General information
Cerebral edema is one of the manifestations of various critical conditions and is quite often encountered in clinical practice with various kinds of diseases and the development of pathologies. There are edema of the brain, spinal and bone marrow.
Brain swelling
Brain edema is an increase in its volume, caused by the accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space (interstitium) and accompanied by an increase in the volume of brain tissue. While an increase in brain volume due to intracellular fluid is defined by the term “swelling” of the brain. However, these processes (edema/swelling) can develop simultaneously and transform into each other, therefore both of these concepts can be defined as cerebral edema. ICD-10 cerebral edema code: G93.6
Edema syndrome develops as a nonspecific reaction of the body to the influence of many pathogenic factors. Possible in a number of diseases/pathological conditions that occur with damage to the nervous system - traumatic brain injury , acute cerebrovascular , infectious diseases, hypoxia , intoxication , brain tumors ( perifocal edema ), acute somatic diseases accompanied by impaired water-salt balance / hemodynamics, with endocrine disorders, blood diseases, after surgical interventions, exposure to ionizing radiation, etc. Brain edema is often one of the manifestations of critical conditions and the direct cause of death of the patient.
As a rule, cerebral edema at an early stage (with timely medical correction) is a reversible process, while with inadequate/late treatment, pathological processes increase and often end with the degeneration of brain nerve cells with disruption of their function and, in general, functional failure of brain structures.
Due to the accumulation of fluid in the interstitium of the brain, an increase in brain volume occurs in conditions of limited intracranial space with the development of mass effect (pathological effect of expanding tissue on neighboring structures, causing compression, deformation, displacement, atelectasis), which is primarily manifested by the development of intracranial hypertension (ICP) ) with a controlled increase in cerebral ischemia , and in severe cases - with displacement of brain structures and infringement of the stem sections in the tentorium of the cerebellum, accompanied by dysfunction of vital centers.
Spinal cord swelling
Most often, swelling of the spinal cord develops with traumatic injuries to the spine. Pathological disorders are formed both as a result of traumatic injury and compression of the spinal cord structures due to its edema-swelling, which is accompanied by ischemia of the brain substance, inflammatory changes and a high risk of developing irreversible disorders of the function/structure of the spinal cord. Compression of the spinal cord causes the formation of primary/secondary softening lesions in the spinal cord and is accompanied by neurological symptoms. Clinical manifestations are determined by the level of localization of edema, its severity and duration. With severe edema, it manifests itself as a syndrome of partial/complete disruption of spinal cord conduction.
Bone marrow edema (trabecular bone marrow edema)
There are subchondral and trabecular edema of the bone marrow. Trabecular edema - what is it? Spongy substance (syn. trabecular tissue) of bone consists of loose partitions/plates, the spaces between which are filled with bone marrow, which ensures hematopoiesis in the human body and the formation of immune chains. Edema of the spongy tissue is manifested by the accumulation of exudate (interstitial fluid) in the trabecular plates. At the same time, the liquid level increases from 10 to 20% or more. In most cases, the diagnosis is made late, since there are no specific symptoms and the disease is detected only on MRI.
According to the literature, bone marrow edema occurs more often in middle-aged patients and mainly affects large joints, the condyles of the tibia/femur. The most common (trabecular edema of the lateral condyle of the femur, bone marrow edema of the hip joints, bone marrow edema in the diaphysis of the radius, swelling of the condyle of the femur, etc.). Spinal bone marrow edema is much less common .
The causes of bone marrow edema are extremely diverse ( bruises / fractures , vitamin D deficiency , rheumatoid arthritis , osteoarthritis , benign / malignant tumors , osteomyelitis , spondylitis , arthrosis deformans , endocrine pathologies accompanied by impaired cellular metabolism, status epilepticus , acute neuroinfections , etc.) . The mechanisms of development of bone marrow edema are poorly understood. It is assumed that its development is facilitated by microvascular trauma, abnormal mechanical loads on bones/joints, metabolic disorders, and venous obstruction. Due to the small volume of the article, only cerebral edema will be considered.
