What do the numbers on the blood pressure monitor mean?
When measuring pressure, you need to pay attention to all indicators displayed on the monitor. The first number shows the systolic (upper) pressure, which occurs at the moment of maximum contraction of the heart muscle. The device records the diastolic (lower) pressure during complete relaxation. The third indicator is also important – heart rate.
If you see unusual numbers on the tonometer, you should not panic. They may mean that the device is faulty. However, if normal upper and low lower pressure is demonstrated by another device, there is a reason to consult a doctor for advice. After a comprehensive examination, a specialist will be able to draw a conclusion about why the pressure values deviated from the norm and draw up a scheme for the most effective therapy.
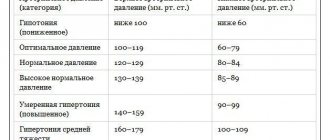
The reference values can be called 120/80 mmHg. Art. with a pulse from 60 to 80. However, for people of different ages, genders, health conditions and lifestyles, they may differ slightly from the ideal, which will not be a deviation from the norm. But only in the case when the pulse difference (the difference between lower and upper blood pressure) is from 20 to 40 units. At a pressure of 120 to 60, the upper value is optimal, but the readings at the time of diastole are underestimated and may indicate health problems. The impressive pulse difference also raises concerns.
No ads 1
Will I be able to increase the lower level on my own?
It's almost impossible to do this. When taking hypertensive drugs, both indicators increase: systolic and diastolic. In order to selectively influence the desired value, a combination of several drugs will be required; it can only be selected through testing, as part of inpatient examination and treatment. It is impossible to do this on your own; you need to consult a doctor. And this will be the best solution to the problem.
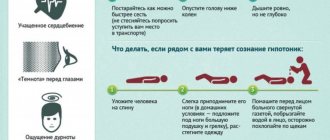
To urgently help your own body, you need to take a horizontal position, free your neck from oppressive clothing, then you should call an ambulance, especially if your blood pressure readings are at critical levels and wait for the doctors to arrive.
You cannot take baths, wet your hands, wash your face, or eat food. Loss of consciousness, vomiting, asphyxia and death are possible.
It is advisable to have someone familiar nearby to assist with syncope.
Nothing more can be done at home; all other measures should be entrusted to medical personnel.
Additional symptoms
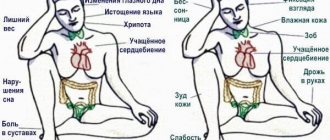
Low diastolic pressure against a background of normal systolic pressure is usually accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- A man has a headache.
- Your heart rate slows or your pulse becomes irregular.
- Dizziness occurs when you suddenly turn your head or come out of the dark into the light.
- Fainting, starting with darkening of the eyes, is possible.
- Memory deteriorates.
- Activity decreases, fatigue occurs even at rest.
- The patient becomes irritable, periods of apathy are replaced by aggression.
With both hypertension and hypotension, a person begins to react sharply to the vagaries of the weather with increased symptoms
Reasons for violation
If the pressure is 120 to 60 mmHg. Art. when the pulse is 50, it is recorded for the first time or bothers a person only occasionally; it can be caused by physiological factors and can be easily corrected. Among the main causes of the condition are:
What does pressure 135 over 65 mean?
- hypothermia;
- dehydration;
- stress;
- starvation;
- intense physical activity, for example, in the gym (pulse and blood pressure drop during rest - the heart regains strength after overexertion);
- pregnancy (during the period of bearing a child, especially in the 1st trimester, blood pressure can fluctuate in the range of 20 mm Hg about the norm and this does not indicate abnormalities in the functioning of the body).
No ads 2
Pressure 125 over 60 or 120 over 60 mmHg. Art., recorded regularly, can be a symptom of serious pathologies, including the following:
- endocrine diseases (adrenal diseases, diabetes mellitus);
- cardiac pathologies (bradycardia, heart failure, congenital aortic valve defects, infectious myocarditis, coronary artery disease, recent heart attack, etc.);
- atherosclerosis;
- kidney diseases;
- malignant tumors;
- acute poisoning;
- pulmonary embolism;
- profuse blood loss due to extensive trauma.
Low diastolic pressure may be accompanied by increased heart rate. Thus, a pulse of 90 is a compensatory reaction to hypoxia and decreased blood circulation.
