Haptoglobin is a blood plasma protein that captures hemoglobins released during the breakdown of red blood cells and transports molecules that contain iron. An important function of this protein is to ensure economical consumption of iron reserves. In the case of intravascular hemolysis, haptoglobin protects the kidneys from negative effects. In addition, it is produced in response to infection in the body. In inflammatory diseases, protein works as an antioxidant, inhibits the growth of certain bacteria, and reduces cell damage.
In a healthy body, the process of red blood cell renewal constantly occurs. Within 24 hours, approximately one percent of the total number of red blood cells circulating in the bloodstream is destroyed. If the number of destroyed cells doubles the norm, haptoglobin will completely disappear from the serum. The absence of this protein entails the sedimentation of hemoglobin molecules in the kidneys. A large amount of hemosiderin and ferritin is formed. The body strives to remove excess iron through urine. These processes cause kidney dysfunction. In the presence of inflammatory processes, a blood test for haptoglobin
will show an increased level, but it is not related to the concentration of free hemoglobin.
general characteristics
Haptoglobin is a protein of the acute phase of inflammation, synthesized mainly in the liver, as well as in adipose tissue, lungs and binds free hemoglobin released from red blood cells. It is stimulated by inflammatory mediators, with a peak increase observed on days 4–6 and normalizes within 2 weeks after removal of the stimulating factors. With hemolysis of erythrocytes, the level of plasma haptoglobin decreases rapidly, which, in the absence of other causes, is a sensitive marker of intravascular hemolysis. Normally, about 1% of red blood cells are destroyed and removed from circulation per day. An increase in this amount to 2% leads to the complete disappearance of haptoglobin. The haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex is quickly taken up from the circulating blood by reticuloendothelial cells, thereby preventing or minimizing the removal of hemoglobin and iron from the body. Haptoglobin prevents kidney damage, since free hemoglobin is excreted in the urine and toxic concentrations of iron cause renal dysfunction. Haptoglobin plays an important role in the control of local inflammatory processes and is a natural bacteriostatic agent in infections with Fe-dependent bacteria (for example, Escherichia coli). Low levels of haptoglobin are observed during pregnancy and in newborns, as well as during estrogen therapy, including oral contraceptives.
Indications for the study
The test is prescribed if the patient has symptoms of hemolytic anemia. These include the appearance of a yellowish tint to the skin, pallor, darkening of urine, and general weakness. It is also carried out when there is a possibility of hemolysis (for example, in patients with an artificial heart valve, in case of damage to a number of toxic substances, during blood transfusion, hemodialysis). The study is carried out when examining patients with liver pathologies, reduced hemoglobin or the number of red blood cells.
The study is used for:
- establishing the cause of anemia;
- monitoring patients with artificial heart valves;
- diagnosis of intravascular hemolysis;
- liver function assessment;
- identifying acute phase reactions;
- monitoring patients after blood transfusion.
Most often, the test results are used to diagnose hemolytic anemia, and also to assess the degree of their severity.
Interpretation:
- Acute infectious diseases, trauma, necrosis, surgery, sepsis, corticosteroid therapy, biliary obstruction, nephrotic syndrome, malignant tumors, plasmacytoma, diabetes mellitus, collagenosis, Hodgkin's disease, fasting.
- Congenital ahaptoglobulinemia, hereditary spherocytosis, hemolytic disease, autoimmune hemolytic anemia; ineffective erythropoiesis, pregnancy, neonatal period, liver disease (cirrhosis), artificial heart valves, intense sports.
Sample result (PDF)
Interpretation of results
The level of haptoglobin depends on liver function, the presence of inflammation and a number of other factors. It can be affected by many medications.
An increase in the amount of protein is typical for:
- development of a malignant process;
- large-scale tissue damage due to injuries, burns, surgical interventions;
- taking medications containing hormones;
- obstruction of the bile ducts.
Reduced protein levels are observed when:
- development of endocarditis;
- genetic diseases;
- artificial heart valve;
- liver pathologies.
About the normal level of haptoglobin in the blood
Normally, haptoglobin successfully performs its assigned functions. The table shows the age norms for this protein.
| Age | Norm, mg/l |
| Infants up to six months of age | 50 – 480 |
| Children from 6 months and teenagers up to 16 years | 250 – 1380 |
| Adults from 16 to 60 years old | 150 – 2000 |
| People over 60 years old | 350 — 1750 |
The specialized medical literature may provide other normal ranges for haptoglobin. this is because each laboratory has its own reference values. To determine the concentration of haptoglobin, blood serum taken on an empty stomach is analyzed using the immunoturbidimetric method. To identify this glycoprotein, modern high-precision biochemical analyzers are used.
