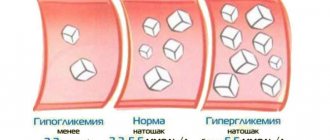
Any food affects your glucose level. That is why digital indicators of a blood test taken on an empty stomach are considered objective. In the absence of abnormalities in the functioning of the endocrine system, the normal sugar level is 3.9–5.2 mmol/l on an empty stomach. 2 hours after eating, it should not be higher than 7.8 mmol/l. A stable excess of the standards allows one to diagnose a prediabetic condition or diabetes mellitus.
One of the components of diabetes therapy is a dietary diet. Before prescribing treatment with antidiabetic drugs, the doctor must explain which foods increase blood sugar and, therefore, are prohibited for a diabetic. And also tell you how to correctly create a menu of foods that are acceptable for consumption.
Why is it important to control your sugar levels?
Maintaining stable plasma glucose levels and avoiding spikes and drops is important. A sharp increase in sugar levels is harmful to health.
- The body releases excess insulin to move glucose into cells. Constant stress on this mechanism can provoke insulin resistance, which triggers diabetes.
- Sudden attacks of hunger may occur.
- The body accumulates large amounts of fat.
Many foods are marketed as beneficial for blood sugar levels, even though they have significant effects on plasma glucose. Even the healthiest ones can cause sudden spikes in sugar, which is especially important for people with diabetes. Study the list to regulate the amount of these foods in your diet.
Foods with high and medium GI
There is no need to calculate the glycemic index yourself. There is a ready-made table of foods that are excluded from the diet of a diabetic patient.
| Products | G.I. |
| dates | 146 |
| wheat bread (white) | 136 |
| cakes, cookies, croutons (fried) | 100 |
| potatoes (fries and fried) / mashed | 95/90 |
| pies and buns | 88 |
| corn flakes, popcorn and pasta | 85 |
| rice porridge, waffles, caramel candies | 80 |
| fried zucchini, baked pumpkin | 75 |
| seasoned croutons, soda | 74 |
| watermelon | 72 |
| cheesecakes, ice cream, jam (jams), milk chocolate, halva, dumplings | 70 |
Nutritional features must comply with:
- stages of the disease (compensated, subcompensated, decompensated);
- type of disease (insulin dependent, non-insulin dependent);
- prescribed doses of medications;
- the presence of complications and concomitant pathologies;
- general condition of the patient;
- level of physical activity.
Depending on the listed individual health indicators, food with an average GI value is allowed. The treating endocrinologist can best advise which foods should be avoided and which ones can be eaten. The table shows limited products with an average glycemic index.
| Products | Gl |
| unleavened dough (flatbread, pita without filling) | 69 |
| croissants without filling | 67 |
| muesli, pineapple, diet biscuit | 66 |
| bananas, melon, boiled jacket potatoes | 65 |
| raisin | 64 |
| pizza with tomatoes (without meat filling) | 60 |
| papaya | 58 |
| mango, oatmeal cookies, persimmon | 55 |
| yoghurts, tomato soup, gazpacho type | 52 |
| buckwheat, buckwheat flour pancakes | 50 |
| green peas (canned) | 48 |
| beans (white, red), kiwi | 42 |
| chickpeas | 41 |
Excessive consumption of foods from the medium glycemic category can negatively affect health. Sugar will increase depending on the amount eaten, since a larger volume of food containing glucose requires greater insulin costs. With insulin deficiency, hyperglycemia may develop. Proper nutrition is a method of treating diabetes. Neglecting recommendations leads to severe complications of the disease.
Fresh fruit juice
Fruit juice has been promoted for decades as an all-natural, healthy drink that's just as good as whole fruit. But 1 fresh orange provides fiber, carbohydrates and vitamins while delivering only 15 grams of carbohydrates.
Fruit juice doesn't provide as much fiber and nutrients, but does have 45 grams of carbohydrates per glass. It can only be used for hypoglycemia, when you need to quickly decide how to increase your sugar. It is better to use fresh and frozen fruits in your daily diet. They contain fewer light carbohydrates.
What increases sugar
- Sweets.
- Dried fruits.
- Sweet drinks.
- Confectionery, bakery, pasta.
- Cereals.
- Legumes.
- Sweet fruits and berries.
