological hemolysis
Where red blood cells are destroyed.
what is blood hemolysis and why does it occur? The types of hemolysis, depending on the reasons for its development, are diverse, as are the reasons themselves:
When studying the properties of red blood cells in the diagnosis of certain diseases, sometimes a blood test is required, such as the osmotic resistance of erythrocytes (ORE), which we will consider separately, although it is directly related to osmotic hemolysis.
Osmotic resistance of red blood cells
The osmotic resistance of red blood cells determines the stability of their membranes when placed in a hypotonic solution.
OSE happens:
- Minimal
- they talk about it when less resistant cells begin to collapse in a 0.46 - 0.48% sodium chloride solution; - Maximum
- all blood cells disintegrate at a NaCl concentration of 0.32 - 0.34%.
The osmotic resistance of erythrocytes is directly dependent on the shape of the cells and the degree of maturity they are at. A characteristic of the shape of red blood cells, which plays a role in their stability, is the sphericity index (the ratio of thickness to diameter), which is normally 0.27 - 0.28 (obviously, the difference is small).
The spherical shape is characteristic of very mature red blood cells, which are on the verge of completing their life cycle; the stability of the membranes of such cells is very low. In hemolytic anemia, the appearance of spherical (spheroid) forms indicates the rapid death of these blood cells, this pathology reduces their life expectancy by 10 times, they cannot perform their functions for more than two weeks, therefore, after existing in the blood for 12 - 14 days, they die. Thus, with the appearance of spherical forms in hemolytic anemia, the sphericity index also increases, which becomes a sign of premature death of erythrocytes.
Young cells that have just left the bone marrow—reticulocytes and their precursors—are endowed with the greatest resistance to hypotension. Having a flattened discoid shape and a low sphericity index, young erythrocytes tolerate such conditions well, therefore an indicator such as the osmotic resistance of erythrocytes can be used to characterize the intensity of erythropoiesis and, accordingly, the hematopoietic activity of the red bone marrow.
Norms and detection of pathology
To determine hemolysis, serum levels of hemoglobin, reticulocytes and bilirubin are measured. Sometimes the life cycle of red blood cells needs to be measured using radioisotope techniques.
To determine whether the destruction of red blood cells is normal, it is necessary to determine the density of their membrane using the osmotic resistance method, which allows one to determine the minimum or maximum destruction.
After taking blood, a special test is performed - the hemolysis index (HI), which measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. In men, the optimal number of red blood cells is 4.3-5.7 * 106 / μl, in women 3.9-5.3 * 106 / μl. The number of red blood cells in a child under 12 years old is 3.6-4.9 * 1012 / cell, 12-15 years old - 3.9-5.5 * 1012 / cell.
Also, in laboratory studies, the hematocrit norm is determined as the ratio of the total volume of red blood cells to the total volume of plasma.
The optimal value for men and women is 0.4-0.52 and 0.37-0.49, respectively.
The norm of hematocrit in children under 1 month is 0.56-0.45, 0.35-0.39 from 1 to 15 years and 0.47 over 15 years.
Determining the sphericity of red blood cells is of great importance. This is the ratio of diameter and wall thickness. The normal value in humans is 0.26-0.28.
Red blood cells at the end of life have a spherical shape. If a similar configuration is observed in young cells, their life expectancy is reduced tenfold, and they themselves die without performing their function.
The appearance of globular blood cells indicates an increase in the sphericity index, which indicates the development of hemolytic anemia.
Young cells (reticulocytes) that have just emerged from the bone marrow are the most viable. Due to the thickened shape of the disc, they have a low spherical index.
If the analysis reveals increased destruction of red blood cells, repeated blood sampling is recommended to eliminate sampling errors and ensure the reliability of the result.
Hemolysis in children
Reticulocyte level in blood test
It is detected immediately at birth, and is caused by the incompatibility of the antibodies of the mother and child. In children, severe swelling, anemia, and jaundice are pronounced. As in adults, pathology is divided into intravascular and intracellular.
Incompatibility between the blood of the fetus and mother is determined during pregnancy and is often treated in utero. Most often, a baby is born by caesarean section. Hemolytic disease usually occurs in premature infants.
