Lacunar stroke is a type of ischemic stroke that results in the formation of a cavity or softening in the tissues of the gray matter of the brain. The term “lacuna” (from the French meaning softening, cavity) was introduced into medical circulation in the 19th century by the physician Decambre. Later, at the end of the 20th century, this term began to be used to name this subtype of ischemic stroke.
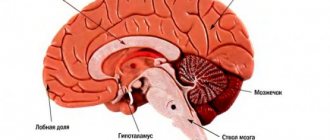
This type of stroke is quite common and occurs in 30% of cases. Lacunar ischemic stroke is characterized by small lesions (less than 1 cm) and occurs due to impaired blood flow in the area of small arteries. Most often, such lesions occur in the area of the brain stem, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. One of the main causes of vascular damage is long-term arterial hypertension.
Due to the small size of the lesion, it is very difficult to identify the clinical picture of this disease. This poses a great danger to human life and health. Such small and practically asymptomatic heart attacks can lead to acquired dementia (dementia). A person not only loses the ability to acquire new skills, but also loses previously acquired ones. One of the types of multi-infarct dementia is Binswangen disease. As a result of this complication, a person’s gait is also impaired.
Diagnostics
Suspicion of a lacunar infarction appears only if the patient suffers from arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus or diseases associated with cerebral vessels. Due to the difficulties caused by the specificity of symptoms, it often takes a very long time to make a final diagnosis. First, the neurologist conducts a survey, and then necessarily prescribes the following examinations:
- Laboratory blood tests;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- Angiography of cerebral vessels.
Modern medicine makes it possible to accurately and quickly identify any disturbances in the functioning of the body. However, in the case of lacunar stroke there are a number of problems:
- Consequences of the disease
- Classification
- Treatment of ischemic stroke of the brainstem and lacunar
- Rehabilitation period
- Treatment of lacunar stroke
- Treatment tactics
- Features of the development of lacunar stroke
- Danger and consequences
- Cerebral infarction (lacunar infarction)
- Clinical picture
- 5 Causes of lacunar stroke
- Forecast and consequences
If the cause of a stroke is an increase in blood pressure, then there may be cases where the deviation from the norm is so insignificant that doctors do not take it into account. Therefore, they begin to look for other reasons why the patient experiences certain symptoms
At this time, the patient’s condition may worsen, which, as it later turns out, was caused by circulatory disorders associated with increased blood pressure. The size of the gaps can be extremely small, which is why even modern equipment will not allow them to be noticed during the first study. This is why sometimes doctors have to perform a CT or MRI again. Gaps may not be identified immediately. This is due to the fact that on CT or MRI they appear in real form only a week after formation. Until this point, they are either visible in a much smaller and lower-density state than they actually are, or not visible at all. Symptoms appear gradually. Even after a serious circulatory disorder, the patient may not have any external signs of a stroke. The condition usually worsens over several days. For this reason, there are great risks of not identifying the disease at all until the patient’s health deteriorates critically. Angiography may not show any abnormalities that could indicate a problem with the blood vessels in the brain. There is no guarantee of their detection even with repeated studies.
All these problems make lacunar ischemic stroke a particularly dangerous phenomenon. Only the highest quality and responsible examination will identify violations in the first days. But even with the work of highly qualified doctors and the availability of modern equipment, there is no guarantee of a quick correct diagnosis.
Causes
Any stroke, including lacunar, develops as a result of the following reasons:
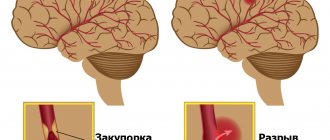
- Atherosclerosis and thrombosis. These pathologies cause ischemia (lack of blood supply to the organ) due to blockage of the vessel by a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque. The first signs of a stroke appear when the lumen of the vessel is blocked by more than 70%. With a lacunar stroke, collateral circulation (bypass as a method of compensation) does not have time to form.
- Cardiogenic embolism. It is the cause of 20% of all strokes. An embolism forms in the heart and its valves, which is a consequence of cardiac arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation provokes a stroke in 4.5% of cases.
- Violation of hemodynamic properties, for example, with a sudden drop in blood pressure due to stenosis of the main arteries of the neck.
- Other diseases: Takayasu's disease (inflammation of the vascular walls and a decrease in their lumen), Moyamoya disease (the tendency of brain vessels to gradually narrow).
