- Causes
- Pathologies
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Our doctors
If your heart is beating fast, it is normal to feel it. In cases where the condition is caused by physiological factors, the state of health returns to normal on its own, without visiting a doctor.
Every person has experienced heart palpitations at one time or another. This condition can be either normal or pathological. Only a doctor can determine the exact cause after an examination, but you can independently determine whether you should rush to a specialist or not to worry.
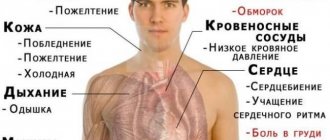
Causes of increased heart rate
When assessing a person’s condition, one must take into account the pulse: is it elevated or normal. If your heart is beating fast, it is normal to feel it. Physiological reasons for this condition:
- strong excitement;
- age up to 7 years;
- exercise stress;
- fright;
- poisoning;
- drinking coffee and other tonic drinks.
In cases where the condition is caused by physiological factors, the state of health returns to normal on its own, without visiting a doctor.
The feeling of palpitations is also characteristic of some pathologies. Most often this is associated with endocrine, vascular and neurological disorders. In this case, a comprehensive diagnosis is required to determine the cause.
The heart beats often and it’s difficult to breathe: what’s the matter?
Normal breathing rate is 16-20 movements per minute. Shortness of breath or dyspnea is a disorder that is characterized by changes in the depth and rhythm of the respiratory process. Inspiratory type disturbance occurs on inspiration, expiratory type - on exhalation. Sometimes a mixed form is observed. In everyday life, shortness of breath periodically appears in every healthy person - adult or child. As a variant of the norm, it is called physiological and goes away after the cause is eliminated (running, physical activity). In situations where difficulty breathing persists for a long time and causes discomfort, you should think about the presence of some pathology.
- Rheumatoid arthritis and anemia. What you need to know
More about symptoms
Shortness of breath due to arrhythmia is a symptom that accompanies many different diseases. Doctors call the main signs of this condition:
- rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath;
- the growing feeling of suffocation that a person experiences;
- change in breathing pattern - it becomes more frequent;
- combination with swelling, wheezing, whistling.
Dyspnea can occur in various forms (subacute, acute and chronic) and has several degrees. The severe stage is detected in patients who experience discomfort at rest, with slight movement or the slightest household stress.
The most common causes of the condition
There are many pathological conditions that manifest themselves in the form of shortness of breath. Conventionally, they can be divided into three main groups:
- cardiovascular disorders;
- respiratory diseases;
- anemia.
Shortness of breath may appear in case of hyperthermia, be a consequence of smoking or drinking alcohol, or develop while taking medications or osteochondrosis. Depending on the etiology of the condition, treatment tactics are selected.
Lung problems
Pulmonary dyspnea is an inspiratory disorder caused by almost all diseases of the respiratory system. When it occurs, a person’s breathing becomes difficult and the heart beats rapidly. The reasons for this condition are:
- smoking;
- respiratory tract infections;
- bronchitis;
- obstructive pulmonary disease;
- pneumonia.
Attention! Against the background of these symptoms, tumor processes, emphysema, tuberculosis, pulmonary actinomycosis, pneumothorax, and sarcoidosis can develop.
Cardiovascular pathologies
Shortness of breath caused by heart pathologies is considered the most important symptom, and in most cases has a chronic course. By the degree of its severity and combination with tachycardia, one can judge the nature and stage of heart failure. The most common causes of difficulty breathing and rapid heartbeat are the following cardiac phenomena:
- heart failure;
- heart defects;
- myocarditis;
- atrial fibrillation;
- acute coronary syndrome;
- cardiomyopathy.
Heart failure is a term that describes not a specific disease, but disorders of the heart caused by the development of its morphological changes. The syndrome is characterized by difficulty breathing, which is initially observed only during walking or physical activity. As it progresses, shortness of breath becomes permanent and appears even at rest.
Symptoms of cardiac dysfunction that often accompany shortness of breath include:
- What to do when your hand joints hurt
- weakness in the legs and arms, drowsiness, palpitations;
- arterial hypo- or hypertension;
- cyanosis - a bluish tint of the skin on the fingers, toes, earlobes, nose, feet;
- frequent dizziness, fainting;
- paroxysmal dry cough, especially during rest hours;
- nocturia – increased urine production at night;
- periodic pain in the heart.
The problem of shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat that occurs against the background of heart failure is dealt with by therapists, cardiologists, and neurologists.
