COVID-19✓ Safe
In general, blood pressure is the total pressure in the arteries, which varies in different blood vessels: the closer the vessel is to the heart and the wider its diameter, the higher the blood pressure. A standard blood pressure measurement in the arm tells you what pressure is in the brachial artery; normally it is 120/80 millimeters of mercury. The first digit of blood pressure indicates systolic pressure. The second or lower number of blood pressure indicates diastolic pressure.
It often happens that it is the lower indicator that increases (i.e., increased diastolic pressure) while the systolic indicator remains normal, for example: 110/95. Usually people do not worry about this, believing that the main thing is the systolic indicator, however, this is a mistake. This condition is really dangerous, as it can portend a heart attack and sometimes a stroke.
When?
Blood pressure depends on many factors: time of day, a person’s psychological state (pressure increases during stress), taking various stimulants (tea, coffee, amphetamines) or medications that increase or decrease blood pressure.
People sometimes have a “fear of white coats” when measuring blood pressure. A rise in pressure at the time of measurement occurs due to stress, which sometimes occurs when visiting a doctor or when a nurse appears. What causes inaccuracy in blood pressure measurements?
In healthy people, the level of diastolic pressure fluctuates within 65±10 millimeters of mercury.
When there is nowhere lower. Understanding the causes of hypotension
A feeling of “lightheadedness” after a stuffy bus, fatigue after a long night’s sleep, “goosebumps” before the eyes after abruptly getting out of bed... These and other symptoms may indicate a decrease in blood pressure - hypotension. And if numerous studies have been devoted to hypertension and treatment principles have been well developed, then with hypotension not everything is so obvious.
What is it, what causes it, how is it recognized and treated? We are talking about this with our permanent consultant, general practitioner, cardiologist at Clinic Expert Voronezh, Kalinina Angelina Anatolyevna.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, what is hypotension? Is this a diagnosis or a syndrome?
Hypotension is low blood pressure. It can be either just a symptom or a diagnosis.
What does “low blood pressure” mean? This is a condition in which blood pressure numbers are lower than expected for a person in a given situation. And what’s interesting: even if the pressure dropped by 20-30 mmHg. and at the same time remained within the normal range, but the person began to feel worse, then this condition can also be regarded as hypotension.
Read the material on the topic: What should a child’s blood pressure be?
Hypotension can be physiological or pathological. Physiological is a variant of the norm. It may, for example, occur in trained athletes, people living in high mountains or hot climates.
Pathological hypotension. These include essential (or primary) hypotension (hypotonic disease), symptomatic (or secondary) hypotension, as well as idiopathic orthostatic hypotension.
Below normal is:
blood pressure below 100/60 mm Hg. Art. in men and 95/60 mm Hg. Art. among women
according to other data - pressure below 100/60 mmHg. in people under 25 years of age, and below 105/65 mmHg. - over 30 years old
The most common pathological condition is essential hypotension. It is expressed by a steady decrease in blood pressure with characteristic manifestations.
Secondary hypotension is a consequence of another disease or drug use.
— What is low blood pressure? At what numbers can we say that the pressure is below normal?
According to some data, blood pressure is below 100/60 mm Hg. Art. in men and 95/60 mm Hg. Art. among women; according to others - pressure below 100/60 mmHg. in people under 25 years of age, and below 105/65 mmHg. - over 30 years old. Moreover, hypotension is said to occur when both indicators (“upper” and “lower” pressure) or one of them decrease.
— High blood pressure threatens a heart attack or stroke. Why is low blood pressure dangerous?
There is an opinion that with an excessive decrease in blood pressure there is also a risk of developing cardiovascular complications, although studies with the required level of evidence have not been conducted.
With age, hypotension may disappear, giving way to arterial hypertension.
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable. If there are no complaints related to low blood pressure, and the person is adapted to it, then hypotension does not cause much harm to the body.
Read the material on the topic: Spinning until you drop! Why do you get dizzy?
The concern is the progression of the disease, repeated episodes of fainting (and possible falls associated with them), the presence of other concomitant pathologies (coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, etc.), as well as the patient’s advanced age (risk of falls, deterioration of blood supply to the brain).
— At what blood pressure levels should you urgently call a doctor? Where is the lowest limit?
Everything here is individual. Those. pressure that is low for one may be normal for another (especially if we are talking about hypotension). Therefore, it is quite difficult to voice the limit of the lowest norm.
However, if the patient has symptoms indicating the development of a threatening condition (pain in the heart or chest, shortness of breath, arrhythmic pulse, vomiting, convulsions, impaired consciousness), this is a reason to call an ambulance with possible hospitalization.
