According to statistical studies, 15% of menstruating women suffer from anemia of varying severity, and not every one of them notes signs of this insidious disease.
And among pregnant women, the percentage of those suffering from a lack of hemoglobin in the blood doubles, so during this period of a woman’s life it is important to regularly take blood tests to detect anemia.
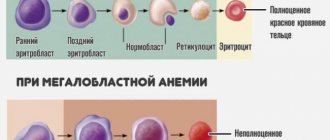
Iron deficiency anemia is most often diagnosed when the hemoglobin protein contains an insufficient amount of iron. However, the human body is designed in such a way that when there is a lack of iron, internal reserves are primarily used, so anemia does not always manifest itself with characteristic symptoms in the initial stages of the disease.
The effect of hemoglobin on the female body
The main task of iron-containing protein is to supply every cell of the body with oxygen and, as a result, ensure the normal functioning of internal organs and systems. Hemoglobin production and menstruation are interdependent processes. For any woman, blood loss, including in the form of spotting, means a decrease in iron, the deficiency of which is dangerous:
- the occurrence of various types of skin pathologies;
- blood pressure disorders;
- rapid fatigue;
- brittle hair and hair loss;
- decreased immunity and, as a result, the body’s susceptibility to any infectious diseases;
- the appearance of problems of the reproductive system.
To avoid this effect, a few days before the onset of menstruation, the hemoglobin level rises sharply, which makes the blood more viscous and prevents heavy bleeding. The onset of menstruation is accompanied by a decrease in hemoglobin: the blood becomes liquid and gradually leaves the vagina. Such changes in the level of hemoglobin in the blood allow you to regulate the menstrual cycle. If the deviation exceeds any norms, this may contribute to a malfunction of some systems, including the reproductive system, and the menstrual cycle will be completely disrupted (there will be a delay or, conversely, premature bleeding).
Can hemoglobin decrease during menstruation? Undoubtedly. A decrease in the content of this protein in the blood is both a cause and a consequence of menstruation. A decrease in hemoglobin levels helps to dilate blood vessels and reduce the viscosity of blood secretions, as a result of which menstruation occurs normally. As menstruation progresses, the amount of hemoglobin in the blood will become even less, because it will leave the body along with menstrual mucus.
Why should you go to the gynecologist if you have anemia?
When diagnosing anemia in women, it is mandatory to visit a gynecologist and undergo appropriate diagnostic procedures: examination using gynecological mirrors, colposcopy, ultrasound of the uterus and, if necessary, tests. First of all, anemia can develop in a woman due to heavy menstruation, when a large amount of blood is lost during menstruation, and the menstruation itself lasts longer than usual. In this case, properly selected hormonal therapy aimed at regulating hormonal levels in the body can help. A test for sex hormones can help identify dishormonal disorders.
When identifying anemia in a woman, it is important to find the cause that provoked this disease. It is its elimination that will allow you to quickly get rid of the pathology. In women, the following diseases often lead to recurrent uterine bleeding, which can affect the amount of iron in the blood:
- endometriosis – proliferation of cells of the inner layer of the uterine mucosa, their localization in atypical tissues or organs;
- fibroids and polyps - benign neoplasms in the uterine cavity;
- malignant changes in the uterus and other female genital organs.
Timely detection of these diseases is a factor in their successful treatment and, as a result, relief from anemia, subject to an integrated approach to therapy.
How to determine hemoglobin level
The simplest and most common option is to go to the nearest clinic and get your blood tested. It is very important not to have breakfast on this day: this test must be taken in the morning and always on an empty stomach, 8-12 hours after the last meal. The doctor will take blood from your finger, after which it will be sent to the laboratory for testing. A few days later (sometimes on the day of the tests), you will be presented with a report - a form with the results, which will indicate the following data:
- hemoglobin concentration;
- total number of leukocytes and erythrocytes;
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
We need exactly the first indicator, which can be presented in the following units of measurement: g/l, U/l or µmol/l. A woman’s blood should be saturated with this substance within 120-140 grams per liter, but if you were tested during your period, lower concentrations are possible. Moreover, the norm of the same results of a general blood test for people of different ages will be different. Only a doctor can evaluate and decipher the results obtained, so you should not rely only on your own conclusions.
Please note that to identify problems in the body or any diseases, a general blood test is required over time. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to do this at least once a year, however, if any suspicion of certain diseases is detected, the doctor may prescribe and more frequent laboratory visits.
