Drug treatment
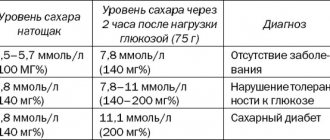
Indication for starting medication is blood pressure level:[1]
- in women with chronic uncomplicated hypertension - systolic blood pressure ≥ 150 and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 95;
- in all other cases (gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, target organ damage, associated clinical conditions) - systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mm Hg.
Important aspects of drug therapy:[1][2][5][8]
- The choice of drug depends on the duration of pregnancy - there are significant restrictions on taking medications in the first trimester, and after childbirth - on the presence or absence of lactation.
- Treatment begins with minimal doses of one drug (usually methyldopa), if necessary, the dose is increased, then another drug is added.
- It is necessary to maintain target blood pressure for 24 hours, so blood pressure should be periodically monitored even when feeling well, in order to adjust therapy in time.
- Hypertension in itself is not a contraindication for vaginal delivery, but drug therapy during labor must be continued.
Antihypertensive therapy for hypertension in pregnant women: methyldopa and β-blockers
Antihypertensive therapy is indicated for increased blood pressure (equal to or higher than 140 and 90 mm Hg) and consists of taking oral medications. Methyldopa 1000 to 3000 mg per day is preferable. If there is a threat of preeclampsia, nifedipine up to 40 mg per day is used, as well as β-blockers (labetalol is most often prescribed, and metoprolol succinate preparations are classified as reserves).
List of prohibited drugs
When planning, during pregnancy and lactation, it is prohibited to take RAAS blockers (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system) - ACE inhibitors, sartans, direct renin inhibitors.
List of allowed funds
- methyldopa;
- selective β-blockers;
- nifedipine.
Algorithm for providing medical care during the development of an attack of eclampsia
Treatment of gestational arterial hypertension and preeclampsia is carried out in an obstetric hospital, where intravenous administration of magnesium is used to relieve convulsive syndrome, 1% nitroglycerin and other drugs that are prescribed in accordance with the patient’s condition and specific tests.
Treatment of acute severe hypertension in pregnant women
If there is a sharp increase in blood pressure, pregnant women can be given a 10 mg nifedipine tablet (in the absence of tachycardia). In stationary conditions, intravenous, very slow administration of nitroglycerin and magnesium is added.
Evaluation of treatment effectiveness
Blood pressure should not be reduced too quickly. It is necessary to reduce the initial high pressure by no more than 25%.
Rehabilitation
In the postpartum period, blood pressure increases, reaching a maximum on the fifth day, at which time an increase in medication doses may be necessary.
During lactation, depending on the severity of hypertension, three options are possible:
- lactation without taking medications (uncomplicated hypertension with blood pressure < 150/95);
- lactation with low doses of medications (uncomplicated hypertension with blood pressure ≥ 150/95);
- refusal of lactation for the sake of full treatment of hypertension (complicated hypertension).
In the case of eclampsia, treatment and recovery are carried out in the intensive care unit with artificial ventilation of the lungs.
Delivery for preeclampsia and eclampsia
With moderate preeclampsia, hospitalization in an obstetric hospital is indicated, careful monitoring of the condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus, but prolongation of pregnancy is possible. In severe preeclampsia, after the woman’s condition has stabilized, immediate delivery is necessary.
Alternative therapy
The effectiveness and safety of alternative medicine have not been proven by scientific methods, so their use during pregnancy can be dangerous for the health of the woman and child.
Prevention of eclampsia
To detect preeclampsia and prevent eclampsia, patients should be screened for proteinuria (protein in the urine).
Prevention of long-term consequences
For arterial hypertension that persists more than 45 days after birth, the woman should be observed by a general practitioner or cardiologist with a choice of medications depending on whether lactation continues. If breastfeeding is stopped, the first-line drugs are RAAS inhibitors (primarily ACE inhibitors).
Causes of high blood pressure during pregnancy
Arterial hypertension syndrome in women during pregnancy can be triggered by several factors. Blood pressure in pregnant women increases due to the following changes:
- the location of the heart changes;
- hormonal changes occur - the level of progesterone and estrogen in the blood increases;
- placental blood circulation increases;
- body weight increases;
- the mobility of the diaphragm is limited.
The development of all hemodynamic changes during pregnancy leads to a complex of problems that trigger arterial hypertension syndrome.
Medicines and breastfeeding
When determining an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes hypotonic medications to the woman, which can negatively affect the quality of milk. But you should not categorically refuse natural breastfeeding. You just need to choose medications that have a low level of effect on breast milk. Such drugs include Dopegit, Dibazol, Verapamil.
"Dopegit" . The hypotensive effect of the drug is expressed in its ability to reduce the frequency of myocardial contractions and minute blood volume. "Dopegit" reduces peripheral blood resistance, which contributes to a rapid decrease in pressure. The maximum effect of the drug after internal administration begins after 4-6 hours and lasts for 1-2 days. The prescription and required dosage are carried out under strict medical supervision. The drug is approved for use by pregnant women and during breastfeeding.
"Dibazol" . The drug has a strong vasodilator effect, which helps lower blood pressure. Dibazol also has an antispasmodic effect, which normalizes vascular tone. The therapeutic effect of the drug begins 30-60 minutes after oral administration and lasts for 2-3 hours. The drug should only be prescribed to pregnant and breastfeeding women by a qualified physician.
"Verapamil" . The drug has a strong hypotonic, antianginal and antiarrhythmic effect. "Verapamil" has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the myocardium, preventing unpleasant symptoms in diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Its use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is permitted only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the risk of possible complications for the baby.
It should be taken into account that medications that do not allow blood pressure to increase should be taken so that the moment of feeding does not coincide with the time of the maximum concentration of the drug in the mother’s blood. Antihypertensive medications should be taken immediately before breastfeeding. This will prevent the active substances from entering the bloodstream and harming the baby.
Complications of arterial hypertension syndrome in pregnant women
The main danger of arterial hypertension syndrome during pregnancy is a hypertensive crisis. In addition, women are also at risk of other conditions that are dangerous to their health:
- plaques form on the walls of blood vessels, which leads to a significant disruption of the already impaired blood circulation and the supply of necessary substances to the placenta;
- High blood pressure can lead to myocardial infarction, resulting in the death of the child. This occurs due to narrowing of the coronary arteries and insufficient blood flow to the heart;
- arterial hypertension can cause pathological processes in the kidneys, and the development of renal failure may occur due to impaired blood circulation in the kidneys;
- due to impaired blood circulation, central nervous system pathologies may occur: possible development of stroke, chronic failure of brain circulation;
- In addition, pregnant women with arterial hypertension often experience the development of endocrine diseases, visual impairment, metabolic syndrome and many other serious complications.
If a hypertensive crisis occurs, a woman requires immediate treatment.