The International Clinic Medica24 does NOT accept or hospitalize patients with transient (transient) and acute cerebrovascular accidents (stroke)
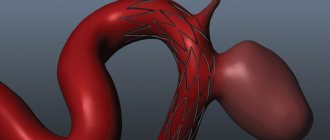
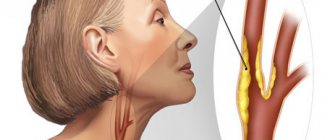
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease of the arteries with the formation of a dense plaque on the inner surface of the vessel, narrowing its lumen. It is clear that such a deformation of the vessel is not able to provide the tissues with an adequate volume of blood; the nutrition of the tissues is disrupted - their ischemia occurs. The most common lesions of the heart vessels are manifested by coronary heart disease, the worst manifestation of which is myocardial infarction. Damage to the blood vessels of the neck and brain in the worst case is manifested by ischemic stroke. Damage to the arteries of the lower extremities leads to the development of ischemic manifestations of varying severity, up to critical ischemia. But veins are not affected by atherosclerosis; they have their own misfortunes: varicose veins and blood clots.
Our expert in this field:
Serebryansky Yuri Evstafievich
Cardiologist, geriatrician, therapist, professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Since the 60s of the twentieth century, a steady increase in the frequency of atherosclerosis and its clinical manifestations in the cardiovascular system has been recorded, which currently hold the lead in morbidity and mortality in developed countries of Europe and America. Gradually, atherosclerosis is taking over the Asian region, where it was practically not noted until the middle of the last century; it comes along with the European way of life. In the structure of mortality from all causes, the share of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) accounts for 55-57%.
Every year, about one million two hundred thousand Russian citizens, mostly men, die from CVDs. Over the last five years, there has been a trend towards a decrease in cardiovascular mortality, however, we are still ahead of European countries: 753 Russians died versus 200 Europeans out of 100 thousand population. How many people actually suffer from atherosclerosis is completely unknown. Atherosclerotic plaques are found in the blood vessels of infants and young men. Thus, almost a third of American soldiers who died in Korea had widespread atherosclerotic vascular disease without any clinical manifestations.
The process of formation of atherosclerotic plaques
At the first stage, a lipid stain appears in the intima of the vessel - a deposition of cholesterol circulating in the blood, attached to proteins. The complex of cholesterol with a protein transporter is called lipoprotein. Contrary to fears, a very small part of cholesterol comes from junk food, and 80% is created in the body “from improvised substances.” Not all fractions of cholesterol are deposited in the intima, but only low lipoproteins (LDL) - these are “bad cholesterol”. “Good cholesterol” is called high-density lipoprotein (HDL). They do not linger in the vascular intima, and they also take excess cholesterol with them. At the lipid stain stage, there is no need to damage the epithelium; in fact, it forms in a clean place.
At the second stage, the spot’s own immune cells come to the spot and try to pull out “bad cholesterol” from the inner lining. These are macrophages that swallow all “garbage” and carry it out. A direct representative of the macrophage family, xanthoma cells are designed to devour lipoproteins. If less lipids are excreted than are supplied, then the spot turns into a plaque. And the loose masses inside the deposit are created by xanthoma cells that die from gluttony of fats. That’s why atherosclerosis was called “hard porridge” in Greek.
By absorbing lipoproteins, immune cells release biologically active substances, helping to form scar - connective tissue that helps strengthen the defect. Immune defenders - T-lymphocytes, on the contrary, try to suppress cell growth by releasing their biologically active substances. There is a constant struggle inside the choroid, so not all lipid spots grow into plaques.
But if the plaque grows, then over time its own vessels begin to grow into it - the vessels of the blood vessels.
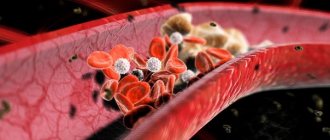
Blood vessels burst, forming microhemorrhages, attracting leukocytes into the plaque, which create the ground for inflammation. Against the background of this active life, the plaque becomes overgrown with calcium, blood clots form and accumulate on the irregularities, which become denser and fuse with the plaque, gradually blocking the lumen of the vessel.
Every year, about one million two hundred thousand Russian citizens, mostly men, die from CVDs. Over the last five years, there has been a trend towards a decrease in cardiovascular mortality, however, we are still ahead of European countries: 753 Russians died versus 200 Europeans out of 100 thousand population. How many people actually suffer from atherosclerosis is completely unknown. Atherosclerotic plaques are found in the blood vessels of infants and young men. Thus, almost a third of American soldiers who died in Korea had widespread atherosclerotic vascular disease without any clinical manifestations.
Stages (stages) of disease development (pathogenesis of atherosclerosis).
Fat streak stage.
