Symptoms and signs
The severity of clinical manifestations directly depends on the degree of proliferation of connective tissue in the myocardium and the percentage of damaged cardiomyocytes. As a result of a decrease in the number of functioning cells, the ability of the heart muscle to pump blood is impaired, which leads to its stagnation in the systemic or pulmonary circulation. If the left side of the heart is affected, congestion occurs in the lungs, which causes shortness of breath (difficulty breathing), which worsens with physical exertion.
Lack of air is especially common at night, which is caused by the horizontal position of the body. The patient is forced to take the “orthopneic” position (sitting on the bed, leaning widely on it with his hands).
When the right side of the heart is damaged, blood stagnates in the systemic circulation. There is coldness and a feeling of chilliness in the arms and legs, heaviness and aching pain in the right hypochondrium, swelling mainly in the lower third of the legs.
Due to heart rhythm disturbances, attacks of dizziness, lightheadedness, and darkening of the eyes appear. With more severe arrhythmias, a person may lose consciousness.
Sanatoriums treating diseases of the cardiovascular system:
Abkhazia: health resorts
Gagra
Amra, Sana Greater Yalta: health resorts
Gaspra
Motherland
Gurzuf
Ai-Danil, Gurzufsky
Livadia
Livadia
Miskhor
Ai-Petri
Foros
Mellas
Oreanda
Lower Oreanda
Yalta
Eagle's Nest, named after Kirov, Krasnodar region: health resorts
Sochi
Rus', Odyssey, Sochi, Boarding house Spring, Black Sea region, Boarding house Harmony, Oktyabrsky, OK Dagomys, Magadan, Golden Ear, Progress, Green Grove, KSKK Aqualoo, Belarus, Metallurg, Cape Vidny, Zapolyarye, Boarding house Orbita-1, Moneron, LOK Gorny air, named after Frunze, SKK Knowledge, Boarding house Burgas, Boarding house Grenada Big Alushta: health resorts
Alushta
Kyiv, Slavutich Krasnodar region: health resorts
Sochi
Stavropol region, Boarding house Fregat, Turquoise, Boarding house Neva, Izvestia, Boarding house Eden, USSR
Anapa
Boarding house Ural, Aquamarine, Ancient Anapa, Ryabinushka, Boarding house Niva, DiLuch, Mechta
Gelendzhik
LOK Solnechnaya, Krasnaya talka, Blue Dal, Druzhba, Sunny Beach, Arkhipo-Osipovka, LOK Horizon
Tuapse
OK Prometheus, Belaya Rus, Zorka Western Crimea: health resorts
Evpatoria
Pobeda, Primorye
Zaozernoe
OLC Northern
Sandy
Chernomorets
Saki
Northern Lights Belarus: health resorts
Minsk Region
Sosny, Priozerny, Yunost, Belaya Rus, Sputnik, Krinitsa, Sosnovy Bor, Berezka, Narochanka (former TOK Naroch), Zhuravushka, Narochansky Coast, Isloch, Zeleny Bor, Naroch, Volma, Podelniki, Rassvet, -preventorium Sputnik, Praleska, Children's sanatorium Solnyshko, Children's sanatorium Nalibokskaya Pushcha, Children's sanatorium Sluch
Brest region
Ruzhansky, Magistralny, Belaya Vezha, Nadzeya, Chabarok, Alesya, Bug, Berestye
Vitebsk region
Borovoe, Lesnoye, Lepel military sanatorium, Lesnye lakes, Children's sanatorium Rosinka, Lettsy, Zheleznodorozhnik
The Grodno region
Ozerny, Energetik, Svityaz, Praleska, Raduga, Svitanak
Gomel region
Silver Keys, Golden Sands, Chonki, Sosny, Gomel branch of the Belarusian Railways
Mogilev region
Dubrovenka, Children's sanatorium Svisloch KavMinVody: health resorts
Kislovodsk
Plaza, Zarya, Villa Arnest, Solnechny, Tsentrosoyuz, Healing Narzan, Jinal, Krugozor, Valley of Narzans, Caucasus, Moscow, named after Ordzhonikidze, Narzan, named after Kirov, Picket, named after Dimitrov
Essentuki
Victoria, Shakhtar, Central Union of the Russian Federation, named after Andzhievsky
Pyatigorsk
Gallery Palace, Pyatigorsk Central Military Sanatorium, Rodnik, Dawns of Stavropol, Mashuk, Tarkhany, named after Lermontov, Lesnaya Polyana
Causes
Myocarditis, and, consequently, this type of cardiosclerosis develops due to the following reasons.
