Stroke is a complex disease directly related to disruption of cerebral blood flow that occurs as a result of blockage of blood vessels due to blood clots or growths, all of which leads to disruption of normal brain function and, consequently, to limited ability to work and life. As a rule, strokes happen to people of pre-retirement and retirement age, however, modern statistics show that this disease tends to “get younger”; every year more and more young people are susceptible to this disease.
Who is eligible for disability after a stroke?
According to the norms of the current Russian legislation, which are based on Federal laws and legislative documents of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, all patients without exception have the right to register disability, subject to the presence of appropriate medical indications. A disease such as stroke, despite its inclusion in the list of diseases for registration of disability, is not always the basis for assigning disability. The right to receive disability after a stroke is granted only to those patients whose brain functions have not fully recovered, that is, they cannot fully live and carry out their work activities as a result of impaired hearing, speech, vision, coordination of movement and other functions.
Diseases for group II
For group II, the indicator is a deviation from the norm of 70-80%. A person is able to perform simple actions (including resorting to special means or the help of other persons). He works despite physical or mental disabilities, but under special conditions. Among the diseases:
- fecal fistula;
- chronic pulmonary insufficiency or absence of one lung;
- irreversible visual impairment;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- mental illness;
- skull defects;
- leg paralysis
What needs to be done to obtain disability after a stroke
Disability for any disease can be assigned only by the Medical and Social Expert Commission, to which the patient must be referred by the attending physician. Disability after a stroke can be obtained both while in a hospital for treatment, and after discharge from the hospital. If we are talking about seriously ill patients, the commission can be passed even at home, if the health care institution issues an appropriate conclusion about the patient’s inability to appear for an examination for health reasons. To obtain disability after hospital you should:
- contact the doctor at the clinic at the place of registration, where at the appointment you can tell about the health problems that have arisen as a result of the illness you have suffered and inform about your intentions to receive disability;
- the attending physician is obliged to make appropriate entries in the patient’s medical record and give him directions to undergo tests and undergo the necessary examinations from specialized specialists, these are, as a rule, an endocrinologist, a psychiatrist, an ophthalmologist and a cardiologist;
- to receive a referral for VTEC, the patient must pass biochemical and clinical tests, undergo an ECG, EEG, REG, CT or MRI examination, Doppler ultrasound, skull X-ray, vascular ultrasound and others - all indications must be entered into the patient’s medical record;
- upon receipt of all the necessary examination results, the attending physician writes out a referral in the established form to undergo an ITU commission;
- upon receipt of a referral, the patient writes an application for an examination, after which a time and date for its conduct are set;
- The commission must provide identification documents, a detailed extract from the medical history and documents that confirm the results of all studies performed, which, together with a personal examination by the patient commission, will be the basis for the commission’s decision to assign or deny disability.
Important! When undergoing examinations, do not hesitate to tell specialists about your health problems that have arisen as a result of your illness, including how they affect your performance.
You can read more about the procedure for registering a disability in our article “How to register a disability.”
New rules in 2021
Government Decree No. 92 of 02/01/2021 extended the temporary procedure for recognizing a person as disabled until the end of 2021.
At the same time, changes were made to the rules for conducting a medical and social examination (MSE) in absentia and the rules for recognizing a person as disabled in 2021 without being called to a commission. ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to apply for disability. Use these instructions for free.
to read.
What disability groups can be established after a stroke?
The commission establishes the disability group as a result of the illness in accordance with the criteria for assessing the patient’s condition. There are many criteria by which group membership can be assessed, the main ones being:
- the patient’s dependence on other persons – the ability or impossibility of self-care;
- the ability to move the patient;
- spatial orientation;
- communication criterion;
- control of patient behavior.
Let's consider the main criteria for establishing disability for each of the groups: Group I (first group of disability) - the basis for establishing a stroke is persistent motor and functional impairments of high severity, which led to a sharp limitation of normal life activities and deprivation of the patient’s ability to self-care, resulting in the need for constant care for the victim. Group II (second disability group) - the basis for the diagnosis of stroke is persistent functional impairment of severe severity. The group is established for patients who have retained the ability to self-care, but are unable to work. Group III (third disability group) - the basis for the diagnosis of stroke is the presence of persistent functional disorders of moderate severity in the patient, which may disappear after some time. The group is established for able-bodied patients with minor health disorders for whom certain types of work may be contraindicated.
Important! Establishing disability in the event of a stroke implies re-examination, taking into account the possibility for the patient to return to normal life and work activity upon restoration of dysfunction. However, after 4 years, if there are no changes, the disability group is established indefinitely.
Main risk factors
Before talking about what kind of prevention is necessary, you should decide who primarily suffers from acute cerebral ischemia. There are groups of people whose risk of disease is many times higher than others. These are the so-called risk groups. They are divided into controlled and uncontrolled.
