Stenting of the carotid arteries is an effective minimally invasive method for preventing ischemic stroke in atherosclerosis and stenosis. If a patient has a narrowing of the carotid sinus of more than 70% in area, then the risk of stroke is about 10% per year. In cases of previous cerebrovascular accidents, the risk of major stroke increases to 50% per year.
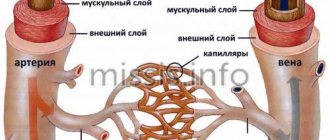
Stenting has a number of advantages over carotid endarterectomy, since it does not require surgical access, is performed under local anesthesia and can be used in weakened patients. The main vessels supplying the brain and neck are the two common carotid arteries. They rise up the neck, where each divides into two branches, the external carotid, which supplies blood to the skin and soft tissues of the head, and the internal carotid (ICA), which supplies blood to the brain. Damage to these vessels by atherosclerosis is the cause of most ischemic strokes.
Carotid artery stenting involves an operation to expand the narrowed vessel from the inside with a special balloon and strengthen the wall with a metal mesh (stent). To prevent complications associated with the entry of pieces of plaque into the brain during angioplasty, an intravascular filter is used, located above the site of the atherosclerotic plaque. This operation is performed without incisions, through a puncture in the leg or arm.
Advantages of carotid artery stenting at the Innovative Vascular Center
Our clinic has extensive experience in treating patients with carotid artery pathology. In recent years, stenting has almost replaced open carotid endarterectomy in our practice, as we have become convinced that this method has undeniable advantages and is suitable for most cases.
We perform stenting of the internal carotid artery after assessing the intracerebral vascular bed in order to eliminate the risk of stroke as much as possible. The price for carotid artery stenting in our clinic is affordable, although a disposable instrument is used to perform the operation in our clinic - a recognized world leader in the development of peripheral endovascular products.
During the use of carotid artery stenting in our clinic, we have not noted a single case of serious complications (stroke, bleeding, thrombosis). The clinic’s vascular surgeons have a differentiated approach to the choice of method for restoring arterial patency. We try to perform open endarterectomy in young patients, and ICA stenting in older patients.
Application area
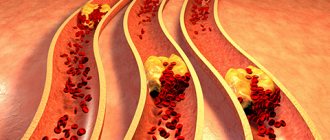
One of the common causes of the development of heart pathologies is a decrease in vascular elasticity and vasospasm. The arteries gradually lose their ability to expand, which leads to local disturbances in blood supply. Also, if the process is chronic, this contributes to the accumulation of cholesterol deposits on the vascular walls. Scientists all over the planet are actively working to develop an effective method to combat this disease. Coronary stenting is one of the existing ways to solve the problem.
Stenting is a procedure for integrating a special dilating device into a vessel. It is a tube with a mesh texture that can take the desired shape when implanted. The device acts as a frame. As a result, the narrow or spasmodic section of the artery should expand, and the blood flow should return to its previous state.
This treatment method belongs to endovascular surgical interventions and is considered minimally invasive. It is performed exclusively by experienced surgeons of the highest category.
Let's consider the stenting algorithm using the heart as an example. The catheter on which the element is fixed is passed through the femoral artery through the introducer. The conductor must be moved to the designated area where it is planned to install the expander. As soon as the catheter is inserted, the artificial frame is fixed, inflated under the action of the balloon, and normalizes blood supply to the heart muscle.
The operation involves local anesthesia. The average duration is relatively short, from 20 minutes to 3 hours. If necessary, the surgeon installs several devices at once.
Preparing for the intervention
- Before the operation of carotid artery stenting, the patient must undergo a number of mandatory examinations:
- Clinical blood and urine tests
- Biochemical blood test (urea, creatinine, electrolytes)
- X-ray of the lungs
- ECG
- Echocardiography
- Ultrasound of the carotid arteries and transcranial Dopplerography
- Multislice computed tomography of the vessels of the neck and brain
- MRI of the brain
- Consultation with a neurologist
- One day before stenting, all patients receive combination antiplatelet therapy with 300 mg of Plavix. Immediately before the intervention on the vessel, heparin is administered intravenously.