- Coxsackie viruses, ECHO, herpes simplex viruses, influenza viruses, Epstein-Barr viruses, cytomegaloviruses.
- Bacteria: staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, mycobacterium tuberculosis, less often - chlamydia, mycoplasma, rickettsia, borrelia, diphtheroids.
- Parasites and fungi: toxoplasma, trichinella, echinococcus, candida, aspergillus.
- Taking medications. Inflammation in the heart muscle can be caused either by the direct toxic effect of medications or by an indirect allergic reaction. Such medications include antibiotics, antituberculosis drugs, antidepressants and antitumor immunosuppressants (cytostatics).
- Autoimmune pathologies: acute rheumatic fever, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis).
The main causes of the development of myocardial cardiosclerosis
Postmyocardial cardiosclerosis is a secondary disease. It is one of the consequences of myocarditis, an inflammatory disease of the heart muscle. Reasons that can lead to myocarditis and, consequently, cardiosclerosis:
- Infection. Damage to Kosaki viruses A and B, influenza, CMV, ECHO, HIV, Epstein-Barr. Bacterial infections. Beta-hemolytic streptococci have a particular affinity for heart tissue. Less commonly, parasitic (trichinosis) and fungal infections (candidiasis) lead to myocarditis.
- Allergy. Damage to the heart muscle often occurs with hypersensitivity to antibiotics, anti-tuberculosis drugs, vaccinations, and sulfonamides. Very rare cases of myocarditis have been recorded after taking Dopegit (a drug to lower blood pressure).
- Toxic damage. Cocaine use, antidepressant abuse. Myocarditis can develop in patients with thyrotoxicosis (due to excess catecholamines).
- Idiopathic character. A pathology caused by an unknown cause, but having all the signs of myocarditis.
The combination of several factors at once (for example, infection with beta-hemolytic streptococcus against the background of thyrotoxicosis) can lead to an increase in the area of myocardial death and, consequently, greater scarring.
The mechanism of pathology development
The pathogenesis (mechanism of development) of cardiosclerosis is as follows: after the resolution of acute inflammatory processes in the myocardium, so-called fibroblast growth factors are released from the destroyed cells. They stimulate the production of the main protein of connective tissue - collagen.
Large quantities of it form fibers that gradually replace normally functioning areas of the heart muscle. As a result, the pumping function of the myocardium deteriorates, and various rhythm disturbances occur.
However, this scenario does not always occur. Most people recover completely from myocarditis without significant residual effects. Why some patients develop cardiosclerosis and others do not is still a mystery. This may depend on the amount of cellular damage, the state of the immune system and many other factors.
Prevention of cardiosclerosis
To prevent cardiosclerosis, as well as to undergo a course of rehabilitation after a myocardial infarction, sanatorium-resort institutions offer special wellness programs aimed at gradually restoring the functions of the heart muscle.
It is important to remember that the sanatorium accepts patients with a non-acute stage of the disease, with the disease at the stage of attenuation or remission.
For cardiosclerosis, a gentle regimen with dosed loads is prescribed so that scarring occurs correctly, without the formation of aneurysms; as well as a special diet in which the amount of animal fats is minimized, the amount of table salt is reduced and daily fluid intake is dosed.