What does an increase in haptoglobin indicate?
The concentration of haptoglobin increases in the following diseases and conditions:
- Large focal myocardial infarction;
- Active rheumatic carditis;
- Acute phase of the inflammatory process;
- Presence of a tumor;
- Nephrotic syndrome, expressed in severe kidney pathology due to impaired metabolism of lipids and proteins;
- Lymphogranulomatosis;
- Rheumatoid polyarthritis;
- Stagnation of bile and disturbance of its excretion;
- Hormonal therapy with corticosteroids.
General information
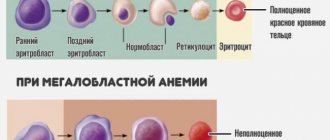
Hemoglobin is part of red blood cells and is involved in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Red blood cells exist for 120 days, after which they are destroyed. In the vessels, normally only a small part of them is destroyed (the main number of these cells disintegrate in the liver and spleen). Iron from broken cells is used by the body in the formation of new red blood cells. If free hemoglobin is not bound, it enters the kidneys and can damage them.
The destruction of large numbers of red blood cells in the bloodstream leads to an increase in the amount of free hemoglobin. Haptoglobin binds it, and accordingly, the concentration of this protein decreases. However, its synthesis does not increase. Therefore, protein deficiency is an important indicator of intravascular hemolysis.
Description
A stool examination aimed at identifying hidden bleeding from parts of the gastrointestinal tract can also be used to screen for colorectal cancer.
Allows you to detect the presence of hemoglobin and haptohemoglobin complex in stool even in cases where visually the color of stool is unchanged, and red blood cells are not detected during microscopic examination of stool. Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract is one of the common problems faced by practicing physicians of all specialties, but the greatest danger is posed by small “hidden” bleedings that cannot be detected without a special study, and often these small bleedings are markers of including intestinal cancer in apparently healthy people.
The ColonView study is carried out using an immunochemical method, which significantly increases sensitivity, and unlike other tests (gavaiac and benzidine), which is specific exclusively to human hemoglobin, which means it does not require adherence to a strict diet, refusal of meat products, some vegetables and fruits that contain large amounts of ascorbic acid, catalase and peroxidase (for example, cucumbers, cauliflower, use of horseradish seasonings).
Fecal occult blood test (ColonView)
Rapid test for the qualitative detection of hemoglobin (Hb) and hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex (Hb/Hp) in stool, used for screening of precancerous diseases and colon cancer.
Synonyms Russian
- Immunochemical fecal occult blood test
- Analysis for hemoglobin and hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex in stool
English synonyms
- Hb and Hb/Hp Stool Test
- Fecal Immunochemical Test
Research method
Immunochromatography.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Cal.
How to properly prepare for research?
- The study is carried out before performing sigmoidoscopy and other diagnostic procedures in the intestines and stomach.
General information about the study
Colon cancer ranks second in the structure of female cancer morbidity, second only to breast cancer, and third in the structure of male morbidity after prostate and lung cancer in Russia. Various methods may be used to screen for precancerous lesions and colon cancer, including:
- direct visualization methods: colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy;
- indirect imaging methods: computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), capsule endoscopy, double-contrast barium enema;
- stool examination: stool occult blood test (guaiac test and immunochemical tests), DNA test in stool.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, imaging techniques require special bowel preparation, which is often uncomfortable and potentially dangerous for the patient. In comparison, fecal occult blood testing is a painless and much more convenient method for the patient. On the other hand, it is enough to carry out a colonoscopy once every 10 years, while a stool test must be taken every year. In general, we can say that the choice of a screening test is determined by the patient's preferences, the availability of the medical center and the doctor's awareness of new methods. One such new colon cancer screening method is the ColonView occult blood test. This test has several advantages over the traditional guaiac test.
The guaiac occult blood test is the most common method of screening for colon cancer today. It allows you to detect hemoglobin based on the pseudoperoxidase activity of heme in hemoglobin. Thus, the guaiac test detects blood by the presence of heme. A significant disadvantage of the method is:
- low specificity and the need to follow a diet; when consuming foods containing heme or other components that exhibit peroxidase activity (red meat, broccoli, horseradish, turnips, radishes, etc.), the test result may be false positive; this simple test thus requires quite complex preparation;
- low sensitivity (20-50%); Due to the low sensitivity of a single test, it is usually recommended to test 3 stool samples.
