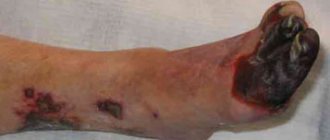
The main cause of narrowing of the carotid arteries is atherosclerosis. As the disease develops, atherosclerotic plaques are formed, consisting of cholesterol, calcium and fibrous tissue. They increase in volume, as a result of which the arterial lumen significantly narrows. This disrupts normal blood flow. When the plaque is localized in the lumen of the carotid arteries, cerebral circulation is seriously affected, which can lead to complications and even death. In this case, the patient is indicated for carotid artery stenting.
The cause of age-related changes in the vessels of the neck
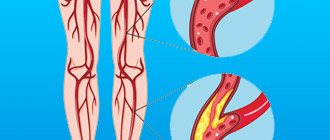
Throughout life, the human body is affected by many negative factors. The environment, lifestyle, and foods consumed play an important role. With excessive consumption of foods high in cholesterol, atherosclerotic plaques form. As you age, they grow, causing partial blockage of the arteries, a condition called stenosis.
Another reason for age-related changes in the vessels of the neck is a decrease in the synthesis of collagen and elastin by the body. Vascular tissues become less elastic and more susceptible to negative influences.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis
The disease may not manifest itself in any way in the early stages. In most patients, the first sign of pathology is a stroke. But atherosclerosis can be recognized by indirect symptoms:
- feeling of weakness, tingling only on one half of the body (right/left);
- inability to control the motor activity of the arm/leg;
- temporary loss of vision in one eye;
- slurred speech.
Symptoms may subside within a few hours, but this is a warning sign. They indicate a high risk of stroke, so you should consult a doctor immediately.
Indications for assignment of a disability group
Disability group III is determined when the patient is forced to leave his job:
- chronic atherosclerosis of the legs has been identified, and professional activity presupposes conditions that are unacceptable for this disease;
- there is a prosthetic limb stump and chronic atherosclerosis of the first degree;
- underwent surgery with subcompensation of blood circulation and atherosclerosis of I and II degrees.
The second disability group is assigned if there is:
- widespread chronic atherosclerosis of the lower extremities of III and IV degrees;
- stump on one limb and chronic atherosclerosis of degree II on the other;
- short stump of the femur of the lower limb;
- non-prosthetic stump of the lower limb;
- femoral stump and atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- suppuration at the junction of the stump and the prosthesis.
Patients are defined as the first disability group if there is a loss of any ability to work and the ability to self-care, and the following occurs:
- atherosclerosis of both lower extremities;
- removal of one and chronic atherosclerosis of the other limb;
- stumps at the level of the thighs of both lower extremities;
- severe combined disorders;
- severe septic complications during operations.
Disability for obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities is assigned, since this disease is characterized by an inevitable complication of the condition with loss of the ability to self-care.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Indications
The operation is indicated for patients with the following problems:
- significant narrowing of the lumen of the carotid arteries (more than 60%);
- symptoms of stroke, micro-stroke;
- high risk of endarterectomy complications.
The intervention can be carried out even if the patient is not bothered by anything and there are no suspicious symptoms yet. It is extremely important to regularly undergo a comprehensive medical examination in order to diagnose asymptomatic diseases and take the necessary measures.
How is the operation performed?
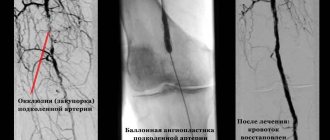
The carotid artery stenting procedure is performed from the femoral approach. The principle of the intervention is similar to stenting other arteries, but there is one caveat. When working with the carotid artery, special protection is used - a filter trap, which prevents destroyed fragments of atherosclerotic plaque from entering small arteries.
Stenting consists of the following steps:
- Installation of a sluice in the femoral artery under local anesthesia;
- The carotid arteries are contrasted using a special substance;
- The issue regarding stenting of one or more affected areas is being resolved;
- A conductor is inserted into the place of narrowing of the artery along the vascular bed, through which a filter-trap is passed;
- Then a stent is inserted into the problem area, which is carefully positioned and secured.