— What does a person experience with low blood pressure? What are the symptoms of hypotension?
The most common manifestations of hypotension are general weakness, fatigue, headaches, a tendency to dizziness, pre- and fainting states. There may also be irritability and deterioration in performance (which, with essential hypotension, is often noted already in the morning). Poor tolerance to transport, stuffiness, heat, movement on an escalator, staying at heights. Nausea, impaired thermoregulation (“chilliness”), sweating, fluctuations in blood pressure - from low to high). Difficulty absorbing information, sleep disorders, noise in the head.
Meteorological conditions, etc. may be reported.
Read material on the topic: What is weather dependence: diagnosis or fiction?
Symptoms of hypotension are more common in young, thin women. They often experience anxiety and low mood.
When collecting anamnesis, hereditary burden may be revealed, i.e. existing or existing cases of low blood pressure in the family.
— What leads to the development of hypotension? For what reasons does this condition develop?
The mechanisms of development of essential hypotension are not fully understood. There are suggestions that it is based on a violation of the so-called neuro-humoral regulation of blood circulation. Hereditary burden is often traced, usually through the female line.
There are many causes of secondary hypotension. It can occur when:
- some endocrine pathologies (reduced function of the thyroid gland - hypothyroidism, adrenal cortex - Addison's disease, autonomic diabetic neuropathy, weakened function of the anterior pituitary gland);
— diseases of the cardiovascular system (heart rhythm disturbances; mitral valve prolapse; pericarditis; heart defects; heart failure; coronary heart disease);
Read material on the topic: Coronary heart disease: diagnosis and treatment
— infections and intoxications;
- shock of various nature;
— neurological pathologies (traumatic brain injury and its consequences; brain tumors; syringomyelia, etc.);
- prolonged bed rest;
- pregnancy;
- lack of fluid;
- allergic reactions;
- taking various medications (psychotropic - antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, for the treatment of insomnia; antiarrhythmic; antihypertensive - reducing high blood pressure; diuretics; for the treatment of ischemia; anesthetics).
— Can hypotension turn into hypertension? Under what conditions can this happen?
Yes. With age, hypotension may disappear, giving way to arterial hypertension. Usually the pressure does not increase too much, but is nevertheless poorly tolerated. Moreover, it is even possible when the pressure numbers are still within the normal range (for example, the upper 130-135 mmHg) and cannot even be formally formulated as hypertension.
Read the material on the topic: It's off scale! Looking for reasons for high blood pressure
However, in a “past” hypotensive patient, they can already cause manifestations of classic arterial hypertension: a feeling of “pulsation” in the head, dizziness, redness of the face, nausea, rapid heartbeat. And this condition may require appropriate treatment (of course, with a very careful individual selection of drugs and dosages).
— What diagnostics do you need to undergo for hypotension in order to identify the cause of low blood pressure?
When diagnosing arterial hypotension, a general analysis of blood and urine is performed, some biochemical parameters are examined (including glucose), blood electrolytes, cortisol, thyroid hormones, ultrasound of the heart and thyroid gland, ECG, and 24-hour blood pressure monitoring are performed.
Read material on the topic: Ultrasound of the heart: when is it prescribed and what will it show?
Other ultrasound, as well as X-ray examinations, fibrogastroduodenoscopy - according to indications.
— It is known that doctors recommend keeping a diary for hypertensive patients. Is it necessary to keep the same diary for hypotensive patients?
Yes, it makes sense.
— Is hypotension treated with medication?
Yes, such treatment exists, but there are not many drugs. Some of them have shown themselves to work well in cases of orthostatic hypotension and essential hypotension with a “smooth”, monotonous course.
In practice, they are used relatively rarely and very carefully.
— What folk methods can help a hypotensive person raise their blood pressure? Do coffee, ginseng or eleutherococcus help with hypotension?
There are a number of studies showing a moderate positive effect on hypotensives of tea, coffee, as well as medications containing caffeine.
More of our articles in the company’s official VKontakte group
Ginseng or Eleutherococcus will also be effective to some extent, but their effect has not been fully studied - there is also no evidence base for them, as well as for the drugs mentioned above.
— Angelina Anatolyevna, what rules and recommendations should a hypotensive patient follow in order to improve the quality of their life and not feel overwhelmed and tired?