It is noteworthy that you can check the level of hemoglobin in your blood even at home. Similar to visits to the doctor, the patient should be tested on an empty stomach in the morning. To get accurate results, avoid smoking or drinking alcohol the day before, as well as exercising or exercising. Women planning to find out their hemoglobin content at home have several “tools” to choose from:
- Rack with test tubes and glass scale. The blood is sent into a test tube and diluted with hydrochloric acid. After a few minutes, the solution will acquire a new shade, after which you need to add distilled water (no more than 10-40 milliliters) to it. The results obtained are compared on the scale provided in the kit.
- Test strips. Read the instructions for use carefully and use one test strip from the package to find out the result.
Blood condition after menstruation
The state of the blood, or more precisely, the level of hemoglobin (the number of red blood cells) after menstruation is an important indicator of health. To make sure that the body is working normally or, on the contrary, there are some abnormalities, a woman can do a blood test for hemoglobin before and after the start of menstruation. During the normal functioning of all organs and systems of the female body, a cyclical change is observed within the permissible limits of the hormonal level. During critical days, it is not recommended to donate blood, since the result will probably not be entirely accurate: the hemoglobin level during menstruation is always underestimated, but from this indicator it is difficult to determine which -reasons for concern.
During critical days, the female body loses approximately 15–30 mg of iron. This is a normal phenomenon, which indicates that hemoglobin has decreased slightly. A pronounced change in the concentration of iron-containing protein is especially characteristic of women who have heavy periods or a long duration of menstruation (about 7 days). However, even in this case, a healthy body immediately makes up for the loss.
The only thing doctors recommend focusing on is the hemoglobin level after menstruation (whether it falls or, conversely, is above normal)
- The norm is considered to be a decrease to 110 g/l. If it is lower, this may indicate signs of anemia.
- In the absence of any pathologies, just a few days after menstruation, this figure increases to the usual figures for a woman - 120–140 g/l.
- Detection of hemoglobin concentrations above normal (about 150 g/l) is not uncommon among female smokers. It has been proven that tobacco tar activates this kind of protective reaction of red blood cells to avoid oxygen starvation.
To maintain the balance of blood cells, it is recommended to eat more iron-containing foods during menstrual periods. As a rule, 3-4 days after the start of menstruation, hemoglobin returns to normal. If a blood test is done after two weeks, but your hemoglobin levels are still low, you should consult a doctor. The manifestation of problems associated with abnormal blood conditions is evidenced by symptoms during menstruation such as a feeling of weakness, dizziness, nausea and difficulty in the gastrointestinal tract. The nature of the bloody discharge can also indicate a disorder: heavy and prolonged bleeding or, conversely, scanty and dark discharge - a signal that you urgently need to visit a gynecologist.
Low hemoglobin during menstruation
If the usual level of hemoglobin in a woman’s blood, even outside of menstruation, is very low, then she is probably familiar with painful sensations and extremely poor health on menstruation days. These representatives of the fairer sex, regardless of how much hemoglobin drops during menstruation, during menstruation regularly have to deal with:
- general weakness;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- low labor productivity;
- other signs of poor health during menstruation.
As a rule, the menstrual cycle of these young ladies is longer than that of others, as a result of which menstruation days can drag on for a week or longer, not without pain and intense discharge. What is this connected with? It's simple. Low hemoglobin during menstruation and throughout the menstrual cycle indicates that the body does not have enough microelement such as iron, which means that fragility of blood vessels, in particular in the uterus, cannot be ruled out. If they are damaged, bleeding is observed for a long time, and additional blood loss only aggravates the situation: oxygen starvation - the risk of hormonal imbalance (so constant shifts in menstruation are also quite possible).
Does hemoglobin drop during menstruation if everything is in order with the body? If the situation is somewhat different, and outside of menstruation a woman has a normal hemoglobin concentration, and its decrease occurs only on critical days, this is absolutely normal. Doctors confirm this, calling this reaction a natural process. Moreover, on the eve of the planned menstruation, appetite often increases, so feel free to pamper your body with foods rich in:
- Iron. Products such as pork or chicken liver, beef or lamb meat, oysters, mussels and other seafood, as well as chicken yolk, lentils, peanuts, buckwheat and wheat bran are especially good in this regard.
- Vitamin B: Carrots, cauliflower, green vegetables, nuts, sardines, oatmeal and many other foods in your refrigerator are complete sources of B vitamins.
At the end of menstruation, low hemoglobin can remain stable for about a week, after which it quickly returns to normal without any treatment. All you need to do is ensure a healthy diet. The body should be monitored more closely if the level of iron-containing protein has decreased significantly - to 110 g / l or lower.
