This is what atrial fibrillation is called in translation from Latin. This is one of the forms of heart rhythm disturbances, which is based on a disorder of the atria. Atrial fibrillation is a fairly widespread disease these days.
We talk about the features of this cardiac pathology with Elena Gennadievna Nikulina, a cardiologist at the regional cardiac clinic.
— TV presenter of a popular health program Elena Malysheva called atrial fibrillation a deadly disease. Why?
— Elena Malysheva outlined a very important problem in one general phrase, but, in my opinion, she exaggerated the colors somewhat. If our patients (and there are many thousands of them in the region, and citizens with coronary heart disease account for approximately 10-14 percent of cases of atrial fibrillation) are told that atrial fibrillation is a deadly disease, imagine how many people will consider themselves hopelessly ill. But this is absolutely not true.
Yes, atrial fibrillation is associated with an abnormal heart rhythm. This is caused by the fact that the chambers of the heart contract incorrectly, while blood is not released to the periphery to other organs in full. The blood supply to the heart is disrupted. There are many complications of atrial fibrillation, but today’s medicine is able to treat, correct and prevent both the pathology itself and its complications, so patients with atrial fibrillation live for many, many years. And it, like some others, becomes fatal only when nothing is done to treat the disease.
— Can atrial fibrillation lead to a stroke?
- Yes maybe. Among all thromboembolic complications, this is the most common - strokes account for 91% of all types of thromboembolism. Unfortunately, such strokes can be extensive and lead to serious consequences. But, I repeat, provided that the patient is not observed by a cardiologist and does not carry out therapeutic measures. Brain stroke and myocardial infarction occur because atrial fibrillation causes improper emptying of the heart chambers. There is stagnation of blood, and where there is stagnation, the ability to form blood clots increases. And these blood clots can shoot, including into the vessels of the brain or coronary arteries. With timely and correct treatment, patients with atrial fibrillation live a long time. Recommended regimens usually include two- or three-component drugs, including anticoagulants, that is, blood thinners, and together they all affect the various phases of thrombus formation.
— Why does such arrhythmia occur?
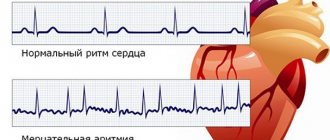
— There are many reasons for the occurrence of atrial fibrillation. The fact is that with this pathology, the normal (that is, sinus) heart rhythm is disrupted and the heart can no longer effectively pump out blood. The atria, instead of working synchronously, only randomly twitch, flutter, and flicker. The ventricles also contract irregularly and more frequently. Erratic contraction of the atria and ventricles is called atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation.
With age, it is diagnosed more and more often: if at 40-50 years of age, atrial fibrillation occurs in approximately 1% of the population, then among people over 60 years of age - in 5%, and after 80 years of age, about 10% of the population already suffers from it. This is due to the fact that in old age, hardening of the walls of the heart and coronary arteries is observed, and coronary heart disease (CHD) develops. Ischemia, as well as its complications - myocardial infarction, often causes atrial fibrillation.
But the most common cause of atrial fibrillation in older people is arterial hypertension. Increased pressure causes stretching of the chambers of the heart and atria, which leads to rhythm disturbances. As well as acquired and congenital heart defects. There are other reasons too. For example, increased thyroid function (thyrotoxicosis) or alcohol abuse. The influence of heredity is noted. But there is no generally accepted theory that would explain the mechanism of development of atrial fibrillation.
— What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
- They can be very diverse. Some patients do not feel any discomfort, and their rhythm disturbance is detected by the results of an electrocardiogram (ECG) only by chance. And for others, in addition to frequent irregular contractions, when the pulse can reach 200 beats per minute, shortness of breath, causeless fatigue, weakness, even fainting appear. There may be dizziness, a feeling of anxiety, restlessness, chest pain, a sharp decrease in blood pressure and other unpleasant symptoms. Atrial fibrillation can appear in attacks, and then they speak of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. But atrial fibrillation can also be idiopathic, that is, of unknown origin.
In any case, with atrial fibrillation, the risk of ischemic stroke increases 7 times!
— Is this disease acquired or could it be congenital?
— Congenital atrial fibrillation, as a rule, does not occur; it is an acquired pathology. It mainly manifests itself in people after forty years of age; the incidence of coronary heart disease and hypertension peaks at this age.
- Who is more susceptible - men or women?
- Same.
— Is there prevention?
