- Nervous, mental disorders;
- Increased temperature due to illness, for example, with sore throat;
- Bleeding;
- Purulent infection.
Tachycardia is caused by physical and emotional stress, smoking, alcohol, lowering blood pressure and hemoglobin levels. Rapid heartbeat is possible with:
- purulent lesions;
- malignant neoplasms;
- use of certain medications.
Doctors distinguish a group of tachycardias, which are provoked by disturbances in the electrical conduction system. Rapid heartbeat can be paroxysmal or chronic. In the first case, it is important to determine the sinus or paroxysmal nature of the tachycardia.
Food and heart rate: what is the connection?
In most cases, frequent myocardial contractions are not a pathology; they are caused by poor nutrition, the use of certain types of products, and irritation of the vagus nerve.
Sometimes an increased heart rate may be a sign of a pathological condition of the myocardium, in which case the help of a specialist will be required. Let us examine in detail what factors can provoke a rapid heartbeat after eating:
- Large portion size. One of the most important principles of healthy eating is frequent and small meals. This allows you not to overload the stomach and normalizes metabolic processes. When a person does not eat for a long time, and then consumes more than he should, the load on the heart increases. Proper blood flow to the stomach and intestines is required to ensure the absorption and digestion of food. This is achieved by increasing the number of myocardial contractions.
- Consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates. When sugar is ingested, the pancreas begins to produce more insulin to utilize it. This often leads to hypoglycemia. Since glucose is the main source of energy, in conditions of its shortage the mechanism for the release of adrenaline and thyroid hormones is triggered. They lead to increased blood pressure and increased heart rate. The same principle of the appearance of rapid heartbeat is activated when completely abstaining from sweets.
- Autonomic fibers of the vagus nerve (vagus) are located in the stomach, esophagus, intestines and myocardium. Large volume of food; products that cause severe irritation to the mucous membrane; flatulence or spasms of the digestive organs lead to stimulation of the vagus, causing tachycardia.
- The same mechanism can explain the increase in heart rate when acidic stomach contents are refluxed into the esophagus. This happens in the presence of gastroduodenal reflux or if a person immediately takes a horizontal position after eating (even with normal functioning of the sphincter between the esophagus and stomach).
An attack can be triggered by following a strict diet and dehydration when there is a lack of potassium, magnesium or excess sodium in the body. You also can’t discount an allergic reaction to some foods.
Why should tachycardia be eliminated?
Rapid heartbeat is a rather dangerous symptom that must be eliminated as soon as possible. Due to frequent contractions, the heart does not get enough rest and quickly becomes exhausted. The result is heart failure - a discrepancy between the body's oxygen needs and the work of the heart.
Therefore, if tachycardia occurs, you should consult a doctor. Even in the absence of specific symptoms that would accompany a rapid heartbeat, it is enough to first visit a therapist. After conducting the necessary examinations, he will refer you to the appropriate specialist.
What diseases to exclude
Do not forget about the pathological reasons for the increase in heart rate. In differential diagnosis, I always exclude the following diseases:
- IHD, cardiosclerosis, angina pectoris;
- heart defects, myocarditis;
- pulmonary failure;
- dysfunction of the internal secretion organs (thyroid, adrenal glands);
- vegetative-vascular dystonia (one of the most common, mythical causes of tachycardia) - we recommend watching the video below about it;
- panic attacks, psychosis and frequent emotional overload;
- anemia.
Sometimes tachycardia occurs while taking certain medications. Cardiac glycosides and caffeine-containing products have these properties. Diuretics indirectly cause rhythm disturbances, as they remove potassium and magnesium and change the water-salt balance.
How can a doctor help with a strong heartbeat?
If you have a complaint about palpitations, you should contact a general practitioner or cardiologist.
When a patient complains of increased heartbeat, it is first necessary to establish its cause - whether it is of physiological or pathological origin. For this purpose, laboratory and instrumental studies may be prescribed, including ECG, echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart), and radiography of the heart. After identifying the cause of the increased heart rate, a course of treatment is prescribed aimed at eliminating pathological factors. Normalization of the heartbeat is achieved through treatment with antiarrhythmic drugs. Such drugs should not be taken on your own; they should be prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the condition of your body, established on the basis of a medical examination. Otherwise, the treatment result may be negative.
