Lesson No. 13: “Nursing process in atherosclerosis.”
Task 1. Give a definition.
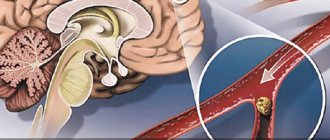
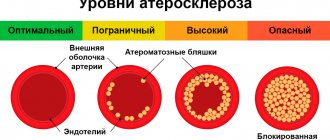
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease of the arteries of the elastic and muscular-elastic type, resulting from disturbances in lipid and protein metabolism and accompanied by the deposition of cholesterol and some fractions of lipoproteins in the lumen of blood vessels
Hypercholesterolemia is a pathological condition in which there is an abnormal increase in cholesterol levels in the blood
Ischemia is a local decrease in blood supply, often caused by a vascular factor (narrowing or complete obstruction of the artery lumen), leading to temporary dysfunction or permanent damage to a tissue or organ.
Hypodynamia is a violation of body functions (musculoskeletal system, blood circulation, breathing, digestion) with limited physical activity and decreased strength of muscle contraction.
Task 2. Indicate the main complaints of patients with atherosclerosis of vessels of various locations.
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels: They are expressed in asthenia, which is accompanied by weakness, fatigue, lethargy and deterioration of concentration and attention. In isolated cases, sleep disturbances occur in the form of insomnia or daytime sleepiness. Most patients complain of headaches and tinnitus. The ability to remember new information is noticeably reduced.
Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities: inability to walk without pain and stops. Atherosclerotic vascular damage leads to significant circulatory impairment and the appearance of “intermittent claudication” with pain in the calves
Atherosclerosis of mesenteric vessels: Sharp burning or sharp pain in the abdomen (in the epigastric region), usually at the height of digestion, which lasts 1-3 hours, sometimes the pain is briefly relieved by nitroglycerin. The pain is accompanied by bloating, constipation, and belching. In the future, foul-smelling diarrhea 2-3 times a day may occur. with undigested pieces of food, decreased secretory function of the stomach. Reflex pain in the heart is possible. On examination - flatulence, high diaphragm, decreased or absent peristalsis, systolic murmur in the epigastrium. Gradually, dehydration occurs and skin turgor decreases.
Task 3. List the foods recommended for consumption in atherosclerosis. Vegetarian soups based on vegetable infusions. First courses should be served with fresh herbs. Parsley and dill help reduce swelling, which often affects patients. The menu for atherosclerosis should include vegetarian beet soup; this dish is rich in fiber and vitamins. Dietary types of meat. You should avoid eating beef, lamb, and pork, especially fatty varieties. It is useful to include poultry (chicken, turkey) and rabbit in the menu. Sometimes you can eat lean veal. Meat should be boiled, stewed or baked. Fish. This product should be included in the diet, as it is a source of protein and healthy omega acids. What fish can you eat if you have atherosclerosis? Preference should be given to low-fat types. Sea fish is more useful than river fish. Vegetable dishes from beets, cabbage, zucchini, eggplant. They can be boiled or stewed. Nutrition for atherosclerosis involves daily consumption of raw vegetables. Salads made from cucumbers and tomatoes are healthy, but they should not be flavored with mayonnaise. Vegetable oils should be used as a dressing. Products from unrefined cereals. They can be consumed in the form of porridges and side dishes. Fruit drinks, compotes, juices (except grape). You can also drink weak black or green tea. Fruits.
List foods that are not recommended for consumption in atherosclerosis.
any conservation; pickled vegetables; baking; salted fish (for example, herring); sausages (especially smoked and with fat); lard and other animal fat; rich broth soups, fatty meat broths; smoked meat and fish products. Alcohol is contraindicated in all patients with vascular pathologies. You should also avoid drinking coffee and strong black tea. These drinks often lead to hypertension.
Task 4. List the factors contributing to the occurrence of atherosclerosis (at least 5).
· Poor nutrition . Constant consumption of food with a high content of fats and cholesterol is lard, eggs, pork meat, fried foods, ghee, poultry skin, etc. (increasing their level in the blood and the risk of developing atherosclerosis);
· Obesity (excessive deposition of fat in the body leads to its deposition in the walls of blood vessels);
· Hereditary predisposition (as a result of a congenital deficiency of certain enzymes involved in the breakdown of fats, their level in the blood increases and is deposited in the walls of blood vessels);
· Male sex (women are protected to a certain extent by female sex hormones); · Smoking (tobacco contains substances that damage the walls of blood vessels, which increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis);
· Diabetes mellitus (high blood sugar leads to damage to blood vessels, disruption of fat metabolism, towards an increase in fat and, as a result, the possible development of atherosclerosis);
· Old age (associated with lifestyle, less physical activity, leading to the accumulation of fat, decreased fat burning, obesity and its deposition in the walls of blood vessels);
· Hormonal changes in the body (in persons with weakened thyroid function, cholesterol levels increase);
· High blood pressure (as a result of this disease, damage to the inner wall of the arteries occurs, leading to the deposition of cholesterol in these damaged areas);
· Chronic alcohol consumption (alcohol disrupts the function of the liver, which has many functions, one of which is the breakdown of fats, resulting in increased accumulation in the blood and deposition in the walls of blood vessels);
· Psycho-emotional stress (increases cholesterol levels in the blood, damage to the arterial wall due to its toxic effect and its deposition on it);
· Menopause (the hormone progesterone is produced, which increases the formation of fat in the female body);
· Coronary heart disease (leads to disruption of the structure of the vascular wall and the loss of cholesterol into it, followed by the formation of an atherosclerotic plaque).
