Read in this article:
- Two blood pressure readings
- What does the difference between upper and lower pressure mean?
- Reduced diastolic pressure
- High bottom pressure
- Increased systolic pressure
- Reduced upper pressure
- Controlling blood pressure is the key to the health of the whole body
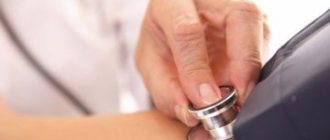
Regularly measuring blood pressure is an important condition for maintaining health. A person may not feel a slight increase or decrease in blood pressure, but such changes indicate negative processes occurring in the body. If measures are not taken in time, there may be a negative effect on the heart and blood vessels, including a heart attack or stroke. This is why it is so important to use a home blood pressure monitor from time to time.
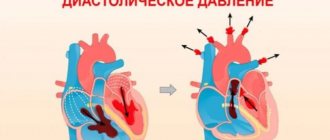
Two blood pressure readings
The device screen displays two parameters, for example, 120/80. They are called upper and lower pressure, scientifically – systolic and diastolic. The first indicates the level of maximum blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels; it is recorded at the moment of contraction of the heart muscle, when blood is pushed out of the heart. The second speaks about the force of blood pressure on the walls of arteries and veins at the moment of complete relaxation of the heart muscle.
Systolic pressure also shows how fast the heart beats. This figure increases with age, so the norm is higher for older people than for young people. Lower blood pressure reflects the force with which blood flows through the vessels. The higher their tone and elasticity, the closer to normal the indicators will be.
The norm is considered to be an upper pressure of 110-130 units (for people over 55 years old - about 140 units), a lower pressure of 65-80 units. The normal difference between them is about 40 units. But the indicators may vary somewhat due to the influence of various factors not related to diseases: emotional or physical stress, time of day and even nutrition.
Examinations and in what order they are carried out
The list of diagnostic measures can be presented as follows:
- Interviewing the patient, assessing complaints, collecting individual and family anamnesis. It is necessary to identify a possible hereditary component. Which is almost always present in matters of cardiological nature.
- Electrocardiography. A method for studying the functional activity of the heart by reading the frequency of contractions and building a picture.
- Echocardiography.
- Changing blood pressure and pulse pressure levels using simple calculations.
- Daily monitoring using a programmable tonometer.
- Electroencephalography. A powerful technique for diagnosing brain structures.
- Study of hormone levels, biochemical parameters of blood, urine, microscopic assessment of biological fluids.
- Angiography.
- Load tests. If there is a high difference in pressure levels, they are indicated, but with great caution and only in a gentle mode.
Specialists: cardiologist, neurologist, nephrologist, endocrinologist. Psychiatrist if necessary. The list can be expanded at the discretion of the “consilium”.
What does the difference between upper and lower pressure mean?
If a significant difference between systolic and diastolic pressure appears due to a feeling of hunger, hypothermia, excessive physical activity combined with insufficient nutrition or constant stress, this does not mean that pathology is developing in the body. When the effect of these factors disappears, the indicators may well return to normal, and there will be no cause for concern. But if the gap between the upper and lower pressure remains at rest, this may already indicate disturbances in the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, or other body systems.
A difference of less than 25% of the upper pressure may indicate several pathological conditions:
- Myocarditis;
- Left ventricular stroke;
- Tachycardia;
- Failure of internal organs;
- Aortic stenosis;
- Heart failure;
- Heart attack due to physical overexertion;
- Cardiosclerosis.
Such conditions are often accompanied by symptoms that are difficult to ignore. These are drowsiness and weakness, headache and dizziness, impaired attention and irritability. This situation can result in hypoxia, blurred vision, and sometimes cardiac arrest, so it should never be ignored. Such indicators on the tonometer screen and poor health require medical consultation and examination.
The difference between the upper and lower pressure exceeding 50 units is considered too large. The main causes of this condition are wear and tear and aging of the cardiovascular system. In such cases, tremors of the limbs and dizziness occur, the person becomes irritable or feels complete apathy, and fainting often occurs. Causes may also include pathologies of the digestive organs or gall bladder, and tuberculosis. Only a doctor can establish the true causes and prescribe effective treatment.