If the lower pressure drops to 40 mm Hg. Art. Emergency assistance should be sought as this condition may indicate a life-threatening condition requiring urgent hospitalization. Trying to raise this pressure on your own with pills or a cup of strong coffee is not recommended.
Important! Some medications can also reduce diastolic pressure. If the phenomenon occurs during the treatment of a chronic or infectious disease, this must be reported to the doctor, who will adjust the dose of the medication or select an alternative that does not provoke blood pressure fluctuations.
If unpleasant symptoms associated with changes in blood pressure appear, you need to visit your general practitioner, who will give you directions for examination.
What to do with such blood pressure?
Elimination of accompanying symptoms is considered an urgent measure, and this does not negate the identification of the cause of this disorder. To do this, you need to go to a therapist, who will prescribe treatment or refer you to see highly specialized doctors (cardiologist, neurologist, etc.).
Drugs that lower or increase blood pressure are not required in this case if you feel normal. If you feel unwell, then it is enough to take something for the headache. To normalize the condition on your own for a long time, it is recommended to adjust your lifestyle.
If diastolic pressure drops, the first aid may be:
- taking a contrast shower or warm bath (depending on personal preference);
- performing gymnastics (several exercises);
- essential oils (tonic, invigorating);
- food and drinks;
- preparations (tincture of ginseng, lemongrass, Rhodiola rosea, golden root).
Do not self-medicate with medications that regulate blood pressure (not prescribed to you by a cardiologist or therapist), otherwise this may result in, at best, a temporary deterioration in your condition, and at worst, death.
You cannot decide on your own to take any medications that affect your blood pressure. If used incorrectly, they can worsen the situation. If you have doctor’s recommendations received at your appointment, you must strictly follow them.
Diagnostic methods
The reason why low blood pressure decreases can be determined through comprehensive diagnostics. The list of survey activities includes:
- General blood analysis. Biochemical research allows us to identify anemia, which often causes low blood pressure, especially in young women.
- ECG. An echocardiogram gives a complete picture of the structure of the heart and whether its functioning is normal. In this way, it is possible to determine heart valve disorders and other severe pathologies in a person of any gender and age.
- X-ray. Through X-ray examination, it is possible to identify a number of diseases that can lead to fluctuations in blood pressure, accompanied by an increase or decrease in heart rate.
Age norms of blood pressure: yesterday and today
You may not know, but the European Society of Cardiology has tightened blood pressure standards. The thing is that earlier recommendations “failed” to prevent complications of vascular diseases. And damage to the brain, heart, eyes and kidneys due to hypertension continues to be a serious medical problem. So what “numbers” are recommended by leading experts? And what can “spoil” blood pressure?
What changed
According to previously existing standards, the blood pressure (BP) of a healthy person at rest should not exceed the following values:
- 120/70 – 130/80 – for people aged 20-40 years,
- 140/90 – at the age of 40-60 years,
- and 150/90 for patients over 60 years of age.
New recommendations from European experts (2018) have significantly tightened the standards, and now the blood pressure “figures” should not exceed:
- 129/80 – for people under 65 years of age
- and 139/80 for older patients.
Which, by the way, corresponds to the recommendations of American cardiologists, adopted a year earlier than European ones.
As you can see, the changes concern not only the upper (systolic), but also the lower (diastolic) pressure. This means that the diagnosis of hypertension itself and the initiation of its treatment are now authorized much earlier.
What can spoil blood pressure?
Of course, one of the most significant risk factors for hypertension is heredity and age-related changes.
Thus, cases of vascular pathologies, especially with a disabling outcome in close relatives, are a serious reason to take the vessels under constant “control”.
And with “age,” the vascular wall significantly loses its elasticity and ability to expand, because:
- firstly, the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers decreases,
- and secondly, the thickened walls of blood vessels due to pressure changes (the vasoconstrictive effect of stress hormones, cigarettes and some other factors) do not have the ability to stretch.
So we can say that vascular pathologies have a “cumulative” nature, beginning to form at a young and active age.
In addition, with age, cholesterol deposition and the formation of plaques are observed, narrowing the diameter of blood vessels and further aggravating the problem.
Blood pressure "under control"
Taking into account the above factors, it is obvious that it is better to start paying attention to blood vessels at a young age and regularly.
