Cardiac diseases are not always detected by routine methods. Especially functional, in the early stages of their development. Long-term follow-up is required, which apparently healthy patients do not receive.
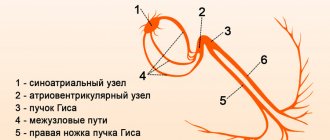
Slowing of intraatrial conduction is a clinical variant of the disorder in which the intensity of the electrical impulse from the natural pacemaker to the atria weakens.
As it progresses, the entire organ, including the ventricles, becomes involved in the pathological process.
The main and immediate cause is the death of the structures of the sinus (SA) node, which precisely forms the very signal necessary for myocardial contraction.
Treatment has different prospects. Secondary forms (caused by non-cardiac diseases), provided that the main factor of formation is eliminated, are completely stopped.
Cardiogenic diseases cannot be eradicated, but there are good opportunities to slow down and even stop the progression, relieve symptoms and equalize the patient’s chances of life with other people who do not have cardiac pathologies.
Development mechanism
Slowing of impulse conduction through the atria is a consequence of the death of cells of the sinoatrial or sinus node.
As a result of insufficiently intense production of the bioelectric impulse, weak activity of the myocardium itself is observed. First, only the atria, then the ventricles and the entire muscular organ as a whole suffer.
Read more about intraventricular conduction disorders here.
Up to a certain point, violations are not visible at all; information about the deviation is provided only by electrocardiography, if you look closely.
As it progresses, bradycardia (slow heart rate) develops. The natural pacemaker produces an insufficiently strong signal, and after reaching a critical cell level, threatening consequences develop. The probability of cardiac arrest increases to 70%; only transplantation can save the patient.
The contractility of the myocardium decreases, the volume of pumped blood decreases, therefore all organs and systems suffer from ischemia. Liver and kidney failure, brain hypoxia, and neurological deficits develop.
Death is a matter of time. Fortunately, such a fatal scenario is not a matter of just one year. There are chances for high-quality diagnosis and the prescription of adequate therapy.
Surgical treatment
If conservative therapy is ineffective, the following surgical methods are used:
- implantation of a pacemaker;
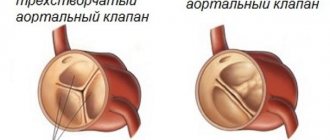
- replacement of heart valves with artificial analogues
Implantation of an electrical stimulator has no age restrictions. In the future, operated patients can lead a full life. They should only avoid exposure to strong electromagnetic waves, including undergoing magnetic resonance imaging.
People with built-in pacemakers should periodically visit a neurosurgeon and cardiologist to check the functionality of the device and adjust its settings.
This implantation is possible even during pregnancy. But, if there is no real threat to life, then doctors recommend refraining from surgery until 8 weeks. The installation of a pacemaker must be carried out under the supervision of an echocardiograph and using means that provide maximum protection for the fetus.
If conduction disturbances are caused by pathological changes in one of the heart valves, then the specialist suggests replacing it with a mechanical or biological artificial analogue. The choice is determined by a number of factors that the doctor evaluates after conducting numerous examinations and obtaining the results of laboratory tests of the patient’s blood.
The mechanical heart valve is reliable and does not require replacement. However, after its installation, a person must constantly use medications that reduce blood clotting.
Biological valves begin to gradually deteriorate after a certain period of operation. Therefore, they are recommended to be installed by elderly people.
Classification and degrees
Typifications that are used in clinical practice.
According to the number and nature of symptoms:
- No manifestations. The most common option. There is no picture at all, the patient feels fine. Changes in the electrocardiogram are absent or insignificant. Diagnosing pathology at this stage is a great success.
- With mild symptoms. Deviations occur when 10-30% of the sinus node cells die.
- With pronounced clinical signs. It can be easily detected by objective methods. Treatment is prescribed urgently, there is a risk of death of the patient.
Depending on the current:
- Paroxysmal type. Symptoms or, in their absence, signs on the ECG are inconsistently detected. Develops in episodes. Each lasts from a few minutes to hours. Such moments may arise repeatedly.
- Persistent form. About the same thing, only the duration is longer. Several days in a row.
- Chronic variety. Symptoms and the objective picture do not disappear at all; they are constantly recorded.
- Spicy. The symptoms are most pronounced; with significant cardiac dysfunction, there is a high risk of cardiac arrest and sudden death of the patient.
Depending on the main feature:
- Sinoatrial node block (SA block).
- Slowing down the sinus cluster.
