Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, abbreviated as PVT, is a type of arrhythmia. Accompanied by a heart rate (HR) from 140 to 220 or more beats per minute. It arises spontaneously and ends unexpectedly. The duration of PNT is at least three cardiac cycles, while maintaining a regular heart rhythm. The attack itself can last from a few seconds to several days.
PNT occurs due to disruption of the nervous regulation of cardiac activity or damage to other organs.
In the first case, excessive nerve stimulation leads to an increase in heart rate.
PNT can also occur in healthy people under the influence of certain factors:
- prolonged physical activity;
- stress;
- consumption of energy and stimulant drinks;
- bad habits.
In the case of organic damage, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia can be caused by:
- damage to the heart muscle due to ischemia, inflammation, intoxication;
- myocardial infarction;
- heart disease;
- pathology of the cardiac conduction system.
In addition to heart disease, other organs can affect paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. It is worth checking the functioning of the kidneys, lungs and gastrointestinal tract, especially if there are chronic or acute diseases.
Symptoms of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
The main symptoms of the pathology include:
- Cardiopalmus. As a rule, it develops with a “prick” or “push” in the heart.
- Increased heart rate.
- Unmotivated anxiety.
- Chest pain.
- Dyspnea.
- Weakness and sweating.
- Noise in the head.
- Decreased blood pressure (with severe tachycardia).
- Steady heart rate.
- Flatulence, frequent and copious urination.
As a rule, paroxysm lasts 3 cardiac cycles. They even received a special name - “jogs” of tachycardia. The duration of an attack can be several hours or even days. In advanced situations, an increase in heart rate is observed in patients for several months. Any symptom of pathology can disappear on its own as suddenly as it appeared.
With prolonged attacks there is a risk of sudden death.
Prolonged paroxysms are also dangerous:
- development of acute heart failure;
- reduction of coronary blood supply;
- the occurrence of myocardial infarction.
Diet food
When paroxysmal tachycardia is diagnosed, the patient needs to constantly monitor blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Gaining excess weight is not allowed. Overeating can trigger the onset of an attack of tachycardia. Therefore, it is important to eat small portions 4-5 times a day.
The last meal should be no later than 2 hours before going to bed. It is important to exclude “provoking” foods and drinks:
- coffee Tea;
- confectionery sweets and buns;
- foods containing a lot of sugar and starch;
- butter, lard and mayonnaise.
Diagnostics
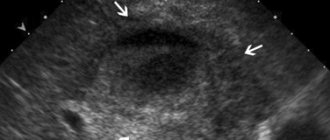
Diagnosis of pathology usually does not cause problems. Pathology can be identified by the characteristics characteristic of attacks. You just need to track your heart rate. With supraventricular tachycardia, for example, the number of heart contractions reaches 250 beats per minute. An ECG during an attack allows you to quickly identify pathology and make an accurate diagnosis. On the cardiogram, the doctor immediately detects a change in the shape and polarity of the P wave. If an ECG was not performed during the attack, daily monitoring is carried out. It allows you to register short episodes of tachycardia. Usually they are not felt by the patient himself.
To exclude organic pathology, additional studies are carried out such as:
- MSCT of the heart.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
- MRI.
Description
Supraventricular (or supraventricular) tachycardias (SVT) are a large group of heart rhythm disorders in which there are 3 or more consecutive heart contractions above 100 beats per minute.
As the name suggests, the source of pathological impulses that cause arrhythmia is located above the ventricles - in the atria, atrioventricular junction and sinoatrial node.
SVTs are much less life-threatening than ventricular tachycardias! The greatest danger is not the tachycardias themselves, but the diseases against which they develop.
The prevalence of rhythm disturbance is 2.25 per 1000 people. Women are predominantly affected. The distribution among age groups (children, adults, elderly) differs for each individual type of SVT. For example, sinus tachycardia (you can read more about it here) is often diagnosed in children, as is early ventricular repolarization syndrome. In the ICD, supraventricular tachyarrhythmias are coded I47.0 and I47.1.
The clinical manifestations of NVT are very diverse - from completely asymptomatic to repeated loss of consciousness.
Treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
Treatment tactics are selected taking into account:
- forms of arrhythmia;
- its etiology;
- duration and frequency of attacks;
- presence of complications;
- general condition of the patient;
- concomitant diseases.
