0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.06.18
3 750
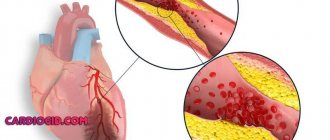
Ischemia
A disabled person is a person with a persistent functional disorder, which can be caused by various diseases or serious injuries and their consequences. A person with disabilities cannot take care of himself for a long time and needs social protection. For example, a person cannot move normally or does not move at all, does not see, and is not able to control his actions.
The procedure for obtaining disability
Many people are interested in whether coronary heart disease (CHD) gives disability. The patient’s condition can only be determined by a special medical examination, usually carried out after surgery, when the patient needs rehabilitation for recovery. There are other indicators of obvious problems of the cardiac and vascular system, which as a result cause IHD.
Statistical data
The commission includes several doctors who are able to assess the current disease, its stage and characteristics of its course with possible complications. Another important aspect is concomitant diseases, which can lead to aggravation of the underlying pathology.
The disability group directly depends on the form of restrictions. For example, when a person cannot move, take physical activity, and also when it is impossible to care for himself. Having found out whether disability is granted, you need to familiarize yourself with other details.
Important! Even if there is one indicator, the patient cannot receive a disability group: this requires several indicators.
Main symptoms
Symptoms that indicate the severity of the disease may include:
- angina (chest discomfort caused by work or emotions);
- atypical angina, i.e. pain in other places (neck, back, arm);
- shortness of breath on exertion.
If you have been treated, be sure to tell your doctor about any symptoms you experience. Any discomfort and pain should be documented. It's also a good idea to point out that they are interfering with your ability to concentrate or complete your daily tasks.
If there are problems with walking, then this information should also be in the records. Those taking a course of medication are advised to pay attention to how they feel after taking it, as well as any side effects that may occur. These include lethargy, headaches, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, depression, memory loss or blurred vision.
Commission
Only a special expert commission can assign disability for IHD. Initially, the patient will need to express a desire to receive a disability group. Such a decision should be made during the next visit to the doctor who treats the patient and keeps records of his condition. The doctor refers the patient to other specialists.
Cardiac ischemia
The commission must provide documentation confirming the diagnosis. After this, the process of considering the possibility of issuing a disability will be launched. The documentation must contain:
- Doctor's referral.
- Statement from the patient.
- Passport (copy and original).
- A copy of the work record book, certified by a notary.
- Medical history, which is in the outpatient card.
- All extracts from medical institutions where previous treatment was carried out (copies and originals).
- Characteristics from work, university.
- Form N-1 report, if the problem is caused by an industrial injury or characteristics of work activity.
After assigning a certain disability group, a person is given a confirmation certificate, as well as a rehabilitation program, according to which the necessary devices are issued for a full recovery course.
What does IHD lead to?
Benefits are issued by the Social Security Administration, and pensions for disabled people are assigned by the Pension Fund. Benefits depend on the assigned group. At the very beginning, the disability will be temporary; throughout the year you will need to undergo 1-2 re-commissions, depending on the group. Sometimes they give a period of 2 years.
How is disability registered?
Disability is registered with MSEC. To undergo it, the cardiologist gives a referral to the patient, enters the examination results into the medical record, and refers him to other specialized specialists. The most accurate diagnosis is made in a hospital setting. Then the patient comes to the medical commission at the appointed time with the following package of documents:
- referral to the commission;
- passport and its copy;
- medical card;
- a copy of the work book;
- an extract from the medical institution where the patient was treated;
- statement.
Typically, cardiovascular diseases are grounds for assigning temporary disability. For group 3, re-examination is carried out every six months, for groups 2 and 1 - once a year. If a child is given a group, then a second commission is appointed depending on the state of health and the severity of the disease. During the MSEC, a person may be refused to extend his disability.
Note: if the patient does not agree with the decision of the MSEC, then he has the right to appeal it through an independent examination.
If the results do not match, you can file a lawsuit to resolve the dispute. Heart disease is not always a reason for disability. A medical examination considers individual cases based on the nature of the disease, its severity, and the presence of circulatory disorders that affect internal organs and systems.
Recommission
Recommission for disabled children depends on the nature of the illness, and pensioners, as well as patients who have irreversible processes, are given disability without a period. In case of recommission, you need to prepare:
- Certificate about the previously assigned group.
- Rehabilitation program.
Disability is prolonged if there are no positive results from the rehabilitation course. The extension depends on the general condition of the patient, the course of the disease, complications, as well as other factors. The patient is sometimes given a refusal, after which disagreement can be certified. To do this, an application is drawn up and sent for medical and social examination. Over the course of a month, ITU employees carry out re-examination. Additionally, the patient can make an independent examination, in which members of the commission do not participate. After this there will be a court whose decision cannot be appealed.