As a result, blood flow in the affected artery is completely restored.
When is it necessary to undergo ITU?
A referral for a medical and social examination requires a number of indications:
- development of therapeutic measures for patients with a positive prognosis as a result of reconstructive surgery;
- employment with lower qualifications and less work;
- assignment of II and I disability groups with a negative labor prognosis;
- ineffective treatment or unsuccessful surgery when circulatory disorders persist;
- identification of indications for obtaining special vehicles;
- identifying the cause of disability.
For review by medical examination specialists, you will need to pass standard tests:
- urine, general and biochemical blood tests;
- on blood clotting;
- rheovasogram;
- Dopplerometry.
Preparing for surgery
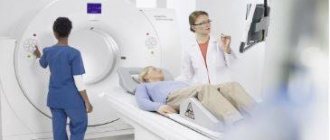
The process begins with diagnostic measures. Before the carotid artery stenting procedure, duplex ultrasound and computed tomography must be performed. Depending on the complexity of each specific case, angiography and magnetic resonance angiography may be indicated. A comprehensive examination is aimed at assessing the scale of the problem and the parameters of cerebral circulation.
No specific preparation is required for stenting. All the patient needs to do is take aspirin for a week before the planned surgery as prescribed by the doctor.
Contraindications, risk factors
The carotid artery stenting procedure is not performed in the following cases:
- Irregular heart rhythm in the patient;
- Individual intolerance to drugs used during the intervention;
- Brain hemorrhage within the previous 2 months;
- Complete blockage of the carotid artery.
There are a number of risk factors that can lead to complications after surgery:
- High blood pressure;
- The presence of sharp bends and other anatomical features of the vascular bed, complicating the stent placement procedure;
- The presence of large plaques, atherosclerosis of the aorta in the area of the beginning of the carotid arteries;
- Blockages in the arteries of the arms and legs.
In cases where surgery is the only way to save a person’s life, it will be performed even if there are contraindications. However, this requires written consent from the patient or his close relative.
Causes and prevention of atherosclerosis
The cause of atherosclerosis is a disorder in fat metabolism - the accumulation of cholesterol (namely low-density lipoproteins) in excess quantities. Cholesterol is necessary for the body because... participates in many important processes such as the production of certain hormones, and is also part of the cell membrane. With a genetic predisposition to the accumulation of cholesterol, with an unbalanced diet, this substance becomes too much, the body cannot cope with its breakdown, and the excess begins to be deposited in the walls of blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis.
Factors contributing to the development of atherosclerosis are considered to be: high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, excess weight, stress, smoking, alcohol, age over 50 years. It is worth noting that the development of the disease often begins at a young age, and by the age of 50-60 the main symptoms appear.
A good method of preventing atherosclerosis is an active lifestyle, balanced physical activity and the fight against excess weight, if present.
Most resources also offer a balanced diet, or more precisely, reducing the consumption of animal fats as the main method of preventing atherosclerosis, i.e. the appearance of excess cholesterol. But some studies indicate that vegetable fats and carbohydrates can provoke an increase in blood cholesterol levels. Therefore, in your approach to your own nutrition, you should be guided by common sense and moderation. Both animal and vegetable fats are necessary for the body to function comfortably, and their excess (like an excess of any other substances) can lead to lipid metabolism disorders. But all researchers agree that consuming vegetables and fruits, adding fish to the diet, and moderate calorie intake are key and proven methods for preventing problems with blood vessels and more.
Possible complications of stenting
ICA stenting is not an absolutely safe operation. The intervention may cause the following complications:
- Embolism of cerebral vessels, which leads to stroke;
- Formation of a blood clot along the installed stent;
- Restenosis is repeated blockage of a vessel. Occurs due to the patient’s failure to comply with the doctor’s instructions after surgery;
- The toxic effect of the contrast agent on the kidneys is observed in patients with acute renal failure;
- Formation of an aneurysm, hematoma in the area of catheter insertion.