Further treatment of the child, and sometimes the mother, is carried out based on the clinical picture. It includes blood transfusions and hormone therapy.
Simultaneously with blood transfusion, glucocorticosteroid treatment is carried out, for example with the drug Cortisone, administered intramuscularly.
Often you have to stop feeding your baby breast milk, which is a non-drug treatment.
Treatment of hemolysis
Therapy for a hemolytic crisis depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and the causes that caused it.
Destination:
- Exchange blood transfusion (for hemolytic disease of the newborn);
- Administration of blood replacement solutions;
- Plasmaphoresis;
- Administration of hormones;
- Hemodialysis.
The effectiveness of the measures is monitored by constant laboratory research.
How to insure yourself against hemolysis when taking tests?
Hemolytic anemia
Unfortunately, when taking tests, almost nothing depends on the patient
However, it is important to make the right choice of clinic. It is worth choosing a medical institution that enjoys a good reputation and where qualified doctors work. In principle, even if hemolysis occurs during the test, it’s okay
Of course, it’s a pity to waste your time and money (in some cases) on a repeat visit to the clinic. The situation is worse with children. Usually a blood test is very frightening for a small child (especially if the blood is taken from a vein) and getting him to come to the laboratory is quite an event. And what mother would want her child to have a vein injected several times?
In principle, even if hemolysis occurs during the test, it’s okay. Of course, it’s a pity to waste your time and money (in some cases) on a repeat visit to the clinic. The situation is worse with children. Usually a blood test is very frightening for a small child (especially if the blood is taken from a vein) and getting him to come to the laboratory is quite an event. And what mother would want her child to have a vein injected several times?
To prevent such situations, do not be afraid to ask nurses and laboratory technicians about the specifics of their work. You can ask under what conditions the material will be stored and what will be done with it later. In most cases, health workers at private clinics are quite friendly and will not be annoyed by such questions.
If you have to take a blood test, make sure you have sterile equipment in advance. It is worth bringing gloves, a syringe and possibly a test tube. It would be nice if the preservative solution was poured into your test tube right in front of you. This will make it possible to ensure that the container is clean and sterile.
If you plan to take tests in a private clinic, you should first read reviews about it. It happens that people complain of constant blood clotting after the test - and this happens in the same clinic. Thus, most likely, the management of the medical institution makes money from repeated tests, which are again paid for out of the patients’ pockets. In these cases, you should demand your money back and retake the test elsewhere.
What to do to avoid hemolysis
To prevent destruction of red blood cells in the body, you should:
Avoid not only eating unfamiliar mushrooms, but even contacting them; take precautions when staying in habitats of poisonous insects and snakes; When working with toxic chemical compounds, use protective equipment; long-term drug therapy is carried out under the control of blood tests.
It is possible to prevent immunoconflict hemolytic diseases in newborns by examining women with negative Rh blood (analysis of amniotic fluid, chorionic villus biopsy). They need the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin after an abortion or the birth of an Rh-positive fetus. Termination of a first-time pregnancy is strictly prohibited.
Hemolysis Clinic
If a person does not have symptoms of atypical hemolysis, and the destruction of red blood cells is not associated with pathology and occurs as planned, then the person will not feel any symptoms, and this is normal, since natural hemolysis is provided by nature.
Acute hemolysis of erythrocytes is characterized by rapid development, and a person’s health condition deteriorates sharply. Most often, an acute condition occurs after a blood transfusion, if the components do not fit, as well as in case of drug poisoning or infection. The insidiousness of acute hemolysis lies in the intensity of the manifestations, and the body simply cannot cope with restoring the number of red blood cells instead of those destroyed. Therefore, hemolysis of erythrocytes in acute form is manifested by anemia and bilirubin intoxication.
In the acute course of the disease, the skin becomes yellowish, and the patient begins to experience nausea and vomiting.
