Diffuse and focal changes - what are they?
Diffuse and focal changes - what is it, what is the difference
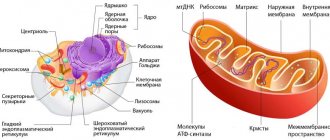
At the conclusion of the ultrasound examination, when pathology is detected, the doctor may indicate the presence of focal or diffuse changes. These are diagnostic criteria that describe the degree of organ damage in various diseases.
general information
With an ultrasound, the doctor must determine the condition of the organ. After carefully examining it, the specialist makes a conclusion - pathology or normal. If the organ is normal, then it is simply described, where it all ends.
If the examination shows a deviation, then the degree of damage to the organ is determined. The doctor must answer the question of what changes are present - focal or diffuse.
Diffuse and focal changes - what is the difference
It should be clarified that the division into focal and diffuse changes is conditional. It helps in the work of specialists to better understand the picture of the disease.
Diffuse is damage to the entire organ. Whatever part the doctor examines, he sees pathological changes. The organ is completely different from a healthy one. It is impossible to determine which area is normal.
Focal changes are a pathological process affecting part of an organ. There are areas that differ from healthy ones. However, all other parts look normal.
Examples of diffuse and focal changes
With advanced hepatitis, an inflammatory disease of the liver, the entire organ is affected. The doctor will see diffuse changes. When the pathology is still at an early stage, healthy areas will also be identified, that is, focal changes.
With a malignant liver tumor at the initial stage, the doctor sees focal changes. When cancer affects the entire organ, it is no longer possible to determine its healthy boundaries - this is a diffuse pathology.
Relationship between changes and disease
What changes have occurred is of great importance. Diffuse damage is always a sign of severe pathology that has already affected the entire organ. However, the presence of focal changes does not mean that the disease is still at an early stage. It depends on the disease.
Ultrasound examination cannot show a specific disease. The doctor can only see anatomical changes. The same diffuse and focal processes can be observed with completely different deviations. Usually, after an ultrasound, when the affected area is identified, other, more accurate research options are prescribed.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
– a state of deficiency of thyroid hormones in the human body.
Primary hypothyroidism
– hypothyroidism, which develops as a result of damage to the thyroid gland itself.
Subclinical hypothyroidism
- elevated TSH level with free T4 level within normal values.
Secondary hypothyroidism
– a clinical syndrome that develops as a result of insufficient production of TSH by the pituitary gland in the absence of primary pathology of the thyroid gland itself, which could lead to a decrease in its function.
Prevalence
Primary hypothyroidism is one of the most common endocrine diseases; a particularly high incidence is detected in iodine-deficient regions. The average prevalence is 4.6% of the population,
Clinic
The most common symptoms of hypothyroidism
: severe fatigue, drowsiness, dry skin, hair loss, slow speech, swelling of the face, fingers and toes, constipation, memory loss, decreased cognitive function, chilliness, hoarseness, depressed mood, uterine bleeding, infertility, depression, dementia, joint pain. Symptoms do not always appear all at the same time; often one group of symptoms predominates.
Upon external examination, patients with severe and long-term deficiency of thyroid hormones may have characteristic external manifestations: general and periorbital swelling, a puffy face with a pale icteric hue, and poor facial expressions.
Instrumental and laboratory research methods: to clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, a study of the level of free thyroxine (FT4), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), antibodies to thyroglobulin and thyroid peroxidase.
The diagnosis of hypothyroidism is established when TSH levels increase and free T4 decreases below normal.
Treatment
Replacement therapy is recommended for all patients diagnosed with overt hypothyroidism. The drug of choice for replacement therapy is levothyroxine sodium (L-thyroxine, Eutirox). The dose is selected by the doctor under the control of the level of free thyroxine (FT4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Prevention
Since the exact reasons why diffuse nodular goiter of the thyroid gland develops are not yet clear, preventive measures are precautionary in nature.
Endocrinologists strongly recommend enriching your diet with foods rich in iodine:
- sea fish;
- crustaceans;
- seaweed;
- whole milk;
- beef.
Adequate nutrition is especially important when the immune system is weakened, in childhood and old age. If one of your close relatives has been diagnosed with diffuse nodular goiter, it is recommended to regularly visit an endocrinologist and monitor hormone levels through testing - at least once a year. Good sleep, a properly organized rest regimen, and an active lifestyle will also help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Complications
Without timely and adequate treatment, diffuse nodular goiter can lead to serious consequences. Therefore, doctors recommend seeking professional help immediately if you discover 3 or more signs of the disease. An advanced stage of diffuse nodular goiter increases the risk of malignancy of the process and the development of thyroid cancer. It often leads to death.
Other complications are possible with diffuse nodular goiter. Choking, problems with swallowing, compression of nerve endings and metabolic disorders can negatively affect the condition of many internal organs and systems.
Diet
In case of diffuse changes in the liver, it is necessary to follow a special diet. In fact, healthy eating rules are not difficult to follow. It is more difficult to overcome psychological dependence on harmful products. Willpower, a positive attitude and a healthy, varied menu help with this.
