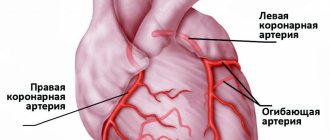
Many people have heard about the features and terrible consequences of myocardial infarction, including death, and most of us have had relatives or friends suffer from this disease. Speaking about the attack itself, the mind immediately associates with its main symptoms: pain in the chest (stabbing, burning, aching, cutting nature), which radiates to the shoulder or under the shoulder blade, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, profuse sweating, loss of consciousness.
But as it turned out, doctors repeatedly record cases where these characteristic symptoms do not appear and a person, without realizing it, suffers a heart attack on his legs.
This phenomenon is also called an atypical form of the disease. As a rule, it is revealed that the patient suffered a heart attack on his legs - randomly, for example, in a cardiogram during an annual medical examination.
Sign up for a consultation
Mechanism of development of acute coronary syndrome
Myocardial infarction, which, along with an episode of unstable angina, is included in the concept of acute coronary syndrome, is an exacerbation of coronary heart disease. During myocardial infarction, necrosis of the heart muscle develops due to acute disruption of the blood supply. In most cases, this occurs as a result of atherothrombosis, in which the coronary vessels are partially or completely blocked by a blood clot. The disease is manifested by sudden intense pain in the chest, tachycardia, “cold sweat”, pallor of the skin and a number of other symptoms.
The goal of treating an acute heart attack is to quickly restore blood supply. However, even after blood flow is established, therapy cannot be stopped, since coronary atherosclerosis, which became the foundation for the development of acute coronary syndrome, is chronic.
How to identify?
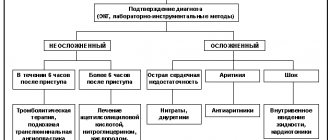
Reliable detection of a previous heart attack with minimal clinical manifestations is possible using objective diagnostic techniques, which include:
- ECG - cardiogram is a functional research method that makes it possible to determine the nature and location of ischemia (insufficient tissue nutrition) or myocardial infarction.
- “Holter” monitoring is the recording of a cardiogram using a portable device for a long period of time (usually about a day), during which the patient leads a normal lifestyle.
- Echocardioscopy is an ultrasound examination of the heart, which makes it possible to visualize affected tissue. It will show the severity of the pathological process, as well as its localization.
- Biochemical blood test - determination of the activity of certain enzymes in the plasma, which increases with the death of a large number of myocardial cells (myocardiocytes).
- A clinical blood test is the determination of a number of indicators that make it possible to assess the functional state of many organs and systems, as well as to identify the inflammatory process that often develops against the background of a heart attack.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes other research methods that help establish or exclude the presence of complications, as well as other concomitant pathologies.
Timely diagnosis of a heart attack suffered “on your feet” is an important measure that helps prevent the development of complications and negative health consequences.
Early consequences of myocardial infarction1
Starting from the first hours after a heart attack and up to 3-4 days, early consequences of a heart attack may develop, including:
- acute left ventricular failure, which occurs when the contractility of the heart decreases. When it occurs, shortness of breath, tachycardia, and cough appear;
- cardiogenic shock. This is a severe complication of acute coronary syndrome, developing as a result of a significant deterioration in the contractility of the heart muscle due to extensive necrosis;
- disturbances of cardiac rhythm and conduction are observed in 90% of patients with acute MI.
- Attacks of early post-infarction angina (PSA). PSC is the occurrence or increase in frequency of angina attacks 24 hours and up to 8 weeks after the development of MI.
- pericarditis is an inflammatory process that develops in the outer lining of the heart, the pericardium. It occurs in the first or third day of the disease and can manifest itself as pain in the heart area, which changes with a change in body position, and an increase in body temperature.
In 15-20% of heart attack cases, thinning and bulging of the heart wall occurs, most often of the left ventricle. This condition is called cardiac aneurysm. As a rule, it develops with extensive damage to the heart muscle. Factors predisposing to the development of cardiac aneurysm also include violation of the regime from the first days of the disease, concomitant arterial hypertension and some others.
