- Contraindications to UAE
- UAE and pregnancy
- Complications after UAE method
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) is a modern method of treating uterine fibroids, which involves stopping the blood flow to the fibroids by introducing special blocking substances (emboli).
The therapeutic mechanism of the procedure is to block blood flow through the branches of the uterine arteries that supply blood to the fibroid. During this manipulation, the vessels supplying the healthy myometrium are not damaged.
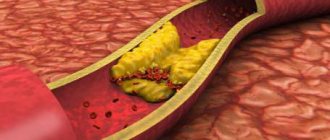
The therapeutic effect of UAE is based on the anatomical features of the structure of the vessels supplying the uterus and myomatous nodes. Myoma does not have an active blood supply. The arteries leading to the myomatous node almost do not connect with other vessels, and form the so-called perifibroid plexus. The blood supply to healthy uterine tissue comes from several arteries (mainly the uterine and ovarian arteries), and has a well-developed collateral network.
The structure of the vessels of the perifibroid plexus differs from normal arteries - their diameter is several times larger, it reaches 0.5 mm. After the injection of a drug containing emboli into the artery of the perifibroid plexus, the blood supply to the fibroid is disrupted, which leads to its fibrosis - replacement with connective tissue. As a result, myomatous nodes significantly decrease in size or disappear. Emboli do not enter normal vessels that feed healthy muscle cells, because such arteries are smaller in size than emboli. It is on these features of the blood supply that the UAE mechanism is based.
History of the method
UAE was first used in the 70s of the 20th century as a method of treating uterine bleeding that occurs after complicated childbirth or after surgery. The French researcher Jacques Ravina was the first to use this technique to treat uterine fibroids. Initially, the technique was intended for preoperative preparation of patients for hysterectomy in order to reduce surgical blood loss. During the observation of women after embolization, the researcher noted that in most patients the manifestations of the disease disappeared or significantly decreased, and a pronounced decrease in the size of the nodes was also noted. Since then, the EMA technique has been actively studied, improved, and spread throughout the world.
“Birth” of a myomatous node
“Birth” (or expulsion) of a myomatous neoplasm can occur several days, several months, and even a year after the procedure. This prognosis becomes known to the patient even before the procedure, during an ultrasound diagnostic examination. For a myomatous node with a diameter of 3 to 5 cm, a visit to a doctor is not required, but if the diameter is larger, then the consultation can be carried out remotely. Most often, the node comes out on its own; medical attention is extremely rarely required. It is worth noting that the process of “birth” of a node is a controlled condition, after which the patient is completely freed from it. It is not a complication and is considered by modern gynecologists as a favorable outcome of UAE.
Technique for uterine fibroid embolization surgery
Uterine artery embolization is a procedure performed in close collaboration between two specialists - a gynecologist and a vascular surgeon. The actual operation is performed by a surgeon, since such an intervention requires extensive experience with angiographic equipment.
The gynecologist determines the indications for the procedure, determines the timing of treatment, preoperative preparation, and monitors the patient after the procedure.
The operation is performed in an operating room equipped with special angiographic equipment. The manipulation itself is practically painless, so general anesthesia is not used. First of all, a puncture of the common femoral artery is performed, where a thin angiographic catheter is inserted. Next, under the control of angiography, the catheter is passed to the uterine artery on one side. A drug containing emboli is injected through a catheter, which blocks the vessels supplying blood to the fibroid; after which the procedure is repeated on the other side. Emboli are white granules consisting of porous plastic (polyvinyl alcohol) of irregular shape and varying diameter. All drugs used for embolization are absolutely safe and do not cause an allergic reaction. As a rule, the entire manipulation lasts about 20-30 minutes.
Advantages of radial access
For the first time in the Russian Federation, UAE was performed at the CELT clinic using radial access, i.e.
through an artery in the hand or forearm. This approach allowed us to reduce the time of surgery, fluoroscopy, and the amount of contrast agent. The operator’s work is also significantly easier, and the patient herself feels much more comfortable. Moreover, according to numerous studies conducted around the world, the radial arm approach is much safer than the femoral artery approach, reducing the risk of complications by more than five times. In our clinic, radial access is performed using original Japanese-made Terumo catheter probes. They are even thinner and smaller than the probes used for femoral artery puncture, making the procedure even less traumatic. After it, the patient does not have to remain in bed. Discharge from the hospital occurs the next day.