Stroke rehabilitation
Stroke is a disease in which rehabilitation and care are of the utmost importance.
Recovery from a stroke begins in intensive care, from the moment vital functions are stabilized. A multidisciplinary rehabilitation team works with the patient, which includes a rehabilitation doctor, physical therapist or exercise therapy instructor, speech therapist, massage nurse, physiotherapist and physical therapy nurse, psychologist, occupational therapist, guard and rehabilitation nurse. Diagnosis is carried out using special scales that reflect the degree of dysfunction and limitations in the patient’s activity, the influence of environmental factors on the rehabilitation potential. The rehabilitation process continues throughout the entire period of hospitalization. At the second stage, patients with serious disabilities who are unable to move independently are sent to rehabilitation departments or specialized hospitals. Those who can walk independently or with support are rehabilitated in outpatient centers based in clinics and sanatoriums.
The rehabilitation process should not be interrupted, so classes must be continued at home. Of course, there are no high-tech robotic complexes or physiotherapeutic equipment at home, but exercise therapy, massage, and work with a psychologist, speech therapist and occupational therapist are possible. For this purpose, telemedicine technologies are used and visits to rehabilitation specialists are organized.
The individual rehabilitation program includes not only a referral for rehabilitation treatment, but also technical means of rehabilitation. However, usually relatives also have to devote significant physical and financial resources to achieve the best effect [7].
Pathogenesis
The development of edema is initially based on microcirculatory disorders. Almost immediately after neuronal damage, regardless of its cause (hemorrhage, trauma, ischemia, tumor, inflammation), cytotoxic perifocal cerebral edema develops, and later, against its background, dysfunction of the capillary epithelium develops with accumulation of fluid in the interstitial space. In the development of endothelial dysfunction, several stages are distinguished, which are accompanied initially by functional (ion edema), then anatomical (vasogenic edema/hemorrhagic transformation) failure, as well as failure of the blood-brain barrier.
The development of cytotoxic edema is based on the accumulation of osmotically active substances inside cells (potassium/sodium/chlorine ions and glutamate molecules), which along the osmolarity gradient contribute to the movement of fluid from the interstitium into the intracellular space. That is, during this phase, cerebral edema is formed due to the trans-epithelial flow of sodium from the vascular bed, along with which chloride ions (to maintain electroneutrality) and water (to maintain osmoneutrality) move. At this stage, there is only a functional impairment of the permeability of the anatomically intact blood-brain barrier. At the same time, against this background, conditions are formed that contribute to the development of the next stages of cerebral edema (in particular, a drop in the concentration of interstitial sodium). The stage of cytotoxic edema does not lead to an increase in the volume of brain tissue and intracranial hypertension.
Developing vasogenic edema is characterized by more pronounced disturbances in the homeostasis of the interstitial space, which leads to disruption of the function/activity of neurons. As a result of increased permeability of the BBB, water accumulates in the intercellular space, which provokes the development of hypoxia and causes a malfunction of the cellular ion pumps of the brain, leading to the passive penetration of sodium ions into the cell, followed by water (the process of cell swelling).
The accumulation of fluid in a limited space according to the Monroe-Kelly formula leads to an increase in intracranial pressure , and in damaged glia (due to edema) the processes of exchange/capture of transmitter amino acids are disrupted. With the development of severe intracranial hypertension, it leads to displacement of the cerebral structures of the increased volume of the brain with herniation of the cerebellar tonsils/stem parts into the foramen magnum. And further compression of blood vessels further aggravates microcirculatory disorders/ischemia of brain cells. Dysfunction of the cardiovascular/respiratory/thermoregulatory centers located in the brain stem is a common cause of death.
As endothelial dysfunction progresses, it is accompanied by pronounced necrosis of epithelial cells and a sharp increase in the size of the intercellular space, which facilitates the passage of blood cells and leads to hemorrhagic saturation of brain tissue, which causes severe disruption of interstitial homeostasis, incompatible with the functioning of neurons and the development of hemorrhagic necrosis , which is associated with severe outcome of cerebral edema. The figure above shows the pathogenesis of cerebral edema.