- Classic sinus bradycardia.
All three forms appear approximately the same. ECG findings vary. The critical option is to stop the natural pacemaker. This is a direct path to death, asystole.
Based on etiology:
- Primary variety. Develops as a result of heart disease itself.
- Secondary. Or external. The result is the influence of other pathological conditions.
There are only three degrees of intra-atrial conduction disturbance:
- First. The patient has no complaints about his health. Objectively, minor deviations in the electrocardiogram are detected. The discovery was purely an accident.
- Second. The symptoms are pronounced, the ECG pattern is clearly visible. Specific signs make it possible to detect blockade or disruption of the sinus node. This is the most common point of diagnosis.
- Third. All manifestations are expressed to the maximum extent. The cardiologist notices “his” patients with the naked eye. A cardiogram verifies conduction disturbances. Treatment is urgent, otherwise cardiac arrest will occur as a result of insufficient stimulation and death of the person.
ECG and other diagnostic methods
Slowing of intraatrial conduction is detected on ECG, EPI or Holter monitoring. Standard electrocardiography is a mandatory and most accessible examination method used in all medical institutions. It is based on the registration of bioelectric signals occurring during heart contractions using graphic images.
Holter monitoring is an ECG that lasts from 24 hours to a week. This method makes it possible to record and track the bioelectrical activity of the heart in everyday situations.
To carry it out, electrical impulse sensors are attached to the patient’s body. The information they read is displayed on the monitor screen and is subsequently interpreted by a cardiologist.
During the examination period, the patient leads a normal lifestyle, including work, eating, physical activity, travel, sleep and other normal activities.
A person must write down information about his physical and emotional state in a diary. It also indicates data on food intake and medications, duration and quality of sleep, and changes in well-being.
EPI (electrophysiological study of the heart) is an expensive method performed in a hospital setting.
There are 2 types of this examination, used in the study of various pathologies.
In the first case, special catheters are installed in the veins of the patient’s upper and lower extremities. Electrodes are inserted through them, through which electrical stimulation of the cardiac conduction system is carried out. In this way, it is possible to cause, eliminate and study the parameters of emerging conduction disturbances.
A simpler type of EPI is the transesophageal insertion of a probe-electrode, through which the left atrium is stimulated. This method allows you to study the most common types of slowdowns in the conduction of cardiac impulses, as well as accurately determine sick sinus syndrome, which is common in older people.
Causes cardiac
All factors need to be considered in the system. During the survey, they are excluded one by one.
A sharp increase in blood pressure
If, against the background of chronic hypertension and a gradual increase in blood pressure, the body somehow manages to adapt to new, albeit difficult, conditions, a rapid increase in the tonometer reading leads to overload of the right atrium.
The result is damage to the cells of the sinus node. If such episodes are repeated, and this is exactly what happens against the background of uncorrected hypertension, more and more cells die.
Progression depends on the course of headache. Crises have an even more severe impact.
Inflammation of the heart muscle or myocarditis
It has a detrimental effect mainly on the atria. Without treatment it leads to tissue destruction and severe scarring.
The sinus node is located in the right chamber, and its partial destruction is possible. Slow conduction is a complication of the disease.
The nature of inflammation can be infectious or autoimmune. Both forms are acute, with a pronounced clinical picture of the heart, blood vessels, respiratory and nervous systems.
Treatment is strictly in a hospital. Endocarditis is a similar pathological process affecting the inner lining of the heart. Less often it leads to a slowdown, but this is also possible.
Coronary insufficiency
Narrowing or blockage of special arteries that supply the heart itself. Tissue necrosis is a variant of the condition. Another is possible. The so-called angina pectoris.
It is not so catastrophic; there is death, but the process does not reach that critical point when destruction leads to damage to large areas.
May last for years. It flows spasmodically. In waves. Each episode destroys part of the myocardium. The result is insufficiency and dysfunction. The sinus node suffers not least.
In addition to the death of cardiomyocytes, scarring of the impulse pathways occurs. The so-called bundle of His and its branches (legs), which leads to blockade.
Atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries or aorta
The essence of the process is the formation of cholesterol plaques that close the lumen of blood vessels. Blood flow weakens, pressure in the atria and ventricles increases.
How the growth of the indicator ends is with an increase in load and tissue destruction at the cellular level.
There is another variant of pathology - narrowing of the lumen of the arteries. This is the result of smoking, vasculitis, when the walls of blood vessels scar and close, alcohol abuse, and other autoimmune pathologies.