After embolization
Immediately after completion of the procedure, patients experience a number of complaints, which are combined into the so-called “post-embolization syndrome” - pain in the lower abdomen, severe weakness, nausea, dizziness, and increased body temperature. These symptoms are the body's response to the cessation of blood flow to the fibroids and usually do not require treatment. Usually this period is short-lived, lasting from 10 hours to several days.
In the period from six months to one and a half years after UAE, patients note a decrease or complete disappearance of all symptoms - due to the reduction in the size of the fibroids and the restoration of the normal anatomy of the uterus, the menstrual cycle is normalized (heavy menstruation is eliminated), and pain is relieved.
Painful sensations
UAE is a painless procedure, but after it there is a nagging pain in the lower abdomen, very similar to the symptoms that accompany menstruation. Their duration ranges from three to four to seven to ten days after the procedure. As a rule, after three to four days the need to take painkillers disappears. It is worth noting that the intensity of pain varies from person to person - however, they cannot be called very strong, capable of causing “painful shock”. At the same time, pain symptoms of moderate intensity are effectively eliminated with anesthesia.
Indications for UAE
- uterine fibroids, manifested by extremely heavy menstruation, pain, dysuric phenomena, symptoms of compression of neighboring organs (except for subserous fibroids on a thin base)
- uterine fibroids in women with severe concomitant diseases, when there are contraindications to any surgical treatment.
- uterine fibroids in the presence of contraindications to hormonal therapy
- uterine fibroids in women who want to preserve reproductive function, if it is impossible to effectively perform conservative myomectomy
Preparation for the UAE procedure
Before the procedure, the uterus is imaged using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound to confirm the presence of a fibroid tumor (fibroid) that is causing discomfort and to assess the size, number, and location in the uterine wall.
Uterine fibroids can also be detected during laparoscopy.
If a woman experiences heavy bleeding between periods, a biopsy of the endometrium (the lining of the uterus) may be recommended to rule out cancer.
Before starting the UAE procedure, you must inform your doctor:
- all medications you take, including herbal and nutritional supplements;
- about the presence of allergies, especially to drugs used for local and general anesthesia or to a contrast agent (containing iodine);
- about recent illnesses or other important medical facts relating to health;
- pregnancy.
If UAE is necessary during pregnancy, we will take every precaution to minimize radiation exposure to the baby.
On the eve of the examination, it is necessary to shave the groin area. It is recommended not to eat or drink at night.
UAE and pregnancy
If uterine fibroids prevent pregnancy or pregnancy, treatment options include conservative myomectomy or resectoscopy for submucosal fibroids. In the presence of uterine factor infertility caused by uterine fibroids, these techniques invariably show high effectiveness in restoring reproductive function.
In some cases, such operations are impossible or ineffective due to the location of the myomatous nodes, their large size or number. In many cases, there are multiple uterine fibroids, or uterine fibroids with an interstitial (intermuscular) location of the nodes. In such cases, attempts to remove nodes are accompanied by intervention in the uterine cavity and can lead to complications such as cicatricial deformations of the cavity, adhesions, synechiae of the uterine cavity, not only not increasing a woman’s chances of carrying a pregnancy, but also exacerbating them.
In such cases, EMA becomes the method of choice as a gentle and organ-preserving method. After reducing the size and fibrosis of myomatous nodes after embolization, the normal structure of the uterus is restored, the topography of the cervical canal is restored, which improves reproductive prognosis. In the group of patients in whom conservative myomectomy is impossible for technical reasons, or its implementation is associated with a high health risk, embolization is the best option for preserving and restoring reproductive function.
What equipment is used when performing EMA?
When performing UAE in our clinic, we use the Philips Allura CV20 angiographic complex (made in Germany, manufactured in 2014), disposable catheters and guides (made in the USA), as well as emboli of the patient’s choice, made in Russia, the USA or Japan.
The angiographic complex consists of a transparent X-ray table and a C-shaped X-ray tube that generates ultra-low doses of radiation and provides maximum visualization of blood arteries, including the capillary order. The high resolution of the angiographic complex eliminates the possibility of medical error and minimizes possible theoretical complications. The entire course of the operation and diagnosis is recorded in the computer and can be recorded on an individual magnetic medium (CD disk or flash card) of the patient.