Treatment of cerebral edema
The diagnosis of cerebral edema, regardless of its origin, implies hospitalization of the patient exclusively in the intensive care unit. This is due to the presence of an immediate threat to life and the need to artificially maintain basic vital functions in the form of breathing and blood circulation, which is only possible with the appropriate equipment.
The complex of diagnostic and treatment measures should include the following areas:
- Combating existing cerebral edema and its progression;
- Clarification of the causes of cerebral edema and their elimination;
- Treatment of concomitant manifestations that aggravate the condition of patients.
Dehydration therapy
It involves removing excess fluid from tissues. This goal can be achieved by using the following drugs:
- Loop diuretics – Trifas, Lasix, furosemide. Their dose must be very high, which is necessary to create a high concentration and rapid onset of the diuretic effect;
- Osmotic diuretics – beckons. Appointed first. After its infusions, the introduction of loop diuretics is recommended. This combination of drugs will have the maximum dehydration effect;
- L-lysine escinate. The drug does not have a diuretic effect, but perfectly removes fluid from tissues, reducing signs of edema;
- Hyperosmolar solutions – magnesium sulfate 25%, glucose 40%. They briefly increase plasma osmotic pressure, enhancing the diuretic effects of diuretics. Additionally, they supply ischemic brain cells with nutrients.
Adequate oxygenation and improved brain metabolism
Achieved by:
- Instillation of humidified oxygen or artificial ventilation;
- Local hypothermia by placing containers filled with ice around the head;
- Administration of drugs that improve metabolic processes in affected brain cells (Actovegin, Mesquidol, Ceraxon, Cortexin);
- Glucocorticoid hormones. Their action is to membrane stabilization of affected cells and strengthen the weakened vascular wall of the microvasculature.
Classification
Due to the specific development of cerebral edema, 4 types are distinguished:
- Cytotoxic OGM - develops as a result of ischemia , hypoxia , exo/endogenous toxic effects on brain cells, causing changes in the permeability (osmoregulation) of cell membranes and dysfunction of glial cells (disorders of cellular metabolism). Cytotoxic edema is reversible within 6-8 hours due to reactivation of the ion pump, which is achieved by restoring cerebral blood flow.
- Vasogenic OGM is based on an increase in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier . Occurs perifocally in the area of ischemia , abscess , tumor, traumatic brain injury, surgery. The main role is played by the transition of fluid from the vessels to the white medulla. Due to the increase in capillary permeability, fluid partially passes from the vessels into the interstitial space), causing an increase in its volume.
- Osmotic OGM develops when the osmolarity of brain tissue increases without disrupting the blood-brain barrier. Occurs with metabolic encephalopathies , hypervolemia , drowning , inadequate hemodialysis and polydipsia .
- Interstitial OGM is the result of a rapid increase in ventricular pressure.
- It is formed when the walls of the cerebral ventricles sweat from the liquid part of the cerebrospinal fluid in the periventricular zone.
According to the degree of compensation there are:
- Compensated OGM (characterized by the absence of dislocation syndrome).
- Subcompensated OGM (characterized by the presence of dislocation syndrome in the absence of vital lesions of brain structures).
- Decompensated OGM (presence of dislocation syndrome and disturbances of vital functions).
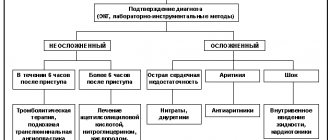
The table below shows a general classification of OGM and characteristics of its forms.
Causes
The causes of cerebral edema are quite numerous, according to which cerebral and extracerebral causes of AMS are distinguished.
Cerebral causes of cerebral edema:
- Brain injuries ( subdural hematoma , brain contusion , basal skull fracture , diffuse axonal injury , intracerebral hematoma ), brain surgery.
- Primary brain tumors ( glioma , medulloblastoma , astrocytoma , hemangioblastoma , etc.) or metastatic lesions of brain tissue that promote displacement of brain structures/disturb the process of outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
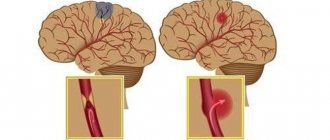
- Cerebrovascular accidents - against the background of arterial hypertension (with a stroke of ischemic / hemorrhagic origin ) or systemic atherosclerosis .