General information
The condition of the heart depends on the quality of its blood supply. And this, in turn, is determined by the degree of vascular patency. When everything is in order, they have smooth walls, and the blood moves without stopping along the right path. But over time, the vessels in some places can become very narrow and become overgrown with atherosclerotic deposits.
All this disrupts blood flow. The tissues of the main organ begin to experience oxygen starvation. The logical consequence in such a situation is the development of cardiac ischemia. Complete blockage of the vessel is especially dangerous. In an area deprived of blood supply, the tissue dies and myocardial infarction occurs. The operations in question make it possible to prevent such an outcome, and sometimes even save the life of a person already in critical condition.
Pain relief during stenting
The intervention is performed under local anesthesia using light sedatives, since it is necessary to assess the patient’s neurological status during stenting. When the balloon is inflated, the patient may experience a slow heart rate (bradycardia) and a decrease in blood pressure (hypotension), so continuous monitoring of cardiac activity during surgery is necessary.
The patient lies on his back, with his arm abducted, on which a blood pressure cuff is attached. The electrodes of the device for taking a cardiogram are glued to the chest. The surgical field is processed and the patient is covered with a sterile sheet.
What happens during the procedure?
First of all, during angioplasty, cardiac catheterization
. Local anesthesia is used to place the catheter - the area where it is inserted is numbed. A thin plastic sheath tube is then inserted into the artery. Typically the tube is inserted through an artery in the groin, but sometimes the tube is inserted through the arm. A long, narrow, hollow tube called a catheter moves through the sheath and then through the blood vessels to the arteries surrounding the heart.
A small amount of contrast material is injected through the catheter. And the x-ray will show how it moves through the chambers of the heart, valves and large vessels. By taking pictures of the movement of the contrast agent, doctors can determine whether the coronary arteries are narrowed and whether the heart valves are working properly. If doctors decide to perform angioplasty, one of the procedures we will discuss below will be performed.
In general, catheterization usually lasts about one and a half to two and a half hours. But given the preparation and recovery time, the entire procedure may take a little longer. You may also need short-term hospitalization to remain under medical supervision for some time.
Visit our Cardiology page
Complications during stenting
- Transient cerebrovascular accidents
Transient ischemic attacks occur in 0.5% of patients during or immediately after carotid artery stenting. May be associated with tiny pieces of plaque entering the brain as the conductor passes through the narrowed area. These may be transient visual or speech disturbances, weakness in an arm or leg, which disappear within the next 3 hours after the intervention.
- Ischemic stroke
The development of stroke, according to the literature, occurred in 1% of patients after stenting, but in recent years, due to the advent of new technologies for protecting the brain, this complication is much less common.
- Reflex bradycardia and hypotension
These phenomena are associated with the effect of the balloon on the vagus nerve passing next to the carotid artery. They manifest themselves as a decrease in heart rate and a drop in blood pressure. With a timely response from the anesthesiologist, this complication is quickly relieved with medications.
- Bleeding from the puncture site
A rare complication, accompanied by the formation of a tense hematoma in the area of access to the vessel. Sometimes open surgery may be necessary to stop bleeding.
Prognosis after treatment
Coronary angioplasty significantly increases blood flow through a previously narrowed or blocked coronary artery. In this case, chest pain (angina) should usually decrease, and the physical capabilities of the body, on the contrary, should increase.
You need to understand that angioplasty and stenting do not cure coronary heart disease, but only eliminate specific circulatory disorders of the heart muscle. To achieve a stable result, you must lead a healthy lifestyle and take medications prescribed by your doctor.
If the symptoms of angina return, then you need to contact your doctor again, and if you have chest pain at rest that does not respond to nitroglycerin, then call an ambulance.
After coronary angioplasty and stenting, the quality of life improves in 95% of patients, with many of them maintaining the effect for more than 5 years.
Postoperative period
The patient is discharged on the 2nd day after surgery with a mandatory follow-up ultrasound scan.
After carotid artery stenting, combination antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel 75 mg/day and aspirin 100 mg/day is prescribed for up to 12 months. Subsequently, aspirin and anti-cholesterol drugs - statins remain.