— This is treatment of the underlying disease, and the most important prevention, if you have been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, you need to prevent its complications: fight thromboembolic complications
It is also extremely important to take care of the prevention of those diseases that provoke the development of atrial fibrillation. And above all, as we have already said, arterial hypertension and coronary heart disease. Of course, alcohol abuse should not be allowed.
* * *
How to recognize arrhythmia?
Normal heart function is invisible to humans. We feel our heartbeat only in certain cases, for example, during serious physical activity or when we are very nervous. If the heartbeat is clearly felt during moments of rest, this may be a cause for concern. In addition to the sensation of heartbeat, arrhythmia manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath;
- too fast or slow heartbeat;
- dizziness;
- chest pain;
- fainting or pre-fainting states.
The listed symptoms do not necessarily mean the presence of arrhythmia. They can be triggered by an unhealthy lifestyle, lack of sleep, excess weight and other factors. If you have these symptoms, it is recommended that you first try to lead a healthy lifestyle and improve your sleep patterns. Contact a cardiologist
worth it if there is no improvement.
Heart arrhythmia - how to treat it so you don’t get sick anymore?
Content
Our heart always works continuously, since it is designed to maintain regular and normal blood flow, passing through the main working fluid to ensure the activity of all vital organs and systems.
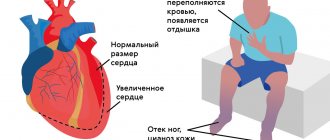
In a natural calm state, the heart rate fluctuates around 60-80 beats per minute, and if there is a violation of this indicator, it increases or decreases. Such deviations are called arrhythmic, since the heart rhythm is disrupted, and the phenomenon itself is largely pathological in nature. And here the question arises, how to treat arrhythmia in order to be healthy, strong and active again. In medical practice, this disease is called atrial fibrillation, which manifests itself in various forms, each of which is characterized by its own characteristics and symptoms.
Atrial fibrillation can lead to many serious consequences if appropriate treatment and prevention measures are not taken in time. Due to disruption of the normal heartbeat, our hematopoietic organ experiences stress and tension, and this negatively affects the entire body.
heart arrhythmia how to treat
If you feel painful spasms in your chest, you start to feel dizzy, short of breath, and you also feel an abnormal heartbeat, then you are at high risk of an arrhythmic reaction, which requires urgent treatment and resuscitation. If you are aware of how to treat cardiac arrhythmia, you can quickly improve your health, preventing the further development of heart disease.
Many people wonder whether it is possible to cure cardiac arrhythmia? This depends on the severity and type of pathology itself, since treatment does not always promise to be progressive and effective. Of course, it is easier to prevent a disease than to eradicate its original source, lodged inside, but if the second situation already occurs, then it is necessary to direct all efforts to improve your health, to recover from a painful pathology, which can lead to other risks and even death outcome.
What are the risks of arrhythmia?
Consequences of arrhythmia:
- the development of thromboembolism, when blood clots form on the atrial walls. Such blood clots can fall off, blocking other organs, and most often they end up in the brain, and this is the highest risk of stroke;
- insufficiency of cardiac activity, due to which the organ works at an increased rate, and swelling appears on the body and shortness of breath simply occurs.
To know how to cure arrhythmia, it is important to distinguish between several types, each of which is characterized by its own signs and symptoms:
- tachycardia – when the heart rate increases and the frequency exceeds 100 beats;
- bradycardia – when the heart rate slows down and the frequency is less than 60 beats;
- irregular heartbeats.
How to protect your heart
The primary and simplest ways to cure cardiac arrhythmia are that if an increase in heart rate is suspected or clearly manifested, the following exercises should be performed:
- pressing on the eyeballs;
- stimulation of vomiting;
- deep breaths and maximum exits, while the mouth and nose should be pinched.
These are vagal techniques, and if they do not help, then they resort to medication and electrical pulse treatment of cardiac arrhythmia.
If arrhythmia manifests itself in the form of bradycardia, treatment methods should be taken that are aimed at the underlying disease. If the situation is extremely difficult, then it is necessary to use electrical stimulation.
For mild arrhythmic conditions, it is recommended to take the following medications:
- settings based on valerian, motherwort;
- altalex;
- antares 120;
- sanosan, Persen;
- novo-passit.
- sedative tinctures: valocordin, corvalol, belloid;
- tranquilizers: Valium, Sibazon, Xanax, Nozepam, Elenium, etc.
Physiotherapy
It is possible to treat arrhythmia with physical exercise, but it is important to consult a doctor who can prescribe acceptable loads and a sports program so that the patient can perform it regularly and thereby stimulate endurance and optimize the functioning of his heart.