In acute hemolysis, the skin becomes yellowish, the patient complains of nausea and vomiting. Pain is felt in the abdomen, but a person cannot accurately indicate its location. Severe pathology is accompanied by fainting and convulsions. Anemia is accompanied by weakness, pallor, and shortness of breath. The spleen enlarges, and the same happens to the liver. The urine becomes dark. The test results reveal changes in the composition of blood and urine - severe hemoglobinemia and bilirubinemia, thrombocytopenia are determined. At the same time, the level of urea and creatinine increases, the factors of fibrinolysis and hemoglobinuria decrease.
As for the subcompensated form of hemolysis, in this phase the process of production of red blood cells by a special process of the bone marrow is enhanced. Considering that the number of red blood cells is gradually compensated, in this case the clinical manifestations are not so striking, but still quite distinguishable. This is an increase in liver and spleen parameters, dermatological manifestations. In this form, anemia is practically not detected, and laboratory tests show an increase in the number of reticulocytes, which indicates that a regenerative process is occurring in the blood.
Separate mention should be made of hemolysis in newborns. The first manifestations of hemolysis begin in children even at the time of their intrauterine development. The cause of hemolysis is the incompatibility of the blood parameters of the mother and child.
The extent to which hemolysis will manifest itself directly depends on the rate of increase in antibody titers in maternal blood. Clinically, hemolysis in infants can develop in one of 3 ways:
- hydropic. This is an unfavorable option for the development of pathology. It is unfavorable with regard to further prognosis, since such pathology increases the risk of stillbirth. This form is characterized by severe swelling of soft tissues, accumulation of a large volume of fluid in the abdominal cavity, in the pericardium and other natural cavities;
- icteric. This syndrome is characterized by a change in the color of the child’s skin, the same applies to vernix lubrication and amniotic fluid. The infant is diagnosed with toxic damage to the central nervous system, which is manifested by readiness for convulsions, oculomotor disorders, rigidity and other conditions that can lead to death;
- anemic. This syndrome does not show any special symptoms in a newly born baby; the pathology can only be noticed in the results of standard laboratory tests. Anemic syndrome can last about 3 months if complications and other pathologies do not occur.
Normal and abnormalities in humans
In a healthy body, due to natural hemolysis, 0.8% of red blood cells die per day, and aging red blood cells are susceptible to this. The final death of red blood cells occurs in the spleen, and then the iron released during cell breakdown undergoes a series of complex transformations and again participates in the production of new hemoglobin, the cells of which will replace the destroyed ones.
If this balance is disturbed, then this leads to the prevalence of blood destruction over blood formation. This is what is called pathological hemolysis.
There are two types of hemolysis:
- intravascular,
- intracellular.
In the first case, the cells disintegrate in the circulating blood and release hemoglobin, which naturally results in an increase in its level in the plasma and an increased amount of hemosiderin in the urine.
Intracellular hemolysis occurs in the bone marrow, liver and spleen. It is typical for hereditary diseases, and most often this is accompanied by an increase in those organs in which the destruction of red blood cells occurred. To identify it, it is necessary to use methods that make it possible to detect damage to the erythrocyte membrane. These methods include a test for the susceptibility of red blood cells to hypotonic solutions of sodium chloride.
In this way, the resistance of hemoglobin-containing cells to osmotic effects is studied. The concentration of sodium chloride at which osmotic hemolysis begins is noted as the minimum indicator of resistance, and the concentration at which the blood completely coagulates is considered as the maximum indicator.
In a healthy person:
- the minimum indicator is in the range of 0.44-0.48%,
- and the maximum is 0.28-0.32%.
Hemolysis of erythrocytes and its types
Hemolysis (gr. haima-blood + lisis-dissolution) is the process of destruction of the membrane of red blood cells and the release of hemoglobin into the blood plasma.
The hemoglobin of erythrocytes, released into the blood plasma, colors it red and the blood becomes transparent - “lacquer blood”. According to the mechanism of origin, several types of hemolysis are distinguished.