Task 5. Write the contents of an emergency first aid kit when taking blood for HIV.
70% solution of medical alcohol; 5% alcohol solution of iodine; Antibacterial adhesive plaster (minimum size 1.9 cm × 7.2 cm) – 3 pcs.; Two sterile bandages measuring 10 cm × 5 m; Sterile gauze wipes with a minimum size of 14 cm × 16 cm – 10 pcs. The listed products must be packaged in a container made of material that is resistant to repeated treatments with disinfectants.
Task 6. Solve the problem.
Patient T., 60 years old, is being treated in the therapeutic department with a diagnosis of cerebral atherosclerosis, CNC 2.
Nursing examination data: complaints of memory loss, dizziness, headache, insomnia, constipation. Has no other complaints.
Considers himself sick for about 20 years, the disease began gradually. She noted a significant deterioration in her condition since the onset of menopause.
He has been smoking since the age of 30 (half a pack of cigarettes a day), prefers fatty foods when eating, and does not follow a diet. She worked as an accountant, is currently retired, and leads a sedentary lifestyle. Doesn't drink alcohol. Heredity is aggravated by obesity, ischemic heart disease, hypertension.
Objectively: general condition is satisfactory. It is difficult to navigate in time and space. Willingly and in detail talks about long-past events, but does not remember what happened yesterday.
The position in bed is active. The skin is dry, turgor is reduced. Height – 165 cm, weight – 76 kg. There is no visible enlargement of the lymph nodes. There is no skeletal deformity. There is no swelling.
The chest is of a normal shape, symmetrical, both halves evenly participate in the act of breathing. NPV=19 per minute. Auscultation reveals vesicular breathing, no wheezing. Heart sounds are muffled, rhythmic, heart rate = 78 beats per minute, blood pressure = 140/95 mm. rt. Art. Pulse 78 per minute, rhythmic, satisfactory filling and tension, the same in both arms.
The patient feels a sense of hopelessness, shows no interest in her own health, and does not believe in the success of treatment.
Tasks:
1) Identify the patient’s impaired needs and problems;
2) Define goals of care and model of care;
3) Create a nursing intervention plan with motivation.
Satisfaction of needs is impaired : move, sleep, eat, drink, rest, work, communicate.
Real problems : constant headache, weakness, sweating, sleep disturbance, anxiety about your future.
Potential problems: deterioration of condition associated with the development of coronary artery disease.
Priority problem : headache
Short-term goal : The patient will notice a decrease in headache pain after 3 days of treatment. Long-term goal: Patient will report headache-free status by discharge and demonstrate knowledge of preventing worsening of condition
| Actions | Rationale |
| Call a doctor | To provide qualified assistance |
| Calm down, unfasten tight clothing, provide access to fresh air, give a comfortable position | Psycho-emotional relief, reduce hypoxia |
| Measure blood pressure, calculate pulse, respiratory rate | Condition monitoring |
| Give 100% humidified oxygen | Reduce hypoxia |
| Give 1 tablet of nitroglycerin (0.0005 g) under the tongue. If there is no effect after 3 minutes, repeat 3 times under the control of blood pressure and heart rate | To relieve spasm of the coronary arteries |
| Give Corvalol or Valocordin (25-35 drops), or valerian tincture (25 drops) | Relieve emotional stress |
| Place mustard plasters on the heart area, hot water bottles on the hands | Distraction procedure |
| Give 0.25 gaspirin orally, chew slowly | To prevent thrombosis |
| Take a 10-lead ECG | For status monitoring |
Possible causes of the disease
It is impossible to name one single reason leading to atherosclerotic restructuring of the artery wall and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Most researchers agree with the fact that atherosclerosis is based on a violation of fat metabolism (more precisely, cholesterol esters) at the level of genetic predisposition. Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a known disease. It is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a decreased rate of clearance of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from the bloodstream due to mutations in the specific LDL receptor gene.
In patients with FH, there is an increase in the blood level of total cholesterol and cholesterol associated with LDL, and the development of atherosclerotic disease. Moreover, familial hypercholesterolemia is the most common genetic disease due to a mutation of one gene (monogenic disease).
Classification of forms of the disease
Atherosclerosis is a systemic disease that affects all arteries, however, depending on the predominance of the severity of atherosclerosis in a particular group of vessels, it is divided into:
- atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries (causing coronary heart disease and angina, which can result in myocardial infarction),
- atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries (causing chronic insufficiency of cerebral blood flow, which can result in a stroke),
- atherosclerosis of the aorta, iliac arteries and arteries of the lower extremities (causing intermittent claudication, which can result in gangrene of the lower extremity or fingers),
- atherosclerosis of the visceral branches of the aorta (impaired blood flow in the internal organs, which can result in infarction of the intestine, kidney, etc.),
- multifocal atherosclerosis (damage to several of the above groups of vessels).