- Neuroinfections ( encephalitis , bacterial meningitis ), purulent processes of the brain (for example, subdural empyema ).
Extracerebral causes:
- Infectious diseases ( influenza , scarlet fever , measles , scarlet fever , toxoplasmosis , mumps , etc.).
- Poisoning with drugs (quinine, antidepressants, neuroleptics, antihistamines, etc.) or various neurotoxic poisons (cyanides, phenols, gasoline, etc.).
- Radiation exposure.
- Development of an allergic reaction ( anaphylactic shock , Quincke's edema ).
- Encephalopathy due to liver/ renal failure , diabetes mellitus , alcohol poisoning.
- A sharp climb without the required acclimatization (mountain edema).
In newborns, cerebral edema can be caused by intracranial birth trauma, severe toxicosis of the pregnant woman, prolonged labor, or entanglement of the umbilical cord.
Cerebral edema in newborns
The relationship between brain tissue and the cranial cavity in newborns is structured completely differently than in adults. This is due to the characteristics of the developing organism and age-related changes in the nervous system. In newborns, cerebral edema is characterized by lightning-fast progression due to imperfect regulation of vascular tone, liquor dynamics, and maintaining intracranial pressure at a stable level. The only thing that saves a newborn is the peculiarities of the joints of the skull bones, which are represented either by soft cartilaginous bridges or are located at a distance from each other (large and small fontanelles). If not for this anatomical feature, any cry of the child could result in the development of compression of the brain and its swelling.
Causes
In newborns, the causes of cerebral edema can be:
- Intrauterine hypoxia of any origin;
- Difficult childbirth and birth trauma;
- Congenital malformations of the nervous system;
- Intrauterine infections;
- Meningitis and meningoencephalitis as a result of infection during or after childbirth;
- Congenital tumors and abscesses of the brain.
Symptoms of cerebral edema in newborns
You can suspect cerebral edema in a newborn based on the following manifestations:
- Restlessness and loud crying;
- Lethargy and drowsiness;
- Breast refusal;
- Tension or swelling of the large fontanel when the child is at rest;
- Vomit;
- Convulsive seizures.
Characterized by a very rapid increase in symptoms and a progressive deterioration in the general condition of the child. In many cases, cerebral edema in newborns cannot be reversed and ends in death.
The presence of risk factors for the development of cerebral edema in a newborn is a reason for clinical observation by specialized specialists. Such a child must be examined by a pediatric neurologist to exclude any signs of intracranial pathology. Mothers should be very attentive during the month after giving birth and respond to any changes in the child’s behavior!
Symptoms
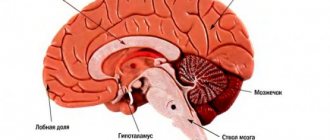
Symptoms of cerebral edema in adults are extremely variable and are caused by dysfunction of various brain structures, disorders of metabolic processes/microcirculation and a developing increase in the volume of brain tissue, especially accompanied by displacement/herniation of certain brain structures, disruption of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics/blood flow in the vessels of the brain. The localization of edema in areas of the brain also plays a significant role, which determines its effect on specific brain structures and forms, in addition to general cerebral symptoms, focal neurological symptoms depending on the affected brain structures. Clinical symptoms of cerebral edema vary significantly depending on the stage of its development, according to which the following are distinguished.
General cerebral syndrome
Clinical signs at this stage are caused by an increase in ICP (intracranial pressure), and their manifestations/severity are determined by the rate of its increase.
headache appears vomiting may occur , often without preceding nausea. The intensity of pain after vomiting usually decreases. Transient dizziness . A common symptom is congested optic discs/transient episodes of visual impairment. Changes in the cardiovascular system are noted: bradycardia , increased systolic blood pressure, decreased breathing (the so-called “Cushing triad).” Characterized by slowly increasing changes in the psyche according to the type of disinhibition: irritability, anxiety, moodiness. Objective symptoms of intracranial hypertension with a slow increase in ICP are congestion of the veins/swelling of the optic disc, radiographically - thinning of the bones of the cranial vault, osteoporosis of the sella turcica.