The ColonView study is one of the immunochemical methods for determining occult blood in feces (FIT, from the English fecal immunochemical test). Unlike the traditional guaiac test, FIT tests use antibodies specific to human globin. We can thus say that FITs detect blood by the presence of globin. Due to this, immunochemical tests for occult blood are more specific than the traditional guaiac test and do not require diet in preparation for the test.
A feature of the ColonView study that distinguishes it from all other FITs is the use of antibodies to both hemoglobin and the hemoglobin-haptoglobin Hb/Hp complex. When red blood cells are destroyed, hemoglobin or its protein components (alpha and beta globins) bind to a special protein, haptoglobin, which prevents their further oxidation. The Hb/Hp complex is more resistant to acid and proteolytic enzymes during passage through the gastrointestinal tract, which makes the ColonView assay even more sensitive.
Thanks to the improved sensitivity of the ColonView assay, one or two stool samples may be sufficient for analysis. It should be noted, however, that 100% sensitivity will be achieved by analyzing three stool samples.
Like other fecal occult blood tests, ColonView should be repeated once a year. Some doctors recommend a combination of screening tests for their patients, such as a flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 years combined with one of the immunochemical stool occult blood tests (ColonView) every 3 years.
Some limitations of the ColonView study should be noted:
- Although some investigators have attempted to use this test to diagnose small bowel bleeding, ColonView is currently only approved for the detection of occult lower GI bleeding;
- The test is intended to screen patients at average risk for colon cancer; it does not replace or change the algorithm for diagnosing colon cancer in patients at high risk.
Some features of interpreting the result of a ColonView study:
- a positive test result does not always indicate the presence of precancerous diseases or colon cancer; with other sources of bleeding (diseases: hemorrhoids, angiodysplasia, anal fissure; use of medications: aspirin, warfarin, any means for use per rectum; menstrual bleeding), the test result can also be positive (false positive);
- a negative test result does not completely exclude precancerous diseases or colon cancer; This is because some tumors bleed intermittently rather than continuously, and because the blood may not be evenly distributed in the stool sample.
Given these features, the result of the analysis should be interpreted taking into account additional clinical, laboratory and instrumental data.
What is the research used for?
- For screening of precancerous diseases (adenomas) and colon cancer.
When is the study scheduled?
- Every year, starting from the age of 50, during a preventive examination of the patient;
- every 3 years starting at age 50 when combined with flexible sigmoidoscopy.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
Positive result:
- the presence of hemoglobin or hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex in the stool (with colon cancer and other sources of bleeding from the lower digestive tract).
Negative result:
- norm;
- false negative result (in the presence of neoplasms that bleed periodically, with uneven distribution of blood in the stool sample).
What can influence the result?
- The nature of bleeding from neoplasms
- Presence of menstrual blood
- Taking certain blood thinners (aspirin, warfarin)
Important Notes
- The test is intended only to detect occult bleeding from the lower digestive tract.
- A positive test result does not always indicate the presence of precancerous lesions or colon cancer.
- A negative test result does not completely rule out precancerous lesions or colon cancer.
Also recommended
- Fecal occult blood test
- Coprogram
- Cytological examination of material obtained during endoscopy (FGDS, bronchoscopy, laryngoscopy, cystoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy)
- Laboratory markers of colon cancer
Who orders the study?
General practitioner, therapist, gastroenterologist, oncologist.
Features of haptoglobin
The behavior of haptoglobin sometimes differs from the functioning of similar acute phase proteins. Since it is produced by the liver parenchyma, its hepatocytes contribute to an increase in HPT in the blood. But a blood biochemistry test does not always confirm the fact of an increase in haptoglobin concentration.
With hemolysis accompanying acute inflammatory reactions, the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is very high. It requires the creation of heavily dispersed complexes and their transportation into the macrophage system. In this case, the concentration of Haptoglobin should decrease. To obtain an objective picture without taking into account the effect of hemolysis, it is important to compare the results obtained with similar tests obtained when diagnosing other proteins from the category of acute-phase proteins.
Author of the article:
Shutov Maxim Evgenievich |
Hematologist Education: Graduated from Kursk State Medical University in 2013 and received a diploma in General Medicine. After 2 years, he completed his residency in the specialty “Oncology”. In 2021, she completed postgraduate studies at the National Medical and Surgical Center named after N.I. Pirogov. Our authors