Treatment is urgent, conservative in the first stages. If ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated.
Heart attack
Acute circulatory disorder in the heart muscle. Leads to rapid destruction of cardiomyocytes. The process is avalanche-like, the longer the ischemia is observed, the more significant the area of destruction.
Major heart attacks are almost guaranteed to result in death. Even with colossal luck, the process will not pass without a trace. Heart regeneration is impossible. The affected tissue is replaced by scar tissue, unable to contract or create impulse. The result is ischemic disease.
Causes of the disease
Heart rhythm and conduction disturbances can occur due to physiological characteristics and cardiac pathologies.
Sinus tachycardia, for example, develops during physical and emotional stress. Respiratory bradyarrhythmia is normal. Atrial fibrillation and flutter are dangerous. They usually develop against the background of diseases of the cardiovascular system. As a rule, heart rhythm and conduction disturbances occur when:
- coronary heart disease;
- vices;
- arterial hypertension;
- cardiomyopathy.
Non-cardiac diseases such as:
- acute poisoning;
- fever;
- stomach ulcer;
- hyperthyroidism;
- adrenal tumor.
Risk factors for the development of pathology include:
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- obesity;
- concomitant diseases (mainly the endocrine system).
Extracardiac causes
Other factors also play a role, although they are not directly related to the heart. They are easier to correct, and there is the possibility of completely eradicating conduction disorders:
- Cardioversion performed. Prescribed to patients with paroxysmal tachycardias and other arrhythmias. The procedure involves placing electrodes and passing a charge through the heart.
A side effect is a slowdown in conduction due to dysfunction of the sinus node. Correction using medications.
This is a reversible condition. The acute period requires resuscitation, but this phenomenon occurs relatively rarely.
- Compression of the neck at the level of the carotid sinus. As a result of wearing clothes with a tight collar, tie, jewelry. The process is also reversible, but threatening acute variants of the condition are possible. Nocturnal cessation of breathing or apnea. It develops in patients with ENT problems, obese people, and severe snoring. Heart pathologies in this category of people are a proven fact. The condition needs to be corrected as soon as possible.
- Stroke affecting the subarachnoid space. Violation of cardiac activity is a purely reflex act associated with dysfunction of the parasympathetic region of the autonomic nervous system. Requires urgent medical attention. A prerequisite for the development of deviations is bleeding. The same effect is observed in traumatic brain injuries with the formation of a hematoma.
- Prolonged or improper use of certain medications. Particularly dangerous are cardiac glycosides, calcium antagonists, beta-blockers, neuroleptics, anxiolytics (tranquilizers), mood stabilizers, psychotropic drugs in general, opioids, narcotic analgesics, corticosteroids in inappropriately large dosages, and others. Correction of the treatment regimen or replacement of drugs is required.
- Excessive amount of potassium in the body. Excessive consumption takes its toll. It is difficult to achieve such a concentration with food; most likely, the patient is taking drugs like Asparkam.
- Excess calcium in the bloodstream. The result of leaching of mineral salt from bones. Observed in cases of cancer and prolonged immobilization. Osteoporosis. The nutritional factor does not play a role.
- Intoxication with salts of heavy metals, tumor decay products (for cancer, especially advanced ones).
- Increased intracranial pressure (hypertension caused by impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid).
Factors are taken into account in the system. Diagnostics puts an end to the issue. It is extremely rare that no cause is found. Then they talk about the idiopathic form. May be revised in the future.
Types of conduction disorders
All pathologies are divided into two groups:
- Changes in rhythm (arrhythmias). Such pathologies can be expressed in the form of atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, bradyarrhythmia, ventricular tachycardia, etc.
- Direct blockade. Some experts classify them as a separate category of pathologies. Blockades are divided into sinoauricular, intraatrial, atrioventricular and intraventricular.
Both types of conditions are equally dangerous.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is variable. In some cases it is absent altogether. The patient does not experience any difficulties in everyday life or when performing work duties.
Attention:
Insufficient conductivity is an incidental finding. There are also acute forms that are aggressive and often end in death.
A sample list of symptoms looks like this:
- Blood pressure surges. Sometimes low, sometimes high. The change in numbers is not due to any external factor, such as physical activity or food intake. This is a spontaneous process. As it progresses, frequent crises with high tonometer readings develop. The effect of the drugs is minimal.
- Peripheral edema. The lower extremities suffer, less often the fingers. Face.
- Dyspnea. After intense physical activity. When the process enters the critical phase (stage 3 and beyond), it is observed in a state of rest.