A special group consists of thromboembolic consequences, in which the lumen of the vessels is completely or partially blocked by blood clots. This often occurs against the background of concomitant varicose veins, blood coagulation disorders and prolonged bed rest.
Due to impaired blood supply, acute coronary syndrome can be complicated by gastrointestinal problems, such as erosions and acute ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract. Mental disorders may also occur - depression, psychosis. They are facilitated by old age and concomitant diseases of the nervous system.
Types and symptoms of their manifestation
There are six types of atypical forms of the disease:
- arrhythmic;
- asthmatic;
- abdominal;
- collaptoid;
- erased;
- cerebral.
Each of these varieties manifests itself differently, and the symptoms of the attack often do not even resemble such a serious disease, which results in a heart attack on the legs.
In the event of an arrhythmic attack, a disturbance in the rhythm of the heartbeat occurs, and cases of cardiac arrest are common.
The asthmatic form is manifested by a strong attack of coughing, reaching the point of suffocation, and no pain in the cardiac region (or radiating under the shoulder blade) is observed.
An abdominal attack is characterized by sharp pain in the abdomen, which intensifies with slight pressure on the pancreas. Very often the attack is accompanied by bloating, as well as nausea and vomiting.
A collaptoid attack is characterized by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, accompanied by dizziness and often fainting.
The most asymptomatic type is the erased type (the most common case of a heart attack on the legs). In this case, there is only mild weakness or sweating, and less often – discomfort in the chest (in the form of mild pain of an undetermined nature).
call me back
The cerebral variety is distinguished by symptoms characteristic of cerebrovascular accident: speech becomes slurred, nausea and vomiting appear, some clouding of consciousness appears, and weakness in the limbs.
Considering the obvious insidiousness of the disease, it should be treated with great caution, avoiding the consequences that a heart attack on the legs may bring; any symptoms - characteristic or uncharacteristic (characteristic of the atypical form) - should be a signal to consult a doctor.
Important! Every 5th of those who suffered a heart attack does not know about it, and in every 4th patient this disease is not recognized.
Late consequences of a heart attack
At the end of the acute period of the disease, so-called late consequences may develop. These include complications that appear 10 days after the manifestation of MI and later:
- post-infarction Dressler syndrome occurs 2-6 weeks after the manifestation of myocardial infarction and is manifested by inflammation of the pericardium, pleura, alveoli, joints and other pathological changes;
- thromboendocarditis with thromboembolic syndrome (the appearance of a wall thrombus in the heart cavity, on the heart valves);
- late post-infarction angina, which is characterized by the occurrence or increase in frequency of angina attacks. Its frequency ranges from 20 to 60%.
Some patients who have suffered an acute myocardial infarction are at high risk for developing repeated complications of coronary heart disease and, above all, recurrent myocardial infarction and unstable angina. This is due to the fact that in patients with acute coronary syndrome, along with the presence of an atherosclerotic plaque, which was complicated by a rupture and blocked the lumen of the coronary artery, there are plaques in other arteries. They can be the cause of repeated episodes of cardiovascular events, the probability of which is very high.
Where to go and what to do if symptoms appear
If the above symptoms appear, you should immediately call an ambulance, which will provide the necessary assistance and take the patient to a specialized clinic for further diagnosis and treatment. Before the doctors arrive, it is better for the patient to lie down and provide access to oxygen - unfasten the collar, open the window. For medications you need to take acetylsalicylic acid tablet. Nitroglycerin is recommended if a person has taken it previously, as the drug can sharply lower blood pressure.
In any case, if you have complaints from the cardiovascular system, you should contact a therapist or cardiologist. The clinic will conduct instrumental and laboratory tests: ECG, general clinical and biochemical blood tests, troponin tests, and angiography if necessary. The doctor will be able to assess the functioning of the heart, the presence of its pathologies, and also identify concomitant diseases and risk factors.