Despite the fact that fatty foods have a zero glycemic index and contain virtually no bread units, they also increase glucose. This happens slowly (digestion lasts 5-6 hours), so the readings can go off scale after this time. A large amount of fatty acids is fraught with the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and tissue insulin resistance.
Oatmeal
Sugar may be added to ready-made oatmeal and other instant cereals: read the label carefully.
Even if you cook porridge on the stove, oatmeal can significantly increase your blood sugar if you don't control your portion size. It contains protein and plenty of dietary fiber, but one cup of oatmeal has 27 grams of carbohydrates (no sugar). Therefore, you need to plan your breakfast properly to control your overall carbohydrate intake.
General principles of nutrition for diabetics
Changing your diet is one of the cornerstones of diabetes treatment. Compliance with the rules allows the patient to manage the disease, which is the best prevention of the development of severe complications. You can develop a dietary menu yourself based on the therapeutic diet “Table No. 9” or consult a nutritionist.
The basic principles of nutrition are:
- eliminating simple carbohydrates that increase glucose levels (primarily various sweets and sugary drinks);
- compliance with the diet (5–6 times a day with 3–4 hour intervals) and drinking regime (1.5–2 liters/day);
- reducing portions;
- control of caloric content of dishes and glycemic index of foods;
- limiting animal proteins and complex carbohydrates;
- refusal to prepare dishes using the culinary method of frying;
- limiting salt and salty foods;
- consumption of foods that lower sugar.
- Keeping a Diabetes Diary.
Recommended daily nutrient ratio: carbohydrates – 45%, proteins – 20%, fats – 35%. Total calorie content – no more than 2200-2500 kcal.
Whole grain bread and pasta
Similar to brown rice, whole grain breads and pastas contain more fiber, vitamins, but contain processed carbohydrates, quickly raising plasma glucose levels.
Some varieties are colored with molasses, which gives them a brown color to create a false impression of greater healthiness. Look at the list of ingredients for whole wheat bread - the longer the list, the worse.
Diabetic food basket
Products that lower blood sugar are more correctly called stabilizing this indicator. Not a single dish can replace a diabetic with the first type of disease, a timely injection of insulin. The complex process of forming glucose molecules from the amino acids of eaten proteins (gluconeogenesis) can affect sugar levels, even hours after eating.
Foods with low glycemic activity help maintain glucose levels at a minimum level for a particular stage of diabetes. A diabetic diet to lower blood sugar is based on regular consumption of foods whose GI does not exceed 35 units. With this diet, it becomes possible to control glucose and reduce the dose of medications.
Healthy vegetables, fruits and berries
Products from this category form the basis of dietary nutrition. They not only curb glycemic levels, but also enrich the body with vitamins, micro- and macroelements. Helps improve the general condition of blood vessels and eliminate “bad” cholesterol. In addition, vegetables and fruits are low in calories, which helps control body weight.
List of products approved by endocrinologists:
What fruits can you eat if you have diabetes?
- Apples. They are a source of: pectin, fiber, iron, vitamins A, C, E, manganese, potassium. Stabilizes digestion processes.
- Pomegranate. Due to the content of tannins and fiber, they stimulate intestinal functions, which have a beneficial effect on the process of hematopoiesis. Helps improve the performance of the pancreas.
- Pears. They have a diuretic and bactericidal effect. Helps cope with fluid retention in the body.
- Pomelo. Along with low GI, it is enriched with potassium, which contributes to the smooth functioning of the heart.
- Jerusalem artichoke or earthen pear. Activates the endocrine function of the pancreas to produce insulin. It is an indispensable vegetable in the menu of diabetics.
- Momordica or bitter gourd. A dietary product that helps reduce body weight, stimulates insulin synthesis and improves metabolic processes.
- Cabbage: white cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli. Contains B vitamins, strengthens the immune system and the vascular system of the body.
- Cucurbitaceae family: pumpkin, cucumbers, zucchini, squash. Combination with protein foods slows down gluconeogenesis. The high water content replenishes fluid deficiency. Zucchini and pumpkin have a higher GI, so they should be used with caution, despite the benefits for the body.
- Cowberry. Acts as a diuretic and insulin catalyst, allowing you to control glucose.
- Kalina. Contains invert sugar, which does not require insulin for transport to body tissues.
- Blueberry. Maintains the health of the pancreas, effectively fights edema, regulates glucose absorption, and has a beneficial effect on the vascular system of the visual organs.