Attacks of VSD and neuroses
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a syndrome that combines many diseases that are similar in their manifestations. It develops against the background of stress, neuroses, endocrine pathologies, physical and mental overload. Paroxysms occur suddenly and can last from 10-15 minutes to 2-3 days, and all this time the heart continues to beat at an increased rate. During the attack and after it ends, hemodynamic deterioration occurs, due to which the organs do not receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients.
The most common type of VSD is tachycardia, namely the sinus type. Shortness of breath against the background of an accelerated myocardial rhythm is mild and does not cause discomfort. The most dangerous type is considered to be the paroxysmal type, in which the heart rate reaches 220-250 beats per minute. Most often it is diagnosed in older people. An increase in myocardial rhythm can be observed even at rest. During an exacerbation, a person suffers from the following symptoms:
- general weakness, drowsiness, fatigue;
- rapid pulse;
- severe shortness of breath;
- tremor of the limbs;
- mild nausea, vomiting;
- panic attacks;
- increased sweating;
- feeling of lack of oxygen.
Attacks are repeated frequently, which is caused by stress and fatigue due to young age and immaturity of the nervous system.
Hormonal imbalance
Humoral regulation is an important link in the chain of vital processes in the body. When hormonal levels change due to a delay in menstruation, menopause, or late pregnancy, cardiac activity primarily suffers, while organic damage to the myocardium is detected in rare cases. Such phenomena lead to increased heart rate, which is called hormonal tachycardia.
Its appearance can be determined by an increased heart rate, which is complemented by symptoms of autonomic disorder:
- headache;
- feeling of lack of air;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- strong noise of blows, echoing in the ears;
- painful sensations in the area behind the sternum;
- "heart jumping out of the chest."
With organic damage to the myocardium, symptoms may be supplemented by fainting states.
Temperature increase
Hyperthermia is considered one of the symptoms of many diseases. Almost always, it indicates the development of an inflammatory process, which, regardless of etiology, provokes increased production of various enzymes and specific substances. Together, they have a special effect on the thermoregulation center, causing an increase in temperature. Trying to cope with the changes occurring, the body begins to intensively secrete sweat.
- Movalis: composition of the drug, release form and pharmacological action
Due to the lack of oxygen, which is necessary for the reaction to proceed normally, breathing becomes more frequent and the load on the heart increases.
It is important to know! When the temperature rises even by one degree, the frequency of myocardial contraction in an adult increases by 10 beats. The child suffers even more; this figure is 50% higher. In a newborn and a year old, the heartbeat can reach 150 beats/min.
Anemia
Anemia is characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood. It acts as an independent disease, or is a symptom of pathological disorders. It can develop against the background of problems with the digestive system, infectious diseases or vitamin and mineral deficiency. Iron deficiency anemia occurs most often.
Shortness of breath is formed due to a violation of hemoglobin synthesis and the production of red blood cells. As a result, the transport of oxygen molecules to the cellular structures of organs and tissues deteriorates, which inevitably leads to hypoxia.
A person develops shortness of breath and a number of other signs appear:
- general weakness;
- fever, chills;
- impaired coordination and reflexes;
- trembling in the body and palpitations.
An increase in the size of the liver can often be observed, and mental disorders are also detected.
Bad habits
Chronic fatigue, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, caffeine-containing products, smoking strong tobacco or a large number of cigarettes, addiction to drugs (even light ones), lack of sleep and wakefulness negatively affect well-being and over time lead to the development of shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. Getting rid of addictions, restoring the correct alternation of periods of active activity and rest will help eliminate unpleasant manifestations.
Side effects from taking medications
The occurrence of shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat can be provoked by medications such as corticosteroids, diuretics, as well as medications prescribed for the treatment of asthma and thyroid diseases. This is due to increased metabolic processes, in which the body experiences an increased need for oxygen, and a stimulating effect on the sympathetic nervous system. As a result, the heart rate reflexively increases, which leads to shortness of breath.
Most often, such symptoms appear at night, when a person is resting. If they occur regularly, you should contact a specialist to replace the medications you are using with other, safer ones.
Variant of the norm
Every healthy person experiences shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat from time to time. In this case, it is called physiological, and can appear under the following circumstances:
- in a closed room with a high concentration of carbon dioxide;
- at high altitudes, where there is a lack of oxygen and hypoxic conditions are created;
- with excessive physical exertion, climbing stairs.
