The intrauterine development of the heart depends on many factors: genetic predisposition, parental health, environmental influences, and the mother’s use of medications in the first half of pregnancy. The formation of the heart valve apparatus occurs in the 7-10th week of gestation; under unfavorable conditions, the development of various congenital heart defects and anatomical features is possible.
Many of them go unnoticed until the patient reaches adulthood and in most cases do not cause any complaints, but are discovered by chance during routine examinations. Changes in the anatomy of the aortic valve occur in 1.5-2% of the population.
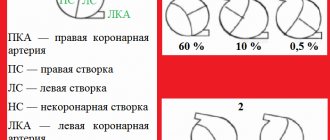
Bicuspid aortic valve: what is it?
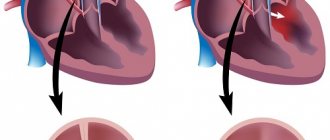
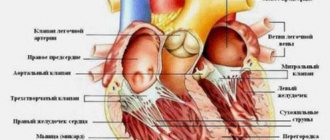
The aortic valve normally consists of three elastic, well-movable connective tissue cusps, which close during a heartbeat and completely block the flow of blood from the aorta back to the heart chamber. Under certain conditions, when the fetal heart is formed, a malfunction occurs and only 2 valves develop.
AK scheme
If there are two tightly closing flaps, their high elasticity, the function of the valve is not impaired, and the person does not have any complaints. However, the bicuspid valve experiences a fairly large load both with pressure and the volume of pumped blood, and after some time its insufficiency or stenosis develops.
Prevention of deviation
Preventative measures are necessary to maintain good health and reduce the risk of complications. These include:
- maintaining a correct lifestyle;
- eating healthy foods with plenty of essential vitamins;
- outdoor sports;
- regular walks outside;
- alternating physical activity with mental activity.
The patient should avoid stress. You should absolutely not overwork yourself. It is important that the load alternates with rest. You need to give up bad habits. The diet should include as many fruits and vegetables as possible. The 2-leaf aortic valve is not dangerous and if the doctor’s recommendations are followed, the patient will not experience any discomfort.
The video talks about the role of the aortic valve and what happens if its operation malfunctions:
Types and causes of anomalies
Cardiologists do not have a clear opinion about the etiological causes of valvular heart defects. However, it is assumed that disruption of a pregnant woman’s lifestyle during the development of cardiovascular organs can have negative consequences. The most common negative factors are:
- A burdened hereditary history, the presence of chromosomal abnormalities or congenital heart defects in first-degree relatives.
Systemic diseases of the connective tissue of the mother and fetus (scleroderma, dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus).- Carrying out X-ray examinations, keeping a pregnant woman in conditions of increased radiation.
- Infectious diseases of a viral and bacterial nature, even asymptomatic.
- Impaired mental state, constant stressful and conflict situations.
- The impact of nicotine and alcohol on the fetus in the case of bad habits in the mother.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- Influence of environmental factors (air and water pollution with salts of various metals).
In the absence of complaints, the bicuspid aortic valve should not be considered a gross pathology and can be regarded as an individual anatomical feature of the body. However, if signs of malfunction appear, you should consult a doctor, determine the type of pathology, and select the correct treatment.
This defect can be independent or combined with other pathologies - coarctation of the aorta, ventricular and atrial septal defects, stenosis and insufficiency of the mitral valve, dissecting aortic aneurysm.
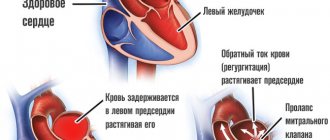
Valve dysfunction is manifested by the development of valve insufficiency or stenosis. In case of insufficiency, a defect is detected, incomplete closure of the valves during the relaxation phase of the heart muscle, and a retrograde flow of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle occurs. It becomes overfilled and stretched, which can eventually lead to the development of chronic heart failure.
Aortic stenosis
The opposite disorder occurs with stenosis of the aortic valve - due to the presence of a narrowing, a small volume of blood is ejected into the aorta, and increased pressure is constantly maintained in the cavity of the left ventricle. As a result, the load on the hearts increases, and the organs receive insufficient nutrition.
Diagnostic measures
CHD - bicuspid aortic valve can be diagnosed using:
- Ultrasound;
- standard ECG and daily monitoring;
- radiographs of the lungs.
First of all, the cardiologist questions the patient and identifies complaints. The doctor determines the possible root causes of the development of the disorder.
Particular attention to the initial examination. Children with heart defects are significantly behind their peers in physical development. When diagnosing a disorder in an infant, a doctor may notice bluish skin, muscle hypotonicity, and slow weight gain.
If a bicuspid valve is suspected, an ECG of the heart is mandatory.
Laboratory tests are necessary to determine the general condition and identify associated abnormalities.
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound. This is the only way to confirm the presence of a bicuspid aortic valve. Other studies are required to clarify the extent of damage and select therapeutic measures.
Symptoms of valve pathologies
For a long time, a person may not be aware of the presence of pathology; only when complaints arise and additional research is carried out, a diagnosis can be established.