With a rapid increase in ICP, severe pain of a paroxysmal/paroxysmal nature appears, often bursting pain, accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring relief with the subsequent development of coma . Bradycardia , oculomotor disorders appear Against the backdrop of ICP progression, mental inhibitions are noted, which is manifested by decreased memory, severe drowsiness , non-communication of the patient, and slower speech/thinking.
Syndrome of rostrocaudal diffuse increase in neurological symptoms
Clinical signs of cerebral edema at this stage are determined by the gradual involvement of certain brain structures in the pathological process. As a rule, the pathological process first involves the cortical, later the subcortical, and ultimately the structures of the brain stem. Edema of the cerebral hemispheres is characterized by impaired consciousness and the appearance of generalized clonic seizures.
The spread of the process to the subcortical/deep structures of the brain occurs with psychomotor agitation, the development of grasping/protective reflexes, hyperkinesis , and an increase in epileptic paroxysms .
When the pathological process moves to the hypothalamic region/upper parts of the brain stem, the degree of impairment of consciousness increases sharply, manifesting as coma / stupor with initial manifestations of impaired breathing and function of the cardiovascular system. A posture of decerebrate rigidity (installation of the limbs in an extension position). The convulsions are of a stem nature ( opisthotonus / hormetonia ), mydriasis (dilated pupils) with a sluggish reaction to light is noted.
Swelling of the tegmentum of the cerebral pons causes specific breathing disorders in the form of periodic breathing, maximum bilateral miosis (constriction of the pupils), truncal gaze paresis and leads to the disappearance of the oculovestibular/oculocephalic reflexes. As the edema moves to the medulla oblongata (lower part of the brainstem), disturbances in vital functions increase, which is manifested by a slower pulse/decreased blood pressure and breathing. Neurological examination reveals areflexia of deep reflexes , diffuse muscle hypotonia , lack of pupillary response to light, immobility of the eyeballs.
Phase of dislocation of brain structures
It is based on the process of dislocation and temporo-parietal/occipital herniation of brain structures, which is manifested by characteristic focal symptoms, the main of which are brainstem symptoms ( bradycardia , decerebrate rigidity , dysphagia etc.) with damage to the oculomotor nerves ( mydriasis , ptosis , divergent strabismus ). Often there is sudden vomiting, stiffness of the neck muscles, convulsions of the extensor muscles, lack of pupillary response to light, a decrease in body temperature, a decrease in heart rate and the development of life-threatening conditions - a sharp drop in blood pressure, depression of consciousness (coma), breathing disorders (cessation).
The particular danger of displacement/herniation of supratentorial structures is determined by the high risk of developing vascular disorders and occlusion of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow pathways, which sharply intensifies the primary pathological processes, which turn from potentially reversible disorders into irreversible ones.
Basic information about the defeat
Cerebral edema itself is not a separate disease. This condition is identified as a symptom of another lesion. The process of swelling begins with the filling of cells and intercellular space with a large amount of fluid. Next, there is an increase in brain volume and intracranial pressure, which entails the death of organ cells.
Periventricular edema occurs in newborns as a result of hypoxia, difficult pregnancy, and traumatic birth injuries.
Coma is a consequence of the progression of swelling, the body’s reaction to tissue compression.
In this way, he tries to protect the brain from possible complications and death. The prognosis of therapy depends on the speed of medical care, the quality of the prescribed treatment and the body’s resources.
Tests and diagnostics
Cerebral edema is an urgent condition that requires urgent medical care in a hospital setting (intensive care/resuscitation department), therefore, the initial diagnosis of acute brain injury should be as fast as possible and carried out during treatment. The primary guideline for diagnosing AGM is clinical symptoms, however, it must not be forgotten that at this stage they can be minimally pronounced. If OGM is suspected, a neurological/ophthalmological examination is carried out, during which pain, verbal-acoustic, behavioral reactions, ocular/pupillary reflexes, the condition of the optic nerve head, and intraocular pressure indicators are assessed. A clinical/biochemical blood test and lumbar puncture are required.