Any regular or prolonged deviation of systolic and diastolic pressure from the norm is a reason to pay close attention to your health. And it doesn’t matter whether we are talking about an increase or a decrease - both options can be dangerous.
When to see a doctor
If at least one of the following symptoms is detected, it is important to urgently visit a cardiologist or call an ambulance:
- Confusion of consciousness such as impaired cognitive function, fainting, hallucinations. Blue skin tone, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. Occurs due to increasing tissue hypoxia.
- Drowsiness, fatigue, apathy for no apparent reason. Reduced performance to zero. The patient cannot concentrate on anything.
- Distraction of attention, inability to focus.
- A headache of a stabbing nature is noted in the back of the head and frontal region.
- Memory problems.
- Arrhythmia such as tachycardia or bradycardia. It is possible to replace one with another.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Severe pain in the chest, persistent, long-term.
- Vertigo. Usually within a day or more.
- Eye disorders such as decreased visual acuity, problems with color perception.
- Tinnitus, hearing loss.
- Muscle weakness.
Manifestations occur in complexes and necessitate correction. This is an important component of therapy.
Reduced diastolic pressure
Low lower pressure is considered to be 50-59 units or less. Such changes indicate a violation of the tone of the vascular wall. When the indicator is less than 50 units, we can talk about a pronounced disturbance of blood flow in the brain, kidneys and other organs.
Diastolic pressure decreases against the background of kidney pathology, for example, Gitelman and Bartter syndromes. This phenomenon is also typical for people with a congenital disorder in the production of certain hormones, including adrenaline. Such changes are accompanied by fever, muscle weakness, vomiting, cramps and abdominal pain.
The first thing to do in such a situation is to consult a doctor. For diagnostic purposes, blood pressure monitoring and examinations are carried out to exclude endocrine pathologies and heart diseases. To increase lower blood pressure, special medications are used.
Treatment
The method of therapy depends on the nature of the process. For endocrine pathologies, a replacement technique or surgical intervention is indicated.
Cardiac causes are corrected surgically or by taking medications: ACE inhibitors, tonics and diuretics in strictly defined dosages.
Nephrogenic factors are eliminated through radical (surgical) measures, less often through conservative means.
Specific symptomatic therapy is even more difficult. It is necessary to select means to normalize both indicators in the hospital.
A significant role is played by lifestyle changes. A calm, measured regimen with proper nutrition and proper rest will help put the body in order and mitigate the negative manifestations of the disease.
High bottom pressure
The cause of high lower pressure is usually impaired elasticity of blood vessels, their spasms or narrowing of the lumen due to accumulated cholesterol. An increased rate is recorded when:
- Kidney pathologies;
- Malfunctions of the adrenal glands;
- Vascular diseases;
- Impaired blood flow;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Overfatigue (physical or mental).
The cause may also be long-term use of certain medications. The doctor’s primary task is to identify the cause of the changes, and only then prescribe treatment. By the way, lower pressure can increase under the influence of external factors, for example, frequent stress, which causes the release of adrenaline and constriction of blood vessels, bad habits that deplete the heart muscle, poor nutrition, which contributes to the accumulation of cholesterol in the blood vessels and the accumulation of excess weight.
Causes of the gap between blood pressure levels (physiological)
There are not many factors in the formation of such a phenomenon. Among them:
Intense hormonal changes in the body
They are more often observed in the fairer sex due to natural characteristics: women give birth to children and every month they experience an imbalance of active substances during the menstrual cycle.
In addition to gestation and menstruation, menopause also affects. It is already inherent in representatives of both sexes, but in men the condition is better amenable to drug correction, flows less aggressively and is partially reversible.
A large gap in pressure is caused by a violation of the regulation of vascular tone and the properties of the blood in the complex.
Stress, fatigue and overwork, especially chronic
Strictly speaking, these are not diseases, but borderline conditions associated with the release of large amounts of hormones from the adrenal cortex.
A decrease in the level of cortisol, adrenaline and norepinephrine in the system is required. An endocrinologist will help.