Typical symptoms
Normally, food intake should cause a slight increase in the heart rate, since the body requires more blood to absorb nutrients and transport them. But a significant increase in heart rate leads to discomfort and sometimes even provokes a heart attack. A person may experience tachycardia after eating as follows:
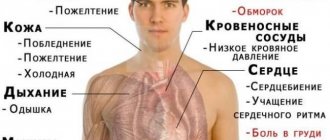
- pulsation in the heart area, temples, neck;
- dizziness and weakness;
- burning or pain behind the sternum;
- panic and fear of death;
- decrease or increase in pressure.
On examination, increased sweating, cold extremities, pale skin and bluish discoloration of the nasolabial triangle are sometimes noted.
Causes of paroxysmal tachycardia
In addition to sinus tachycardia, paroxysmal tachycardia is distinguished. It differs in that the impulse causing heart contractions does not come from the sinus node, but from other, pathological pacemakers. With this type of tachycardia, the heart rate reaches 180 - 240 beats per minute. This condition can occur against the background of various heart lesions, so it is best to consult a cardiologist. The symptoms of paroxysmal tachycardia are very specific:
- rapid heartbeat,
- dyspnea,
- weakness,
- feeling of tightness in the chest,
- pale skin,
- pulsation of the neck veins.
Foods that cause tachycardia
There are a number of substances that enter the body with food, as well as food products, that cause an increase in heart rate after eating. Especially if a person has heart disease or other chronic pathologies.
These properties have:
- spicy foods and spices;
- alcohol;
- extracts and infusions of hawthorn, ginseng, bitter orange oil;
- caffeine (found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, chocolate);
- heavy fatty foods;
- tyramine (an amino acid found in cheeses, dried or overripe fruits, and dried meats);
- theobromine (found in chocolate);
- salt and soda.
There is an assumption that rapid heartbeat immediately after eating develops from monosodium glutamate. This food additive is included in many semi-finished and instant products and canned food.
Watch what you eat
- Heavy, fatty and dense foods can also contribute to heart palpitations. So be mindful not only of what you eat, but also in what quantity.
- If you think that certain foods cause heart palpitations, keep a food diary.
- Pay special attention to substances such as caffeine, alcohol and sugary foods and drinks that you consume to identify the connection between your diet and heart palpitations. Write down not only what you eat, but also how you feel, noting palpitations, sleepiness or malaise.
- Then be sure to consult with your doctor and discuss what role diet may play. As a rule, not only eliminating a few foods helps, but also making changes to your daily menu.
- For example, switching to a mostly plant-based diet and limiting the amount of red meat, saturated fat and sugar can reduce the risk of arrhythmia.
Expert advice
To prevent the development of tachycardia after eating, I recommend:
- eat little and often (up to 5 times a day);
- remove from the diet all foods that provoke an attack and negatively affect the digestive processes;
- eat slowly and chew food thoroughly;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- use ready-made canned food, noodles and instant porridge as little as possible;
- promptly treat diseases of the stomach and intestines;
- take mild sedatives (valerian, motherwort);
- after a meal, stay upright for a while and move around so that a lump of food soaked in acid does not backflow from the stomach into the esophagus;
- exercise at home or go to the gym (a trained heart contracts much more slowly as it works more productively).
Breathing exercises, meditative practices for relaxation, and yoga are of great benefit.
If an attack of rapid heartbeat is accompanied by shortness of breath, chest pain and fear of death, then it is necessary to provide the patient with complete rest, give a sedative and call a doctor.
Rapid heartbeat with normal blood pressure
However, increased heartbeat can be felt regardless of blood pressure. The pressure may be low or normal, but the patient complains of palpitations. This is possible with vegetative-vascular dystonia, anemia, thyroid diseases and a number of other diseases. You should not try to determine what you are sick with, much less begin treatment only on the basis of comparing your heartbeat and blood pressure. In all cases when you are concerned about increased heart rate, you must undergo an examination as prescribed by your doctor.
Attacks of suffocation
Allergy
49003 November 19
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Attacks of suffocation: causes of occurrence, under what diseases they occur, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Choking, or asphyxia, is a painful, life-threatening, pathological condition that is characterized by a lack of oxygen and the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the tissues.
Choking is an extreme degree of shortness of breath when a person feels a sudden lack of air, increased heart rate and fear.
Choking is a symptom of serious diseases and conditions, which are characterized by impaired airway patency, and is observed in certain pathologies of the cardiovascular, musculoskeletal and nervous systems.