- Black currant. Stimulates metabolic and immune processes, saturates the body with vitamins.
Most vegetables have low calorie and GI content and are optimal foods for diabetes
Legumes and cereals
Not all cereals have a low glycemic index, but when cooked (cooking), the GI decreases. Therefore, porridge must be included in the menu of people with diabetes. Legumes help enrich the diet with minerals and vitamins; when consumed regularly, they can inhibit the breakdown of nutrients. Green beans are used in folk medicine as a product that reduces sugar levels.
Cereals: oats, pearl barley, wheat improve metabolism, normalize digestive processes, and replenish micro- and macroelements. In addition, porridge allows you to maintain a feeling of fullness for a long time and reduce the risk of blood sugar changes. Legumes: beans, peas, chickpeas. They have low glycemic activity. The process of absorption of complex carbohydrates does not require insulin. Rich in minerals and vitamins.
Spices
Spices are believed to lower sugar. They do not have a direct effect on the quantitative composition of glucose, but due to their active participation in the process of gluconeogenesis, glucose absorption slows down, so sugar levels remain at the same level. Spices allowed for diabetes include oregano (oregano), cinnamon, cloves, ground pepper (black, red, white), ginger and garlic.
Protein products
Protein foods do not lower sugar, but their correct combination with permitted vegetables helps maintain glucose balance and prevent sudden “jumps” in glycemia. The sources of protein in the diabetic menu are:
- Dietary poultry meat (chicken, turkey). When cooking, it is necessary to remove oily skin from poultry.
- Nuts (hazelnuts, almonds, peanuts). It should be consumed in small quantities so as not to put stress on the weakened pancreas.
- Mushrooms. Despite the low GI, they are considered a heavy, filling food. Allowed for limited use.
- Seafood (mussels, shrimp, crabs) and lean fish. Have minimal effect on blood glucose levels. Enrich the body with protein and minerals (zinc, selenium, calcium, etc.).
Coffee
Scientists have determined that low doses of caffeine help reduce the risk of developing diabetes. The journal Diabetologia published data showing that increasing coffee consumption by one cup per day reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 11%.
But coffee can raise blood glucose levels due to sweeteners, creamers, and flavorings. In some particularly sensitive people, high caffeine levels may affect glucose levels. It is better to monitor the reaction after drinking coffee (even black) to track how this affects the indicators.
The effect of food on blood glucose concentrations
Sugar levels are proportional to the amount of carbohydrates eaten and their rate of absorption into the systemic bloodstream. Carbohydrates are classified into simple (fast) and complex (slow). Simple ones include:
- monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, galactose);
- disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose).
Such components increase blood sugar in a short time, since they are instantly absorbed. Monosaccharides and disaccharides are contraindicated in diabetes. The mechanism for reducing sugar levels is its timely transportation to the tissues and cells of the body to provide them with energy. The hormone insulin delivers glucose, so in its absence or insufficient synthesis, the sugar level increases. Complex carbohydrates or polysaccharides are processed more slowly by the body and the process of increasing sugar is not as accelerated as when absorbing monosaccharides.
Proteins have a lesser impact on glucose levels because they take several hours to be absorbed, broken down, and utilized. Dietary fiber and fiber slow down digestion and inhibit the entry of sugar into the bloodstream. Fats affect glucose absorption in different ways. Animals and refined vegetables in combination with monosaccharides can significantly increase the concentration of glycemia. Thus, in diabetes, preference is given to foods that minimally increase blood sugar. At the end of the 20th century, the concept of the glycemic index of foods was introduced. This is a digital indicator of the rate of absorption of carbohydrates into the bloodstream, measured from “0” to “100”.
It is the glycemic index (GI or GI) that is the main criterion for choosing foods for diabetics.
A high GI corresponds to a mark from 70 to 100. Such food raises blood sugar and disrupts metabolic processes. For people with diabetes, this threatens a sharp deterioration in their health, even leading to hyperglycemic coma. Products with an average index (from 30 to 70 units) are allowed for consumption in limited quantities. The optimal GI value for a diabetic is from 0 to 30. With consistently elevated glucose levels, such foods will not cause harm.
About calorie content
Diabetes mellitus often accompanies the patient's overweight. Obesity can be a cause of type 2 diabetes (non-insulin-dependent) in women or a consequence of poor nutrition in diagnosed diabetes. In addition to the carbohydrate content of a dish, a diabetic patient needs to consider the number of calories in foods. The diet should not be overloaded, so the daily calorie intake should be kept within 2200–2500 kcal.