The following foods, drinks and dishes must be excluded from the patient’s menu:
- black tea, coffee;
- tomatoes and juice from them;
- any alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks;
- sweet soda;
- fat meat;
- any strong broths;
- barley, millet, pearl barley;
- mayonnaise and other fatty sauces;
- sausage and any smoked meats;
- fatty fish;
- white bread and baked goods;
- fatty fermented milk products;
- marinades, salted and spicy vegetables;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- fresh berries and fruits;
- chocolates and other confectionery products;
- spices.
In case of diffuse changes in the liver, it is necessary to eat such dishes and drinks as:
- weak green tea, dried fruit compote, rosehip decoction;
- rye and bran bread, crackers from it, unsweetened biscuits;
- dietary meat: chicken, turkey, rabbit, veal;
- lean fish - pike, pike perch, cod;
- vegetable oil and butter in small quantities;
- skim milk and dairy products;
- eggs;
- boiled and stewed vegetables;
- buckwheat, oatmeal, rice porridge;
- leaf salad;
- fresh bell pepper;
- pasta;
- marmalade, honey, fruit jam.
You need to eat small portions 5-6 times a day. Preference should be given to steamed, boiled and baked products. Soups and aspic are prepared from lean meat and fish. You can eat a small amount of squash caviar, vinaigrette, and sauerkraut. Sugar is replaced with xylitol. The amount of salt should not exceed 3 grams per day.
Treatment with folk remedies
If a patient experiences unpleasant symptoms, some traditional methods of treatment can be practiced to improve the condition. However, you must first coordinate the use of such methods with your doctor.
- Honey with pumpkin . Carefully remove seeds from a small pumpkin and fill with honey. Leave in a dark place for 20 days. Drink liquid from pumpkin three times a day, 1 tbsp. spoon.
- Oat infusion . Pour 500 g of oats into 1 liter of boiling water and leave for an hour. Strain and drink half a glass of the product three times a day.
- Lemon remedy . Grind 1 kg of lemons with peel in a meat grinder (remove the seeds first), 300 g of garlic and 300 g of parsley. Mix everything and place in a glass jar. Store in the refrigerator and consume 3 tsp. in a day.
- Herbal mixture . Mix lingonberry, blueberry, strawberry leaves, as well as corn silk and bean pods in equal proportions. 2 tbsp. l. Place the mixture in a thermos and pour 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for 1 hour, drink throughout the day.
- Potato juice . Grate two medium potatoes and squeeze out the juice. Drink half a glass twice a day.
- Kefir and buckwheat . Grind the buckwheat in a coffee grinder and pour in 1 tbsp in the evening. such flour with 1 glass of kefir. Drink in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Lingonberry tincture . Pour 500 ml of water over lingonberry leaves (2 tablespoons of raw material) and boil for 20 minutes. Drink 250 ml of the product twice a day.
Diagnostics
The disease can be detected by:
- a careful initial examination of the patient with a study of the patient’s medical history and complaints;
- Trichoscopy - examination of hair and scalp using a trichoscope for a detailed examination of areas of baldness;
- clinical and biochemical blood tests, clarification of glucose and insulin levels;
- blood test to study hormonal levels;
- studies for helminthiasis;
- blood serum analysis for trace element content.
Depending on the causes of the disease, it is possible to involve specialized specialists in the diagnosis: an endocrinologist, psychotherapist, gynecologist or gastroenterologist.
List of sources
- Gubergrits N. B., Linevskaya K. Yu., Belyaeva N. V. Differential diagnosis in gastroenterology. From symptom and syndrome to diagnosis and treatment: practical work. hands - Kyiv: Trush E. N. [ed.], 2021. - 623 p.
- Danilov M.V., Fedorov V.D. Pancreatic surgery. Guide for doctors. M.:b Medicine, 1995. 312 p.
- Zakharova O.P., Egorov V.I., Karmazanovsky G.G. Surgical treatment of pancreatic tumors: computed tomographic criteria for resectability. Annals of surgical hepatology. 2011. 16. No. 1. pp. 84-91.
- Zimmerman Ya.S. Chronic pancreatitis // Bulletin of the Pancreatology Club. - 2009. No. 1. - P. 38-47.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The exact causes of the development of the disease have not been fully established. Doctors say that adenomyosis occurs against the background of hormonal disorders, but there are other predisposing factors that can trigger the pathological process of endometrial growth. These include:
- any traumatic manipulations in the uterine cavity that violate the so-called protective zone between the endometrium and myometrium;
- early or late sexual life;
- complicated childbirth;
- long-term and uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- physical inactivity, obesity;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- abortions;
- use of an intrauterine device.
Read also
Diabetes mellitus, type 2
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, which results from impaired insulin secretion, insulin action, or both...
Read more
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a progressive metabolic disease of the skeletal bones, which results in a decrease in bone density and disruption of its internal structure. The result of osteoporosis is...
More details
Symptomatic arterial hypertension
Arterial hypertension is a very common disease of the human cardiovascular system. According to statistics, 20-30% of the population suffers from arterial hypertension, aged 60 years and above...
More details
Hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is a persistent increase in the level of the hormone prolactin in the blood. Hyperprolactinemia syndrome is a complex of symptoms that occur against the background of increased prolactin levels, the most characteristic...
More details
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a “pandemic of the 21st century.” The prevalence of metabolic syndrome is 20–40%. In the Russian Federation, 40% of the population have 2 components of metabolic syndrome, 11% –...
More details