Physiotherapist
Biryukova
Svetlana Alexandrovna
Experience 27 years
Physiotherapist of the highest qualification category
Make an appointment
The inflammatory process that develops in the tissues of the internal venous membranes and is accompanied by partial or complete thrombosis of damaged areas of blood vessels is called thrombophlebitis. As a rule, the disease first affects the veins of the lower extremities that run close to the skin (superficial). If left untreated, the process gradually spreads to the deep venous vessels. If in the acute period the patient does not receive proper treatment, the inflammation becomes chronic with remissions and relapses, but often chronicity occurs even with timely therapy.
Features and reasons for development
Under certain conditions, the inflammatory process affects the walls of blood vessels of any location, but in the vast majority of cases the disease affects the veins of the lower extremities, and primarily the superficial vessels deformed by varicose veins. Deep veins, along with superficial ones, become inflamed in approximately 10% of patients. The clinical picture is formed under the influence of a number of factors: an increase in the blood clotting index under the influence of changes in its composition, blood flow speed, the presence of deformations or damage to the vascular wall, etc.
The causes of thrombophlebitis include:
- genetic predisposition factor;
- varicose veins, which leads to stagnation of blood in the veins of the legs;
- wound or injury of the lower limb, accompanied by a purulent process;
- postoperative recovery period (including after medical abortion);
- postpartum period;
- long stay of the catheter in the vein;
- bed rest or immobility of the patient;
- dehydration of the body;
- age after 40 years.
The development of the inflammatory process is promoted by any disease or condition associated with decreased immunity.
Thrombophlebitis - symptoms and treatment
Therapeutic and preventive measures for thrombophlebitis are complex and can be conservative and surgical. The main objectives are to maximize the elimination of risk factors, reduce and alleviate local symptoms in acute thrombophlebitis, prevent the spread of thrombophlebitis to the deep vein network and prevent venous thromboembolic complications.
Surgical treatment
Not long ago, the gold standard for the treatment of ascending thrombophlebitis was crossectomy (Troyanov-Trendelenburg operation), but practice results have shown that this method of surgical intervention is the most traumatic and life-threatening for patients.
When the process goes beyond the sapheno-femoral or sapheno-popliteal anastomosis, thrombectomy is performed from the main veins. Surgery can be performed using regional anesthesia or intubation endotracheal anesthesia. The preference for thrombectomy method depends on the level of location of the proximal part of the thrombus.
In case of perforator thrombosis, thrombectomy from the perforator vein is performed. In case of embolic thrombosis of the femoropopliteal segment, ligation of the superficial femoral vein (SFE) is indicated.
In case of embolic-dangerous iliocaval thrombosis, plication of the inferior vena cava is performed.
The figure shows the implantation of a vena cava filter into the inferior vena cava, the indication for which is embolic iliocaval thrombosis.
Laser treatment
According to the latest revised clinical guidelines, endovenous laser coagulation (EVLC) is a low-traumatic and safe technique for ascending thrombophlebitis. This method can be used to operate on any category of patients. As a rule, surgery is performed under local tumescent anesthesia.
Conservative treatment
Today, for existing indications, the most effective method will be anticoagulant therapy. In medical practice, it is customary to distinguish between direct-acting anticoagulants, which help reduce thrombin activity in the blood, and indirect-acting anticoagulants, which prevent the formation of prothrombin in the liver. Low molecular weight heparins belong to the group of direct-acting anticoagulants. These include medications such as Enoxaparin sodium (Anfibra, Clexane, Hemapaxan, Lovenox), Dalteparin (Fragmina) or Tinzaparin, which must be administered subcutaneously 1-2 times during the day. The use of low molecular weight heparins results in maximum effectiveness and minimal side effects. Indirect anticoagulants are Warfarin derivatives, which require special caution and a high degree of laboratory control (INR). Currently, the greatest interest is in drugs that do not require laboratory monitoring of INR and with lower risks of complications, for example, such as Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) or Pradaxa.
In addition, the patient is prescribed long-term wearing of compression hosiery and auxiliary pharmacotherapy, phlebotonic drugs (Detralex; Venarus; Phlebodia 600), etc. It is also advisable to prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and local treatment.