Systemic factors that increase the likelihood of developing a stroke:
- Arterial hypertension.
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
- Blood diseases: blood clotting disorders, increased number of red blood cells per liter of blood.
Any of these reasons triggers a chain of pathological mechanisms that lead to ischemia and necrosis of brain tissue. Normally, the volume of blood flow in the brain is 55-60 ml per 100 g of substance per minute. Thus, the first pathobiochemical reactions occur when blood circulation decreases to 50 ml per 100 g. The first reaction is that the production of proteins in brain cells is inhibited. The primary marginal ischemic zone is formed.
When the blood supply drops to 35 ml per 100 g, an alternative pathway for energy production is activated - glucose is broken down (glycolysis). As a result of the oxidation of glucose, molecules of pyruvic acid and two molecules of ATP (one of the energy sources) are formed. An alternative pathway is the anaerobic pathway, that is, energy is generated without the participation of oxygen reaction, since during ischemia there is little oxygen in the brain. Due to the anaerobic pathway for energy production, lactate accumulates.
Lactate (lactic acid) is a normal compound that appears, for example, in muscles after intense exercise. However, due to increased glycolysis, lactate becomes too much. Lactate itself is a breakdown product that needs to be disposed of. But in the ischemic zone there is a lot of it. The accumulation of lactate shifts the acid-base balance towards acidity (pH decreases). Local acidosis occurs, which is manifested by a typical clinical picture for such a condition.
When the volume of cerebral circulation decreases to 20-25 ml, the cortex, due to lack of oxygen and nutrients, is inhibited. Drowsiness, apathy and indifference occur. When the minute volume of blood flow drops to 10 ml, irreversible organic changes occur in the brain due to the death of neurons. During the first two days, alternative sources of nutrition support the weakened vital activity of the cell. However, after 48 hours the cell dies completely.
Preventive measures
Lacunar cerebral infarction can be prevented by quitting smoking and reducing the amount of salt, fat, and sugar in the diet. It is recommended to regularly consume fruits and vegetables, and include at least 30 minutes of physical activity (walking, exercise, gardening) in your daily schedule. It is advisable to limit alcohol consumption and maintain optimal body weight. For people over 50 years of age, it is advisable to regularly measure their blood pressure. Hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke.
Patients who have had a stroke or lacunar infarction are at high risk of recurrence, which is often more severe. Therefore, secondary prevention is necessary. It includes lifestyle changes, elimination of risk factors, pharmacological, and in some cases surgical or endovascular treatment of existing diseases that can cause a stroke.
Classification
Clinical classification is based on clinical symptoms and is discussed in the section on symptoms of lacunar infarction.
In the development of the disease there are:
- the most acute period is the first 3 days;
- acute – 28 days;
- early recovery – the next 6 months after suffering a circulatory disorder;
- late recovery – for 2 years.
Due to mild symptoms and the absence of pronounced motor, speech and sensory disorders, it is very difficult to describe the features of each interval. Therefore, this division is of secondary importance.
Treatment of ischemic stroke of the brainstem and lacunar
The most common brain disease that leads to disability and death is stroke. Stroke is often caused by blockage of blood vessels. This is caused by elevated cholesterol levels. If you want to be healthy and not encounter this disease, watch what you eat.
Ischemic stroke treatment
Treatment in the acute period is the most important, then treatment of ischemic stroke proceeds as follows:
- normalize respiratory function normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system correct blood pressure antioxidants vitamins neuroprotectors
After the rehabilitation period, regular consultations and examinations with the attending physician and a visit to the sanatorium are prescribed.
Treatment of ischemic stroke of the brain is quite serious, since the flow of blood to the brain is stopped. The first thing they do is hospitalize the patient. They are already conducting a thermogram, which will help determine the degree of brain damage and the type of stroke, and based on this they make a prescription for stroke treatment.
After treatment and discharge, the patient continues to undergo rehabilitation, since it is necessary to eliminate the consequences of a stroke as much as possible, restore the functions of the brain and other affected parts of the body.
Ischemic stroke left side treatment
Each side of the brain is responsible for a specific area of human life.
Right hemisphere for:
Which hemisphere is affected, those abilities are distorted, speech and many other visible signs of a stroke are often affected.