Osmotic hemolysis
may occur in a hypotonic environment (salt content less than 0.85%). If a red blood cell and other cells are placed in a hypotonic solution of plasma, then according to the law of osmosis, part of the plasma liquid. The concentration of NaCl solution at which hemolysis begins is called the minimum osmotic resistance of erythrocytes. Normally, it fluctuates between 0.48-0.46%. The concentration of NaCl solution at which complete hemolysis occurs is called the maximum resistance of erythrocytes. It is equal to 0.34-0.32%. Osmotic hemolysis is possible only in vitro, because In the whole organism, the blood under no circumstances can achieve such pronounced hypotonicity. Determination of osmotic resistance is one of the laboratory methods for determining the maturity and functional usefulness of red blood cells. Immature, young erythrocytes have increased resistance, and old erythrocytes have decreased resistance. At the same time, the gas transport activity of both is reduced, so an excessive change in the osmotic resistance of erythrocytes indicates a violation of their function. Osmotic resistance is one of the indicators of a general blood test, characterized by two numbers, for example, a result of 0.33-0.47% NaCl is normal. The smaller number indicates the maximum, and the larger number the minimum resistance of erythrocytes to hemolytic effects.
Ultraviolet and other types of radiation, large doses of sound (especially ultrasound), electric current (lightning strike, electrical current) cause physical hemolysis.
Under the influence of penetrating radiant energy in the erythrocyte membrane, the pores of the membrane expand. Normally, the shell consists of layers of lipid, proteins and contains a large number of pores (channels) with diameters of about 200 A.
Chemical hemolysis
can be caused by chloroform, ether, solutions of acids and alkalis, and certain medicinal substances (for example, sulfonamides) that destroy the protein-lipid membrane of erythrocytes.
Biological hemolysis
can be caused by hemolysins of plant origin (mushroom poisoning). It is also caused by various compounds of animal origin (snake bites, insect bites (bees), poisons of human parasites (worms), pathogens tetanus, staphylococcus. Biological hemolysis is enhanced by hemolytic jaundice of newborns (anti-Rhesus factor), radiation sickness, and by transfusion of incompatible blood groups.
Temperature (or thermal hemolysis
) occurs when blood is frozen/thawing as a result of the destruction of the erythrocyte membrane by ice crystals. And in accidents, blood freezes in the distal parts of the extremities.
Mechanical hemolysis
occurs under strong mechanical influences on the blood, for example, when shaking an ampoule with blood, during prolonged circulation of blood in the system of artificial blood circulation machines. In a healthy person, minor mechanical hemolysis can be observed during prolonged running on hard surfaces or during work involving prolonged strong shaking of the body.
Physiological hemolysis
- this is a process that constantly occurs in the body, as a result of which the spleen is captured from the bloodstream and destroyed by macrophages. Therefore, hemoglobin is absent in the circulating blood plasma (or its minimal amounts are detected - traces). With the bites of bees, poisonous snakes, transfusion of group-incompatible blood, malaria, or very heavy physical exertion, hemolysis of red blood cells can occur in different parts of the vascular bed. This is accompanied by the appearance of hemoglobin in the circulating blood plasma (hemoglobinemia) and its excretion in the urine (hemoglobinuria).
Types of red blood cell hemolysis
Destruction of the erythrocyte cell membrane occurs inside and outside the body during laboratory diagnostics. Blood hemolysis always occurs normally and serves to remove non-viable cells, but it can increase with adverse external influences or diseases.
Physiological and pathological
Red blood cells live for about 4 months and are then destroyed by cells in the liver, bone marrow or spleen. As a result, hemoglobin is released, which turns into a pigment - bilirubin. Cell debris is disposed of by macrophages (cleaner cells).
In case of diseases or penetration of poisons with a hemolytic effect, the breakdown of red blood cells occurs faster, which is accompanied by a lack of oxygen delivery to tissues (anemia), an excess of toxic bilirubin (jaundice), the spleen may enlarge, and the functioning of the liver and kidneys is disrupted.
Acute and chronic
Massive destruction of cells is caused by transfusion of incompatible blood according to group or Rh factor, antigenic composition, as well as poisoning. Acute conditions requiring emergency medical care include hemolytic disease of the newborn. It is associated with an immune conflict between the child’s red blood cells and antibodies from the mother’s blood.
