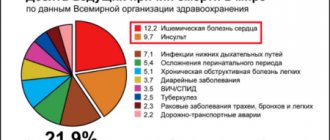
The term “Coronary heart disease” includes a group of diseases:
- myocardial infarction
- atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis
- angina pectoris.
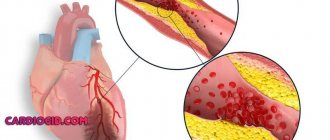
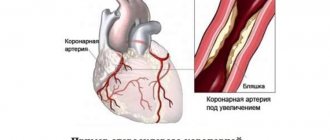
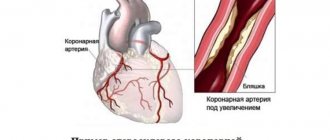
Angina pectoris (synonymous with angina pectoris) is characterized by attacks of sharp chest pain and discomfort in the chest due to lack of blood supply to a certain area of the heart. The severity of the attacks varies, and in rare cases it ends in death. The main cause of the disease is atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries of the heart.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a number of other diseases that may manifest as pain in the heart area should be excluded: spinal osteochondrosis, herpes zoster, diseases of the esophagus and stomach, lung diseases, cardioneurosis, pericarditis.
Angina pectoris: general information
If, as you age, you begin to notice that heart pain occurs after physical activity, immediately consult a cardiologist. There is a high probability that you are developing a heart disease called angina pectoris FC 2. Attacks of pain pass, so many people tend to ignore them. However, the result and direct consequence is myocardial infarction. An even worse option: sudden cardiac arrest. Do not expose yourself to mortal risk - get examined using professional diagnostic equipment at the first symptoms of angina pectoris! Now you have a unique opportunity to undergo a free consultation with a specialist and a set of preparatory examinations when enrolling in a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart:
Promotion
Just until the end of autumn, undergo a free consultation and a set of preparatory examinations* when registering for a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart.**
Send a request
* Check the details of the Promotion by phone. **Has contraindications; consultation with a doctor is required.
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) Cardiac shock wave therapy (SWTS)
Hurry up to apply, the promotion period is limited.
FAQ
How to avoid angina pectoris?
To avoid angina pectoris, it is necessary to prevent the development of atherosclerosis if possible, because in the vast majority of cases it is the cause of angina. As is known, many factors directly influence the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Gender, age, heredity are predisposing factors that cannot be changed, but other factors can be controlled and even prevented:
- high blood pressure
- smoking
- high cholesterol
- overweight
- diabetes
- low physical activity
- stress
Changing these factors is in your hands!
Is it possible to completely recover from angina?
Angina pectoris, as a rule, occurs as a result of damage to the coronary arteries supplying blood to the myocardium by atherosclerosis, and this is a chronic incurable process. However, with a properly selected treatment regimen, it is possible to ensure that long-term remission occurs and angina attacks will not bother you. Also, at present, if necessary, it is possible to install a stent into the narrowed lumen of the vessel to restore blood circulation, or MCS/CABG surgery is a surgical intervention that restores the blood flow of the heart below the site of the narrowing of the vessel. In this surgical procedure, another path for blood flow is created around the narrowing site to the part of the heart that is not supplied with blood.
Where does it hurt during an angina attack?
Characteristic of angina is paroxysmal pain behind the sternum, in the center of the chest. The pain is of a compressive, pressing nature, more often associated with physical or psycho-emotional stress and goes away when it stops. The pain may radiate to the left arm, shoulder blade, lower jaw and collarbone. If nitrates are used, the effect on angina is not delayed, it develops immediately, within 1-2 minutes.
Are there ways to cope with an angina attack without medications?
Since many people experience angina attacks during physical activity, sometimes simply stopping the activity (walking, etc.) and resting can lead to the cessation of pain. However, people suffering from angina pectoris should always have nitroglycerin or nitrospray with them in order to relieve an attack of pain within one to two minutes. You should not delay the time before taking nitroglycerin, since pain is a manifestation of myocardial ischemia (insufficient blood supply), and if it persists, then foci of necrosis may occur in the myocardium (myocardial cells may die). If angina attacks become more frequent, you should urgently consult a cardiologist.
What medications will help with an attack of angina?