Treatment of ischemic stroke drugs
Drug treatment of ischemic stroke:
- Anticoagulants - nadroparin, heparin, enoxyparin, daltoparin
- Neuroprotectors - glycine, piracetam, cerebrolysin, pentoxifylline, vinpocetine, calcium channel blockers and instenon
- Recovery - ginkgo biloba, vinpocetine, pentoxifylline, piracetam, phenotropil
In principle, these drugs are the standard treatment for ischemic stroke.
Drugs for the treatment of ischemic stroke:
Ischemic stroke treatment and recovery are interconnected, since after hospitalization the treatment does not end, there is also a course of physical therapy and massage.
Stem ischemic stroke treatment
A brain stem stroke is one that occurs in the brain stem.
Causes of brainstem stroke:
- hormonal contraceptives, taken for a long time
- control heart rate
Ischemic stroke symptoms, treatment, symptoms:
- pale skin or red face
- blood pressure increases
- breathing and blood circulation are impaired
Repeated ischemic stroke treatment prognosis In half of the cases the disease recurs, but in 70% it leads to death. You need to monitor your health before a relapse occurs.
Lacunar ischemic stroke treatment
Lacunar ischemic stroke provokes heart attacks.
Often in the evening I had a headache and high blood pressure, and in the morning the first symptoms appeared - fatigue, numbness, disorientation.
Lacunar ischemic stroke can be treated well; you need to start treatment on time and remember that lifestyle is the key to recovery.
Prevention
Lacunar ischemic stroke is a disease that mostly affects older people. Statistics are misleading and more and more young people are being affected. The reasons for the rejuvenation of the disease lie in the increasingly accelerating pace of life, increasing causes of stress, and bad habits. Having suffered a stroke, a person does not change his life and does not listen to the signals that the body sends. Lack of attention to yourself leads to irreversible consequences. For preventive purposes you should:
Use regular aspirin. It prevents vascular infarction. Attending physicians recommend that patients take soluble aspirin after discharge from the hospital. Take inventory of your menu. It is required to completely eliminate fast food and everything connected with it. Limit salt intake. After illness, it is strictly forbidden to use cholesterol- and sugar-containing foods in the diet. Closely monitor the dynamics of blood pressure values. Create a special notebook for daily recording of indicators and do not allow it to increase critically. Stop drinking alcohol and quit smoking. Do physical exercise, take walks in the fresh air. Monitor your body weight. After a myocardial infarction, it is necessary to undergo a recovery course. As prescribed by your doctor, take medications that prevent the formation of blood clots
Pay attention to the prothrombin index. If you suspect a stroke, immediately call a doctor and talk about how you are feeling. The consequences of an untreated disease will not allow the patient to lead a full life.
The lifestyle must be transferred to a calm, measured direction. Try to avoid unnecessary stress, heavy physical exercise, and forget about overwork. For those at risk, set a rule: undergo an MRI annually. Monitor the dynamics of the disease and, based on the results, make adjustments to therapy with the attending physician.
People around the patient should show patience and understanding. It must be remembered that after the development of lacunar syndromes ends, brain functions are restored. The period of recovery and return to a full life of a person who has suffered a lacunar stroke depends on a friendly attitude, sensitivity and attentiveness to the victim. First aid in case of recurrence should be provided by them.
Rehabilitation period
During the rehabilitation period, a whole range of measures is carried out, both medical and pedagogical, legal, social and psychological. All of them are aimed at restoring lost functions as a result of a lacunar stroke.
Principles of the rehabilitation program:
- If rehabilitation measures are started as early as possible, for example, from the first days of the onset of symptoms of the disease, recovery occurs much faster and more fruitfully. This is an excellent chance to avoid possible secondary complications, such as contractures, congestive pneumonia, thrombophlebitis and others.
- Rehabilitation should be carried out only under the supervision of specialists. If events are organized incorrectly, the chance of full recovery will be significantly less.
- Recovery requires the participation of a physical therapy methodologist, a neurologist, a physiotherapist, a psychotherapist, an occupational therapist and a speech therapist.
- The rehabilitation process involves the presence and support of the patient’s loved ones. It is best to entrust the patient with the most basic household chores on weekends or in the afternoon.