The symptoms are:
The first symptom of the development of aortic valve insufficiency is most often a rapid heartbeat and a feeling of pulsation in the head, which is associated with high cardiac output.- When blood flows back into the left ventricle, cerebral circulation suffers, which is manifested by impaired consciousness, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, a feeling of noise in the head, and in rare cases, fainting.
- Quite often, shortness of breath develops during physical activity and a sudden feeling of weakness.
- Due to the increased load on the heart, angina pectoris and atrial fibrillation may develop.
- With the development of right ventricular failure, the patient develops swelling of the lower extremities and complains of a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium.
Complaints from patients with the development of stenosis are associated with increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation (pulmonary hypertension). The main complaint is also a decrease in tolerance to physical activity, the appearance of shortness of breath and an unproductive cough. These attacks may be accompanied by increased heartbeat, numbness of the limbs and sudden muscle weakness.
Question of military service
Some young guys plan to enter naval schools or go to military service after reaching adulthood. Others want a reprieve. Therefore, a natural question would be whether an army with such a diagnosis as bicuspid aortic valve is possible. If, due to a valve defect, reverse blood flow is observed, that is, it flows in the opposite direction from the norm, then conscripts must be released from service. They are given a deferment and recognized as having limited fitness. This corresponds to category B.
But in the absence of signs of reverse flow and other complications, the congenital defect itself is not considered an argument for preventing conscription.
Diagnosis of disorders
If you have any complaints, you should definitely consult a doctor. He may suspect the presence of pathology by conducting a physical examination, if there are any murmurs, additional sounds, or changes in the size of the heart.
Diagnosis of the bicuspid aortic valve is usually not difficult, since one of the popular and accessible research methods is ultrasound scanning. Echocardioscopy allows not only to determine the anatomical structure of the organ, but also the degree of dysfunction.
In modern clinics it is possible to conduct transesophageal cardiography. This is a study where a special sensor is inserted through the mouth into the esophagus using a special probe. This makes it possible to more accurately visualize the valve apparatus and measure the volume of blood ejected by the heart.
It is also possible to indirectly confirm the presence of pathology and its complications using a chest x-ray with contrast. If there are contraindications to radiation, magnetic resonance imaging may be performed.
The degree of functional impairment can be assessed using an exercise tolerance test, during which an electrocardiogram is recorded.
Treatment Options
The severity of the symptoms of the disease entirely determines the treatment tactics. If before the examination the patient did not have any health problems, the body was subjected to intense physical activity, no specific therapy is required. However, after confirming the diagnosis, the doctor must register him with a dispensary, which obliges him to take a series of tests several times a year.
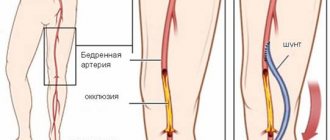
A different approach is required by a severe form of pathology. The patient is indicated for surgery with installation of an aortic valve prosthesis. Surgical intervention does not involve open manipulation of the chest. Modern techniques allow the installation of a prosthesis through the skin. The implant is inserted through the subclavian or femoral artery. After the operation, the patient is prescribed constant medication to reduce blood clotting.
Treatment and life prognosis
Once a diagnosis of bicuspid aortic valve is made, one of the main keys to successful treatment is lifestyle modification. This means that it is necessary to optimize physical activity, follow a diet with limited salt intake, and quit smoking and alcohol.
If complaints arise, you should definitely consult a cardiologist to assess the degree of disturbances and select treatment. For initial symptoms, drug support is possible, but the main treatment for congenital defects is surgical.
At the moment, several surgical techniques have been developed.
Valvuloplasty
The most common:
- Valvuloplasty. Dissection of fused septa or the aortic ring can be performed percutaneously by passing a catheter through the inguinal artery.
- Prosthetics. Replacing the valve with a biological or mechanical prosthesis.
After surgical treatment, patients require ongoing antithrombotic therapy. For this, enteric forms of Acetylsalicylic acid or Clopidogrel are used.
It is also necessary to monitor the level of cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins to prevent atherosclerotic lesions of blood vessels and valves.
The prognosis for life in such people is favorable in the absence of severe heart failure and other serious diseases. In some situations, repeat surgery may be necessary.
How is the disease treated?
The only effective method of combating pathology is surgery. It is aimed at installing an artificial valve. But first, the feasibility of its implementation will be considered. For example, if a person is diagnosed with BAV without hemodynamic disturbances, he is not bothered by any symptoms, and he can easily tolerate normal physical activity, then there is no need to perform surgery. In this case, the doctor will recommend observation by a cardiologist and systematic ultrasound examination.
If the doctor identifies an anomaly, then it is necessary to decide whether valve replacement surgery is required.
In situations where there really is a threat to the patient’s health, the question of surgical intervention and valve replacement will be very relevant. It should be noted that thanks to the wide capabilities of modern medicine, operations are highly successful. They can be carried out in several ways. Everything will depend on the patient’s health condition. The survival rate after prosthetics is quite high, so there is no doubt about the effectiveness of surgical treatment.