If you are interested in the best and most effective restoration of health, then only treatment for arrhythmia in Israel can restore your strength, good spirits and good heart function, so that you no longer worry about the health of your organs.
Prevention and treatment
Physical activity during arrhythmia should be agreed upon with a cardiologist in order to competently and safely plan the course of your training. First, you will study with a rehabilitator, and then you can switch to individual lessons.
Regular physical activity contributes to the reflex expansion of blood vessels, stimulation of blood circulation, thereby increasing the resistance of the body and heart to various stresses.
Your daily routine should include morning exercises, which allows you to “turn on” your heart for the whole day, charge it with tone and strength for further active actions. Depending on the severity of the arrhythmia, the type of load on the body is selected.
Interesting! Walking short distances is very beneficial. The rhythm of movements should be unhurried in order to adapt the body to such events, and gradually you can increase the distance traveled.
If your body allows, you can practice light jogging, and to regulate the indicators, a special device is used in the form of a pedometer or heart rate monitor, the screen of which displays your heartbeat, frequency, pulse, and the number of steps taken.
An Israeli doctor told how to get rid of heart arrhythmia forever
If an arrhythmia takes you by surprise, this is not a reason to give up and panic, because valuable advice and useful information on how to treat cardiac arrhythmia will help you quickly and accurately find the answer to your questions in order to restore your health.
What can cause arrhythmia?
Factors that contribute to the development of arrhythmia relate to the structure of the heart and previous diseases of the cardiovascular system, for example:
- heart disease;
- heart failure;
- congenital abnormalities of the heart structure;
- myocarditis;
- coronary heart disease, etc.
Sometimes arrhythmia begins due to conditions or habits not directly related to the heart. In addition to heart diseases, scientists identify the following causes of arrhythmia:
- hormonal disorders;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- frequent consumption of caffeine;
- taking certain medications.
How to treat various cardiac arrhythmias?
Content:
Arrhythmia is a disturbance in the functioning of the heart. It is characterized by a deviation of the heart rate from the norm (it is 60 - 80 beats per minute for an adult), as well as disruptions in the rhythm and sequence of the atria and ventricles. Considering the prevalence of this disease, the question of how to cure arrhythmia arises for many people.
Arrhythmia is a general concept for all diseases associated with irregular heartbeats. In fact, there are many types of it, which differ radically from each other and require different treatments. Therefore, when symptoms of the disease appear, the primary importance is to quickly diagnose and determine the cause of the disease. Because only on the basis of tests, it is possible to carry out correct and effective treatment that will not harm the body.
An increase of 1 degree in human body temperature leads to an increase in heart rate by 10 beats per minute.
Symptoms
Chronic diseases and disorders of the central nervous system can also be causes. Unfortunately, even the healthiest person is not immune from the occurrence of this disease, since it can develop due to strong emotional stress and stress.
Main symptoms:
- The most obvious manifestation of the disease is a person’s feeling of his heartbeat. During normal operation, it does not work noticeably. In case of failures, there are sensations of irregularity, a sinking heart, sharp and stronger beats.
- Weakness, dizziness, possible fainting.
- Shortness of breath, lack of air.
- Increased or slowed heart rate for no apparent reason.
Diagnosis of the disease
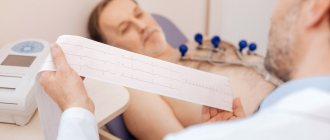
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is the most common way to detect heart problems. Using this procedure, a cardiogram is obtained - a graphical representation of the pulse. And based on it, you can immediately draw conclusions about the state of a person’s health. The advantage of cardiograms is the speed and accuracy of the indicators.
Holter monitoring (HM) is the same ECG, but more advanced. Sensors are attached to a person, which read data and transmit it to a small recorder. HM allows for daily monitoring of the patient, thanks to which it is possible to obtain extensive information about malfunctions of the heart, make a more accurate diagnosis and correctly predict possible health risks.
This method is used to monitor patients, to check the effectiveness of treatment, and also in cases where patients experience frequent attacks, but they could not be recorded during the clinical period.
Electrophysiological study. This method is used in cases of severe heart disease and when it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis using conventional methods. Its essence lies in the introduction of special sensors to a person through the veins, which are attached to the walls of the heart and from there transmit information about impulses.
Treatment
The most common treatment for heart failure is medication. Its essence lies in the patient taking medications aimed at improving the functioning of the heart muscles, as well as eliminating the causes that caused it. In most cases, this is enough to cure the disease.