It is impossible to change anything if there is a hereditary predisposition, gender (men), or old age. It is these three factors that increase the risk of stroke and are considered uncontrollable.
Controlled factors include the following conditions:
- Hypertension. Persistent and difficult to correct with drugs high blood pressure from 160/90 mm Hg. Art. increases the possibility of stroke by 4 times, and at a pressure of 200/110 mm Hg. 10 times.
- Heart rhythm disturbances. With atrial fibrillation, blood hemodynamics are disrupted. Blood clots that form in the cavities of the heart muscle rush into other vessels and are a common cause of stroke. As a rule, the disease caused by this cause is characterized by severity and a negative prognosis.
- Diabetes. Violations of the rheological properties of blood and changes in the vascular wall with this disease occur 5 times more often.
- Smoking. Promotes the accelerated formation of atherosclerotic changes in the carotid arteries, which causes a 2-fold increase in the possibility of vascular accident.
- Atherosclerosis. High lipid levels are directly related to circulatory problems.
- Alcohol. Regular intake of large doses increases the risk by 3 times.
- Obesity.
- Passive lifestyle.
- The influence of constant stress.
- Diet disorder.
Limitations in work activity after a stroke
Of course, intensive work activities are contraindicated for all patients who have suffered a stroke. We list the most commonly used restrictions:
- elimination of psycho-emotional and heavy physical stress is required;
- do not work under conditions of sudden temperature changes and vibration loads;
- any interaction with toxic and harmful substances is excluded;
- It is prohibited to carry out activities in a prolonged forced position of the body in tension, especially regarding the neck and head.
When considering the restrictions in a patient’s work activity after a stroke, first of all, the complications that arose as a result of the disease are taken into account; it is also necessary to assess his capabilities and limitations in his life.
Diseases for group III
It can be difficult to distinguish healthy people from group III disabled people based on external signs. Citizens with this group have the right to work, since the rate of loss of function is 40-60%.
Diseases for assignment to disability group III include:
- incipient cancer;
- absence of one eye;
- ptosis of one eye (permanent, persisting after treatment);
- bilateral deafness;
- jaw defects in the absence of the ability to chew;
- facial defects that can only be corrected through surgery;
- defects of the skull bones;
- paralysis of the hand or one of the limbs, causing muscle wasting;
- the presence of a foreign object in the brain after injury;
- installation of a foreign body in the heart area (pacemaker, artificial valve);
- amputation of the hand, one or more fingers;
- one kidney or lung.
New procedure for passing the ITU
The current regulations reflect what new rules in 2021, when receiving a disability group, are followed by medical organizations, ITU and the Pension Fund. A medical organization, in a referral for medical examination issued to a citizen for the first time, indicates information about the results of medical examinations necessary to obtain clinical and functional data depending on the disease, reflecting:
- the citizen's health status;
- the degree of dysfunction of organs and systems of the body;
- state of the body's compensatory capabilities;
- carried out rehabilitation or habilitation measures.
In the initial referral to the ITU, they do not indicate the need for other medical examinations for citizens:
- having diseases, defects, irreversible changes or disorders included in the list approved by Government Decree No. 95 of February 20, 2006;
- sent to ITU for the purpose of developing an individual rehabilitation or habilitation program for a disabled person (disabled child) in the presence of previously conducted examinations within 12 months confirming diseases, defects, irreversible changes and the severity of dysfunction of organs and systems of the body.
The decision to establish disability (category “disabled child”) for the first time and to develop an individual rehabilitation or habilitation program is made by the ITU Bureau based on information about the citizen’s health status contained in the referral issued by the medical organization.
About stroke
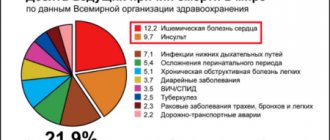
Stroke is a serious pathological condition that develops against the background of a sudden disruption of the blood supply to brain cells, which is fraught with necrosis of areas of brain tissue with the development of neurological symptoms.
Stroke is not an independent pathology, but a consequence of progressive local or systemic vascular disease with various disorders. In the structure of sudden mortality, stroke firmly ranks second after diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The etiology of stroke is diverse. All causes are classified into two groups - common provoking factors and diseases:
- Etiological factors. These include the patient’s age group, genetic predisposition, smoking, obesity, alcohol abuse, and low physical activity.
- Pathologies. Damage to the carotid arteries, hypertension, atherosclerotic changes, heart attack, rheumatoid endocarditis, atrial fibrillation, cervical osteochondrosis, etc.
In medicine, there are several types of strokes, and all of them pose a danger to human health and life.
A complete list of cash payments from the state for Russians who have suffered a stroke