A microinfarction is easier to prevent than to cure. To do this, it is advisable to regularly visit your therapist and follow his instructions. The doctor can give recommendations on a healthy lifestyle, diet and exercise, and prescribe the necessary medications. To prevent blood clots, acetylsalicylic acid (Cardiomagnyl) drugs are often prescribed, which thin the blood and reduce the risk of myocardial infarction.
Prevention
- Check your blood pressure at home. High blood pressure can lead to a heart attack. Sit and rest for 5 minutes before taking your readings. Measure your blood pressure at least 2 times a day at the same time, for example, in the morning and evening.
- Quit smoking. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause damage to the lungs and heart. Electronic cigarettes or smokeless tobacco also contain nicotine and are no less dangerous.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet. A heart-healthy diet is one that is low in saturated, unhealthy fats and sodium (salt). It helps reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. Limit the amount of fat you consume to 25-35% of your total daily calories. Your doctor may recommend an eating plan that lowers your cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Limit your sodium (salt) intake. Too much sodium can affect fluid balance. Do the exercises. Ask your doctor about the exercise plan that's best for you. Exercise strengthens the heart, lowers blood pressure and helps prevent heart attacks. The goal is 30 to 60 minutes of activity almost every day.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your doctor how much you should weigh. He can help you create a safe weight loss plan if you are overweight.
- Manage stress. Stress can increase your risk of heart attack. Learn ways to control stress, such as relaxation, deep breathing and music. Talk to someone about what's upsetting youSource: Innovative Methods to Prevent Myocardial Infarction. Volodkin A.A. , Zaikov G.E. NBI-technologies, 2013. p. 103-106.
Sources:
- Myocardial infarction. Zhmurov D.V., Parfenteva M.A., Semenova Yu.V. Colloquium-journal, 2021. p. 56-61
- Outcomes of recurrent myocardial infarction. Shulaev A.V., Muradimova Z.R., Marapov D.I., Zakirov I.K., Mazitov M.R. Practical medicine, 2021. p. 142-144
- Complications of myocardial infarction in the elderly. Khalmukhamedov B.T. Eurasian Journal of Cardiology, 2021. p. 29-30
- On the issue of overdiagnosis of myocardial infarction. Kim A.O., Kausova G.K. Bulletin of the Kazakh National Medical University, 2018. p. 28-29
- Innovative methods for preventing myocardial infarction. Volodkin A.A. , Zaikov G.E. NBI-technologies, 2013. p. 103-106
“You are cured, you can live as before”
This is a very common misconception among patients who were quickly put on their feet by doctors and did not realize how serious their illness was. “Now we can cure a person who has suffered such a deadly disease, so that he returns to work, lives an active life and does not feel sick,” explains Professor, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences Simon Matskeplishvili. “And here lies a great danger.” Because, having once suffered a heart attack, the patient often runs the risk of having another one if he behaves incorrectly.” The risk of a repeat disaster is from 10 to 20% in the first year.
How to reduce this risk? Continuity of treatment is extremely important. “A patient with a heart attack no longer spends a month in the hospital as before. He is discharged after a few days, feels fine and does not consider it necessary to follow our recommendations for continuing therapy,” says Professor Matskeplishvili. “It is especially difficult to convince that medications need to be taken long-term, often, for life.”
Treatment and rehabilitation after myocardial infarction using enhanced external counterpulsation
UNC is an effective alternative to coronary artery bypass grafting, a modern and safe procedure. This non-surgical treatment method is widely used in modern medicine and professional sports. Its goal is to improve the blood supply to the heart without causing any surgical trauma to the patient. For this purpose, special cuffs are used that are placed on the patient’s limbs. Air is injected into the cuffs at a certain rhythm (coordinated with the contractions of the heart muscle) and then removed.