Small lipid spots (only one or two millimeters) are immediately present on the walls of the vessel. Then they grow and “unite” with each other. Macrophages destroy them and transform into foam cells, from which fatty stripes appear. This is a normal process, the presence of which does not in any way indicate that a person may develop atherosclerosis in the future.
Stage of fibrous plaques.
The growth of connective tissue develops from fatty stripes, from which fibrous plaques are subsequently “born”. Initially, they are not solid and can be dissolved - with early detection and assistance provided to the patient. Later, fibrous plaques harden as calcium salts are deposited in them.
Stage of complex disorders.
The next stage is a violation of the integrity of fibrous plaques: cracks and tears appear on them. Platelets attach to such a plaque, causing partial or complete blockage of the vessel.
How a vessel is damaged
This is important to know, because without understanding the process of formation of the atherosclerotic beginnings - plaques, it is impossible to tune in to the prevention of atherosclerosis. The creation of a plaque is closely related to our lifestyle; only conscious motivation will allow us to understand what needs to be changed in our personal life so as not to end up in a hospital bed prematurely, or worse. At the moment, there is no single scientific theory of the occurrence of atherosclerosis; about a dozen options are proposed to explain the development of the pathological process.
The creation of atherosclerotic deposits in a separate vessel is carried out in several stages, during which opposite processes simultaneously occur in the vascular intima. Lipoproteins and immune cells penetrate and are simultaneously excreted, entire cell clones multiply and die, intercellular substance is formed and disintegrates, blood vessels grow and calcification occurs. All these processes find their expression in the formation of a dense atheromatous plaque. Atherosclerosis in Greek is a hard paste.
The inside of the vessel is covered with single-celled endothelium, which, together with the underlying connective tissue, forms the inner lining - the intima, which is in direct contact with the blood flow. The middle shell of the vessel is represented by smooth muscle cells immersed in the intercellular substance with elastic membranes. Next comes loose fibrous connective tissue with many elastic and collagen fibers - adventitia or the outer lining of the artery.
Make an appointment with a cardiologist today
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Complications of mesenteric thrombosis
- Gangrene of the intestine. If the blood flow to the intestines is completely blocked, then its death develops.
- Perforation. The dead section of intestine may rupture. As a result, the contents of the intestines spill into the abdominal cavity, causing an infectious process in the peritoneum (peritonitis).
- Scar changes in the intestinal wall. Sometimes these dangerous complications do not develop, but the damaged intestinal wall is replaced by a scar, causing narrowing of the intestinal tube and the development of intestinal obstruction.
Risk factors for atherosclerosis
The main factors contributing to the development of plaques are considered to be smoking, arterial hypertension and lipid metabolism disorders. Additional factors that help and aggravate: age, diabetes, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, hereditary predisposition, and in women also postmenopausal age. Factors whose influence on the development of the disease in a particular person can be excluded are called modifiable, and in atherosclerosis they are the majority. But it is impossible to exclude the influence of age, heredity and gender; these are non-modifiable factors.
The leading and fundamental cause of the disease is smoking. Tobacco contains several hundred harmful substances and compounds, not just the drug nicotine. It has been proven that giving up this not just harmful, but destructive habit significantly reduces the risk of developing atherosclerosis, and with it all cardiovascular diseases.
An increase in the level of cholesterol and “bad cholesterol” LDL, which is called hyperlipidemia, contributes to their deposition in the choroid. In studies, reducing the level of “bad cholesterol” by 1.0 mmol/L reduced mortality from CVD by 22%. Cholesterol can be partially corrected by diet; remember, only 20% comes from food. The remaining 80% of cholesterol is synthesized by the body according to the genetic program; this amount of cholesterol must be reduced with special drugs - statins. Cholesterol levels depend on diet, physical activity and even the season; in winter it is higher, but “good” cholesterol is also higher at this time of year.
Arterial hypertension is so closely related to atherosclerosis that both diseases can be considered twins. Some scientists consider both diseases to be different sides of a single process, where one pathological condition necessarily turns into another, and it doesn’t matter which one was legalized first, the main thing is that both are together and pull each other. With a prolonged increase in pressure, spastic narrowing of the vessel contributes to the formation of an atherosclerotic plaque in it; atherosclerosis narrows the vessels, contributing to an increase in pressure. Plaques “like” to form in the forks of the vessel into branches, where turbulent waves of blood supplied under high pressure strike.
Obesity is inherently a voluminous manifestation of excess cholesterol and metabolic disorders. It is necessary to understand that a man's waist should be no more than 94 cm, and a woman's - less than 80 cm, and this is not a desire for beauty, but a vital necessity. Losing 10 kg of weight reduces the level of “bad cholesterol” by 0.2 mmol/l, while increasing insulin sensitivity and decreasing triglyceride levels.