In some cases, urgent hospitalization of the patient is required. Planned hospitalization is carried out if the patient suffers more than 2 attacks per month. An in-depth examination is carried out in the hospital. Experts also determine appropriate treatment tactics and indications for surgical intervention.
To relieve paroxysm, vagal maneuvers are performed.
These include:
- straining;
- Valsalva maneuver;
- Aschner's test;
- Chermak-Goering test;
- wiping with cold water.
Such relief of an attack is not possible in all cases. Additionally, antiarrhythmic drugs are administered. For prolonged paroxysms that are not relieved by medications, electrical pulse therapy is performed. After the attack is over, patients are subject to constant monitoring by a cardiologist. It is he who determines how to treat the disease.
If attacks occur repeatedly, they should be warned.
For this purpose they prescribe:
- Cardiac glycosides.
- Beta blockers, etc.
Any of the drugs may or may not give the desired result. Therefore, their selection often takes a lot of time. Trial therapy begins with individual or combined administration of the above medications.
Surgical interventions are performed for:
- severe supraventricular tachycardia;
- ineffectiveness of measures aimed at preventing attacks.
The disease can be eliminated by:
- Electrical, mechanical, laser, cryogenic or chemical destruction of additional impulse pathways or ectopic foci of automatism.
- Radiofrequency amblation.
- Implantation of pacemakers.
- Implantation of electrical defibrillators.
Today, doctors pay special attention to techniques that ensure rapid recovery and are as safe as possible for the patient in terms of postoperative complications. The cardiologist will tell you about all intervention options. If necessary, he will refer you for a consultation with a cardiac surgeon.
Having been involved in treatment for many years, our specialists know exactly which technique to choose and will definitely take into account your wishes and individual characteristics. We do not inflate our prices for professional support. In our clinic in Moscow you can get help even with limited financial resources. The approximate price of consultation with specialists and examination is indicated on the website. Our specialist will determine the exact details at your appointment.
Mechanism of development of the pathological process
{banner_banstat0}
Understanding the ways in which SVT is formed plays a major role in identifying ways to eliminate the accelerated rhythm and restore adequate performance of the entire organism as a whole.
Supraventricular (supraventricular) tachycardia is the result of the appearance of an additional (ectopic) focus of the electrical signal in the cardiac structures.
Brief anatomical information
In the normal state of affairs, the heart works autonomously. Its tissues, represented by cardiomyocyte cells, are capable of spontaneous excitation, without external stimuli.
Based on this, one can understand why the organ continues to work in seemingly dead patients.
The sinus node or natural pacemaker is responsible for the normal generation of the impulse. This is a collection of the most active structures.
But, against the background of the work of the named formation, the formation of third-party sources of signals is possible. They usually appear in the atria or atrioventricular node.
Both options are dangerous, but to a lesser extent when compared with the ventricular type of tachycardia.
Thus, treatment consists of eliminating the atypically changed area and restoring adequate conduction of cardiac structures.
Prevention
Prevention of pathology is always aimed at its early detection, treatment of the underlying disease and elimination of factors that increase the likelihood of developing attacks. Our specialist will tell you about all the measures.
General recommendations boil down to:
- Giving up bad habits. You definitely need to quit smoking and not abuse alcohol.
- Moderate and proper physical activity. As a rule, for pathologies of the cardiovascular system and a tendency to them, it is recommended to take walks in the fresh air, do swimming and gymnastics.
- Diet. If you are prone to pathologies of the cardiovascular system, you should give up coffee and strong tea, fatty, fried and salty foods.
- Reducing stressful situations.
- Establishing a work and rest schedule. You should sleep at least 8 hours a day.
Secondary prevention measures are aimed at reducing the risk of recurrence of attacks.
They consist of:
- Antiarrhythmic drugs.
- Sedatives.
In addition, it is very important to promptly detect all the causes of the pathological process. To do this, you should undergo a complete diagnosis, which is not limited to just an ECG.