To prevent the development of dizziness, nausea, palpitations, and weakness in the future, you should change your lifestyle - move more, engage in active sports, adapt to significant altitudes, adjust your diet, and lose weight. The manifestation of strong emotions (joy, pain, fear, anger) can also provoke these states. Posing no threat to health, they go away on their own within a few minutes and do not require medical intervention.
Pathologies in which the heart beats strongly
If there are no physiological reasons, but the heart is pounding, you need to look for pathology. Conditions in which symptoms are observed:
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system: infection, heart disease; arrhythmia, cardiosclerosis, hypertension, heart failure, pericarditis;
- endocrine diseases: diffuse toxic goiter, hyperthyroidism;
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
- anemia;
- menopausal syndrome;
- neurosis.
When the heart is beating strongly and a person experiences chest pain and fear of death, you should immediately call an ambulance. This could be an attack of angina. It is quickly relieved with nitroglycerin, but the patient requires examination and medical supervision.
Symptoms
- Sensation of pulsation in the fingertips, chest and temporal region;
- “Cotton” legs;
- Weakness;
- Feeling of anxiety;
- Panic attack;
- Ringing or noise in the ears;
- Near fainting;
- Sweating;
- Cold extremities;
- Sweaty palms.
Sometimes it happens that heart pathologies manifest themselves during an examination by the attending physician, but the patient himself does not suspect anything. Symptoms of progressive diseases are very vague and chaotic. You should listen to your body and pay attention to the following conditions:
- frequent heartbeat (tachycardia);
- the heartbeat often slows down (bradycardia);
- shortness of breath;
- feeling of cardiac arrest;
- dizziness;
- attacks of suffocation;
- pale skin;
- tingling in the limbs;
- pulsation of arteries in the neck and collarbones;
- fainting or a feeling of fainting;
- chest pain;
- fatigue;
- insomnia;
- mood swings;
- fitful beats of the heart during moments of sleep and rest.
Diagnostics
If you have increased heartbeat, you should consult a therapist. He will refer you for an examination, with the results of which the patient will go to a specialist: a cardiologist, endocrinologist or neurologist. The list of diagnostic measures if the heart is beating strongly includes:
- general blood analysis;
- ECG;
- blood test for thyroid hormones;
- Ultrasound of the heart (EchoCG);
- daily monitoring of pulse and heart activity according to Holter;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
If the disease cannot be detected by laboratory and instrumental methods, a consultation with a psychiatrist may be required.
Read also: Heartache
Treatment of increased heart rate
Treatment tactics depend on the diagnosis. Treatment options:
- antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed in the presence of cardiac arrhythmias;
- tranquilizers are required for neurosis;
- antibiotics are prescribed if there is a heart infection;
- nootropics and antispasmodics are needed for neurocirculatory dystonia;
- thyreostatics or radioactive iodine are indicated for thyrotoxicosis and hyperthyroidism;
- Hormone replacement therapy is carried out for menopausal syndrome;
- for anemia, treatment is prescribed taking into account its type: iron supplements, vitamin B12, etc.
If after 10–14 days of treatment a person does not feel better, further examination is carried out to determine the cause. Sometimes you just need to change the drug to a similar one due to the individual characteristics of the patient.
The feeling of palpitations can be considered normal in several cases. But if the condition recurs frequently and without provoking factors, you need to consult a doctor to find out the cause.
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
How to deal with the problem?
The therapeutic course is prescribed by a cardiologist, therapist or endocrinologist, which depends on the source of the sensation of heartbeat. Often the pathology is caused by physical fatigue, hormonal imbalance or impaired functioning of the central nervous system. Treatment may include sedatives, which include:
The doctor may prescribe sedatives like Novo-Passit.
- "Valerian";
- "Novo-Passit";
- "Glicised."
When you feel palpitations, but no abnormalities in the pulse are detected, then it is worth reviewing your daily diet. It is recommended to consume more foods rich in magnesium, potassium and calcium. To replenish them, certain medications can be prescribed that improve the condition of blood vessels and normalize blood circulation. It is recommended to drink more water throughout the day.
Folk remedies
When a patient is faced with the problem of feeling a heartbeat, alternative medicine recipes can be used. It is possible to eliminate unpleasant feelings with the help of valerian or adonis, from which a tincture is prepared. Garlic and onion broth is no less useful, helping to get rid of the feeling of heartbeat. Take the medicine before meals in the morning, 1 tbsp. l. It is possible to cope with the disorder with the help of a medicinal mixture, which is taken 3 times a day. It contains the following ingredients:
- Melissa;
- dill seed;
- valerian root;
- hop.