It is necessary to try to identify factors that cause a decrease in pressure and try to avoid/exclude them. Among them is sudden standing up (to prevent a decrease in pressure for this reason, you must first sit down, bend over, then raise your body and head, and stand up); long stay in an upright position; being in stuffy rooms, high air temperature; physical work, especially in hot conditions, as well as the possible loss of fluid associated with this (therefore it is necessary to control fluid loss).
You need to get enough rest, sleep, and follow a work schedule.
The diet (or, rather, the principles of nutrition) for hypotension consists of frequent meals in small portions, limiting the intake of hot food and drinks; foods rich in easily digestible carbohydrates. You can increase your salt and liquid intake (up to 2–2.5 liters of liquid, 8–10 g of salt per day).
Read material on the topic: Life without meat: food, philosophy or benefits for the body?
People with hypotension should avoid alcoholic beverages. Carefully monitor the intake of any medications, and be sure to warn your doctor about your tendency to low blood pressure.
It is imperative to look for and treat pathologies in which hypotension is secondary, i.e. is one of the manifestations of the underlying disease.
There are special gymnastics aimed at training vascular tone. Its principle is that a person who is in a horizontal position is transferred to a vertical position for a short time. The pressure decreases at this time. Such cycles are repeated, and the vessels gradually “get used” to maintaining the pressure at the proper level, which is especially important if you are prone to fainting. Such gymnastics should only be performed under the supervision of a qualified specialist.
You may also be interested in:
Why is electroencephalography needed? Complete patient guide
What is hidden behind the diagnosis of dyscirculatory encephalopathy?
Vegetative-vascular dystonia: go there - I don’t know where, cure that - I don’t know what
For reference:
Kalinina Angelina Anatolevna
In 2007 she graduated from the Voronezh State Medical Academy named after. Burdenko.
From 2007 to 2008 she completed an internship in therapy, in 2010 she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “General Medical Practice (Family Medicine)”, and in 2017 – in the specialty “Cardiology”.
Since 2015, he has held the position of general practitioner at Clinic Expert Voronezh. Reception is conducted at the address: st. Pushkinskaya, 11.
Why?
- heredity;
- unhealthy diet: eating foods high in fat (french fries, hamburgers, bacon, chips, ice cream, etc.);
- highly salted foods cause increased diastolic pressure; obesity;
- drinking alcohol (especially red wine, cognac, vodka) sharply increases DD;
- nicotine constricts blood vessels, which increases DD;
- the main reason for a sudden increase in DD is stress;
- sweetened soft drinks.
Treatment of high diastolic pressure
How to reduce diastolic pressure with normal systolic pressure, since conventional antihypertensive drugs lower both lower and upper pressure? You don’t need to do this yourself; you need to see a doctor. The main treatment will be to eliminate the primary pathology that led to an increase in lower pressure.
In pregnant women, increased lower blood pressure is often one of the first symptoms of a dangerous complication of pregnancy - OPG-preeclampsia.
To normalize blood pressure, the following groups of drugs can be used:
- Diuretics (diuretics) – stimulate diuresis, remove excess fluid from the body and eliminate swelling.
- Beta blockers - block receptors sensitive to adrenaline, resulting in relaxation of blood vessels and lowering blood pressure. The heart rate also decreases. These drugs are contraindicated in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Calcium channel blockers (calcium antagonists). They prevent the flow of calcium ions from the intercellular substance into the muscle cells of blood vessels and the heart. A decrease in Ca2+ concentration in the smooth muscle of blood vessels promotes their dilation and a decrease in blood pressure.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors). They reduce the concentration of angiotensin in the blood, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure.
- Sympatholytics. Normalizes the tone of blood vessels.
- Antispasmodics. Relaxes muscle cells, including those forming the walls of arteries.
Medications for high diastolic blood pressure should be taken in strict accordance with the doctor's prescription. It is unacceptable to independently change the dose of prescribed medications and the schedule for taking them.
How?
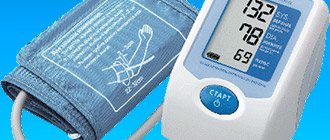
The symptom of high diastolic pressure is headache. To check what your blood pressure is, you need to measure it using a sphygmomanometer (tonometer). Modern digital semi-automatic tonometers allow you to limit yourself to only a set of pressure (until a sound signal), further release of pressure, registration of systolic and diastolic pressure, and sometimes pulse and arrhythmia, the device carries out itself. Automatic blood pressure monitors themselves pump air into the cuff; sometimes they can produce data in digital form for transmission to a computer.
In what cases do we talk about pathology?