An attack of angina must be stopped as soon as possible from the moment of its occurrence, because prolonged ischemia will lead to the development of necrosis, i.e. myocardial infarction. If an attack occurs for the first time in your life, call an ambulance. You can take a nitroglycerin tablet on your own or use a nitro spray under the tongue. The effect will occur within 1-2 minutes and does not last long, 10-15 minutes. It is better to take the drug while sitting or lying down, as a short-term decrease in blood pressure, dizziness, headache, tinnitus may occur - these symptoms are safe and are a consequence of the action of nitroglycerin. If pain returns, you can take nitroglycerin again, because it does not accumulate in the body; multiple doses of the drug are possible during the day (up to 6 tablets per day). If your blood pressure is high, you need to lower it to normal levels.
All patients who have suffered an attack of angina pectoris need to have an ECG performed and a decision by a cardiologist on hospitalization.
Why is it necessary to quit smoking? How does smoking worsen angina?
If you smoke and have angina, the best thing you can do to help your heart is to quit smoking!
Studies have shown that the mortality rate in those patients with angina who quit smoking decreased by 2 times compared to those who continued to smoke. Why? Angina is based on a lack of oxygen in the heart muscle, and smoking increases the level of carbon dioxide in the blood, and it displaces oxygen in the blood. This leads to oxygen starvation of the heart muscle. Smoking also increases blood viscosity. Smoking increases the frequency and aggravation of angina attacks and greatly increases the risk of myocardial infarction. Quitting smoking eliminates the adverse effects of nicotine on the coronary arteries, and angina attacks disappear or become less frequent.
Important: replacing cigarettes with cigars and pipe tobacco, switching to cigarettes with less tar and nicotine do not reduce cardiovascular risk!
Contrary to popular belief, abruptly quitting smoking is not harmful; overcoming this bad habit has an undeniable positive effect, regardless of smoking experience.
You need to be prepared for the fact that sometimes depression and irritability occur when quitting smoking, in which case you can seek help from a psychotherapist.
I suffer from angina pectoris, but I dream of losing excess weight. What physical activities are acceptable for people with such problems?
For people suffering from angina, 30–45 minutes of physical activity per day is recommended. The best choice is walking (preferably at a brisk pace) or Nordic walking with ski poles, cycling, swimming. It is important that the exercises do not cause pain, palpitations, or shortness of breath. When practicing swimming or water aerobics, you should remember that cold water can provoke angina attacks, so the water temperature in the pool should be comfortable for you. It is better to do water aerobics under the supervision of a trainer and according to a program specially adapted for people with cardiac problems. In this case, the loads should increase very gradually. However, to lose weight, you need not only physical activity, but also proper nutrition; a nutritionist will help you choose the right menu during your consultation.
Can you have angina if there is no pain?
Unfortunately yes. For example, with diabetes mellitus, diabetic polyneuropathy develops, and the patient may not feel pain, this is the so-called silent ischemia. This condition is dangerous because the patient does not take action in time, and myocardial infarction will develop. In some cases, shortness of breath during exercise can be considered equivalent to pain, so you can suspect the presence of angina pectoris and come for examination to a cardiologist.
What is cardiac angina?
The disease is the most common form of coronary heart disease. Its danger should not be underestimated, because against its background heart failure develops quite quickly. Not far from a heart attack!
The disease develops in men after 55 years, in women - after 64. The reason is a partial (50-70%) narrowing of the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart tissue. The narrowing occurs due to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels and the formation of blood clots. They impede blood circulation, the heart lacks oxygen and nutrients. Especially during times of physical and emotional stress, when the heart muscle works actively and requires more oxygen. The arteries are not able to satisfy her need. That's when you experience attacks of pain.
Distinctive features of angina pectoris FC 3
The most common form of cardiac angina is FC 3, it develops in acute ischemic disease and has several features:
- The attacks are spontaneous and not necessarily caused by physical exertion;
- The patient's mobility is limited, he tries to rest more;
- Pain occurs when climbing one flight of stairs or walking 100-500 meters;
- Patients can control their condition and feel well the approach of attacks.
The main distinguishing feature is that you can always determine the beginning and end of an attack.
Some doctors regard FC 3 as a disability, and in combination with other diseases, for example, tachycardia, the clinical picture worsens. The disease is accompanied not only by pain, but also by associated pathologies.
How does the disease develop?