Treatment of lacunar stroke
Patients with lacunar infarctions are treated in neurological departments. They are necessarily prescribed antihypertensive therapy, drugs to restore nervous tissue, and prevention of thrombosis and embolism.
Antihypertensive therapy includes the prescription of ACE inhibitors (enalapril, lisinopril), diuretics (indapamide, furosemide), vasodilators (nifedipine, diltiazem), etc.
Patients with lacunar stroke need constant monitoring of blood pressure levels, but it is important that it does not become too low
In cases of severe atherosclerotic damage to the carotid and vertebral arteries, as well as in patients over 75 years of age, the pressure should not be quickly reduced, as this can cause even greater disruption of blood flow in the brain.
Antithrombotic therapy is considered an important stage in the treatment of cerebral infarctions. Patients are shown aspirin, heparin, clopidogrel. With the cardioembolic mechanism of stroke, when the cause is blockage of the perforating arteries by fragments of blood clots or deposits on the heart valves, anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin) are necessarily prescribed.
To prevent subsequent lacunar strokes, which tend to recur, aspirin up to 325 mg is prescribed. If the patient does not tolerate aspirin well, then its dosage is reduced to 50 mg per day and treatment is supplemented with dipyridamole at a daily dose of 400 mg in two doses.
Aspirin is indicated in the presence of microangiopathy, a combination of brain pathology with cardiovascular lesions. With concomitant lipid metabolism disorders, diet and lipid-lowering drugs (statins) are prescribed.
To improve microcirculation in the brain tissue, nicergoline, vinpocetine, and nootropil are used. It is advisable to prescribe neuroprotectors (akatinol, magnesium sulfate), B vitamins. If depression develops, antidepressants (fluoxetine, amitriptyline) are indicated.
In addition to drug therapy, patients undergo rehabilitation courses to restore motor function, sensitivity, speech, etc. Massage, physiotherapy, special exercises for paresis, and speech training help. You can restore memory and intellectual abilities by solving problems, memorizing poems or short texts.
Patients with cardiovascular pathology predisposing to thrombosis and embolic complications are observed by a cardiologist, who always prescribes aspirin and, if necessary, anticoagulants. If atherosclerosis of the carotid and vertebral arteries is diagnosed, then surgery may be needed to improve blood flow.
After suffering a lacunar stroke, patients are prescribed maintenance therapy with neuroprotectors, vitamins, and vascular medications, which are prescribed in courses 1-2 times a year.
The prognosis after a lacunar infarction is considered favorable, since the resulting neurological disorders regress quite quickly, and a complete restoration of impaired functions is possible
At the same time, this pathology should be given due attention by a neurologist, since repeated heart attacks occur in at least every tenth patient, and in a third, after a few years, signs of vascular encephalopathy with intellectual deficit and mental disorders increase
According to some data, after 10 years only 30% of patients remain alive, most of whom have severe signs of dementia. To avoid such developments, you need to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and take measures to prevent circulatory disorders in the brain.
2012-2020 sosudinfo.ru
Display all posts with the tag:
Stroke
Go to section:
Diseases of the brain and blood vessels of the head, cerebrovascular diagnostics, anatomy, pharmacology
Recommendations to SosudInfo readers are given by professional doctors with higher education and specialized work experience.
One of the leading authors of the site will answer your question in the form below.
Treatment tactics
For adequate therapy and in the future for the purpose of preventing recurrent cerebrovascular accidents, patients are prescribed aspirin to reduce the aggregation of blood elements (sticking together and forming blood clots) and improve its fluidity. The most acceptable dose is considered to be 75 mg of acetylsalicylic acid, produced specifically for these purposes.
If it is impossible to take aspirin due to intolerance or side effects, it is possible to replace it with dipyridamole at a dose of 200 mg daily or 75 mg of clopidogrel. Dosages are specified and regulated by specialized specialists.
Normalization of blood circulation is achieved by prescribing drugs that improve microcirculation. The optimal choice is nicergoline, vinpocetine, pentoxifylline. First, a course of intravenous drips is carried out, followed by a transition to long-term use of tablet forms.
At the same time, neurotrophics are recommended - medications that optimize the supply of oxygen to the brain and stimulate recovery. These are Cerebrolysin, Actovegin, citicoline and ginkgo biloba preparations (memantine, tanakan, bilobil).