{banner_banstat1}
This condition is considered pathological in 99% of cases. In 1% of situations, physiological factors for the development of isolated diastolic hypotension are possible. The latter should be considered in more detail.
Age
During early and late puberty, and possibly throughout puberty, surges in blood pressure occur.
This is a normal process, and the reason is the influence of a hormonal factor: the nature of the production of androgens and estrogens, as well as cortisol, catecholamines and adrenal hormones in general, changes.
Interesting:
More often, adverse events from the cardiovascular system are observed in male adolescents; girls are considered more resilient due to their physiology.
The second peak of changes in blood pressure regulation occurs at 50-60 years of age, the period of the so-called premenopause, menopause and postmenopause.
It would be a misconception to believe that menopause is a purely female phenomenon. It also exists in men and is caused by a similar process by a decrease in the concentration of androgens: testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, androstenedione and other substances.
In women, we are talking about disturbances in the production of estrogen and progesterone. Hence pressure surges, constant hypertension or hypotension. Clinical variants of the conditions are different.
Body type
{banner_banstat2}
Pressure of 110 over 50 can occur in people with a special body constitution. For example, in slender representatives of both sexes with an asthenic physique.
This is not the norm, as has already been said. Most likely we are talking about a concomitant pathological process.
Hypotension is rare in thin, large, or obese patients. In this case we are talking about a clear pathology.
Peak hormonal states
In addition to menopause and the already mentioned puberty, representatives of the fairer sex have two more conditions: menstruation in any phase and pregnancy.
Both are associated with disturbances in the regulation of vascular tone. Most often, severe hypotension occurs. Clinical variations of this process also vary.
Other factors
Features of professional activity, place of residence. In this case we have to talk about adaptive mechanisms.
Metallurgists and residents of the southern regions “suffer” from physiological hypotension. This is how the cardiovascular system protects itself from overload.
The influence of diet and bad habits is possible, but these factors are not so significant and rather provoke hypertension.
Dangerous!
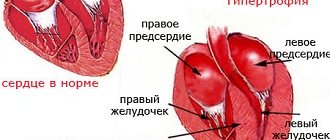
If blood pressure is persistently above 140/90 millimeters of mercury and left untreated, the risk for heart attack, peripheral artery disease, stroke and myocardial infarction increases. Congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, and renal failure may occur.
You cannot ignore systematic headaches and constantly resort to citramon for salvation. And if, when measuring pressure, DD is above 80 mm. Hg, it is vitally important for you to contact a doctor at the Pulmonology Center.
How and with what is high blood pressure treated?
Pharmacists offer a range of effective antihypertensive drugs that not only reduce blood pressure, but also protect the heart, blood vessels, kidneys and brain suffering from high levels. A wide variety of pharmaceuticals of different classes allows doctors to select the optimal treatment regimen for a particular patient.
Self-administration of antihypertensive medications is strictly prohibited. After all, when prescribing medications and choosing their dosage, not only blood pressure indicators and the patient’s age are taken into account, but also the data of his laboratory tests and the presence of concomitant diseases. Therapy with modern drugs is lifelong and has several significant features.
- As a rule, several drugs are prescribed at once, acting effectively in combination.
- There is still an opinion among people that they should be taken only when blood pressure levels are elevated, and that when blood pressure levels are normal, they can be skipped. This approach completely eliminates the ongoing therapy. Blood pressure medications should be taken even on days when the patient feels well. After all, the indicators normalized as a result of treatment will immediately jump when the active substances of the medicinal formulas are completely removed from the body.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment is mixed, systematic. It is aimed both at eliminating the root cause of the development of the hypertensive process and at relieving the symptoms that inevitably arise during the course of the disease.
Lowering the lower pressure if it is 100-110 or more must be done carefully, using selective drugs. Rough exposure to classical medications will not work. A complex of medications is needed. Combinations are determined only by a cardiologist.
Since the problem is complex, only an experienced doctor can help. Errors are possible and even probable. But you can’t do anything on your own. It is recommended that all efforts be directed towards finding a competent specialist.
During treatment, and even after therapy, you need to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Don't drink, don't smoke, move more, but within reason, eat right, drink enough fluids, reduce salt intake to an acceptable minimum. These simple recommendations may help save your life.
What to do?
First of all, experts recommend reviewing the patient’s diet and adjusting the level of physical activity. If this does not help bring blood pressure levels closer to normal, medications are selected on an individual basis.