It is at such moments that common signs of angina pectoris appear in women and men: you feel a lack of air, arrhythmia. At this time, chemical changes occur in the myocardium associated with metabolic disorders, a decrease in the synthesis of substances, and the accumulation of acids. The functions of the myocardium are gradually disrupted, and its metabolism changes.
What causes this disease? There are certain factors:
- high cholesterol levels;
- obesity when consuming excessive amounts of fats and carbohydrates;
- physical inactivity disrupts lipid volume;
- smoking causes oxygen starvation of cells and arterial spasm;
- arterial hypertension causes myocardial tension;
- anemia, intoxication contribute to oxygen starvation;
- diabetes mellitus increases the risk of ischemia;
- increased blood viscosity is a direct risk of blood clots;
- psycho-emotional stress (especially in women) worsens myocardial nutrition.
Stable angina (tension): signs and symptoms
If periodic attacks that occur as a result of exercise last more than 1 month, doctors diagnose “stable angina.” The pain is relieved after taking nitroglycerin.
Depending on how strong the load can cause an attack in the patient, functional classes of the disease are distinguished.
- Angina pectoris FC 1 is characterized by good tolerability, and signs of angina in men and women are noticeable only with excessive stress.
- Angina pectoris FC 2 is manifested by some limitation in normal activities: an attack begins when walking more than 500 m, climbing to the 1st floor, or emotional excitement. With coronary artery disease and angina pectoris FC 2, the first hours after waking up are difficult to bear. Cold weather also has a negative effect.
- Angina pectoris FC 3 is already a serious limitation of normal physical and emotional activity. Obvious signs appear during normal walking at a distance of 150-200 m on level ground, or climbing one floor. Also, angina pectoris FC 3 develops due to anxiety.
- Stable angina pectoris FC 4 occurs after minimal exertion. The patient is unable to perform simple physical activities. This class closely borders on resting angina, i.e. one that is not associated with loads.
This classification allows the doctor to act more accurately when prescribing medications and treatments.
First aid for a seizure
Angina pectoris is a chronic disease. Therefore, a complete cure is not always possible and only through surgical intervention.
But first of all, the patient and his immediate environment need to learn how to provide first aid during attacks.
Nitroglycerin and drugs based on it are the main means for stopping a crisis. At the first symptoms, the patient needs to put one tablet under the tongue and dissolve it. If the attack is severe, you can give it twice. It is better if the oral cavity is sufficiently moist. The maximum dose, 5 tablets, is taken in extremely severe cases when medical help is not expected.
You can also use a spray instead of tablets. The results of the action of nitroglycerin can be seen within a couple of minutes.
- IHD, exertional angina: diagnosis and treatment
Sometimes they try to stop the attack with validol. This is a grave mistake, since this medicine not only does not help, but can cause serious harm to health.
But those around you can use simple ways to ease the crisis. To do this, it is necessary to stabilize the patient’s condition as much as possible, both physically and morally:
- the person must be allowed to stand for a while and catch his breath if the attack was provoked by intense physical activity;
- if the cause is stress, the patient needs to be reassured;
- it is important to provide the person with a sitting or semi-sitting position, as well as an influx of fresh oxygen;
- the body should be freed from any oppressive objects, including belts, collars, and excess outerwear;
- You can place heating pads with warm water on your feet.
Angina at rest: signs and symptoms
It is characterized by the manifestation of characteristic symptoms in a calm state - at night and especially in the morning after waking up. Typically, angina at rest is diagnosed using 24-hour monitoring. Most often, attacks are caused by increased blood pressure and psycho-emotional stress. Unfortunately, any troubles at work or family quarrel can provoke an attack. And sometimes it is enough to change the position of the body.
This type includes vasospastic angina, the cause of which is a sudden spasm of the coronary vessels. And also post-infarction - manifesting itself 10-14 days after the heart attack.
Unstable angina: signs and symptoms
Unlike stable angina, this type of disease changes its behavior, so it is important to constantly be under medical supervision in the first two months after the first attack. Obvious symptoms of unstable angina: changing frequency, duration, intensity of attacks. They can also start at night.
In turn, unstable angina is divided into:
- into classes depending on the nature and severity (initial, subacute and acute stages);
- into groups according to the conditions of occurrence (primary, secondary, post-infarction);
- into groups during therapy (the disease develops during procedures, medication, intensive treatment).