Procedures used for cardiosclerosis:
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- dry carbon dioxide baths;
- therapeutic walking;
- baths (radon, iodine-bromine, mineral);
- underwater shower-massage;
- infrared sauna.
Diagnostics: how to suspect and determine
From personal practical experience I can say that the main thing is to know how the disease developed. A thorough survey allows you to establish the fact of myocarditis. It may be indicated by the appearance of pain in the heart, a feeling of palpitations, shortness of breath and constant weakness.
A general examination (physical examination) of the patient also plays an important role. In such patients, I usually pay attention to the color of the lips (it may be bluish), swollen veins in the neck, thickening of the terminal phalanges of the fingers (the so-called drumstick sign) and an enlarged liver.
Auscultation of the heart and lungs occupies a special place. The patient can hear noises, dull tones, irregular rhythm, and moist rales in the lower parts of the lungs. In severe and advanced cases, when there is severe circulatory insufficiency, an auscultatory phenomenon appears - “gallop rhythm”, characterized by the appearance of a third tone between two physiological ones.
After a survey and general examination of the patient, I make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm or exclude it, you need to undergo an additional examination, including the following.
- General and biochemical blood tests - they do not provide enough data to diagnose cardiosclerosis itself, but sometimes they reveal abnormalities that could cause the development of myocarditis.
- Electrocardiography. The ECG shows nonspecific changes: ST segment elevation and negative T wave. Cardiac rhythm and conduction disturbances are often detected in the form of supraventricular and ventricular extrasystoles, atrial fibrillation and flutter, atrioventricular block and bundle branch block.
- Chest X-ray - may reveal enlarged heart borders and signs of pulmonary congestion.
- Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart, ECHO-CG) - allows you to see thickening of the myocardial walls, dilatation (expansion) of the atria and ventricles, areas of impaired muscle contractility.
- Endomyocardial biopsy - according to modern recommendations, the diagnosis of cardiosclerosis is established by histological examination of the myocardium. However, due to the technical complexity, I rarely prescribe this procedure to my patients.
Treatment and its methods
The need for hospitalization depends on the severity of the patient's condition. In most cases, outpatient treatment is sufficient. The use of antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal drugs is pointless, since at the time of the formation of cardiosclerosis the pathogen has already left the body.
The first stage of treatment is to limit physical activity. Professional sports are strictly contraindicated. Aerobic exercise and physical therapy are allowed. I explain to my patients that they should follow a low-salt diet, consuming no more than 2-3 grams per day. This is necessary to prevent fluid stagnation in the body.
The basis of treatment is drug therapy. To slow the progression of heart failure, I use medications from the following pharmacological groups: ACE inhibitors (Perindopril, Ramipril), beta-blockers (Bisoprolol, Nebivalol) and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (Spironolactone). For severe congestion, I prescribe diuretics—loop diuretics (“Furosemide”, “Torasemide”).
Treatment methods for arrhythmias are determined by their type, severity and accompanying symptoms. With atrial fibrillation and flutter, blood clots form in the cavities of the heart, which can migrate and clog a vessel in an organ, such as the brain, thereby causing an ischemic stroke. Therefore, to prevent thrombosis, I use anticoagulants (Warfarin, Dabigatran, Apixaban, Xarelto).
If arrhythmias are accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness and fainting, it is worth considering the option of taking medications that normalize cardiac activity, such as Propafenone, Sotalol. If there is resistance to drug therapy, surgical intervention is performed - radiofrequency ablation. For severe atrioventricular blockade, installation of a pacemaker is indicated.