A control ultrasound scan is performed one month after stenting surgery. The patency of stented segments should be assessed at intervals of 6 months. If signs of restenosis are detected, the patient is prescribed a multislice computed tomography scan with contrast.
Types and types of coronary stents
Stents differ from each other:
- Length. The size of the stents varies from 8 to 38 millimeters.
- Diameter. There are from 2.25 to 6 millimeters.
- By design. They differ in the shape of the elements from which they are created.
- Material. They are made from steel, cobalt-chrome, PLLA polymer and others.
- Coated. Stents are available without coating or with drug coating Sirolimus, biolimus and others.
- Method of disclosure. They can open either independently or with the help of a balloon on a catheter.
- By type of drug coating. The medications used are Sirolimus, everolimus, paclitaxel and others.
By lenght:
Stents are available: 8, 10, 13, 16, 18, 23, 28, 33, 38 mm.
By diameter:
Stents are available: 2.25, 2.5, 2.75, 3, 3.25, 3.5, 3.75, 4, 4.25, 4.5, 4.75, 5, 5.25, 5.5, 5.75, 6 mm.
By design:
- mesh (made of woven mesh);
- tubular (from a tube);
- wire (made of wire);
- ring (from separate rings).
According to the material from which the frame is made:
- stainless medical steel;
- cobalt-chrome alloy;
- alloy of platinum and chromium;
- polylactose acid (PLLA) polymer.
By type of coverage:
- Uncoated with bare metal.
- Drug-coated, which releases a drug that reduces the likelihood of future artery narrowing.
- With double coating - external and internal, to heal the artery itself and prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Coated with antibodies, attracting endothelial cells, reducing the risk of thrombosis.
- Dissolving, made from a material that dissolves and releases a drug coating that prevents the recurrence of stenosis.
By opening method:
- self-expanding;
- opened by a balloon.
By drug coverage:
- Sirolimus;
- Zotarolimus;
- Everolimus;
- Biolimus;
- Paclitaxel.
Depending on the manufacturer, stents may differ in their characteristics and price. In Russia, the production of stents is carried out in accordance with GOST R ISO 25539-2-2012.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis
The disease may not manifest itself in any way in the early stages. In most patients, the first sign of pathology is a stroke. But atherosclerosis can be recognized by indirect symptoms:
- feeling of weakness, tingling only on one half of the body (right/left);
- inability to control the motor activity of the arm/leg;
- temporary loss of vision in one eye;
- slurred speech.
Symptoms may subside within a few hours, but this is a warning sign. They indicate a high risk of stroke, so you should consult a doctor immediately.
Lifestyle change
Atherosclerosis, as a rule, is caused by an incorrect lifestyle, and in order to fully recover after surgery and avoid arterial stenosis in the future, it is necessary to change your lifestyle to a healthy one.
The transition to a healthy lifestyle is:
- Do morning exercises, move and walk quietly for 30 minutes - 1 hour about 3-4 days a week.
- Completely eliminate active and passive smoking.
- You can safely enjoy swimming, skiing, use an exercise bike or treadmill evenly and measuredly for up to 6 hours a week.
- Avoid alcoholic drinks.
- Avoid fatty, fried and salty foods.
- Do not consume more than 4 grams of salt per day.
- Drink tea instead of coffee.
- Attend examinations by your attending physician.
- Eat more vegetables, fruits, fish, rye and bran bread.
The diet and exercise program is prepared by the attending physician. For successful recovery, you must fully adhere to the schedule he has drawn up.
All articles →
| Our company offers high-quality stents for coronary vessels. You can familiarize yourself with the entire range of manufactured medical equipment for cardiac surgery in the website catalog. We are pleased to present you a coronary stent at a price affordable for every consumer! | Go to catalog > |
When is bypass surgery performed?
Shunting is performed in the following cases:
- it is impossible to install a stent without surgery;
- the affected vessel has a miniature diameter;
- large extent of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- two or more vessels are affected, which is accompanied by multiple blockages of the lumens.
The operation has a number of contraindications. Bypass surgery should not be performed on elderly patients with severe concomitant diseases. Sometimes doctors are forced to urgently perform an operation even if there are contraindications, but then the risk of death increases significantly, of which the patient’s relatives must be notified.