In advanced cases and severe diseases, surgical intervention is possible. At the same time, pacemakers and defibrillators are implanted on the human heart. Which take over part of the functions of the heart and stimulate its work.
Important! You can start taking medications aimed at stabilizing the heartbeat only after diagnosis and with a doctor’s prescription.
Treatment recommendations
- First of all, it is necessary to determine the disease that caused it and begin to treat it. Since most often heart rhythm disturbances are a consequence of other diseases.
- Take into account all the factors that provoke attacks and be prepared for them. For example, stress or magnetic storms.
- Regularly take medications prescribed by your doctor and undergo examinations
- Take medications that prevent the formation of blood clots. It is advisable to add blood thinning foods to your diet. For example, garlic or flax seeds.
- Take medications aimed at strengthening the heart muscle.
- Reduce negative emotional load and stress as much as possible.
- If possible, give up coffee, alcohol and cigarettes.
- Maintain proper nutrition.
These are the most common recommendations on how to treat cardiac arrhythmia, and in fact, following most of them is recommended for any person. However, for people suffering from heart failure, a correct lifestyle ensures a reduction in stress on the body. Therefore, it is the key to health and elimination of attacks of illness.
All arrhythmias are divided into types based on information about the heart rate and the part of the heart that began to fail.
Tachycardia
Occurs when the heart rate is more than 90 beats per minute. Tachycardia is divided into physiological and pathological. With physiological, there is a natural increase in a person’s pulse. It can be caused by physical exertion, stress, sudden movements, and increased body temperature. An increased heart rate may be a result of taking certain medications. And taking into account the individual characteristics of each person’s body, its normal state. With pathological tachycardia, changes in pulse are, first of all, a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and therefore, there is a need to treat it.
Symptoms: rapid pulse, dizziness, anxiety, pulsation of the cervical artery, possible fainting.
Complications: heart failure, myocardial infarction.
Treatment: most often, tachycardia does not require drug treatment. If an increased heart rate occurs, it is recommended to lead a calmer lifestyle and give up bad habits: alcohol, cigarettes, coffee, Coca-Cola, strong tea, chocolate.
That is, introduce as few pathogens into the body as possible. You can take Corvalol or valerian tincture. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe lidocoine, rhythmylene, or digoxin. Do not forget that such drugs can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor.
Bradycardia
Characterized by a heart rate below 60 beats per minute. It may be a normal condition for professional athletes and people exposed to frequent physical activity. In these cases, bradycardia is a protective mechanism of the human body from constant overload of the heart. However, even with a natural decrease in heart rate, this leads to low blood pressure and corresponding consequences. It’s not for nothing that all athletes are at risk of hypotension. It is almost impossible to cure.
Symptoms: weakness, increased fatigue, drowsiness, feeling of depression, fainting, hypotension.
Complications: heart failure, severe decrease in vital signs of the body.
Treatment: for mild manifestations of arrhythmia, targeted treatment may not be required. In some cases, a low pulse is a consequence of myocardial disease, the treatment of which also eliminates bradycardia. However, if the heart rate drops below 50 beats per minute and it is impossible to eliminate bradycardia with medication, implantation of a pacemaker is required.
Atrial fibrillation
The most common and most dangerous type of arrhythmia. It occurs due to a violation of the synchronicity of the atria; in fact, this phase of the cardiac cycle falls out of work. This leads to weak blood conductivity in the atria, it stagnates in them, and in the absence of timely treatment, blood clots form. Due to the physiology of our body, these blood clots enter the carotid artery, and from there to the brain. As a result, the patient experiences an ischemic stroke.
Symptoms: rapid heartbeat, which can reach 180 beats per minute, irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, dizziness.
Complications: heart failure, stroke.
Treatment: Can be a difficult and lengthy process. During drug treatment, an individual combination of drugs is selected for each patient. In some cases, cardioversion treatment is used. During which, electrical impulses are transmitted to the heart, helping to restore normal rhythm. Particular attention must be paid to prevention and routine diagnosis, since atrial fibrillation contributes to the occurrence of blood clots.
Extrasystole
Characterized by heart contractions that are out of tune with the general rhythm. The source can be both atria and ventricles. For a healthy person, the norm is considered to be no more than 4% of such contractions per day of their total number. As a person ages, the risk of extrasystole increases significantly - after overcoming 50 years of age, this disease is observed in 70% of people.