List of used literature
- Stryuk R.I., Shoikiemova D.U., Borisov I.V.; State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after. A.I. Evdokimov" Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia / Pregnancy as a risk factor for heart rhythm disturbances
- POKROVSKAYA E.M., 2, Ph.D., N.A. VOLOV 2, Ph.D., I.S. VASILYEVA 2, GORDEEV I.G. 1, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, PAVLIKOVA E.P., 2, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor 1 State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “Russian National Research Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Department of Hospital Therapy No. 1, Faculty of Medicine 2, State Budgetary Institution "City Clinical Hospital No. 15 named after. O.M. Filatova "DZ Moscow / NEW OPPORTUNITIES FOR TREATING PATIENTS WITH HEART FAILURE DUE TO POST-INFARCTION CARDIOSCLEROSIS
- Berezin A. E., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Internal Medicine No. 2 of the 1st Medical Faculty of Zaporozhye State Medical University / Combined potassium and magnesium preparations in the treatment of patients with high cardiovascular risk.
Complications: what causes death and in what cases
Adverse consequences are observed in diffuse forms of cardiosclerosis. These include acute heart failure, including pulmonary edema and cardiogenic shock (a sharp decrease in the pumping function of the heart).
With severe rhythm disturbances, sudden cardiac death may occur due to ventricular fibrillation and asystole (complete cardiac arrest). These conditions very often end in death. They occur in approximately 5-10% of cases of post-myocardial cardiosclerosis.
Typology of the disease
Today, two approaches to the classification of cardiosclerosis are proposed. The first relies on the history of the disease and proposes to subdivide it into atherosclerotic and myocardial. The second approach is based on the localization of the disease, depending on which cardiosclerosis can be either diffuse or focal. Let's look at these terms in more detail:
- The atherosclerotic form of the disease got its name in honor of the pathology that causes it - atherosclerosis of the arteries.
- Myocardial cardiosclerosis is a direct consequence of various types of myocarditis.
- The diffuse type of the disease is diagnosed when necrosis affects muscle tissue relatively evenly.
- In focal cardiosclerosis (also known as scar), connective tissue replaces muscle tissue in individual areas of the heart, varying in size.
Consequences of cardiosclerosis
- Aneurysms and heart defects.
- Arrhythmia.
- Thromboembolism.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Chronic heart failure.
Clinical case
A 49-year-old man came to see me with complaints of weakness, increased fatigue, difficulty breathing, and frequent attacks of dizziness.
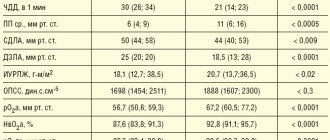
Last night I lost consciousness, which was the reason for visiting the doctor. During the interview, it turned out that six months ago, after a cold, the patient developed chest pain, to which the patient did not attach much importance. Auscultation revealed a weak, irregular heartbeat of 42 beats per minute. The ECG revealed complete atrioventricular block, the ventricular contraction rate was 35-47 per minute. Echo-CG showed thickening of the myocardial walls, zones of hypokinesis (reduced contractility) and a small ejection fraction (45%). I suspected postmyocardial cardiosclerosis. At the medical consultation, it was decided to perform an endomyocardial biopsy. The resulting histological specimen revealed myocardial fibrosis and degenerative cell changes.
The final diagnosis was: “Myocarditis, unspecified. Complications: NYHA class II CHF, complete AV block.” The patient was prescribed medications to treat heart failure and had a permanent pacemaker implanted. After the operation, the patient feels satisfactory, dizziness and shortness of breath are no longer bothersome.
Myocardial cardiosclerosis - is it accepted for military service?
If myocardial cardiosclerosis is diagnosed, whether a teenager with such a pathology is accepted into the army is a completely logical question for a teenager. Before release from service there must be:
- Myocardial cardiosclerosis (ICD-10 code).
- Heart rhythm dysfunction.
- Heart failure 2 FC.
If a conscript has tachycardia, shortness of breath, chest pain, or heart failure is confirmed by instrumental methods, then the presence of points 1 and 2 or 1 and 3 gives the right to receive a ticket B - conditionally fit.
Myocardial cardiosclerosis without heart failure, and with it 1 FC, refers to the pathologies included in ticket B.