Diet
The purpose of personal menu correction is to reduce the load on the heart muscle and kidney apparatus, remove excess cholesterol from the blood, reduce body weight, and replenish the lack of vitamins and minerals in the body. It is important to give up animal fats, fatty meats and fish, smoked meats and canned food. Reduce consumption of high-fat dairy products, store-bought sauces, and limit salt intake.
Include a sufficient amount of fruits and vegetables, cereals and legumes in your diet, drink up to 1.5–2 liters of drinking water, compotes, homemade fruit drinks, and juices. Avoid strong coffee and energy drinks; it is better to drink weak tea.
Important! You shouldn’t choose your diet based on stories from friends or what you can read on the Internet. It is better to check with your doctor or qualified nutritionist about the possibility of menu adjustments.
Lifestyle change
To reduce blood pressure, it is recommended to quit smoking and alcohol abuse. You should normalize your sleep and limit yourself from stressful situations. Innovative technologies have led to the fact that a sedentary lifestyle is the scourge of modern society. You need to fight this: when working sedentarily, take breaks for light warm-up, take evening walks, and go to the pool on weekends. This is only a small part of what experts recommend to combat hypertension.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy (physical therapy) is necessary for general strengthening of the body, supporting the functioning of the respiratory system, heart and blood vessels, and central nervous system. Regular performance of a set of exercises normalizes the tone of the vascular bed, strengthens the walls of capillaries, activates metabolic processes, and trains the heart muscle. If you have diastolic hypertension, you should avoid lifting weights, fast rhythmic gymnastics, and exercise at low or high temperatures.
Several exercises that will help correct blood pressure, including diastolic:
- Walk in place, raising your legs high. Your knees should rise above your waist. Perform for 40 seconds.
- Squats without using weights. Perform 2-3 sets of 10 times with breaks between sets.
- Tilts of the body in a standing position to the sides, forward and backward. Perform exercises slowly and smoothly, without jerking.
- Intense walking in the morning after a night's sleep. The distance should not exceed 3 km, at first – 1.5–2 km.
- Swimming.
Medicines
The drugs used to lower blood pressure are described in the table below.
| Group of drugs | Representatives | Mechanism of action |
| ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme) | Cilazapril, Lisinopril, Enalapril, Fosinopril | Blocking kinase-II, reducing the formation of angiotensin-II, accumulation of bradykinin. The effect is practically independent of the patient’s age |
| Calcium antagonists | Nifedipine, Verapamil | Prevents the penetration of calcium into vascular and cardiac cells through calcium channels. The result is vasodilation |
| Diuretics | Hypothiazide, Indapamide, Diuver, Lasix | Acceleration of fluid removal from the body, which causes a decrease in blood pressure numbers |
| Alpha blockers | Prazosin, Terazosin | Impact on adrenergic receptors of blood vessels and heart, blocking their sensitivity. Poorly tolerated by patients and therefore rarely used |
| Beta blockers | Atenolol, Metoprolol, Bisoprolol, Talinolol | Reduce the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle, help reduce the numbers on the tonometer |
Characteristic symptoms
Isolated diastolic hypertension, what this means, has now become clear. But you need to find out what symptoms accompany the disease in order to consult a doctor in time. The main manifestations of pathology are:
- unexpressed headaches, accompanied by dizziness and weakness;
- blurred vision, flickering “spots”, blurred image;
- shortness of breath that occurs regardless of physical activity;
- weakening of the capillary walls, manifested by periodic nosebleeds.
During periods of exacerbation of the disease, a person feels discomfort, his performance decreases, and emotional and physical decline is noted. Since pressure 100/100 is uncertain, that is, it is not clear which drugs can improve well-being in a particular situation, it is better not to self-medicate. You should contact a specialist to find out the reasons for such tonometer readings; he will select a suitable treatment regimen.
Diagnostics
In case of newly identified pathology, it is advisable to examine the patient in a hospital setting. If not possible, during outpatient appointments. A cardiologist will help.
If necessary, an endocrinologist, neurologist and nephrologist are involved. Such a “consultation” is not always required, but in most cases.
Accordingly, the list of studies is as follows:
- Assessment of complaints, collection of anamnesis. To objectify symptoms. This is an important step that determines the diagnostic vector.
- Determination of blood pressure levels in both arms.
- Holter monitoring using an automatic programmable tonometer.
- Electrocardiographic study. To assess cardiac function and identify minimal abnormalities. Unfortunately, few people are able to read the result correctly.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasonography.
- Study of hormone levels in the blood.
- Biochemistry of venous blood.
- General analysis of hematological fluid (CFA).
- Study of neurological status, condition of the kidneys and excretory system.