The relationship between hemoglobin levels and menstruation has long been proven scientifically. Firstly, the appearance of menstruation is caused by the fact that the uterus gets rid of the endometrium, as a result of which its renewed layer is formed. Secondly, each new menstrual cycle is accompanied by a shortage of new blood in the body, which must be replenished within seven or more days. In other words, low hemoglobin after menstruation or during menstruation is normal, although if even after two weeks nothing has changed or the protein concentration continues to decrease, you should be examined by a gynecologist.
Low hemoglobin during menstruation
Iron protein levels are usually low during menstruation. But this condition is normal. To accurately assess the result, it is not recommended to take a blood test during menstruation, since the interpretation may be incorrect. With iron deficiency in the body, monthly bleeding lasts a long time and is painful. This happens due to hormonal imbalance caused by insufficient oxygen supply to tissues.
Iron deficiency increases the likelihood of damage to blood vessels, which are found in large numbers in the uterus. When hemoglobin protein is low, the blood becomes too thin. Therefore, the discharge lasts longer, is more intense, and causes a lot of unpleasant sensations. With normal iron protein levels, a temporary drop is felt within a week after the end of menstruation. Sometimes complete restoration of blood composition occurs faster. If recovery does not occur within two weeks, you should consult a doctor. This condition indicates the presence of diseases and disorders in the body.
High hemoglobin during menstruation
Excessive concentrations of iron-containing proteins in the body during or after menstruation affect only a small percentage of women and can be due to a variety of reasons. Symptoms in this case include:
- weak discharge during menstruation;
- sleep disturbance;
- frequent dizziness;
- pain in the heart area and more.
Such symptoms are the result of excessive oxygen content in the blood, which increases the load on many internal organs and, first of all, the heart.
The increased rhythm of its work causes pain and provokes disruptions in the menstrual cycle: menstrual periods may begin earlier than scheduled or on time, but with minimal discharge. It is very important that such signs do not recur many times, otherwise you subsequently risk complications in the form of serious diseases: in addition to increased blood pressure and a significant change in blood viscosity, vascular thrombosis may occur, cholesterol plaques may form, and even myocardial infarction may occur. Thus, if your hemoglobin level increases during or after your period, doctors may prescribe special medications to thin the blood: this allows you to resume menstruation and prevent complications.
There are often situations when women are looking for independent ways to quickly increase hemoglobin: the menstrual cycle for these young ladies is extremely difficult, since constant weakness does not allow them to work normally or do any other things. In some cases, representatives of the fairer sex even resort to medical help, although quite often it is enough to simply eat as many foods containing iron as possible between menstrual periods.
Increased hemoglobin during menstruation
During menstruation, increased concentrations of iron-containing protein are rare. A large amount of iron in the body increases the flow of oxygen and increases the load on the cardiovascular system. This causes chest pain in the heart area. Unpleasant sensations develop due to heart rhythm disturbances and increased contraction frequency. Sometimes excess iron in the body provokes digestive problems.
With a high level of hemoglobin index, menstruation begins earlier than expected. Due to the high viscosity of the blood, the discharge is scanty. After symptoms persist for several months, the condition becomes normal. A high concentration of iron-containing protein is normal in adolescence, when the body has not yet fully formed. But if the hemoglobin factor increases in a woman of reproductive age, a doctor’s consultation is necessary. This condition may be a symptom of heart disease or diabetes.
Normal hemoglobin during menstruation
It is well known that the norm of hemoglobin outside menstruation can vary from 120 to 140 g/l. The only exceptions are athletes or those who like to lift weights in the fitness room: for them this figure can easily reach 160 g/l, and this is not a sign of pathology. A deviation can also be observed in those who smoke: in this case, the protein concentration increases to 150 g/l.
A natural phenomenon is considered to be similar to other days of the menstrual cycle or reduced hemoglobin during menstruation: the norm is about 110-130 g/l, depending on the age of the woman. In particular, we present to your attention the average hemoglobin indicators by age, which are called normal:
- maturing organism (11-15 years) - 110-130 g/l;
- young girls (15-18 years old) - 115-135 g/l;
- girls aged 18 years and older - 120-140 g/l.
With large blood loss or prolonged menstruation, this indicator can be at the level of 105-115 g/l, which is understandable from a physiological point of view.
Young mothers whose hemoglobin level drops to a minimum level deserve special attention: to 110 g/l during the first and third trimester, and also to 105 g/l during the second. It is believed that pregnancy is proceeding normally if this indicator does not exceed 120 g/l. This is due to the fact that carrying a baby is accompanied by a more active consumption of iron, which goes towards the formation of the placenta and the development of the embryo. Moreover, the volume of blood in a woman’s body during pregnancy increases by at least 50%, due to which the bone marrow performs its functions slowly and cannot provide the blood with hemoglobin in the usual amount.