The percentage of nutrients should be distributed as follows:
- carbohydrates – 45%;
- proteins – 20%;
- fats – 35%.
In addition to the fact that fast carbohydrates increase glucose levels and are potentially dangerous for a diabetic, they are transformed into fats in the liver and stored as fat reserves in the body tissues, increasing the patient’s body weight. The correct diet is determined by three main criteria: the qualitative and quantitative composition of nutrients, the calorie content of dishes, and the glycemic index.
Limited products
Excluding high GI foods from the menu does not mean that you can eat everything else without restrictions. A special feature of the diet is the limited consumption of foods with an average glycemic index. It is not recommended to exclude them completely, but they must be strictly controlled. This applies to both a single meal and the total amount of products of this category entering the body during the day (week).
Popular foods with an average GI:
- lavash, pita, other unleavened flatbreads – 69;
- muesli, unsweetened pastries without filling, pineapples – 67;
- boiled potatoes (“in their jackets”), bananas, melons, raisins – 64–66;
- pizza or pita without meat component – 60;
- persimmon, mango – 55;
- tomatoes, yoghurts – 52;
- buckwheat porridge (without sugar) – 50;
- kiwi, blueberry – 40–43;
- canned beans, corn, peas – 48–42.
Dosed consumption of the listed products will not cause harm to the body and will not increase glucose levels in the analysis.
Food groups that increase sugar
Products prohibited for high sugar:
People who regularly eat fast food are more susceptible to diabetes than others
- pasta, bread, starch, flour, some cereals, grains;
- potatoes, carrots, beets, corn;
- fermented baked milk, cream, yoghurts with fillings, whole milk, cheese;
- some fruits, berries - bananas, grapes, tangerines;
- sugar, honey, chocolate;
- preservatives, smoked products;
- alcohol;
- fish and meat products.
For diabetes of any type, these components should be abandoned. Even consuming small portions can dramatically cause hyperglycemia. You can learn about foods that lower sugar levels from this publication.
Fully or partially limited products
The following are completely excluded from the diet: baked goods made from butter and puff pastry, curd mass, sweet desserts and ice cream, rice, semolina and pasta, as well as milk soups with these cereals. You should not consume sweet juices (grape, apricot, pear), sugar-filled lemonades, preserves and jams.
Not only foods rich in carbohydrates are prohibited, but also fatty ones: fatty broths, duck meat, goose, pork, smoked meats, sausages, fatty fish, canned food with butter, fatty and hot cream sauces.
It is advisable to prepare dishes without salt and sugar and exclude salted cheeses and pickled vegetables. Liver and dishes made from it, egg yolks, honey and spices (pepper, horseradish, mustard) are allowed in limited quantities.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| pineapples | 0,4 | 0,2 | 10,6 | 49 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
| sago | 1,0 | 0,7 | 85,0 | 350 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| glazed cheese | 8,5 | 27,8 | 32,0 | 407 |
| curd | 7,1 | 23,0 | 27,5 | 341 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| sardine in oil | 24,1 | 13,9 | — | 221 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| lemonade | 0,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 26 |
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| Fanta | 0,0 | 0,0 | 11,7 | 48 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
What happens if you don't follow the diet?
Failure to follow a diet can cause serious consequences. Among them:
- Diabetic coma is the body's reaction to a sharp increase in glucose. Accompanied by confusion, breathing problems, a strong odor of acetone, and lack of urination. Coma can occur with any type of diabetes.
- Ketoacidosis - provokes the appearance of a large amount of waste in the blood. A characteristic symptom is a disruption of all functions in the body, which leads to loss of consciousness of a person. Usually appears in type 1 diabetes.
- Hypoglycemic coma - occurs due to a sharp decrease in glucose. This phenomenon is provoked by alcohol consumption, non-compliance with the diet, and the systematic use of sweeteners. Occurs in all types of diabetes.
You should not use sweeteners often or in large quantities. They have many side effects that lead to various pathologies. It is safe to use them no more than 1-2 times a week.
Products that increase blood sugar should absolutely not be consumed by people who suspect hyperglycemia. A small amount can provoke a sharp increase in glycemia. A person may lose consciousness and face the development of various pathologies.
How to stop vomiting in a child, read here.