All instruments and consumables used during the EMA procedure have Registration Certificates of Roszdravnadzor and permission for circulation on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Complications after UAE method
Uterine artery embolization is one of the safest procedures in gynecology; the risks of complications after it are minimal.
Complications include:
- formation of a hematoma on the thigh at the site of arterial puncture. This situation does not require additional treatment and goes away on its own.
- allergic reactions to X-ray contrast agent (preparations containing iodine).
- infectious complications
- menstrual irregularities for 3-6 months after the procedure, or temporary amenorrhea. The reason for this complication is a temporary deterioration in the blood supply to the endometrium after embolization.
The results of the procedure and the success of its implementation are assessed after 6 and 12 months, during which time the process of reducing myomatous nodes is completed; as a rule, their volume is reduced from 40 to 70% of the original. When performing an ultrasound examination, myomatous nodes are visible as dense fibrous formations with a lack of blood flow; the structure of the myometrium and blood flow in the uterus and ovaries are not affected.
Women who have undergone uterine artery embolization should be regularly monitored by a gynecologist and undergo pelvic ultrasound at 6-month intervals. The issue of planning pregnancy after embolization is decided individually depending on the rate of fibroid degeneration; As a rule, you can plan a pregnancy 12 months after the procedure.
Uterine fibroids are currently one of the most pressing and common problems in gynecological practice. Myoma is in 2nd place among gynecological diseases. This disease is diagnosed in almost 25% of women of fertile age, of which in 3% of cases this formation is first discovered during a routine examination. Myoma can occur in young and elderly nulliparous women, after childbirth, during pregnancy, menopause, and after gynecological operations. The incidence of the disease among all women by the age of 35 reaches 35-45% of cases. The peak of the disease occurs at 35-50 years of age. If the frequency of diagnosis in reproductive age is about 20%, then in premenopausal age it reaches 35% of cases.
For many years, doctors preferred to solve the problem radically, sending women with uterine fibroids under the “surgical scalpel.” Hysterectomy is still practiced today. However, hysterectomy is not just a painful procedure - the operation carries serious risks to overall health. The development of medical technologies and the gradual abandonment of radical interventions have made it possible to introduce into practice a method of treating uterine fibroids that is less traumatic for the patient, which is uterine artery embolization (UAE) .
Historical background: 1979 J. Oliver - the first report on UAE to stop postpartum and postoperative bleeding. Since 1990, Jacques Ravina in France has used uterine artery embolization as a preparatory step before hysterectomy to prevent intraoperative blood loss. At the same time, it was noted that the majority of patients with uterine fibroids after embolization, the symptoms that bothered them disappeared, which is why some women began to refuse open surgical operations altogether. The observed clinical effect allowed the authors to use uterine artery embolization as an alternative to surgical treatment, first in patients with extremely high surgical risk, and then in the rest of the category of patients. 1994 Ravina J. - the first report on uterine artery embolization as an independent method of treating uterine fibroids. In 1996, EMA received FDA approval in the United States. 2004 - the Committee of the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE) and the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) adopted a standard for the use of UAE in the treatment of uterine fibroids. In 1998, by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, EMA was included in the list of permitted endovascular interventions in Russia and is part of high-tech operations for VMP.
To date, interest in this type of operation is steadily growing and is actively used in developed countries around the world. Embolization of the uterine arteries abroad and in Russia is currently widely used as a treatment for uterine fibroids, as well as to stop massive hypotonic bleeding in the early postpartum period and during minor gynecological interventions!!! One can note a steady increase in the number of endovascular interventions performed in our country.
The therapeutic mechanism of UAE is that the cessation of blood flow in the perifibroid space is achieved by introducing embolization particles into the uterine arteries, leading to ischemia with subsequent atrophy and involution of the myomatous node.
Indications for uterine artery embolization are virtually unlimited and include:
- all “symptomatic fibroids”, i.e. fibroids causing bleeding, pain, a feeling of heaviness, frequent urination, etc.
- growing “asymptomatic fibroids”, regardless of the number of nodes, their location and size
- nodular forms of adenomyosis.