Damage to the coronary arteries
Disability due to ischemic heart disease
Patients with coronary heart disease cannot be involved in certain jobs:
- Work that requires strong physical exertion.
- Activities related to machine tools and other mechanisms.
- Work that may be dangerous for other people if the patient suddenly experiences a morbid crisis and is unable to continue working.
- Extreme work, activity at heights.
- Working with harmful substances that negatively affect human health and can cause a crisis.
Important! If the patient receives a certain group and can continue to work, it is better to change place so as not to endanger health and not aggravate the disease .
When diagnosed with angina pectoris, patients receive temporary disability:
- For the first functional class (FC 1) it is about 8-10 days.
- In case of angina pectoris FC 2, a disability group is issued, more precisely, exemption from work for a period of 14-21 days.
- FC 3 implies release from work for a period of 28 to 35 days.
- If a person suffers a small-focal heart attack, he is released from work for 60-90 days.
- If the infarction is large-focal, but has no complications, release is given for a period of 90-120 days.
- In the case of a transmural infarction with complications, temporary disability is issued for 150-180 days.
Disability in case of coronary artery
disease In case of coronary heart disease, disability is assigned in the following cases:
- When a patient is diagnosed with stage 3 hypertension.
- There are lesions of various internal organs with irreversible changes.
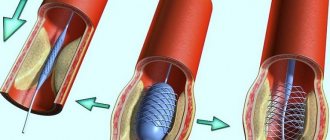
This stage is characterized by frequent crises due to circulatory disorders. Disability is also assigned for angina pectoris if the patient has undergone bypass surgery, after which the blood flow and heart muscles are completely restored.
Disability groups for ischemic heart disease
Angina pectoris is assigned to different disability groups, depending on various factors:
- Third group. They are given to people who cannot engage in work in their profession: they need low-skilled work, as well as some restrictions on functional responsibilities. Due to this, it is possible to achieve a reduction in physical and psycho-emotional stress. This group will include people who have had mild heart attacks, as well as patients with angina pectoris FC 2-3.
- Second group. This includes people who cannot engage in professional activities, since the pathology progresses, and attacks occur more often, due to which the rhythm is greatly disturbed. The second group includes patients who have suffered a large-focal infarction, which resulted in complications, and who have angina pectoris FC 4.
- First group. It can be given to those patients who cannot do any work, because such a disabled person cannot take care of himself and requires care with the help of other people. This group includes patients who have had a transmural infarction, which caused complications, and who have angina pectoris FC 4.
Disability groups for ischemic heart disease
Important! Signs of ischemia appear earlier in men because they drink alcohol more often than women and smoke more.
Heart diseases claiming group
Below we will consider common heart diseases for which the patient can receive benefits from the state.
Cardiac ischemia
With IHD (coronary heart disease), the patient cannot work if the work is combined with heavy physical activity, for example, a loader, an athlete, the patient maintains an electromechanical installation, work is associated with danger to other persons, train drivers, drivers, the patient drives work in extreme conditions.
In these situations, when diagnosing coronary artery disease, the patient is recommended to change his workplace, which will reduce the negative impact on the body and especially on the nervous system. Medical examination, considering the impossibility of working, pays attention to:
Is disability given after a heart attack?
- stage of the disease;
- how serious is the functional impairment of the cardiovascular system;
- stability of the patient's condition;
- the presence of complications before and after surgery;
- the effectiveness of the treatment, both conservative and surgical.
The assignment of disability is influenced by how the impairment affects the patient’s normal life and whether there is a limitation in activity. If he continues to serve himself and there are no restrictions on his life activity, then the group is not given. The likelihood of receiving government benefits increases if, in addition to the main disease, a concomitant disease develops.
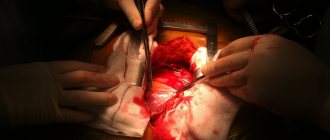
Surgical intervention is not a reason for permanent disability.
Disability groups
For this disease, the following disability groups are assigned. Group 3 can be given for mild heart attack, angina pectoris FC 2-3. The patients retained the ability to work. But there is no opportunity to engage in highly skilled work.
Group 2 is given for large-focal infarction, angina pectoris FC 4. The patient loses the ability to work, his symptoms progress, and his heart rhythm is disturbed. Group 1 is assigned to a complicated heart attack, angina pectoris FC 4. The patient is diagnosed with complete loss of ability to work and there is a loss of self-care skills.