These conditions are characterized by fever, chills, pain in the abdomen and lumbar region, vomiting, severe weakness and dizziness. Blood pressure decreases, and in the absence of intensive treatment, acute renal failure develops with a fatal outcome.
Chronic hemolysis occurs in congenital hemolytic anemia. It can be asymptomatic, but can appear after infectious diseases or taking medications that damage red blood cell membranes. Among acquired pathologies, the most common are autoimmune forms, in which the body produces antibodies against its own red blood cells. They occur in a permanent form or are accompanied by hemolytic crises.
Intravascular and intracellular
Normally, there can only be intracellular hemolysis in macrophages that destroy non-viable red blood cells. Congenital enhancement of this process occurs with genetic inferiority of red blood cells. It is characterized by yellowness of the skin, sclera, enlarged spleen, free bilirubin, and decreased haptoglobin (hemoglobin-binding protein).
With the development of hemolytic anemia, the membranes of red blood cells can disintegrate already inside the bloodstream. This leads to an abundant appearance of free hemoglobin. If the liver cannot cope with its processing into bilirubin, then it is excreted in the urine - hemoglobinuria occurs. The spleen in such cases is normal, the disease is accompanied by:
- pain in the kidneys, abdomen, heart due to vascular thrombosis;
- weak yellowness of the skin;
- signs of intoxication - nausea, fever, chills;
- a sharp increase in hemoglobin and low haptoglobin.
Watch the video about the types of blood hemolysis:
The natural process of hemolysis is the norm
During natural hemolysis in a healthy body, physiological death of old red blood cells occurs. This process occurs in the red bone marrow, liver and spleen.
In pathological hemolysis, red blood cells die prematurely due to stretching and rupture of the cell membrane. Discocytes are affected by unfavorable factors, due to which hemoglobin is released from the membrane into the blood plasma.
After the release of the red pigment, the plasma takes on an unnatural appearance and becomes shiny. This sign of hemolysis is easy to see with the naked eye.
Types of hemolysis
There are several classifications of hemolysis. The criteria for division are different bases. When separated according to the method of formation, hemolysis is isolated:
- physiological, characterized by naturalness and necessity (red blood cells die because they have fulfilled their functions and are no longer able to implement them - their place is taken by young cells);
- biological, which occurs under the influence on the human body of factors such as insect venom, metabolic products of various microorganisms, transfusion of donor blood incompatible with the blood of a sick person;
- chemical, caused by reagents of a chemical nature (they destroy the erythrocyte membrane, releasing hemoglobin);
- electrical, which occurs due to electric shock (often due to non-compliance with the rules for operating household appliances);
- osmotic, characteristic of a hypotonic environment, when the concentration of substances dissolved in it is lower than the solvent.
- thermal, characteristic of freezing and thawing processes.
- mechanical, which occurs when blood is exposed to a factor of a mechanical nature (for example, if a test tube with a biological fluid is shaken).
Depending on the location of occurrence, hemolysis is divided into:
- intravascular, when the destruction of red blood cells occurs in the vascular bed (often detected when the plasma contains a large amount of free hemoglobin, and the urine contains a high level of hemosiderin);
- intracellular, occurring in organs such as the spleen, bone marrow, liver (often develops as a hereditary pathology).
Concept of hemolysis and classification
Not everyone knows what it is and whether it is dangerous. This process occurs in the body after the service life of red blood cells - 4-5 months. When this process is completed, the cells die.
The danger lies in the rapid destruction of red blood cells, as there is a risk of developing pathology.
- Physiological (biological, natural) process is the death of red blood cells that have completed their cycle;
- Pathological - does not depend on the physiology of the body.
In the first case, new cells take the place of departed cells, and this process is divided into:
- Intracellular, found in organs (liver, bone marrow, spleen);
- intravascular hemolysis, in which plasma proteins transfer hemoglobin to liver cells, converting it into bilirubin, and red blood cells are destroyed directly in the bloodstream.
Pathological destruction is the death of viable red blood cells from any impact. The process is classified according to impact factors:
- Chemical - destruction of the lipid-protein membrane due to the action of aggressive products such as chloroform, alcohol, ether, acetic acid, alcohol;
- Mechanical, by breaking the membrane, for example, by vigorously shaking a tube or using a cardiac lavage (hemodialysis) machine for blood transfusion
- thermal, when too low or high temperature causes the death of the cell membrane of red blood cells (burns, frostbite);
- biological is possible as a result of poisonous products entering the plasma (bee, snake, insect bite) or transfusion of incompatible blood group;
- osmotic hemolysis, when red blood cells die under the influence of an environment in which the osmotic pressure is lower than in plasma (intravenous administration of saline, the concentration of which is lower than 0.85-0.9%).
There is also electrical hemolysis - the death of red blood cells due to electric current.
Causes of the phenomenon
The breakdown of red blood cells in the blood serum occurs for several reasons. In acute hemolysis, an accelerated course of the reaction and a significant deterioration in the person’s condition are noted.
The main reasons contributing to this:
- transfusion of blood with components that are not suitable for the patient, which is possible due to the lack of samples as a result of a laboratory technician’s error;
- acute infectious lesion or toxic effect on the body, leading to severe hemolytic anemia and having an autoimmune nature;
- isoimmune hemolytic anemia (problem of newborns), with which the baby is born, due to Rh conflict with maternal blood.
The appearance of pathological hemolysis is caused by:
- human poisoning with vinegar, toxic poisons (arsenic, lead), mushrooms, bee, snake bites;
- penetration of mercury or heavy metals into the blood;
- blood damage in the presence of toxoplasmosis, viral hepatitis, streptococcal pathogens, plasmodium parasites.
Sickle-shaped anemia and uncontrolled treatment with medications can cause blood damage. Some analgesics, sulfonamides, diuretics, and drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis can provoke increased death of red blood cells.
Hemolysis is possible due to violations during testing, which makes them unsuitable for further research. This happens as a result of too rapid blood sampling, failure to maintain sterility, improper storage and transportation, which causes destruction of the membranes.
The patient’s unpreparedness for the analysis, for example, eating too fatty foods the day before, also has a negative impact, since the decomposition of fats stimulates the development of hemolysis.
Manifestation of hemolysis
Chronic hemolysis, which accompanies diseases such as leukemia and sickle cell anemia, occurs without severe symptoms, like many other physiological processes.
Causes of acute hemolysis requiring emergency care:
- Transfusion of blood incompatible with the group and Rh factor;
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, or anemia caused by poisoning;
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn, where every breath the newborn takes makes the situation worse.
If the patient is conscious, he experiences the following symptoms:
- Feeling hot;
- Severe chest compression;
- Pain in the lower back, possibly in the chest and abdomen.
Other symptoms:
- A sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- Hyperemia of the facial skin, turning into cyanosis;
- Spontaneous urination and defecation;
- According to laboratory studies, intravascular hemolysis occurs in the circulatory system.
With radiation and hormonal therapy, during anesthesia, signs can be erased. After a few hours, the acute symptoms subside, leaving lower back pain.
After a short time, a relapse occurs with the following manifestations:
- Hyperthermia;
- Jaundice of the skin and sclera of the eyes;
- Severe headache;
- Renal dysfunction: protein and hemoglobin in the urine, cessation of urination, then anuria, uremia, death.
Coagulogram indicators:
- Anemia caused by the release of hemoglobin into the plasma after the destruction of red blood cells;
- Thrombocytopenia;
- High bilirubin levels;
- Violation of blood clotting processes.
The urine becomes red or black, and protein, potassium, and hemoglobin are found in it.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of the process of destruction of red blood cells, which patients primarily note:
- Yellowing of the skin.
- In some cases, pale skin is noted.
- Hypotension (low) blood pressure.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Delamination of the nail plate.
- Poor hair condition.
It also happens that a person does not even suspect that he has such severe pathological processes as hemolysis in his body. The presence of blood hemolysis is detected by a clinical blood test.
During an exacerbation, the patient experiences the following signs of hemolysis:
- Frequent nausea.
- Vomit.
- Dizziness.
- Regular feeling of excessive fatigue.