With the development of signs of dementia and the formation of a lacunar state, anticholinesterase drugs and precursors of acetylcholine, a biologically active substance involved in the conduction of impulses along nerve trunks, are prescribed. These are prozerin, neuromidin, galantamine in the required dosages.
With parkinsonism, the patient needs to take specific drugs to reduce tremors (cyclodol, amantadine).
To restore mental abilities and reduce the manifestations of dementia, it is necessary to use the patient’s intelligence as much as possible, forcing him to memorize poems, allowing him to solve simple mathematical problems.
Since the leading cause is hypertension, its adequate reduction can be considered as one of the links in the treatment process. The therapist and cardiologist select an adequate dose and combination of drugs. When prescribing a correction regimen, the patient’s age and the presence of significant concomitant diseases are taken into account: diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease.
Features of the development of lacunar stroke
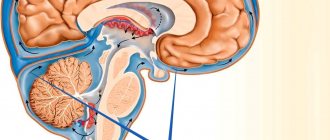
Lacunar stroke is a type of ischemic brain injury that occurs in people suffering from arterial hypertension and related vascular changes. Elderly people are the main risk group. This type of stroke is characterized by pathological changes in small-caliber perforating arteries. A characteristic feature of a lacunar stroke is the formation of lacunae, that is, small cavities, in the depths of the brain.
Lacunae are round or irregular in shape and range from 1 to 20 mm in diameter, although formations larger than 15 mm are rare and are considered gigantic. Inside these cavities there is blood or plasma with fibrin. Their walls look like a bag, which can rupture when exposed to certain factors. Foci of necrosis are located deep in the gray matter; damage to the cerebral cortex does not occur even in the event of minor bleeding. A person can live with small gaps in the brain without even realizing it until histological analysis is carried out. All people associate stroke with severe neurological disorders, leading to paralysis and disruption of the patient’s usual life activities.
But there are types of pathology during which external symptoms do not appear, brain disorders are weak and characterized by regression. The person continues to live his usual life, unaware of the changes that have occurred. These types include lacunar ischemic stroke, which is called silent.
Research, statistics
Frequency of strokes, incl. lacunar, in our country is 2 times higher than in other countries of Western Europe. It is the third leading cause of death in the world. In 85% of cases, the disorder is caused by blockage of blood vessels and interruption of the supply of oxygenated blood to a certain part of the brain.
In 90% of cases, stroke occurs in people over 45 years of age, mainly in men. But in women the condition is more dramatic. This is often associated with the hormonal burden of women (childbirth, menopause, hormonal therapy, contraception) and a higher incidence in older age groups.
Determining the cause of the increased incidence in our country is not easy. A number of studies show a connection with an unhealthy lifestyle, lack of physical activity, type of diet, and a large number of smokers. But to some extent, unfavorable statistics are also associated with underestimation of risk factors leading to stroke.
Danger and consequences
When a patient is diagnosed with a single case of lacunar stroke, the prognosis for him is often favorable. In most cases, the victim completely recovers impaired brain functions, and only some patients may still experience partial impairments of sensitivity or motor function.
If a stroke relapse occurs, then certain negative consequences are possible, for example, a lacunar state of the brain (not uncommon in people with vascular dementia). In addition, the formation of lacunae in the area of the brain stem is especially dangerous, since this is where the respiratory and cardiovascular centers are localized.
If we talk about life prognosis, then the mortality rate as a result of lacunar stroke is only 2%, but this percentage increases with a second attack. However, it is quite difficult to say anything about life expectancy in this case. Much depends on the age of the person, the location of the pathological foci, the severity of concomitant ailments, as well as the timeliness of the assistance provided.
Preventive measures
In a person, even if the pathology suffered did not cause serious harm to health, life after a lacunar stroke changes. This is necessary to prevent the re-formation of lacunae that disrupt brain function.
Tips for preventing lacunar stroke are useful not only for people who have suffered a small focal ischemic attack, but also for those who have a predisposition to developing the disease (hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.). Doctors recommend:
- monitor blood composition (cholesterol levels and viscosity);
- stabilize blood pressure;
- regularly spend time in the fresh air;
- provide regular physical activity (gymnastics, swimming, cycling);
- stop eating at fast food outlets and add a large amount of vegetables and fruits to the menu;
- limit salt intake;
- give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
These simple methods will help you avoid the bitter experience of learning what it is, the formation of lacunae in the brain tissue. And for those who have already suffered an attack, preventive measures are necessary to prevent a relapse.