- Discomfort and pain in the chest of moderate intensity. Severe attacks are uncharacteristic, although this is also possible with a parallel course of angina pectoris. Nitroglycerin has no effect.
- Darkening in the eyes, tinnitus, headache, fog in the field of vision, flickering, vertigo, inability to navigate in space, fainting. The result of insufficient blood circulation in cerebral structures.
- Weakness, drowsiness, decreased performance. Already from the second stage. In some cases, symptoms are also detected at the first stage.
- Bradycardia. Decrease in heart rate. Up to 50-60 beats per minute and below.
During acute periods or moments of deterioration, apathy or psychomotor agitation, fear, suffocation, pallor of the skin, mucous membranes, and cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle are also noted.
As part of the development of heart failure, ascites is possible - an enlargement of the abdomen due to the accumulation of fluid.
How does pathology affect the functioning of the body?
With a partial disorder of sinoarterial conduction, no symptoms appear, but with a complete disorder, an adult may experience pain in the chest and dizziness caused by poor blood flow in the brain against the background of rare heart contractions.
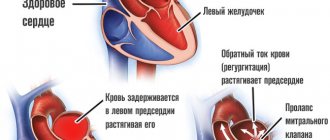
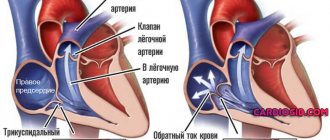
As for interatrial block, it does not pose a threat to life. But its presence increases the risk of developing atrial fibrillation, which is a serious threat to human health. This disorder is accompanied by shortness of breath at rest and when walking, swelling of the legs, bluish discoloration of the skin, and discomfort in the chest.
Atrioventricular block is not always expressed by symptoms, but its combination with bradycardia can lead to an attack of MAS (Morgagni-Adams-Stokes). The patient at this moment may suddenly feel weak in the body. It is possible that you may experience dizziness or even loss of consciousness. Seizures associated with deterioration of blood supply to the blood vessels of the brain may also occur. This condition requires emergency medical attention. Inaction can cause cardiac arrest.
The intraventricular type of pathology occurs due to a disorder of ventricular conduction through the bundle branches. Partial blockade does not always manifest itself, but complete blockade is accompanied by a rare pulse, loss of consciousness, and pain in the chest.
Diagnostics
It takes place on an outpatient basis. Impaired intra-atrial conduction means that there is damage to the sinus node. A thorough examination is required to detect the causes of this phenomenon.
Sample list:
- Oral interview with the patient by a cardiologist. When complaints appeared, whether they exist at all, how much they interfere with daily activities and other points are subject to clarification.
- Anamnesis collection. Family history, lifestyle, past or current pathologies.
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate. The classic picture is that blood pressure is unstable, even when the procedure is repeated after 10-15 minutes, an increase in the indicator prevails. Heart rate is consistently below normal.
- Daily monitoring. Gives a lot of information about the dynamics of the same levels over 24 hours. The result is an indirect confirmation of the presence of conduction disturbances in the atria.
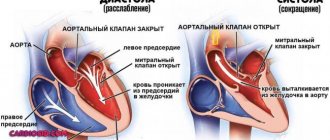
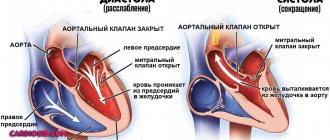
- Echocardiography. Visual assessment method. Deviations of anatomical development are detected only with gross defects, after a heart attack, inflammation and other moments. In advanced forms, the left ventricle enlarges and blood flow is disrupted.
- X-ray of the chest. An increase in the pulmonary pattern and an increase in the size of the heart are detected.
- ECG. Profile research. Gives basic information. Typical features: decreased pulse, deformation or complete disappearance of atrial waves (P), heart rate does not increase during physical activity, detection of replacement sliding complexes. A slowdown in AV conduction on the EGC is recorded even in the early stages.
EPI is also performed (for severe concomitant diseases, the technique is not used); if necessary, a consultation with a neurologist is prescribed.
Therapeutic measures
Slowing of intraatrial conduction on the ECG, occurring in an acute form, requires specific therapy.
| Drug groups | Drug names | Action provided |
| Anticholinergics | atropine, scopolamine, platyphylline | Reducing smooth muscle tone, improving the conduction of electrical impulses in the heart. |
| Vasopressors | norepinephrine | Increased blood pressure |
| Glucocorticoids | hydrocartisone | Stopping and relieving inflammation |
| Diuretics | lasix, furosemide | Removing excess potassium and fluid from the body. |
| Cardiac glycosides | cordigitite, lantoside, adonis-bromine | Elimination of arrhythmia, stimulation of the heart muscle. |
In some cases, the doctor decides on the advisability of using sedatives.