Treatment of thrombophlebitis of superficial veins and acute thrombophlebitis
Recently, international consensus has accepted the equality between the terms “acute thrombophlebitis” and “thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins”, which determines the commonality of pathogenetic mechanisms, complications and treatment tactics.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Intermittent pneumocompression is a physiotherapeutic method of massaging tissue using special multi-chamber cuffs with different operating pressures. This technique has excellent lymphatic drainage properties, helps reduce swelling and can be used for thrombophlebitis of the veins of the lower extremities.
Electromyostimulation using the VENOPLUS device - this patented technique consists in the fact that electromyostimulation leads to muscle contraction and activation of the muscle-venous pump. It can also be used for thrombophlebitis of the veins of the lower extremities.
Gymnastics for thrombophlebitis
This disease poses a threat to life if a blood clot breaks off, so gymnastics is contraindicated.
Leeches for thrombophlebitis
Currently, the first line of therapy is the use of low molecular weight heparins. Hirudotherapy has a much lower effect.
Ointments for thrombophlebitis
The use of ointments is possible in the complex treatment of thrombophlebitis. NSAIDs are used in the form of ointments to relieve pain. Such ointments include Fastum Gel, diclofenac, ortofen and others. It is also possible to use ointments with heparin (Lioton, hepatrombin).
Nutrition for thrombophlebitis
Nutrition does not affect the course of thrombophlebitis. It is worth adjusting the diet only if the disease occurs against the background of obesity.
Can folk remedies help?
Decoctions, tinctures and compresses have no proven effectiveness and therefore cannot be recommended for the treatment of thrombophlebitis. Thrombophlebitis is a disease that can threaten the patient’s life and therefore requires immediate and adequate treatment.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation usually takes place at home. Compliance with any special regime is not required. If the patient smokes, he should stop smoking if possible.
How to recognize the disease
Symptoms of thrombophlebitis are pronounced if the disease occurs in an acute form and is localized in the superficial veins. It is easy to recognize by:
- acute pain concentrated along the inflamed saphenous vein;
- redness, swelling, increased temperature in the area of the inflamed area of the vessel;
- swelling of the vein, which is clearly visible on the surface of the skin;
- the presence of seals in some parts of the vein in places of thrombosis;
- a general increase in body temperature, but not higher than 37.5-38°C;
- swelling of the soft tissues of the limb.
The elevated temperature lasts for several days, then subsides regardless of the condition of the limb, and other pronounced signs of thrombophlebitis gradually disappear. Often, patients do not consult a doctor, limiting themselves to applying a soothing ointment to the affected area. However, refusal of qualified assistance is extremely dangerous, since if a blood clot breaks off, severe complications can develop in a very short time, from ischemic or gangrenous thrombophlebitis to pulmonary embolism. Under no circumstances should you massage the affected area of the vein, as in this case the risk of blood clot rupture increases significantly.
The inflammatory process that develops in the deep veins of the limb is especially dangerous. Most often, it is asymptomatic or with minor general signs of malaise, by which it is impossible to recognize and localize the disease. The risk of thrombosis increases if the superficial veins are affected by varicose veins, accompanied by insufficient function of the valves of the perforating veins that connect the superficial and deep vessels.
Are you experiencing symptoms of thrombophlebitis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Treatment of thrombophlebitis with folk remedies
Thrombophlebitis is a disease caused by a complication of varicose veins in the legs. Treatment of thrombophlebitis with folk remedies is the same as for varicose veins of the legs.
Before describing treatment methods, I would like to highlight the main causes of the disease.
Reasons for appearance:
- Injuries, bruises of the lower extremities;
- Vein diseases;
- Increased blood clotting;
- Infectious diseases;
- Taking hormonal drugs;
- Blood diseases;
- Complications after surgical operations.
To prevent thrombophlebitis, it is recommended to add figs, cranberries, sea buckthorn and blueberries to the diet. Citric acid helps slow blood clotting, and lemon oil reduces high blood pressure.
Tinctures from medicinal plants
When the veins begin to become clogged, it is advised to take foot baths and drink decoctions of medicinal plants.