The effect is a 4-fold increase in blood supply to the affected areas of the heart and the formation of new vessels in it. High rates can be achieved in 90% of patients in whom the risk of heart attack is reduced or its consequences are reduced. Your body's metabolism, cholesterol levels and blood pressure will be normalized, and you will be able to increase the amount of physical activity.
On the topic “Enhanced external counterpulsation”, watch the recording of the program “About the Most Important Thing” on the Russia 1 TV channel, which was filmed with the participation of our cardiologist, cardiovascular surgeon Alexei Utin. Also, the filming contains a clear example of the procedure itself, which took place in our clinic.
Diagnostics
Once a heart attack occurs, the patient needs prompt medical attention to open the blocked artery and reduce the damage. At the first sign of a heart attack, you need to call an ambulance. The best time to treat a heart attack is within 1-2 hours after symptoms appear. A longer wait means more damage to the heart and less chance of maximally complete recovery and rehabilitation after a myocardial infarction. Source: On the issue of overdiagnosis of myocardial infarction. Kim A.O., Kausova G.K. Bulletin of the Kazakh National Medical University, 2021. p. 28-29.
Emergency doctors will ask the person about all the symptoms and perform several tests:
- An ECG (electrocardiogram) can determine how much heart muscle has been damaged and exactly where (types of heart attack). It can also monitor heart rate and rhythm. If there are signs of damage according to the ECG, immediate hospitalization is indicated. The clinic urgently performs additional diagnostic methods.
- Blood tests . Different levels of cardiac enzymes in the blood may indicate damage to the heart muscle. These enzymes are usually found in heart cells. When these cells are damaged, their contents, including enzymes, leak into the bloodstream. By measuring the levels of these enzymes, the doctor can know the size of the heart attack and when it started. The tests can also measure troponin levels. Troponins are proteins inside heart cells that are released when the cells are damaged due to lack of blood supply to the heart.
- Echocardiography . This imaging test can be used during and after a heart attack to see how the heart is working and which areas are most damaged. An ECHO can also determine whether any parts of the heart (valves, septum, etc.) have been damaged due to ischemia.
- Cardiac catheterization . The patient may require cardiac catheterization in the early hours of a heart attack if medications do not relieve ischemia or symptoms. The catheter can provide an image of the blocked artery and help the doctor decide on treatment.
Stages of treatment of myocardial infarction
- At the prehospital stage, if there are symptoms of the disease, the patient is given first aid and transported to the clinic.
- The hospital stage involves carrying out medical measures aimed at maintaining body functions and combating negative consequences.
- The rehabilitation stage is carried out in sanatoriums where special conditions have been created.
- At the stage of dispensary observation and outpatient treatment, the patient periodically visits the cardiology clinic and the doctor at his place of residence.
The high professionalism of doctors and the technical equipment of the clinic where you are being treated after a myocardial infarction are extremely important. With qualified specialists and high-quality rehabilitation, you will avoid complications and continue to live a full life.
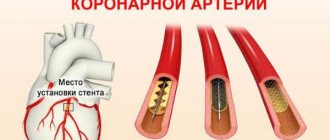
Coronary artery bypass grafting
It is also a very effective method of treating myocardial infarction. The purpose of this operation is to create a new path for the blood, bypassing the vessel affected by atherosclerosis. For this, a special shunt is used - a part of the patient’s own vessel, taken from the thoracic artery or radial artery of the arm. It is sewn into the narrowed or blocked artery above and below the site of the lesion. Thus, the volume of blood required for heart function is normalized. Doctors are able to restore blood circulation in the affected area of the heart muscle in a short period of time.
The operation eliminates the very cause of the heart attack and is often performed as planned so that the patient can avoid a heart attack. The risk of developing a heart attack after surgery is significantly reduced, and the patient regains ability to work with a normal amount of physical activity.
Coronary artery bypass grafting is a type of open intervention for a beating heart. That is, to carry it out it is necessary to open the chest. There are options for surgery with or without artificial circulation.