Normalization of sleep and wakefulness, physical activity, and diet optimization also play an important role.
Puberty
It should not be said separately. Puberty causes a real hormonal “storm” in the body of a young man or girl.
In a teenager, the difference between blood pressure readings and blood pressure itself changes unpredictably throughout the day. The reason is a rapid disruption of the regulation of vascular tone at the neurogenic and biochemical levels.
This is an interdisciplinary problem, but treatment is usually not required. Everything comes to naught on its own.
However, in the case of a significant increase in the gap (more than 60 units), specific therapy is necessary, therefore, during the entire teenage period, it should be observed, at a minimum, by a cardiologist. If necessary, see an endocrinologist and neurologist.
Physical overload
Advertising:
Caused by hormonal factors. The body responds by releasing corticosteroids and catecholamines. Sometimes the synthesis of active components is inadequate to the situation, especially in the presence of concomitant pathological processes.
Subjective factors
Gender, age and body type may play a role in certain cases, but infrequently, so they are not of great diagnostic significance.
Subjective factors, such as smoking, also have an impact. Abuse of alcohol (and some do not need to drink a lot, the body is designed in such a way that it cannot tolerate ethanol and has low resistance to the negative effects of alcohol), psychoactive substances (drugs, especially cocaine and a more dangerous variety - heroin).
Increased systolic pressure
High upper pressure is a sign of:
- Overactive thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis);
- Severe anemia;
- Bradycardia (decreased heart rate);
- Aortic valve insufficiency;
- Reduced elasticity and increased density of the vascular wall (for example, atherosclerosis of the aorta).
This condition is called isolated systolic hypertension or systolic hypertension. Upper blood pressure often increases during adolescence. This is due to hormonal changes in the body and is not considered a deviation. With the completion of puberty, the indicators return to normal. True, such changes increase the chances of developing hypertension in adulthood.
Treatment of systolic hypertension is generally similar to those taken for normal hypertension. This also applies to prevention. The main thing is to identify the disease in time, regularly monitor your blood pressure and take medications prescribed by your doctor, including those that help lower blood pressure. In addition, you need a diet, adequate physical activity, and protection from stress.
What causes the pathological condition?
{banner_banstat5}
A decrease in the pulse difference is accompanied by an increase in the diastolic value or a decrease in the systolic value. Sometimes this occurs simultaneously. The triggers for this difference are the following somatic diseases:
- lipid metabolism disorders, pancreatic dysfunction;
- hypertension of any degree;
- cholesterolemia leading to vascular stenosis;
- imbalance of cerebral blood flow;
- kidney pathology;
- arrhythmias of various origins;
- aortic stenosis;
- myo-, pericarditis, myocardiopathy;
- left ventricular failure;
- tumors of the urinary system;
- neoplasms in the adrenal glands;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- aortic aneurysm;
- cardiogenic shock;
- hypocaloric diets, dehydration, hypothermia.
Age is a cause of isolated systolic hypertension or IHS.
Over time, the layer of muscles in the vessels, which is responsible for their elasticity and lumen, becomes thinner. Against this background, plaques of calcium, blood clots, and cholesterol form. Arteries demonstrate fragility and respond inadequately to fluctuations in biomarkers. As kidney nephrons age, they lose their main function and stop regulating blood pressure.
The myocardial receptors that correct the response of the arteries to the systolic ejection of blood are subject to destruction. At the same time, the oxygen supply to the centers responsible for vascular tone deteriorates; they lose the ability to balance it. All this distinguishes patients over 60 suffering from age-related hypertension.
Reduced upper pressure
Low upper pressure may be associated with lifestyle or illness. In the first case, we are talking about constant overwork and systematic stress, lack of sleep and excessive physical activity. As for pathologies, a decrease in systolic pressure is caused by:
- Thyroid diseases, hormonal imbalances;
- Diabetes;
- Vegetovascular dystonia;
- Arrhythmia;
- Heart failure.
The cause may be prolonged depression. In any case, to normalize the pressure, you need to consult a doctor and identify the factors that contributed to the decrease in pressure. Usually the doctor recommends mainly preventive measures such as strong tea, contrast showers, and healthy sleep. But in some cases, drug treatment is required.
Treatment tactics
{banner_banstat9}
The treatment regimen consists of two elements: symptomatic and etiological. It is important to remove the main manifestations to normalize the patient’s standard of living, stabilize the condition to an acceptable level, and then eliminate the root cause.
This can be done using different methods: through hormone replacement, surgery on the kidneys, brain, blood vessels, etc. Comprehensive assistance is required from various branches of science and practice.
A big role is given to the normalization of lifestyle and correction of diet and physical activity regimen. Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol is a good help in therapy.
A large difference between the lower and upper pressure means that a pathological process is taking place. What type and why it arose is a separate question that doctors of different specialties will have to solve.
The treatment is long and complex. It may last a lifetime (maintenance doses of medications are determined by doctors). Self-therapy is categorically unacceptable: it is a dead-end path, most likely leading to death in the end.
Controlling blood pressure is the key to the health of the whole body
Blood pressure is a common name for two indicators: systolic (upper) and diastolic (lower). If any of them goes beyond the normal range, as well as an excessively large or very small difference between the indicators, they can be symptoms of various diseases. In order not to miss the onset of pathology and take timely measures, it is necessary to regularly measure blood pressure and consult a doctor if the measurement results do not correspond to the norm.
Clinical manifestations
{banner_banstat6}
In case of pathology of pulse difference, which is provoked by somatics, the patient complains of:
- fatigue;
- mood instability;
- forgetfulness, lack of concentration;
- constant pre-fainting state;
- bluishness of the skin.
In case of cardioshock, the symptoms are different:
- pale dermis, mucous membranes;
- profuse sweat;
- fainting;
- dyspnea.
Isolated systolic hypertension is sluggish, almost asymptomatic, but is characterized by:
- ringing in the ears;
- fainting;
- incoordination;
- emotional lability;
- arrhythmia.
The mild course of the disease spontaneously gives way to a crisis when physical inactivity, diabetes, myocardial dystrophy, kidney pathology, AMI, and a history of stroke predominate.
Forecast
{banner_banstat10}
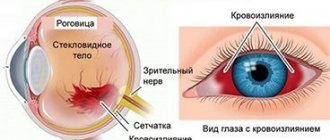
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, regular medical examinations, and medical examinations, the prognosis is favorable. Age-related hypertension is particularly insidious. ISH is not aggressive, but can be complicated by spontaneous hemorrhages in the retina, brain, and kidneys.
Fragile vessels cannot withstand pulse changes. Vascular rupture causes unpleasant symptoms, worsens the quality of life of patients, and requires special treatment.
The key to active longevity is the doctor’s individual approach to each patient, adequate therapy, and maintaining the upper limit at 140 mm Hg. Art.
Diagnostics
{banner_banstat8}
After a conversation with the patient, the doctor prescribes a full clinical and laboratory examination, taking into account the direction in which the tonometer deviation occurred. Mandatory for everyone is an ECG, as well as an EchoCG, which evaluates the electrical activity of the myocardium, the condition of the heart chambers, and the large arteries adjacent to them. Additionally prescribed:
- UAC, OAM;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the urinary system;
- MRI of the aorta;
- angiography of the renal arteries.
The ISH study algorithm is simple: 24-hour monitoring of blood pressure over time. In addition, they prescribe: blood sugar tests, lipid and coagulograms, ultrasound of cerebral vessels. If necessary, the patient is consulted with an angiosurgeon, neurologist, diabetologist, nutritionist, and psychotherapist.
Prevention
{banner_banstat9}
The patient’s lifestyle is important: giving up bad habits, diet, dosed exercise, walking, proper rest. It is necessary to calculate the daily drinking ration together with your doctor, at least 2 liters of clean water daily. Instead of saunas and hot baths, take a contrast shower. The diet should consist of vegetables, fruits, and foods containing iron: liver, tomatoes, fish, apples. A healthy lifestyle is especially relevant for those who have crossed the forty-year mark.