Predictions and prevention
The consequences of primary angina pectoris are unpredictable, and in the case of stable angina, it can be myocardial infarction, multi-vessel damage to the coronary arteries, cardiosclerosis, persistent narrowing of the main trunk of the coronary artery. Three percent of patients experience death.
The main methods of prevention:
- weight loss;
- to give up smoking;
- balanced diet;
- relief from arterial hypertension;
- preventive use of prescribed medications.
People suffering from exertional angina should definitely contact a cardiac surgeon, who will decide on the need for surgical intervention.
Symptoms of angina in women and men
Pain
Most patients report the following symptoms of an angina attack. First of all, cutting, pressing pain in the chest. Many people complain that their heart “burns” or their throat “tightens.” At the same time, you instinctively want to press your hand or fist to your chest. Often the pain migrates to the left shoulder, neck, arm, and shoulder blade. It may grow or disappear suddenly. Symptoms clearly and distinctly appear during exercise, when the patient is diagnosed with IHD angina pectoris FC 2.
Pain can occur after physical exertion, stress, high blood pressure, or overeating. At night - due to stuffiness or low air temperature. Often the attack is accompanied by arrhythmia.
External symptoms and signs of angina pectoris
It is quite simple to identify an attack by its external manifestations. Pay attention to the following signs of angina: the person turns pale, sweat appears on the forehead, his face expresses suffering; fingers lose sensitivity, hands become cold; the patient breathes intermittently and rarely; the onset of an attack is accompanied by a rapid pulse.
Treatment
Therapy begins with the elimination of all provoking factors that can affect the condition of a person suffering from the pathology. The attacks are controlled by taking nitroglycerin. After making a diagnosis, the cardiologist can prescribe the patient long-acting nitrates, antiplatelet agents, calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers.
The persistence of symptoms during conservative treatment becomes a reason to refer a child or adult for surgery. During the intervention, surgeons perform stenting of the coronary arteries and perform endovascular angioplasty. Clinical recommendations provide for the possibility of coronary artery bypass grafting against the background of exertional angina. The effectiveness of surgical treatment is 90-95%.
What can the disease be confused with?
As for diseases not related to the cardiovascular system, based on the symptoms and signs, angina pectoris can be mistaken for:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- gastrointestinal diseases (diaphragmatic hiatal hernia);
- pleurisy, pulmonary embolism;
- pinched nerves.
Usually this disease is confused with the onset of myocardial infarction. The signs are really very similar. The main difference is that an attack of angina is relieved by taking nitroglycerin. In case of a heart attack, the medicine does not work or relieves pain only slightly and temporarily.
Where can I get diagnosed and treated?
Rest assured that your heart is not in danger! If the first symptoms and signs of angina appear, consult a qualified healthcare provider. Cardiologists at the CBCP Center for Circulatory Pathology are ready to help you. The clinic will offer professional consultation and modern types of diagnostics, through which the doctor will receive objective, detailed and accurate information about the disease.
If you discover serious violations, do not despair! The level of medicine at CBCP makes it possible to effectively treat complex cardiovascular diseases using medicinal and non-surgical methods.
Why does angina pectoris FC 3 develop?
The main reason for the progression of cardiac diseases associated with a lack of oxygen in the myocardium is atherosclerotic plaques that appear due to elevated cholesterol levels in the blood. They clog blood vessels, preventing blood from circulating normally. Several factors can provoke atherosclerosis:
- Increased blood pressure - the walls of blood vessels become thinner and more susceptible to damage, which simplifies the formation of plaques;
- Male gender is another risk factor. If women have the hormone estrogen in their blood, which helps eliminate cholesterol, then in men this harmful substance accumulates in the body;
- Poor nutrition is the main reason. Patients whose heart condition requires diagnosis and treatment usually abuse fatty, smoked, and fried foods. They do not watch what they eat, may be overweight, and constantly overeat;
- Cardiovascular diseases are one of the provocateurs of attacks and are often hereditary;
- Insufficient level of physical activity;
- Increased heart rate – when the heart rate increases, the body requires more oxygen. An attack can be triggered by playing sports, emotional shock, and even a regular walk at a slow pace.
However, it is not enough for the patient to remove physical stress - the pain will continue despite the reduction in stress. In the most severe cases, when an attack occurs at rest, and functional class 3 changes to FC 4, surgical intervention is required.