The main contraindications to UAE are conditions that make it difficult or exclude the possibility of performing endovascular intervention: severe anaphylactic reactions to radiocontrast drugs, uncorrectable coagulopathies, severe renal failure, malignant tumors of the uterus and ovaries. UAE is also contraindicated in pregnant women, patients planning IVF, patients with acute infectious diseases of the uterus and appendages, after previous radiation therapy of the pelvic organs, and with autoimmune connective tissue diseases.
The UAE technique is as follows: under local anesthesia, puncture and catheterization of the right common femoral artery (groin area) is performed with the installation of a special medical instrument - an introducer. A catheter is sequentially inserted into both uterine arteries under fluoroscopy control, followed by infusion of a suspension of embolizacin particles of various diameters into the arteries, resulting in a complete reduction of arterial blood flow in the uterus. The main goal of the procedure is embolization of the vessel supplying the myomatous node, where the average size of the artery is 0.5 mm.
The procedure is considered complete after obtaining a satisfactory angiographic effect from embolization - the “stop-contrast” effect in the proximal parts of the uterine artery and the absence of contrast in the distal segments of the artery. The average duration of the procedure is approximately 20 minutes.
The following can be used as embolic agents in the treatment of uterine fibroids: polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), acrylic microspheres, hydrophilic embolizations, etc. The embolic drug used is absolutely safe, biologically inert and cannot cause allergic reactions.
Side effects and complications (post-embolization syndrome): the most common occurrence after uterine artery embolization is the occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen in the first hours after the intervention. This pain is associated with cessation of blood flow in the fibroid and indicates the effectiveness of embolization!!! To relieve pain, all patients in the clinic are given epidural anesthesia, which allows for complete pain relief!!! As a rule, the next day after embolization, patients are discharged from the clinic. Full recovery takes 3-7 days. Another feature of the postoperative period is a slight increase in temperature within 5–10 days after embolization (a manifestation of the body’s systemic reaction to embolization). This phenomenon is safe and does not require specific therapy. Complications after UAE are extremely rare, occurring in no more than 1% of patients, which is significantly lower than the frequency of serious complications after myomectomy and hysterectomy. The most common complication is the formation of a hematoma (bruise) at the site of the puncture of the artery. As a rule, this does not require additional treatment and goes away on its own within 10–15 days. Complications such as infection (endometritis) and temporary amenorrhea occur in no more than 0.3% of cases, and are most often successfully eliminated by conservative therapy. The duration of all symptoms of post-embolization syndrome ranges from 3 to 14 days with a progressive decrease in their severity. A repeat visit to the gynecologist and ultrasound is scheduled 3, 6, 12 months after the procedure.
Results of uterine artery embolization: the first manifestation of the effectiveness of UAE is the normalization of symptoms - menstrual bleeding is normalized, its volume and duration are reduced. Symptoms of compression also decrease and disappear, only this process is longer and can last several weeks. The decrease in myomatous catches, as well as the overall size of the uterus, most actively occurs during the first 6-8 months after UAE. On average, by the year the volume of nodes decreases by more than 4 times. Small fibroids disappear completely. After 2 weeks after UAE, there are no fibroids left as such; they are replaced by connective tissue that is not able to grow again. An important feature of UAE is that there is no risk of disease recurrence after the intervention - the effect occurs on all nodes, regardless of their size ( the probability of disease relapse after open surgery - myomectomy is up to 40%, myomectomy can cause placenta accreta during pregnancy!!! ). In the long-term period, more than 98% of women after UAE do not need any additional treatment for uterine fibroids.
In conclusion : UAE is used in patients as an independent method of treating uterine fibroids, as well as for the prevention of hypotonic bleeding in various obstetric and gynecological pathologies, for example, cervical pregnancy and uterine bleeding caused by remnants of placental tissue, which allows to reduce blood loss and preserve the uterus during hysteroscopy / curettage of the uterus. The introduction of UAE into clinical practice has provided the possibility of organ-preserving treatment of uterine pathology, which until recently required hysterectomy .
Necrosis of the uterus
Modern medicine excludes such a phenomenon as uterine necrosis after UAE. Similar cases occurred in the late nineties, when the procedure was performed using emboli of the wrong diameter or characteristics that were not suitable for the case. A negative role was played by incorrect preparation of patients, as well as an incorrect understanding of the symptoms of the birth of myomatous neoplasms. But even so, such cases were extremely rare. Today they are completely absent.