Pregnant women are prescribed magnesium supplements, which do not have a negative effect on the development of the fetus. Other medications aimed at improving intraatrial conduction are used only for clinical indications when there is a threat to the mother's life.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the form and course. Early stages that do not produce obvious symptoms and do not interfere with the patient in any way do not require urgent supervision. Further examination and clarification of the etiology of the process is necessary.
In case of secondary origin, the underlying disease is eliminated. Cardioprotectors, such as Mildronate, and vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed as a supportive measure.
The patient is monitored every 3 months. Deterioration of the condition is the basis for surgical intervention. The way is implantation of a pacemaker, which artificially creates the required electrical impulse.
As a measure to prepare for surgical treatment, the use of antiarrhythmics (Amiodarone), antihypertensives (Perindopril in different trade variations, Moxonidine, Diltiazem or Verapamil, others, at the discretion of the treating specialist), diuretics, and cardioprotectors is indicated. Cardiac glycosides as needed.
Also indicated are cessation of smoking, drinking alcohol, excessive physical activity, and consumption of fatty foods (treatment table No. 10).
Correction methods and treatment: what and when to do
An isolated disturbance in the conduction of impulses along the interatrial fibers, which is not accompanied by clinical symptoms, does not require treatment. Drug therapy is prescribed for the development of arrhythmias with hemodynamic disturbances: atrial fibrillation, extrasystole, paroxysmal tachycardia.
Groups of drugs used:
- antiari, Cordarone, Etatsizin, Bisoprolol.
- cardiac glycosides: Digoxin;
- diuretics: Eplerenone, Spironaloctone, Torsemide.
High-degree intraatrial blocks that cause symptoms of heart failure require a pacemaker (artificial pacemaker). Installation of electrodes in both atria allows synchronizing the work of the myocardium.
Forecast
Depends on the diagnosis. Primary forms cannot be cured, but in the early stages they can be corrected with medication, the survival rate is 90% or higher.
Secondary ones require relief of the cause. Mortality due to atrial conduction disorders generally ranges from 10-60%, acute forms are fatal in 40% of situations. The death of more than 90% of sinus node cells almost always leads to death.
Young patients without bad habits, with a good family history, relatively healthy, have a better chance of survival.
Prevention
Prevention of pathologies of the cardiovascular system is aimed at:
- adherence to sleep and wakefulness;
- eliminating the risks of stressful situations;
- changing your lifestyle and giving up bad habits.
Moderate physical activity (mainly water procedures) is beneficial. To prevent arrhythmia, it is very important to follow a diet. Diet excludes salty, fatty and spicy foods, coffee and strong tea. Don't get carried away with the liquid. You need to drink 1-2 liters of water per day. It is also important to enrich the diet with vitamins and microelements.
If you have a genetic predisposition to pathologies or a history of them, it is very important to regularly visit a cardiologist and undergo a full examination. Be sure to include in the program such studies as:
- general blood analysis;
- ECG;
- ECG under load.
The examination will not take much of your time, but will help prevent the development of pathology and the occurrence of complications.
Complications
The cause of intraatrial conduction disturbance is weakness or dysfunction of the sinus node.
The condition threatens with the following consequences:
- Cardiac arrest or asystole. The result of insufficient stimulation of cardiac structures, in particular the muscle layer.
- Heart attack. The result of poor nutrition. Little blood flows through the coronary arteries. Hence acute necrosis or, at least, repeated attacks.
- Stroke. Death of nerve cells and tissues. Ends in death or permanent neurological deficit.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Fainting and injuries incompatible with life.
- Vascular dementia.
All conditions, one way or another, lead to a minimum of severe disability. There is no point in delaying therapy, if indicated.
Treatment of cardiac conduction disorders
- Medication - the doctor may prescribe vitamins and restoratives, a diet (limiting fatty and sweet foods, eating more fresh vegetables and fruits), as well as drugs to cure or reduce the symptoms of the disease that caused the blockade (if the cause is known).
- Surgical – used in case of ineffectiveness of drug treatment, frequent fainting and malignant (life-threatening) course of the disease. An electrical pacemaker (ECS) is installed - a small device that generates the correct heart rhythm, which sets the heart to contract correctly and rhythmically.