Symptoms: premature heart contractions, lack of air.
Complications: angina pectoris, impaired blood supply to the brain, development of atrial fibrillation.
Treatment: most often, extrasystole occurs as a consequence of other diseases, so the main treatment is directed specifically at the causes. It is also highly recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Assistant surgery
In Russia, about 2.5 million people suffer from atrial fibrillation. But people are used to taking it lightly. Like, so what if the heart beats out of rhythm. Meanwhile, this very common disease in the world can lead to very tragic consequences.
The Bakulev Center uses a surgical method for eliminating atrial fibrillation, which has no analogues in the world. The first unique operations, the methodology of which was completely developed at the center, were carried out here under the leadership of academician Leo Bockeria. The monitors show areas of the heart where arrhythmia originates. A catheter is inserted into the patient through a small incision, which, having reached dangerous places, acts on them, completely destroying the disease. True, this method is possible if the case is not complicated in any way.
In difficult situations, traditional surgical intervention is still used. The task is the same - to stop the arrhythmia. Surgeons say the procedure is more complicated than a heart transplant. The organ is isolated from the circulatory system, temporarily connecting the body to an artificial analogue, they operate, freezing the problem areas, and then return everything back. The success rate of such operations here is close to 100%.
The Bakulev Center is the only clinic in the world where both methods of treating atrial fibrillation are practiced at once. The patient's rehabilitation period is very short. On average, a week after surgery, the patient returns home completely healthy.
Heart is pounding
It is clear that with each heartbeat there is a sequential contraction of its parts - first the atria, and then the ventricles. Only such alternation ensures efficient functioning of the heart. With arrhythmia, which has received the wonderful name “atrial fibrillation,” one of the phases of the cardiac cycle is lost, and specifically, atrial contraction. Their muscle fibers lose the ability to work synchronously. As a result, the atria only twitch chaotically - flicker. As a result, the ventricles begin to contract irregularly.
Why does atrial fibrillation appear?
In young people, the cause of arrhythmia is often mitral valve prolapse, in other words, sagging, weakness of one of the valve leaflets between the left atrium and the left ventricle. This pathology usually occurs in secret and is detected by chance. Atrial fibrillation may be its first manifestation. But not only an unhealthy heart is the cause of arrhythmia. A variety of diseases can give it a start. And not just diseases.
Very often, an attack of atrial fibrillation is provoked by drinking more alcohol than usual. There is even such a concept - “cardiac arrhythmia of special days.” Any day you can expect the occurrence of arrhythmia in people with diseases of the thyroid gland (especially with its excess function) and some other hormonal disorders.
Arrhythmia often develops after surgery, a heart attack, or various stresses. Its development can be stimulated by rich food, constipation, tight clothing, insect bites, and certain medications. For example, taking diuretics for the purpose of losing weight often lands “your own doctor” in a hospital bed. There is a high risk of developing atrial fibrillation in people with diabetes, especially if diabetes is combined with obesity and high blood pressure. In general, doctors are not always able to find the cause of arrhythmia.
How to find out about the onset of the disease? It is indicated, for example, by palpitations, when the heart is pounding so much that it seems like it is about to jump out of the chest. There may be a feeling of interruptions in the heart. “It will knock, knock, and suddenly freeze” or “something will turn inside,” this is how patients describe their condition. But often the arrhythmia proceeds unnoticed. Only by feeling the pulse can you establish the irregularity of heart contractions. Often the disease is detected only during a clinical examination using an ECG. But it can be even worse: the first manifestations of the disease are burdens.
Why is atrial fibrillation generally unsafe?
It is often accompanied by tachycardia, in other words, an increase in heart rate. With all this, a colossal load falls on the heart. As a result, chest pain may appear - symptoms of angina pectoris or even myocardial infarction. Arrhythmia may reduce the efficiency of the heart. This will lead to another burden - cardiac failure. With all this, the person feels suffocated, it seems to him that there is not enough air.
Can arrhythmia go away on its own?
In principle, it can. But if the arrhythmia persists for several hours or complications appear, you must immediately seek medical help. In general, even if the arrhythmia disappears on its own, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor. Repeated rhythm disturbance can occur at any time and end catastrophically. Therefore, self-medication will not help enough.
As a good song says: “No matter how much you cure your heart with validol, there are still continuous interruptions.” The fact is that it is best to restore the normal rhythm on the first day from the onset of arrhythmia. It is possible to eliminate arrhythmia later than this period, but then additional preparation will be needed. For atrial fibrillation