- Increased body temperature.
Exacerbation of hemolysis may be accompanied by dizziness
The process of breakdown of red blood cells in many cases leads to the development of anemia, a rather dangerous disease, which, in turn, can lead to the formation of stones in the bile ducts (cholelithiasis).
Tests for red blood cells
A red blood cell count and cell count is usually done as part of a complete blood count (CBC).
A general blood test is the most common analysis, informative for almost any pathological process. This test can also be used to diagnose and/or monitor a number of diseases that affect the production or lifespan of red blood cells. You can take a general blood test with determination of 5 fractions of leukocytes at any CityLab medical center.
For an accurate diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe additional tests:
- Reticulocyte count - determines the number of immature red blood cells.
- Iron test - this trace element plays an important role in the production of red blood cells.
- Vitamin B12 and folic acid levels – these vitamins are also important for red blood cell production.
- A blood test for ferritin reflects iron reserves in the body.
- Serum iron, total iron-binding capacity of blood serum are additional parameters reflecting the process of iron metabolism in the body.
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General Practitioner (family doctor), Ultrasound Doctor, Chief Physician
Hemolysis of red blood cells symptoms
The kidneys stop functioning normally, the amount of urine, its color and density changes, and kidney failure may occur.
The blood does not clot well and even a minor cut causes profuse bleeding. Hemolysis is a clear contraindication to any abdominal surgery, as well as to dental procedures involving the implantation of dental implants and dissection of gum tissue.
Decay products are not eliminated by the body on their own and provoke convulsions and fainting. The activity of the heart is disrupted, arrhythmias become more frequent.
Diagnosis of blood hemolysis.
The diagnosis is made, first of all, after a general and biochemical blood test, which will reveal a low content of hemoglobin, platelets, red blood cells and an increased level of bilirubin. A general urine test will contain red blood cells, which should not normally be present, and urobilin. Ultrasound and computed tomography of the abdominal organs will show changes in the liver and spleen - their hypertrophy. Kidney pathology can only be diagnosed when the process is advanced.
Treatment of blood hemolysis.
If the level of drop in hemoglobin has reached critical levels, then a blood transfusion of red blood cells is performed.
Glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants are also prescribed to stop the autoimmune process.
If there is significant destruction of the spleen tissue, surgical removal is indicated.
Hemodialysis is prescribed to remove toxic substances from the bloodstream.
Sometimes hormonal drugs are indicated as complex therapy.
To normalize the general condition, vitamin therapy, a diet high in minerals and easily digestible foods, and moderate physical activity are prescribed.
Treatment of hemolysis is carried out by a hematologist.
Blood hemolysis is a disease that responds well to therapy. If you consult a specialist in a timely manner and follow all recommendations, the disease does not cause complications and, over time, complete remission occurs.
Where does hemolysis occur?
Types of hemolysis depending on location:
- Intravascular hemolysis. Occurs in the circulating blood, where red blood cells are affected by the environment.
- Intracellular hemolysis. Occurs in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow - organs involved in hematopoiesis or the accumulation of blood cells.
In some cases, hemolysis can occur outside the human body when a blood clot dissolves and stains the plasma in the laboratory.
Causes of hemolysis in blood tests:
- non-compliance with the technique of collecting biomaterial and the rules for its storage;
- deliberately provoking the process of erythrocyte lysis, necessary to obtain a population of other blood elements.
For hemolysis, the properties of blood plasma and serum and their differences are very important. Plasma fibrinogen (hereinafter fibrin) is the basis of a blood clot that sinks to the bottom of the test tube, converting plasma into serum. In the circulatory system, blood does not normally clot. This occurs in exceptional cases - with disseminated intravascular coagulation, when a person’s life is at risk. But even there, serum is not formed; it is formed only outside the human body from fibrin strands that transform into a blood clot.
A blood biochemistry test taken with an anticoagulant, or taken in a dry tube without the use of anticoagulants, will have incorrect results due to hemolysis of red blood cells.