Any operation is a risk. But in the case of stenting, the benefits are much greater than the potential complications.
Disability atherosclerosis - consequences of untimely treatment
Atherosclerosis also has several disability groups. Atherosclerosis provokes disability and gets it due to complications, and complications arise in turn due to the lack of timely treatment (advanced stage)
Disability – does atherosclerosis contribute to this?
The risk of developing complications from atherosclerosis and disability are also associated with the personal characteristics of the body, hereditary predisposition also influences this, and the combination of these factors increases the risk of complications. If there is no medical supervision, timely treatment and prevention of atherosclerosis, as a result, all this results in the progression of the disease. Disability due to atherosclerosis can be determined using the following diseases: persistent and transient cerebral circulatory disorders (micro strokes and strokes), obliterating atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction due to acute disruption of coronary blood supply, aneurysm and aortic stenosis. All of these diseases are very complex, difficult to treat, and in severe cases can lead to disability.
Let's look at stroke and disability
With strokes, the patient may acquire a disability associated with paralysis and paresis, as well as impaired movement in the limbs, as well as a decrease in intellectual abilities, thinking abilities and mental abilities.
Let's look at myocardial infarction and disability
It cannot be said that myocardial infarction is a more dangerous or safer disease. A patient who has suffered a massive heart attack will not be able to perform simple physical activity, and in extremely severe cases, discomfort may also occur during rest. Heart failure progresses, which makes it impossible to lead a normal lifestyle, as a result of which such patients require outside help.
Obliterating atherosclerosis affects the lower extremities, to be more precise, the vessels of the lower extremities, it is necessary to understand that this is also a serious disease and, in the absence of timely recommendations from ITU experts, at the moment when the degree of disability is determined, can lead to very disastrous consequences , namely to amputation of limbs and disability.
ITU determines the disability of atherosclerosis; they are slow and reluctant to assign the required disability group to patients, namely, the selection of therapeutic measures that prevent the progression of such a fleeting, formidable and incurable disease also depends on the degree of development of whitening.
© Therapist Elena Gabelko
Carotid artery stenting after stroke
Surgery is not performed within 2 months after a stroke. After the body recovers and returns to normal, doctors can decide whether to prescribe stenting. Here it is also necessary to weigh all the risks and assess the current state of health of the patient. However, a previous stroke is not a categorical contraindication to endovascular intervention.
Rehabilitation period
Recovery after stenting takes minimal time. The patient will stay in the clinic for 6-24 hours, depending on the current condition. This is necessary so that the doctor can monitor the occurrence of complications. You should drink plenty of fluids for 2-3 days after surgery to flush the contrast agent out of your body. It is also necessary to limit physical activity, follow a diet, and give up bad habits. A healthy lifestyle will help prevent the development of complications and restenosis.
Still have questions about carotid artery stenting?
Free consultation with AngioClinic specialists
Author
Salmina Daria Vladimirovna
Geneticist. Graduated from the Chelyabinsk State Medical Academy. She completed an internship at the Northwestern State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov.
Diagnostics
To diagnose atherosclerosis, both laboratory and instrumental methods can be used:
- general blood analysis;
- blood cholesterol level test;
- angiography (injection of a contrast agent into the blood, which reflects X-ray radiation and gives the specialist a detailed map of the condition of the vessels of the entire body);
- CT, MRI;
- coronary angiography (to study the coronary arteries);
- ECG, echocardiography (echocardiography);
- Holter ECG monitoring (to detect disturbances in heart rhythms);
- Ultrasound (to study the condition of the aorta, kidney vessels, heart).
Diagnostics usually does not cause problems for an experienced doctor - for this, our center has all the necessary equipment. After all, modern high-tech devices will be required - the better the equipment, the more detailed the examination data will be, which will help the doctor choose the optimal treatment method.