Hypertension
People with hypertension are given disability if a complicated form of the disease is diagnosed. Benefits are provided for frequent crises that disrupt cerebral circulation and affect internal organs and systems. A medical commission establishes a disability group and recommends a review of working conditions, taking into account anamnestic data that is associated with the number of episodes of increased blood pressure, the course of the disease, determining the presence of complications of hypertension and determining its severity, and assessing working conditions.
In addition, the medical examination takes into account the following factors when confirming the fact of incapacity:
- the nature of hypertension, how quickly the disease progresses;
- patient's age;
- degree and stage of the violation;
- the presence of visceral organ structures, their severity;
- presence of concomitant diseases.
Determination of disability depends on the severity of the pathology
When asked whether they give disability for hypertension, doctors say that usually patients are assigned to the third group, which requires changes in working conditions. Patients are diagnosed with stage 2 hypertension with asymptomatic damage to internal organs. In case of first degree hypertension, which is accompanied by periodic increases in blood pressure and the absence of damage to internal organs, the group is not assigned. For hypertension of the second or third degree, MSEC considers the possibility of granting disability.
UPS
In case of severe congenital heart defect, the child is given a disability. Most often, this benefit is given for the following congenital anomalies:
- mitral disease, expressed by abnormal formation of the mitral valve. These pathologies include mitral insufficiency, mitral stenosis;
- abnormal functioning of the arterial valve, for example, aortic stenosis;
- The most common heart disability is the Tetralogy of Fallot, which is considered the most complex. The child definitely undergoes surgery, which is not a 100% guarantee of cure.
After the diagnosis is established, the medical commission takes into account the consequences of the disease and the severity of the disturbance in the functioning of the body. MSEC takes into account the following signs that are the basis for recognizing a child as disabled: impaired functioning of the body, limited life activity, which manifests itself in the difficulty of movement, impaired communication, self-care, orientation, and the need for social protection.
After assessing all the signs that give an idea of the patient’s condition as a whole, the commission members determine the degree of impairment and limitation of his life activity, on the basis of which the question of which group to give disability to the small patient is decided.
Arrhythmia
In case of arrhythmia, the main aspects of obtaining disability are the following factors: the severity of the heart rhythm disorder, contraindications of working conditions, the nature of the therapy: conservative or surgical. The examination of the patient is aimed at determining the severity of cardiac arrhythmias.
For this purpose, the duration of the attack, the frequency of attacks, the state of blood circulation, identification of complications and risk possibilities are assessed. The patient is assigned the second or first group in the presence of diseases such as heart failure, syncope, thromboembolism, and its complications.
After CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting)
After surgery for coronary artery bypass grafting, disability is not always assigned. A small proportion of patients who have undergone this operation can count on government benefits. The medical commission takes into account the following aspects:
- age characteristics of the patient;
- condition of the heart muscle before surgery;
- presence of concomitant chronic diseases;
- whether there is a risk of a heart attack;
- general condition of the patient before and after surgery;
- deterioration of memory and thinking.
Usually, after interventions, patients are given group 3 disability from 6 months to a year. Next comes re-examination. If the clinical picture does not improve, then the group is reassigned or a second group is given.
More details about high blood pressure groups
Hypertension is a problem of modern man associated with the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels. The pathology may be an independent disease. Initially it is caused by periodic crises. In severe form, high blood pressure is constantly observed, which leads to stroke, heart attack and other diseases, possibly with death.
Disability due to coronary artery disease and hypertension is due to a significant decrease in performance. All patients must be registered, and also periodically undergo examinations, undergo preventive measures and take medications.
Disease in diabetics by class
The disability group for hypertension is assigned depending on the development of the disease, or more precisely on its phase:
- At the first stage, there is no organic damage to the heart muscles. An increase in pressure is not observed all the time, but performance is maintained. Hypertensive patients need to be protected from stress; it is better for them to work during the day. Do not be in places with high noise levels or work with chemicals. If you contact ITU, they can help you find a suitable job.
- In the second stage, a person has constantly high blood pressure, and there are also changes in the muscles of the heart. In addition to the restrictions for the first stage, work at height, work near conveyors and activities with high alertness are additionally prohibited. Such people have their daily working hours reduced and may be assigned disability.
- In the third stage, patients are unable to work. They receive disability, but in some cases work is possible at home. The heart muscle has obvious changes.
The following groups are assigned:
- At stage 2 of the disease, group 3 is given.
- Group 2 is issued for progressive disease, as well as with pathologies of forms 2-3.
- Group 1 is given to those who have stage 3 disease with a progressive nature.
To learn more about the problem of getting disability due to angina, watch the video: