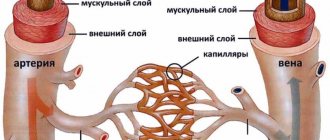
Bypass grafting of the arteries of the lower extremities below the inguinal ligament are:
- femoral-popliteal bypass surgery,
- femoral-tibial bypass,
- femoral-distal popliteal bypass.
Above the inguinal ligament the following is performed:
- aortofemoral bypass surgery,
- aorto-bifemoral bypass (aorto-femoral bifurcation bypass),
- aorto-iliac bypass surgery,
- iliofemoral bypass,
- femoro-femoral cross bypass,
- aorto-mesenteric bypass, depending on which vessel needs bypass.
What is heart bypass surgery?
{banner_banstat0}
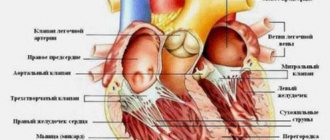
Coronary artery bypass grafting is an open-heart surgical procedure in which a bypass path is formed for cardiac blood flow, bypassing the affected arteries.
CABG surgery is performed using fragments of other vessels of the patient, which are most often taken from the lower extremities. Surgery is performed only in specialized clinics by highly qualified cardiac surgeons, with whom a transfusiologist works together to provide artificial blood circulation. It should be noted that the principle of this complex operation was developed by the Soviet doctor Vladimir Demikhov in the sixties of the last century.
When is vascular bypass used?
The operation “Bypass surgery of the vessels of the lower extremities” is used strictly for the following indications:
- Peripheral artery aneurysms (dilation of the vessel caused by damage to its walls);
- Atherosclerosis of veins (deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of the vessel);
- Chronic diseases with damage to the arteries of the lower extremities;
- Varicose veins;
- Thrombosis and thrombophlebitis;
- Primary manifestations of gangrene of the legs;
- Drug treatment is ineffective.
Bypass surgery of the vessels of the lower extremities is not performed when:
- It is possible to perform angioplasty;
- The patient is completely paralyzed;
- Poor test results;
- The work of individual organs is disrupted.
Varieties
Depending on which vessel is used for the bypass, there are two types of heart bypass:
- aortocoronary – CABG;
- mammarocoronary – MCS.
CABG, in turn, is divided into:
- autovenous, when the great saphenous vein of the leg is used;
- autoarterial - when using the radial artery (if the patient suffers from varicose veins).
For MCS, the internal mammary artery is used.
In addition, there is a division of bypass into:
- standard – using an artificial blood supply device (heart stopped);
- without the use of artificial blood supply to the heart (the heart does not stop), which requires the highest qualifications of the surgeon;
- hybrid, when different types of additional procedures are combined.
Indications for surgery
{banner_banstat1}
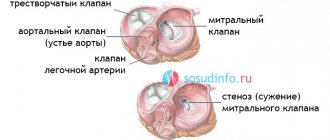
Bypass surgery of affected cardiac vessels is performed for arterial stenosis causing ischemia. The most common cause is atherosclerosis, when the lumen of the arteries is blocked by atherosclerotic plaques, or thrombosis.
These pathologies are the main indications for surgical intervention. Additional examination is carried out when:
- retrosternal pain radiating to the left arm, shoulder, lower jaw, neck;
- hypertension;
- tachycardia; constant nausea, heartburn.
For what diseases is bypass surgery performed?
The presence of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels (atherosclerosis). In a healthy person, the walls of blood vessels and arteries are a smooth surface without any obstructions or narrowings. In a person suffering from atherosclerosis, blockage of blood vessels occurs due to cholesterol plaques. If the disease is neglected, it can lead to the death of tissues and organs.
Cardiac ischemia. The traditional case of bypass surgery is coronary (coronary) heart disease, in which the coronary arteries supplying the heart are affected by cholesterol deposits in the vessel. The main symptom of this disease is narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, which leads to insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle. In such a situation, complaints often arise of pain behind the sternum or in the left half of the chest, the so-called angina pectoris or angina pectoris.
Having excess weight. A shunt inserted into the stomach divides it into large and small. The small intestine connects to the small intestine, causing the volume of food eaten and the absorption of nutrients to be significantly reduced.
Article on the topic
Rules of life after coronary artery bypass surgery
Impaired blood flow in the vessels of the brain . Insufficient blood supply to the brain (ischemia) can be either limited or global. Ischemia impairs the brain's ability to function normally and, if left untreated, can lead to tumors or brain infarction. Treatment of cerebral ischemia is carried out by a neurologist in a hospital with the help of medications (vasodilators, drugs against the formation of blood clots and to thin the blood, nootropic drugs to improve brain function) or through surgery (in the later stages of the disease).
Contraindications
CABG surgery is not performed in the following cases:
- with renal failure;
- uncompensated diabetes mellitus;
- chronic nonspecific lung lesions;
- malignant neoplasms;
- post-stroke hypertension.
There are also relative contraindications for bypass surgery:
- heart failure;
- obesity;
- scarring of the heart, minimizing cardiac blood output below 30%;
- Menkenberg's arteriosclerosis - damage to all coronary arteries;
- elderly age.
AMI is considered as a contraindication at the discretion of the physician.
Preparing for the intervention
{banner_banstat2}
The basis of preparation for CABG surgery is coronary angiography, a procedure that thoroughly examines the relief of the coronary endothelium. To carry it out and subsequent detailed examination, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital. To perform coronary angiography, special catheters are inserted into the left and right coronary arteries, through which X-ray contrast is applied. X-rays then scan the endothelium. The procedure allows you to accurately determine the location and degree of narrowing of the vessel, while the patient receives a high dose of radiation. In addition, the manipulation cannot be performed if there is an allergy to iodine (x-ray contrast).
Therefore, in addition to coronary angiography, CT coronary angiography is used. It is more accurate, more expensive, but eliminates radiation exposure. True, contrast is still necessary, and a person weighing more than 120 kg cannot fit into the device.
If the examination reveals narrowing of the arteries by more than 75%, CABG is prescribed to minimize the risk of AMI or its recurrence. In addition to coronary angiography, the following are required: CBC, OAM, general biochemistry, coagulogram, lipidogram, ECG, EchoCG, ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
If the patient takes anticoagulants, their use is agreed with the doctor: usually a break is taken for two weeks before surgery. Other groups of pharmacological agents also require consultation with a doctor.
The day before coronary artery bypass surgery, the patient is examined by an anesthesiologist, correlating anesthesia with the height, weight, age of the person being operated on, and individual intolerance to drugs. On the eve of the intervention, the patient is sedated (taken sedatives). Necessarily:
- do not eat after 18:00;
- do not drink after midnight;
- prescribed medications are taken immediately after dinner;
- in the evening - shower.
Tests and diagnostics
Complete information about the state of the vascular system of the heart is obtained after coronary angiography and multislice computed tomography. Both research methods make it possible to assess the degree of damage to the coronary vessels and determine further treatment tactics.
MRI of the heart and coronary vessels
Magnetic resonance imaging is considered a non-invasive diagnostic test, which is based on the nuclear magnetic resonance method. MSCT allows you to obtain a clear image of the heart and assess the condition of the coronary vessels. Absolute contraindications:
- the presence of clamps, staples and metal implants;
- the presence of an insulin pump, pacemaker, ferramagnetic implant and other electronic systems.
The price of the study ranges from 15 to 35 thousand rubles. Compared to the magnetic resonance imaging method, cardiac CT is more informative in terms of assessing the condition of the vascular system of the heart.
Additional examination methods:
- coagulogram;
- biochemical and general blood test;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- lipid spectrum;
- chest x-ray;
- Ultrasound scanning of the lower extremities;
- ECG;
- EchoCG;
- Analysis of urine.
Progress of the operation
{banner_banstat3}
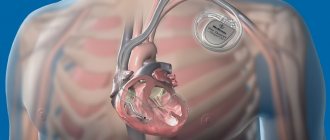
To perform a heart bypass, the doctor needs to cut the sternum, which then takes a long time to heal, which determines the length of the rehabilitation period. Depending on the type of CABG, a heart-lung machine is used or not. The heart is not stopped unless additional manipulations are required: removal of an aneurysm, replacement of valves. Bypass surgery on a beating heart has the following advantages: no complications from the immune system or blood; intervention time is shorter; rehabilitation is faster.
The essence of the operation is to create a workaround.
To do this: the surgeon opens access to the heart, takes a vessel for a shunt, if the heart stops, perform cardioplegia and turn on the artificial blood flow equipment. If the heart is beating, special devices are applied to the intervention area. The bypass itself involves stitching together blood vessels: one end of the bypass is connected to the aorta, the other to the coronary artery, which is located below the stenosis. After this, the heart is started again and the equipment is turned off. The sternum is secured with metal staples, and the skin on the chest is secured with regular sutures. The bypass lasts about four hours.
Complications
{banner_banstat4}
Often after surgery, the patient experiences a feeling of pain, heat, and discomfort in the chest. This is not a reason to panic; you need to inform your doctor about this, who will prescribe relief medications. The most common complications after cardiac bypass surgery are: pulmonary congestion, anemia, pericarditis and other inflammatory processes, phlebitis of veins adjacent to the shunt, immune disorders (during cardiac arrest), arrhythmias.
To prevent congestion in the lungs, it is recommended to inflate balloons up to 20 times a day. Anemia can be controlled with a special diet and, if necessary, with blood transfusions. Treatment of other complications is individual for each patient.
Symptoms
After surgery, patients are admitted to the intensive care unit, where urinary tract catheterization and artificial ventilation are performed. Painkillers are administered and antibiotics . Heart function is assessed on a monitor in the form of electrocardiography. After stabilization of the patient’s condition, the patient is transferred to independent feeding and breathing. The range of movements increases gradually, step by step.
At first, patients are bothered by chest pain, which is due to the specifics of the operation being performed, because it is open to the public. As the sternum grows together, the pain subsides. Also, discomfort is observed in the area where the vein was taken. All symptoms are temporary and the patient gradually returns to his usual lifestyle.
Rehabilitation
The recovery period is long. You cannot wash for two weeks after bypass surgery, as the wounds are extensive and there is a risk of secondary infection. Daily dressings, treatment with antiseptics. You will need to wear a chest bandage for six months to prevent the stitches on your sternum from coming apart.
Average rehabilitation is about three months. During this period, blood and blood flow will normalize, and the sternum will heal. An assessment test for the possibility of a full life is a stress test (for example, bicycle ergometry).
Which is better: a stent or a shunt?
If we compare two methods for correcting myocardial ischemia and hypoxia through the vessels supplying the muscle, the advantages and disadvantages of stenting and bypass surgery of the heart vessels become obvious:
| Evaluation criterion | Stenting | Bypass surgery |
| Scope of intervention | Minimal, intravascular | Technically complex intervention |
| Operation duration | From an hour to three | From three to nine or more |
| Heart failure | Need not | More than half of operations take place with the heart stopped |
| Incision | Deleted | The sternum is cut |
| Anesthesia | Local, less often - taking into account the individual threshold of pain sensitivity | Deep anesthesia |
| Rehabilitation | A few days | Up to six months |
| Acute cases | Relief of AMI is practiced | Not allowed due to the severity of the intervention |
| Capillaries | Correction of vessels with a diameter of 3 mm is possible | Cannot adjust small branches |
| Restoration of blood flow | For several years | Up to 10 years or more |
Treatment
Drug therapy is aimed at:
- maintaining normal blood pressure and pulse levels;
- prevention of thrombosis;
- lowering cholesterol , leveling the lipid spectrum;
- improvement of trophism and nutrition of the heart muscle.
Medicines
The main drugs prescribed after stenting and bypass surgery:
- Brilinta;
- Plavix;
- Bisoprolol;
- Lisinopril;
- ThromboASS;
- Atorvastatin;
- Preducted.
Lifestyle recommendations after surgery
{banner_banstat6}
Coronary bypass surgery is a reliable way to prevent heart attacks and angina attacks, since it eliminates ischemia for decades. However, the shunt can narrow; in every fifth patient this happens after a year, and after 10 years - in 100%. To minimize this possibility, you should adhere to seven rules:
- complete cessation of alcohol and cigarettes;
- anti-atherogenic nutritional profile (DASH diet included);
- movement: exercise therapy, walking, sports (swimming);
- minimizing stress;
- a balanced drinking diet (30 ml of water per 1 kg of weight);
- eight hours sleep;
- annual medical examination.
Price
Since 2021, coronary artery bypass surgery is included in the system of state guarantees, that is, it is carried out under the compulsory medical insurance policy. The condition is a primary referral from a local doctor. Surgical intervention is performed in all government medical organizations at the appropriate level. If it is not possible to perform CABG at the regional level, referrals to federal medical centers are used.
If a patient wants to undergo coronary artery bypass surgery in a specific private clinic or abroad, he is not entitled to compensation for treatment. The average cost of an operation in Moscow is 120,000 rubles, St. Petersburg – 85,000 rubles, Kazan – 32,500 rubles.
Let us emphasize once again that bypass surgery is performed on an open heart, which requires special equipment, highly qualified doctors and a specialized hospital.
Causes
CABG improves coronary blood flow, which reduces the severity of pain and reduces the number of angina attacks. After surgery, patients can better tolerate physical activity, improve performance, and improve their psychological state. Surgeries to reconstruct the cardiac vasculature reduce the risk of myocardial infarction .
Indications for shunt installation:
- critical narrowing of the coronary arteries;
- angina pectoris grade 3 and 4 (attacks occur during normal physical activity and at rest);
- aneurysm due to coronary sclerosis ;
- inability to perform stenting;
- narrowing of the coronary arteries in combination with post-infarction aneurysm and structural defects of the heart .