Causes
Many reasons contributing to the occurrence of supraventricular tachycardia can be divided into 2 groups:
- Extracardiac - external factors, diseases or conditions not related to the heart that can trigger arrhythmia:
- emotional stress or physical stress;
- consumption of nicotine, alcohol, caffeine, medications (cardiac glycosides, antidepressants, diuretics);
- endocrinological diseases - for example, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis) or an adrenal tumor that produces adrenaline and norepinephrine (pheochromocytoma);
- fever;
- anemia;
- electrolyte disturbances - excess or, conversely, deficiency of certain minerals in the blood (potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium);
- shift in acid-base balance (blood pH).
- Intracardiac - This includes organic heart diseases:
- coronary heart disease (CHD);
- chronic heart failure (CHF);
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- cardiomyopathy;
- pericarditis;
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis;
- chronic cor pulmonale
First aid for an attack of pancreatitis
To reduce pain, you can use a heating pad filled with cold water. It needs to be applied to the abdominal area, namely to the epigastric region (the area under the xiphoid process, corresponding to the projection of the stomach onto the anterior abdominal wall). This allows you to reduce the intensity of pain, slightly reduce swelling and inflammation.
The patient must comply with the hospital regime. This will reduce blood flow to the organ, and therefore reduce inflammation.
Eating is prohibited. The digestion process can cause more severe pain, nausea and vomiting. And the diet will reduce the production of enzymes that increase the inflammatory response and pain. You need to fast for 3 days. You can drink clean water without gases.
It is imperative to call a doctor for an examination, even if the patient is not exactly sure that this is an attack of acute pancreatitis. As we already know, this pathology can subside and then rapidly recur. At this time, you can take a painkiller to reduce discomfort.
Classification
{banner_banstat1}
Based on the location of development of the deviation, three main types of pathological process can be distinguished:
- Increased atrial activity. Occurs in 80% of cases. The most common option. Maybe even in completely healthy people. In such a situation, tachycardia lasts from a minute to five, or a little more if the provoking factor is intense.
- Increased excitability of the atrioventricular node. Leads to persistent changes in the functional activity of the muscular organ.
- Mixed option. Relatively rare, characterized by high resistance to drug therapy, requires surgical care.
Depending on the nature of the process, it is possible to distinguish the following types:
- Paroxysmal tachycardia. It occurs in waves, in fits and starts. Each episode lasts from a few minutes to a couple of hours. Accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture, especially if it develops for the first time. Outside of organic pathologies, it does not pose a danger to life or health. Specific drug correction is not always necessary.
- Persistent option. It's already harder. Formed from the previous type in the absence of competent help. The duration of paroxysms is longer, approximately 3-4 days, sometimes up to a week.
- Permanent variety. Appears spontaneously, at any moment. Chronicization of the process causes permanent interruptions in the functioning of the heart, hence the impossibility of normal life activities and self-care in everyday life. However, the patient gradually gets used to the condition and partially stops paying attention to it.
The therapeutic methods are different at each stage. So, at the first stage you can still get by with lifestyle correction, but at the last stage there is little point in this.
Surgery, radiofrequency ablation or open surgery on cardiac structures is required. The route of exposure is determined by a cardiologist or specialized surgeon in difficult clinical situations.
Forms of pancreatitis
Acute – characterized by acute girdling pain in the upper abdomen. Pain often appears after eating fatty foods or alcohol. Unpleasant sensations can be either barely noticeable or unbearable, radiating to the scapula or sternum. Nausea, vomiting, and stool disturbances are observed. Due to the obstructed flow of bile, the skin takes on a yellowish color.
Chronic - the main localization of pain is on the upper part of the abdominal wall with irradiation to the back, chest (left side), lower abdomen. Unpleasant sensations occur after eating heavy fatty foods, alcoholic drinks, and constant stress.
The development of chronic pancreatitis is characterized by nausea, loss of appetite, bloating, bowel dysfunction, and sometimes vomiting.
The chronic form of the pathology differs from the acute form by periods of remission and exacerbation. As the disease progresses, periods of exacerbation become more frequent; intestinal disorders, disturbances in normal digestion, and weight loss are possible.
Chronic pancreatitis often causes complications (stomach bleeding, cancer, cysts and abscesses, liver damage, diabetes mellitus, enterocolitis). That is why you need to take the disease seriously and, at the slightest suspicion of the development of inflammation, consult a doctor.