Cerebral infarction (lacunar infarction)
One of the types of cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke) is lacunar infarction, which is a small (up to 15 mm in diameter) brain damage that occurs when local blood circulation and gas exchange are disrupted. The reasons for this situation are varied and not fully understood, but most often it is blockage of supply vessels as a result of changes in their walls (atherosclerosis, inflammation), emboli (blood clots, fat droplets, bacterial colonies, etc.). Most of them are found in the periventricular region, basal ganglia, and thalamus - the central, deep structures of the brain. Lacunar infarctions account for 20-30% of all strokes.
Lacunar infarction can occur at any age, but the likelihood of its occurrence increases with age and reaches its maximum after 85 years. More often, cerebral circulatory disorders occur in men. The most significant risk factors for the occurrence of lacunar cerebral infarctions are:
- hypertonic disease,
- diabetes,
- chronic renal failure,
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis,
- abnormalities in the circulatory system and heart defects,
- rheumatism,
- cardiac arrhythmias,
- disorders of the blood coagulation system, blood diseases.
Clinical picture
Clinical symptoms of cerebral infarction may be insignificant or distinct, but short-lived. This depends on the location of the lesion in the central nervous system. More often it is represented by mono- or hemiparesis, disorders of statics and coordination of movements, syndrome of speech disorders and memory. General cerebral symptoms (lethargy, lethargy, confusion, headache, nausea and vomiting) are usually absent.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most preferred method in determining the location, and most importantly, in assessing the stage of development of the ischemic process. In the acute phase, the most information is carried by diffusion-weighted images (abbreviated as DWI) - images obtained using a specialized pulse sequence provided in expert-class MRI scanners, which we use in the study of all patients without exception.
Using DWI, you can see a minimal change in the diffusion (speed of movement) of fluid in brain tissue at the molecular level, which is the first sign of ischemic brain damage. In addition, when examining the brain of a patient with suspected lacunar infarction (as in all other cases), we use the entire set of pulse sequences that comply with the international standard to identify possible associated changes.
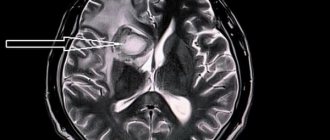
The patient is 32 years old. After visiting a neurologist, she went to the MRI room to rule out systemic damage to the central nervous system with a preliminary diagnosis of transient ischemic attack.
When scanning the brain in several modes, a lacunar infarction with a diameter of 7 mm was discovered in the cortical parts of the left parietal lobe. An acute infarction is clearly visible on DWI (a pulse sequence available in expert-class tomographs), but is poorly visible in a mode with signal suppression from free fluid.
A correct and timely diagnosis, including taking into account cause-and-effect relationships in the development of the pathological process, which is significantly facilitated by the MRI examination method described above, will predetermine the tactics of treatment measures.
After treatment, the patient's condition improved. On MRI after 3 months, positive dynamics are noticeable.
Detection of such changes is possible only with high-field magnetic tomographs of 1.5 T or 3 T, and also requires sufficient research time.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic has a Philips Achieva 1.5T high-field tomograph, and we have an individual approach to each patient.
Registration for an MRI examination is carried out by specialists, and the examination lasts as long as necessary.
To sign up for the study, as well as find out more information about MRI, please call: 8 (495) 304-304-9.
Clinical picture
In most cases, the attack can be sudden, very quickly leading to blockage of the arteries, but it can last up to five days. Precursors may include ischemic attacks that cause disruption of cerebral circulation in small cerebral arteries.
During an attack, you may experience high blood pressure and an irregular heart rhythm. Single cysts - lacunae do not lead to paralysis of the body. Detection of the lacunar form of cerebral infarction is complicated by the implicit manifestation of symptoms:
- Impaired motor skills are expressed in the inability to move the limbs; they become less sensitive.
- Loss of coordination. The patient may complain that everything is floating before his eyes, there is an unsteady gait and disorientation.
- The lacunar form of the disease is characterized by neurological disorders, expressed in the deterioration of memory, the ability to analyze, there is no logic of reasoning, and other processes of the brain are disrupted.