The main methods of instrumental diagnostics are computed tomography and nuclear resonance imaging, which allow one to visualize the localization/extension of the area of hyperhydration and identify signs of compression syndrome. According to indications, ultrasound of the skull in different projections, echoencephalography/electroencephalography, neuroophthalmoscopy, and cerebral angiography can be performed.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with thromboembolism of cerebral vessels , metabolic disorders , and status epilepticus .
The first signs of cerebral edema
Symptoms are determined by general and local disorders. It is impossible to determine what is primary, therefore an analysis of the initial signs of pathology is required:
- Severe pain or increasing chronic pain in the head;
- Cloudiness of consciousness;
- Fainting;
- Meningeal syndromes are disorders of conscious activity;
- Paresis and paralysis of half the body;
- Visual pathology;
- Coordination disorders;
- Reduced blood pressure;
- Constant muscle contractions (convulsive);
- Strabismus.
Mortality due to intracerebral edema is often observed, so it is important to identify at least one sign to prescribe additional diagnostic methods - neuroimaging (MRI and SCT of the head).
Diet
Nutrition in the first 1-3 days of AGM is carried out parenterally, for which protein hydrolysates, glucose solutions, amino acids, plasma, albumin, a complex of vitamins, and special nutritional mixtures are administered. The timing of the start of enteral nutritional support through a tube is determined depending on the patient's condition, however, to restore gastrointestinal motility, it should begin as early as possible. For this purpose, special quickly digestible high-calorie nutritional mixtures are used, enriched with vitamins/microelements, a set of essential/essential amino acids in optimal dosages ( Nutrizon Energy , Nutrizon , Berlamin , Nutrizon Protein , etc.). It is recommended to use highly concentrated mixtures to reduce the volume of fluid administered, but at the same time provide the body with the necessary amount of calories. The patient can begin eating by mouth after regression of brain disorders.
Diagnostic measures for cervical edema
The symptoms listed above may be signs of other damage to the body. Therefore, before starting treatment, a comprehensive diagnosis is required to determine the prerequisites and factors for the progression of the pathological condition. The set of measures includes:
- anamnesis and analysis of symptoms;
- neurological examination for possible complications or causes related to neurology;
- examination of the fundus for possible detection of papilledema;
- lumbar puncture to determine the level of intracranial pressure;
- computed tomography to determine the condition of hard tissues;
- magnetic resonance imaging for visualization and assessment of soft tissues and GM.
Advertising:
To determine intracranial pressure, a special sensor is also used, which is installed in the cavity of the ventricles of the brain. It is almost impossible to determine the diagnosis on your own. But if the first symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. If you lose consciousness, it is important to call an ambulance and provide first aid using a cold compress. Emergency doctors must give injections of glucose, piracetam, and Lasix.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of cerebral edema, since it develops secondary. Among the general recommendations, we can only cite the need to follow some rules:
- Minimize the risk of head injury: use protective devices when moving (protective helmet when rollerblading/biking/skating, skiing; seat belts when driving in a car, do not jump your head into a body of water, etc.).
- Treat infectious/somatic diseases in a timely manner.
- Monitor your blood pressure .
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- When climbing to altitude (mountains), do not forget about the need to acclimatize to the altitude.
Consequences and complications
The consequences of cerebral edema, even in cases of rapid relief, can manifest as long-term consequences (absent-mindedness, disturbances in sleep/motor activity, communication abilities, depression). In severe cases, the consequences of cerebral edema can develop in the form of:
- decerebral syndrome (characterized by persistent extensor muscle rigidity, strabismus, severe mental defect);
- decortication syndrome (characterized by impairment/disappearance of speech, motor and mental skills;
- posthypoxic encephalopathy (characterized by dysfunction of the cortex with the development of a cerebral intellectual-mnestic defect).