- In case of inflammation of the veins, when a blood clot forms, it is advised to take mouse pea grass. To do this, brew a tablespoon of dry herb in boiling water (500 ml) and leave for half an hour. Take 100 ml before meals three times a day.
- For thrombosis on the legs, brew white sweet clover herb; to do this, pour 1 tablespoon of the herb into 500 ml of boiling water and leave overnight, after wrapping it up. Strain in the morning. It is necessary to take half a glass orally 3 times a day. The main condition is to perform the procedure under the supervision of doctors. You can brew the roots of white clover; to do this, cook 1 spoon of crushed roots to a boil in a small saucepan with water, then keep on low heat for 20-25 minutes. Leave for about 40 minutes. Take one tablespoon orally 4 times a day before meals.
- If thrombophlebitis appears after pregnancy and childbirth, an infusion of horse chestnut and vodka is recommended. 20 g of horse chestnut seeds are infused in 200 ml of vodka for about a week. The solution must be shaken every day. Then strain thoroughly and consume 15 drops before meals, 4 times a day.
- Another popular infusion for thrombophlebitis is a tincture of nettle leaves. A tablespoon of nettle is infused in a glass of boiling water for about an hour. Then you need to strain and consume two tablespoons before meals, 4 times a day.
- For thrombosis of the deep veins of the legs, take an infusion of honey and onion juice (blue will not work). A glass of onion juice is mixed with a glass of honey and left for three days at room temperature, then put in the refrigerator for a week. Take one spoon before meals, three times a day.
- In the treatment of thrombophlebitis, the healing properties of infusion with mumiyo are known. Dissolve 7g of mumiyo in 500 ml of warm water and consume a spoonful for a week on an empty stomach. Repeat the course in a week. Usually three courses of such treatment are carried out.
Compresses and applications
- When thrombophlebitis develops, compresses from a decoction of bodyaga are applied to the affected areas. Brew a couple of spoons of bodyaga in 500 ml of boiling water, leave for several hours, then apply to the sore spot for an hour. You can apply the compress in the morning and evening.
- Another folk remedy for the treatment of thrombophlebitis in the form of a compress involves a mixture of yogurt and wormwood. The resulting mass is applied to a bandage and applied to the diseased veins. It is better to wrap the leg with film on top. Session is 40 minutes.
- Sea salt is also popular among people. Twice a day, apply a compress of sea salt to the blood clot.
Trituration
- Place acacia flowers in a 3-liter jar, leave a space at the top near the throat, add vodka there. It is necessary to insist for at least a week, in a dark place. Rub on affected areas morning and evening.
- Fill the jar halfway with Kalanchoe leaves, add water up to the throat. Leave in the dark for several weeks. Once ready, strain and rub on sore feet morning and evening.
- Horse chestnut fruits 10 pcs. pour 0.5 liters of vodka. Leave for 14 days. Rub the affected veins twice a day.
- For applications, you can combine sage, St. John's wort and chamomile. Brew about 1 spoon of the mixture per glass of water in boiling water. Leave for a couple of hours. Apply gauze soaked in the solution to the sore leg, wrapping it in film.
Therapeutic baths
- Place branches of willow, chestnut, and oak in a container and fill with water, put on gas and after boiling, cook for 30 minutes. Then add chamomile and St. John's wort. Leave for 12 hours. Pour the broth into the bath and add a couple of pieces of bread. Take a bath every evening for 35 minutes, at a temperature of 35-40 degrees.
- After work, you can make foot baths using dried cucumber tincture.
In advanced stages, when trophic ulcers are present, the following is recommended:
- Before cleaning the ulcer, crushed horsetail powder is sprinkled on the wound, covering it with a cabbage leaf on top.
- After cleaning and treating the wound, the affected area is lubricated with sea buckthorn oil.
- For healing, yarrow juice can also be applied to the wound.
Diagnostic methods
During the initial consultation, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the affected limb and collects an anamnesis, however, many important data necessary for diagnosing thrombophlebitis can only be determined with the help of instrumental studies:
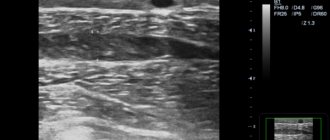
- Ultrasound of superficial vessels to determine the extent and location of blood clots;
- Doppler ultrasound to identify the characteristics of blood flow in the vessels of the limb;
- rheovasography, which helps to identify disturbances in the blood supply to tissues and organs;
- Ultrasound duplex scanning of veins is the most informative study that allows you to determine all important diagnostic indicators - the speed and direction of blood flow, the condition of the venous wall, the level of preservation of the vein lumen, etc.