Do not forget that excess body weight leads to physical inactivity - a decrease in physical activity, which in turn directly leads to atherosclerosis. Physical activity reduces LDL concentrations.
Excess fat in the diet directly affects atherogenesis, promotes obesity, which leads to the development of diabetes. With a lack of vitamin E and essential phospholipids from dietary fats, the synthesis of “good cholesterol” is disrupted. Therefore, moderation is important in everything.
With type 2 diabetes, which usually develops in adults, the risk of death from heart disease increases threefold in men and fivefold in women. And cardiovascular diseases are a clinical manifestation of atherosclerosis. In diabetes mellitus, small vessels are necessarily damaged, which is called “microangiopathy,” and later larger arteries are also involved - a complete blessing for creating plaques on the unsmooth lining of already narrowed vessels.
You can’t easily overcome a hereditary predisposition, but now genetic testing makes it possible to diagnose familial hyperlipidemia and other deviations from normal lipid metabolism in order to promptly begin lifelong correction with the help of medications.
Make an appointment with a cardiologist today
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis
Clinical manifestations are determined not so much by the extent of vessel involvement in the pathological process as by the specific localization of the plaque narrowing the lumen. And almost total closure of the vessel is not necessarily required; ischemia can occur with very moderate obliteration, for example, if the plaque is combined with an increase in pressure, as is known, caused by vasospasm.
As a rule, vascular beds are affected by atherosclerosis. When localized in the cerebral basin - the vessels of the brain - headaches, dizziness, noise in the head, memory and intellectual impairment develop. The apotheosis of cerebral atherosclerosis is ischemic stroke of the brain. Atherosclerotic damage to the blood vessels of the heart responds with angina pectoris, which at a critical moment becomes myocardial infarction.
Plaque damage to the renal artery will lead to increased blood pressure, and the starving kidney will decrease its functionality. If atherosclerosis of the renal artery occurs in parallel with the development of diabetic microangiopathy, then it is worth preparing for renal failure. In the arteries of the abdominal cavity affected by plaques, which are responsible for the blood supply to the intestines, blood clots can form, and the desolation of the vessel leads to ischemia of a segment of the intestine and even surgery for necrosis of the intestinal wall.
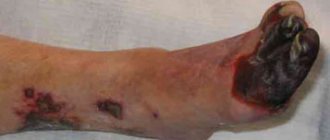
Atherosclerotic damage to the arteries of the lower extremities brings severe suffering to the male half of humanity, and all of them are heavy smokers. It starts, as always, small, but ends up with amputations as a result of critical ischemia of the limb. But even before amputation, the poor fellows are not allowed to sleep peacefully due to pain in their legs, not allowing them to take a horizontal position in bed, since the intensity of the pain syndrome increases significantly.
Atherosclerosis occurs secretly, but leads to suffering.
Treatment approach at the Innovative Vascular Center
Timely diagnosis of mesenteric ischemia allows for adequate treatment and saving a person’s life. In our clinic, if mesenteric ischemia is suspected, angiography is urgently performed and the blood clot is removed from the intestinal arteries. Only such treatment gives the patient a chance to survive. If enough time has passed since the onset of the disease, then restoration of blood circulation and laparoscopy are performed, which makes it possible to determine the need to remove dead sections of the intestine. Without treatment, all patients die. With treatment, more than half can be saved.
Treatment of atherosclerosis
There is no radical treatment, you can somewhat weaken the onset of the disease with the help of medications, you can restore the patency of a vessel affected by plaques, you can replace the vessel with a prosthesis, but the process will continue. In all cases, lifestyle modification is required with the elimination of smoking, increased physical activity, and changes in diet. Blood pressure must be maintained at the target level - below 130-140/80-90 mm Hg. Art., correction of the manifestations of diabetes mellitus is necessary.
Atherosclerosis is easier to prevent than to deal with its clinical manifestations. And prevention is based on modification of risk factors, always taking into account that without quitting smoking nothing meaningful will happen.
The material was prepared by a cardiologist, geriatrician, therapist, professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Medical Sciences at the international clinic Medica24 Yuri Evstafievich Serebryansky.
How is atherosclerosis treated, what options exist?
For atherosclerosis, treatment is carried out comprehensively. A person must adhere to a diet. The diet is drawn up by a doctor, limiting fatty foods (primarily animal fats), simple carbohydrates and salt, and the person must also give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol, and perform light physical activity (therapeutic exercises). In addition, the patient begins taking a course of medications, the task of which is to remove excess cholesterol from the human body, as well as aimed at reducing the activity of the body’s “production” function of cholesterol. If the above steps do not work, as well as in the case of a high probability of arterial blockage, then the patient is prescribed surgical intervention.
Unfortunately, atherosclerosis is an irreversible disease and it is completely impossible to cure it.