The most severe complication is death from cerebral edema.
Who's at risk
High-risk groups include people with severe diabetic ketoacidosis, as well as children who are experiencing acidosis for the first time. Factors that increase the likelihood of swelling are: dehydration, inflammation and blood clotting.
As a result, blood flow to the brain decreases and a cascade of ischemia and edema reactions occurs. Intracranial pressure increases, blood pressure and heart rate decrease. A brain herniation can compress vital structures in the brain stem. Patients with hyperactive ketoacidosis are at greater risk. High levels of ammonia above 200 µmol/L in the blood may be an indicator of the risk of developing intracranial hypertension.
In hepatic encephalopathy, cerebral edema is caused by a decrease in perfusion pressure in the brain vessels, swelling of astrocyte cells due to the accumulation of ammonia and increased glutamine production. Against the background of edema, intracranial pressure increases, ischemic contusion and brain hernia develop.
Often, cerebral edema develops in children who have suffered hypoxia and have hydrocephalus. Cerebral edema can complicate the course of strokes and traumatic brain injuries.
Forecast
The prognosis for acute hypertension can vary significantly depending on its etiology, severity, localization, level of intracranial hypertension , and the presence of brain dislocation. Brain edema in the initial stage is a reversible process; as it increases, neuronal death/destruction of myelin fibers develops, leading to irreversible changes in brain structures.
However, even in surviving patients after cerebral edema, in the vast majority of cases there are residual effects, which can vary significantly from subtle manifestations in the form of increased intracranial pressure , frequent headaches , forgetfulness, irritability, absent-mindedness, depression , sleep disturbances, emotional disorders, slowness intellectual processes) to severe disorders of motor/cognitive functions, mental sphere, leading to the patient’s disability.
Severe complications develop especially often during stroke and coma . Accordingly, the prognosis for cerebral edema after a stroke, like the prognosis for coma, is disappointing, at best with disability due to impaired coordination/motor disorders and mental disorders, at worst the patient’s death occurs. Mortality rates for cervical edema, depending on the etiology and severity, vary between 35-70%.
Signs of an incipient stroke
The onset of a hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe headache;
- increased blood pressure;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- weakness in the limbs;
- visual impairment;
- seizures [1].
The onset of ischemic stroke is gradual; within an hour, some of the following symptoms appear:
- facial asymmetry, numbness;
- difficulty speaking – incoherent, impaired understanding;
- double vision, visual disturbances;
- headache;
- numbness, limited mobility in the limbs, often on one side;
- dizziness, imbalance, staggering, staggering gait;
- confusion with disorientation, subsequently there may be loss of consciousness [3].
If one or more of these signs appear, you should:
- Sit the patient down, providing access to fresh air.
- Call emergency medical help immediately.
- If the patient is conscious and able to chew and swallow, give him one aspirin tablet.
The patient must be hospitalized in a neurological or neurosurgical department, where stroke treatment will be carried out. The sooner the patient is in the hospital, the more effective the therapy.
List of sources
- Pavlenko, A.Yu. Cerebral edema: conceptual approaches to diagnosis and treatment / A.Yu. Pavlenko // Emergency Medicine. - 2007. - No. 2 (9). — P. 11-15.
- Principles and methods of diagnosis and intensive therapy of cerebral edema and swelling: method. recommendations / V.I. Cherny [and others]. - Donetsk, 2003. - 49 p.
- Slynko E.I. Traumatic injuries of the spine and spinal cord / E.I. Slynko, A.N. Honda. - K.: PP Gamma-Print, 2010. - 288 p.
- Martynov V.A., Zhdanovich L.G., Karaseva E.A., Ageeva K.A., Khasanova L.A. Edema-swelling of the brain: tactics of patient management // Infectious diseases: news, opinions, training. 2018. – T. 7. – No. 1. – S. 124-13.
- Zadvornov A.A., Golomidov A.V., Grigoriev E.V. Clinical pathophysiology of cerebral edema. Part 2 // Bulletin of anesthesiology and resuscitation. – 2021. – T. 14. – No. 4. – S. 52-60.