The presence of regular and/or prolonged stress, smoking, drinking alcohol, a sedentary lifestyle, excess weight and diseases of the kidneys, heart or adrenal glands are reasons to periodically check the degree of damage to the vascular wall. And for this, a blood test for ultrasensitive C-reactive protein is suitable.
The marker reflects vascular damage long before the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots on the damage, as well as changes on ultrasound and any clinical signs. Therefore, it can be used for the earliest detection of the degree or risk of vascular pathologies.
In addition, it is worth taking control of cholesterol and its fractions, even outside of eating “fatty” foods. After all, lipid levels have a direct relationship with:
- liver health (since this is the place of its formation),
- level of sex hormones,
- overweight,
- as well as diseases that disrupt fat metabolism (diabetes mellitus, lack of “thyroid” hormones and some others),
and cholesterol “balance” disorders can be detected at absolutely any age.
Periodic “jumps” in pressure and the development of arterial hypertension can also be provoked by:
- imbalance of salts (sodium, potassium, chlorine),
- disorders of urinary function of the kidneys
- and excess renin.
And the latter also makes hypertension resistant to standard therapy. And assessment of the renin level is used to exclude the renal nature of the “pressure”.
Treatment
What to do if the examination reveals a serious pathology that requires treatment? In this case, you should not adjust blood pressure, but focus on solving the primary problem. Only by eliminating the reason why the pressure dropped from the usual 120 to 80 to 120 to 65 or 60 mm Hg. Art. you can improve your well-being.
With a pressure of 120–122 at 60–66 mm Hg. Art. alcohol, namely red wine, in small doses is not only allowed, but recommended by doctors
If no concomitant diseases are found, then you can stick to home methods to solve the problem. Namely:
- When your head starts to hurt due to decreased blood pressure, you can take a tablet that has an antispasmodic effect, for example, Spazmalgon or Citramon, which slightly increases blood pressure.
- Traditional medicine recipes, previously agreed upon with your doctor, will help strengthen blood vessels and normalize the heart rate: decoctions of elecampane, yarrow, infusions of Chinese lemongrass, tinctures of ginseng and eleutherococcus. The course of treatment is at least 40 days.
- It is important to include sports in your schedule: jogging in the nearest park, going to the pool or doing yoga. If you have no free time at all, you can limit yourself to morning exercises.
- Problems with blood pressure may be associated with disrupted sleep patterns. In this case, it is worth eliminating shift work or night work, which prevents you from fully resting at night for at least 8 hours.
- The most dangerous habit that negatively affects blood pressure is smoking. Nicotine reduces the volume of the lungs, causing the heart to work at an increased pace, and clogs the blood vessels and liver cells. By giving up this bad habit, you can quickly get rid of blood pressure fluctuations without the use of medications.
- Nutrition plays a leading role in normalizing blood pressure. It is better to opt for 5 meals a day in small portions. Food should be varied, rich in healthy vitamins and microelements.
Advice! The Mediterranean diet, consisting mainly of sea fish, vegetables, and olive oil, has the most beneficial effect on the body as a whole and the state of the cardiovascular system as a whole. For snacks, you should choose nuts, fruits, dried fruits, rather than empty carbohydrates.
Which doctor should I contact?
Often, changes in lower pressure occur without any special symptoms, and a person may feel normal. But there are signs, if they appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Dangerous symptoms:
- often headaches, unpleasant sensations are localized in the temporal and occipital parts;
- drowsiness, weakness;
- numbness of the tip of the tongue;
- dizziness;
- constant feeling of cold;
- nausea, dark circles before the eyes.
Which specialist should you contact in such cases? First, you should visit a therapist. Based on the initial examination and the results of clinical tests, he will give a referral to a cardiologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, gastroenterologist.
If you have problems with blood pressure, you should first consult a therapist
Important! There is no need to self-diagnose or take medications on the advice of relatives and friends. Failure to contact a specialist in a timely manner can lead to serious consequences.
Why is a decrease in diastole pressure dangerous? Congestion occurs, the heart has to work harder, which leads to an increase in systolic indicators - the risk of developing ischemia, stroke, and heart attack increases. For older people, insufficient blood supply to brain tissue is fraught with Alzheimer's disease, which is almost impossible to cure.