How to avoid
When collecting blood for analysis, it depends a little on the patient. The main thing is to choose a clinic that has a reliable reputation. In case of hemolysis of the sample, it can be taken again. But few people would be pleased to lose time, and in some situations, money, due to poor quality of service. It’s even worse if hemolysis occurs during blood sampling from an infant or child. The analysis procedure itself, especially from a vein, causes fear in children. It will be unpleasant for parents to watch the suffering of a baby whose veins are pierced several times.
To avoid hemolysis of the blood sample being taken, as well as the cost of personal time and money for repeated analysis, it is best to take the procedure seriously and take care of the sterility of the instruments. It is a good idea to have a syringe, sterile gloves and a test tube with you. It is a good idea to personally control the addition of the preservative to the test tube.
Before choosing a private clinic for a blood test, you need to read reviews about its work. Frequent complaints from patients about blood clotting when selected for analysis in a particular laboratory indicate that it is better to go to another institution.
Unscrupulous management of a medical institution may specifically prescribe repeated procedures in the hope of receiving money for them again. In these cases, you must demand a refund and contact another laboratory.
Features of therapeutic effects
The essence of the treatment process, regardless of the cause of the pathological destruction of red cells, is similar in different situations. It includes the following main steps:
- Eliminate the root cause. If a congenital pathology occurs, measures are taken to reduce its negative impact on the human body.
- Acceleration of the elimination of harmful metabolic products. For this purpose, forced diuresis is performed, a cleansing enema is prescribed, the stomach is washed, hemosorption and hemodialysis are performed.
- Carrying out treatment for complications that arise that pose a threat to health.
- Carrying out symptomatic therapy.
- Treatment of insufficient functioning of the kidneys and liver.
In the presence of congenital diseases, the therapeutic process will be slightly different. It all depends on the specifics of the disease and the neglect of the process. In any case, congenital pathology requires mandatory monitoring by a doctor.
Hemolysis of red cells is a necessary process. However, in some situations it becomes harmful to the body, transforming into pathological. To prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to seek medical help promptly when the first symptoms of deterioration in health are detected. In addition, the implementation of preventive measures remains relevant: timely treatment of emerging diseases, prevention of poisoning by various chemicals and correct compliance with the requirements for the use of medicines. Such measures will help maintain the normal course of all processes in the body.
Hereditary disease
Hereditary hemolytic anemia is divided into several subtypes. The current classification of hemolytic anemia, inherited, includes several forms.
Non-spherocytic
This type of anemia is distinguished by the accelerated breakdown of red blood cells, which occurs due to weakened enzyme activity. These enzymes are responsible for the correct life cycle of red blood cells and the required level of hemoglobin in the blood. A violation of the structure of one of the chromosomes causes the development of a hereditary form of the disease. This type of anemia is not inherited in all cases.
Microspherocytic
Hemolytic anemia or Minkowski Shoffard disease develops due to the appearance of a mutation or inheritance of mutated genes, on which the production of special proteins and protein molecules involved in the creation of the red blood cell wall depends.
A change in structure leads to disruption of the functionality of red blood cells, a decrease in their size, a decrease in the level of resistance to destruction and premature decay with the release of free hemoglobin. The ability to circulate red blood cells in the intravascular space decreases.
sickle cell
In sickle cell hemolytic anemia, an abnormal pathological form of hemoglobin is formed, the red blood cells change and take the shape of a sickle. The peculiarity of this type of disease is that red blood cells are deprived of the ability to change their shape and move freely inside the vessels.
Violation of the correct movement and speed of circulation leads to the rapid destruction of red blood cells. Premature breakdown causes increased release of hemoglobin and the appearance of increased levels of bilirubin in the blood.
Thalassemia
This is a separate group of hereditary hemolytic anemias that arise and develop against the background of disruption of the process during which normal hemoglobin is formed.
Due to pathological chemical processes in protein cells, the sequence of oxidation is disrupted, which provokes premature disintegration of the erythrocyte membrane and their hemolysis.
In most cases, hereditary forms of hemolytic anemia are transmitted from parents to children. However, a characteristic feature of hemolytic anemia is its selectivity. The occurrence and development of hemolytic anemia of this type is not possible in all cases.