To immediately contact a doctor, one of the following symptoms of a stroke is sufficient:
- A sharp manifestation of weakness in the legs, fainting, loss of consciousness;
- Distortion of the face, numbness of half the body, limbs, impaired skin sensitivity;
- Difficulty in speech and impairment of its perception;
- The patient begins to feel dizzy and finds it difficult to maintain coordination of movements;
- Severe pain in the head appears;
- Cramps, increased muscle tone.
The disease can occur in the form of a micro-stroke or without clinical manifestations at all. It can develop at any age. Cases of the disease have been described in patients who have just turned 25 years old.
Features of the pathology:
- stroke develops only against the background of hypertension;
- there are no headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, loss of consciousness or disturbances thereof;
- neural symptoms increase gradually over 2-48 hours (usually the patient’s disturbances develop during night sleep, and in the morning he wakes up with symptoms of a stroke);
- the prognosis for this disease is favorable; after an attack, complete or partial restoration of brain function is observed;
- examination of cerebral vessels using contrast agents does not show any abnormalities; computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can reveal small foci of low density, but not always, especially if the infarction is small.
Doctors describe about 20 clinical syndromes that can be observed with the development of lacunar stroke. The following are most often diagnosed:
- The isolated motor variant is the most common and occurs in 60% of patients. Lacunae form within the capsule and pons. The patient develops paralysis of one half of the body, usually the limbs, sometimes the face. Plegia is observed on the side opposite to the lacuna. No further neurological symptoms develop.
- The isolated sensitive variant is observed in almost 20% of patients. The lacunae in this case are localized in the ventral thalamic nerve ganglion. Disturbances of all types of sensitivity develop: temperature, nociceptive, tactile, muscle-articular. Manifestations of the disease can involve the head, arms, legs and torso. Typically, after what period sensitivity is fully or partially restored.
- Atactic hemiplegia develops when pathological foci appear in the capsule and pons of the brain. Occurs in 12% of patients. The patient experiences muscle hypotonia in the arms or legs, pyramidal disorders, and impaired coordination of movement on the side of the injury.
- Dysarthria and clumsiness of the hands when moving are observed in 6% of patients; pathological foci form in the pons of the brain. The patient has a speech impairment; on the one hand, paralysis of the limbs and head may develop.
The following syndromes are also often diagnosed:
- dyskinesia;
- false bulbar syndrome;
- parkinsonism syndrome;
- forced gait in small steps;
- urgency to urinate, incontinence;
- hemiparesis and loss of sensation of one half of the body.
With the development of a lacunar stroke, there is no disorder of consciousness or vision, systemic impairment of formed speech (aphasia), or other symptoms of damage to the cerebral cortex.
Main reasons
The occurrence of a stroke is always associated with arterial hypertension. Chronic exposure to high blood pressure causes various pinpoint damage to cerebral vessels, up to 1 cm in length:
- death of artery wall cells, leakage of fibrin into the affected area (fibrinoid necrosis);
- release of plasma from the bloodstream (plasmorrhagia);
- impregnation of the vessel wall with a specific protein, making it look like a glass tube (hyalinosis);
- replacement of the artery wall with connective tissue;
- fat deposition, usually without the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
The nerve cells located around the affected artery begin to receive an inadequate amount of oxygen and nutrients. When their deficiency becomes critical, neurons die. Over time, a lacuna forms at the site of necrosis.
Another mechanism for the formation of cavities is typical for infarctions located at some distance along the main vessel. The middle layer of the artery consists of muscle cells - myocytes, which are destroyed under the influence of arterial hypertension. The vessel ceases to cope with pumping blood, its distant branches remain half-empty, which leads to necrosis of neurons.
Rarely, the death of neurons to form lacunae is caused by the rupture of tiny protrusions of brain vessels (aneurysms). This form of the disease belongs to the hemorrhagic subtypes of cerebrovascular accident.
Previously, it was believed that arterial hypertension was the only cause of lacunar stroke. More thorough studies have shown that in some patients, cerebral infarction develops as a consequence of a combination of atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries and high blood pressure. But atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries themselves, which supply the brain, extremely rarely cause the formation of cavities.
Other risk factors for lacunar stroke (3):
- type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- suffered micro-strokes;
- elderly age.