Varieties of suffocation
According to the mechanism of occurrence and development, the following types of asphyxia are distinguished:
- mechanical asphyxia
is suffocation that occurs as a result of restriction or cessation of air flow into the airways when they are narrowed (for example, due to swelling of the subglottic space with the development of false croup in children), obstruction (or otherwise blockage) of the airways and their compression (for example, for tumors). - traumatic asphyxia
is suffocation that occurs due to severe compression of the chest. Often occurs during traffic accidents. - toxic asphyxia
is suffocation that develops as a result of depression of the respiratory center, paralysis of the respiratory muscles (diaphragm) or when the transport function of the blood is impaired (carbon monoxide poisoning).
Possible causes of suffocation
With the development of bronchial obstruction (a decrease in the diameter of the small bronchi due to spasm or swelling), the attack develops suddenly and may be accompanied by precursors: a feeling of pressure behind the sternum, anxiety, and itching.
Attacks of bronchial asthma often occur after contact with an allergen, during acute respiratory diseases.
Choking gradually increases, and it becomes difficult for a person to breathe, the breathing frequency increases, and exhalation lengthens. The condition is somewhat facilitated by taking a specific position: sitting or standing, resting your hands on a table, bed or windowsill. This way breathing is restored due to the involvement of auxiliary respiratory muscles. An attack of suffocation may be accompanied by pronounced wheezing, which can be heard at a distance, cyanosis (the skin color takes on a bluish tint) and swelling of the veins. The duration of the attack can vary from several minutes to several hours. At the end of the attack, a cough appears, followed by the discharge of colorless sputum.
Choking may be a manifestation of developing pulmonary edema in diseases of the cardiovascular system. Stagnation occurs in the circulatory system of the lungs due to a decrease in the pumping function of the heart, so the lung tissue becomes saturated with the liquid part of the blood. The accumulated liquid enters the respiratory tract, obstructs the movement of air, causing suffocation, and comes out in the form of pink foam.
Pulmonary edema is often a consequence of myocardial infarction.
The cause of suffocation in children is often the entry of a foreign body into the upper respiratory tract. This happens due to inattention and haste when eating, laughing, coughing and sneezing while eating. Children left unattended may swallow small toys or parts of them. In adults, foreign bodies often enter the respiratory tract during alcohol intoxication. For older people, dentures pose a danger.
Choking in children can be a consequence of the development of false croup. Due to inflammation of the mucous membrane, the larynx swells and the lumen of the airways narrows significantly. Associated symptoms are a barking cough, hoarseness, a rough voice, a slight rise in body temperature and the participation of accessory muscles in the breathing process.
With a thermal or chemical burn of the respiratory tract, a reflex spasm (narrowing) of the bronchi occurs, as a result of which a person cannot take a full breath.
Diseases that may cause asthma attacks
The main group of diseases that cause asthma attacks are diseases of the respiratory system:
- bronchial asthma,
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD),
- pneumothorax (air entering the pleural cavity, causing the lung to compress),
- tumors of the mediastinal organs and respiratory tract (larynx, trachea, bronchi),
- acute stenosing laryngotracheitis, or false croup (typical of preschool children),
- epiglottitis (inflammatory disease of the epiglottis),
- lung cancer.
Other causes of suffocation include the following:
- pulmonary embolism (blockage by thrombotic masses of the vessel through which blood enters the lungs. Blood clots most often form in the veins of the lower extremities, and when they break off, they enter the pulmonary artery);
- pulmonary edema;
- traumatic brain injury;
- Quincke's edema (allergic reaction);
- burns of the upper respiratory tract;
- epilepsy;
- overdose of certain medications and drugs;
- panic attacks.
Which doctors should you contact if you have an attack of suffocation?
First of all, in the event of an attack of suffocation, you need to call an ambulance.
The selection of primary treatment to prevent further episodes of suffocation and shortness of breath is carried out by or. Depending on the accompanying symptoms, consultation with specialized specialists, for example, a pulmonologist, an endoscopist, an allergist, a toxicologist, may be required.
Diagnostics and examinations for asthma attacks
Depending on the accompanying symptoms, the following examinations may be prescribed:
- clinical blood test;
Blood pressure lowering products
If your blood pressure rises after eating, it makes sense to reconsider your diet and fill it with food that normalizes your condition and strengthens blood vessels. These include:
- spinach;
- raw almonds;
- bananas;
- white beans;
- potato;
- turmeric;
- Cayenne pepper;
- sunflower seeds;
- low-fat dairy products;
- ginger;
- green tea;
- chokeberry;
- black chocolate.
Such food has a beneficial effect on blood pressure, normalizes heartbeat, and prevents the formation of plaques on the walls of blood vessels. But it is not able to have a pronounced effect on pressure in the form of a sharp drop.
Citrus fruits, consumed in large quantities, have an excellent ability to lower blood pressure.