In addition, the doctor prescribes general laboratory tests to clarify the patient’s general health, and a coagulogram to determine blood clotting indicators and the tendency to form blood clots. Additional studies may be prescribed according to indications.
Thrombosis
Venous thrombosis of the lower extremities is a more dangerous condition than thrombophlebitis. With thrombosis, blood clots (thrombi) appear in the deep veins, which, under certain conditions, can enter the pulmonary artery and block (pulmonary embolism).
Causes of thrombosis:
- increased blood clotting;
- injury to the inner wall of blood vessels;
- slow blood flow as a result of a person sitting or lying for a long time;
- pregnancy.
Symptoms of thrombosis:
- swelling of the affected limb as a result of slowed blood flow;
- blueness of the skin of the leg;
- darkening of the skin on the leg, which can even with a minor injury lead to the formation of a trophic ulcer;
- unexpected pain in the leg (due to inflammation in the bloodstream).
But most often, thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities is characterized by the absence of pain in the patient. Depending on which veins are damaged by the clot, your ankle, foot, or thigh may swell. Overnight, while the person rests in a horizontal position, the swelling may disappear.
How to treat
To treat thrombophlebitis, modern medicine uses various methods, from drug therapy to surgical intervention, depending on the severity of the disease and its stage. Most patients are usually prescribed conservative therapy, the goal of which is to stop the inflammatory process and reduce the risk of vascular thrombosis. For this purpose, the doctor prescribes:
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs;
- anticoagulant medications;
- enzyme therapy;
- treatment with phlebotonics;
- local compresses and ointments;
- in the presence of a purulent process - antibiotic therapy.
The patient is prescribed bed rest, but he can be treated at home if there is no risk of complications. Mechanical support of the blood vessels is important: it is necessary to bandage the affected limb with an elastic bandage and/or wear special compression garments. If there is a risk of disease progression and transition to deep veins, surgical removal of the thrombosed vessel is prescribed.
Thrombophlebitis - folk remedies
Thrombophlebitis (from thrombus and phlebitis) is an inflammation of the vein wall with the formation of a blood clot that clogs its lumen. May occur with varicose veins. as a complication after childbirth. operations, infectious diseases (typhoid, etc.).
Thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities develops as a result of damage to the venous walls, previous varicose veins, and local inflammatory process of individual sections of the vascular wall. Clinically, a reddened, sensitive, warm area of skin is identified and a thrombotic vein is felt in the depths.
Treatment of thrombophlebitis . bandage on the affected surface, the patient should lie in bed with the leg raised 15-20 cm; Vishnevsky ointment and warm compresses.
How to prevent further development of the disease
Measures to prevent thrombophlebitis are equally effective both for those who have already suffered from an acute form of the disease and for people who are at risk of developing inflammation of the veins. These include:
- constantly wearing compression hosiery or supporting veins with elastic bandaging;
- proper organization of work and rest;
- moderate physical activity on the legs, providing support for the function of venous valves and preventing the progression of varicose veins;
- following a special diet;
- providing regular unloading for the legs in the form of a lying position with the legs raised above the body.
If these rules are followed, the risk of thrombophlebitis is significantly reduced.
Main risk factors for the development of thrombophlebitis
Among the risk factors for the development of thrombophlebitis are the following:
- varicose veins;
- prolonged immobility of the body during a long trip by plane or car;
- prolonged bed rest (for example, after surgery);
- stroke;
- venous catheterization;
- pregnancy, childbirth, abortion and other gynecological operations;
- hormone therapy;
- blood disorders (for example, increased blood clotting);
- obesity;
- malignant diseases;
- dehydration (including while taking diuretics);
- decreased immunity;
- infectious diseases, etc.
The presence of one or even more than one factor increases the risk of developing thrombophlebitis. Contact a phlebologist!