How exactly to examine the patient is decided by specialists.
Additional reasons for strange readings
In some cases, the appearance of numbers 110/110 on the tonometer may be the result of a malfunction of the device itself. Possible problems:
- cuff damage;
- malfunctions from the tubes;
- air supply pump failure;
- incorrect operation of the electrical part of the device;
- battery discharge (if the device has one).
The rules for measuring indicators may have been violated. This is typical for incorrect placement of the cuff in relation to the vessels. And also strange numbers can appear if a person talks while measuring blood pressure, fidgets in a chair, or moves the hand on which the device is fixed.
To ensure that the results obtained are correct, it is worth measuring blood pressure after 5–7 minutes on the other arm, following the diagnostic algorithm. If 110/110 indicators reappear, you can borrow a tonometer from friends, neighbors or relatives to prevent damage to your own device.
The main reasons for the increase in DBP
{banner_banstat1}
Increased lower pressure is multifactorial, there are reasons hidden inside the heart and blood vessels (only 20%), and there are extracardiac (80%). In addition, physiological and pathological triggers of elevated diastolic markers are distinguished.
| Causes | The essence of pathology |
| Physiological | |
| Long-term smoking abuse | Nicotine and tar provoke vasospasm, impaired blood flow, hemodynamics, and blood pressure increases. Since cigarette toxins primarily affect the lungs and kidneys, renal blood pressure (RBP) increases. |
| Alcohol | It works in a similar way, only instead of the lungs, the liver is involved in the process, metabolic processes are disrupted, the vessels either dilate or contract, hypertension increases, as soon as the body’s compensatory capabilities end, myocardial ischemia develops with infarction |
| Abuse of salt | More than 5 g/day leads to fluid retention in the body, hemodynamic disturbances, and an increase in DBP |
| Hyperload | Physical or mental stress stimulates the synthesis of catecholamines - this is a natural defense mechanism in which a person does not feel pain or fatigue, but against this background blood pressure rises rapidly, with the lower one overtaking the upper one |
| Stress | Vasospasm provokes an increase in blood pressure |
| Endocrine disruptions | Puberty, menopause, menstruation, pregnancy - cause hormonal changes in the body, change vascular tone, arterial markers |
| Pathological | |
| Myocardial ischemia | General hemodynamics and cardiac output are disrupted, DBP increases |
| Atherosclerosis | Reducing the lumen of arteries, capillaries, and veins due to atherosclerotic plaques impairs blood circulation and leads to an increase in diastolic indicator |
| Infringement of the arteries supplying blood to the brain | Causes ischemia of the brain, its centers, pathology of the musculoskeletal system, which increases the lower pressure to 100 units and above |
| Endocrine diseases: diabetes, hyperthyroidism, Cushing's syndrome | The balance of hormones in the body is disrupted, dopamine biologically active substances, thyroid hormones, stress hormones predominate, vascular spasm develops against the background of metabolic disorders, which causes an increase in vascular parameters |
| CRF, CKD (chronic kidney disease) | The synthesis of renin is disrupted, which leads to an imbalance in blood pressure control with the development of malignant hypertension, DBP is a marker of such a process |
| Post-stroke condition | Often a DBP of 100 units indicates a disruption in brain function, which occurs against the background of a stroke, requiring long-term correction |
What can you do at home?
Actually, nothing. You should urgently call doctors (emergency medical care) and wait for a team led by a paramedic.
Before the doctor arrives, you should take a horizontal position and simply relax as much as your condition allows. No sudden movements or special breathing techniques are needed.
You can take medications only with the permission of the treating specialist and strictly in the prescribed dosage. No more, no less.
A sharp drop in blood pressure will also not lead to anything good (this is how classic antihypertensive medications work), and here a combination of drugs and their dosages is required.
How to reduce lower pressure if it is 100 or more, minimally affecting the upper one:
- take 1/4 Captopril tablet.
- take calcium antagonists (1 tablet of Diltiazem or Verapamil).
Exceeding dosages and taking unspecified medications is strictly prohibited. What this will lead to is unknown.
The described measure is also not a treatment and does not lead to normalization of blood pressure in the long term.
Attention:
Baths, dousing with water, folk remedies, basins with hot water - all these are sabotage techniques. This kind of advice is given by people far from medicine. Self-activity is fraught.
Upon arrival, doctors need to talk about complaints and, if possible, resolve the issue of hospitalization.
If it is impossible to go to the hospital for at least a few days, you should immediately contact a cardiologist to prescribe or adjust therapy.