From this article you will learn: why there can be high upper blood pressure with normal lower blood pressure. At what age does this most often occur, how to establish a diagnosis, how dangerous this pathology is, and how to treat it.
Author of the article: Yachnaya Alina, oncologist surgeon, higher medical education with a degree in General Medicine.
Article publication date: 05/05/2017
Article updated date: 02/05/2020
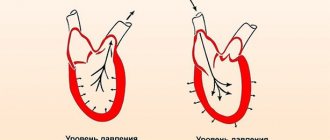
An increase in only the upper pressure is called isolated systolic arterial hypertension (abbreviated as ISAH). The identification of such hypertension as a separate type is associated with the difference in the mechanism of its development (compared to “classical”), in the effect on target organs (kidneys, heart, retina, brain) and in the prognosis.
The incidence of ISAH is 2.4–14%, the main contingent of cases is over 60 years of age. The increase in the percentage of this form of hypertension directly depends on age, and by the age of 70–80 years it is diagnosed in more than 80% of patients with arterial hypertension.
The reason for the increase in upper (systolic) pressure, while maintaining normal lower (diastolic) pressure, is a decrease in the distensibility of the main arterial vessels, especially the aorta, as the main one. Under physiological norms, the central arteries, due to their elasticity, accept and suppress the force of cardiac output, uniformly passing blood further throughout the body. If the aortic wall becomes rigid, higher pressure is needed to “push” blood out of the heart, while the function of small vessels does not suffer and the level of diastolic tension remains the same.
Increased pressure in the central arteries leads to a number of pathological changes:
- The growth of muscle tissue (hypertrophy) of the left ventricle with a gradual decrease in its function is a failure of the heart.
- Violation of the “smoothness” and speed of blood distribution through large arteries (decreased blood supply to organs).
- Traumatization of the inner layer of blood vessels (endothelium) by blood flow under high pressure leads to the replacement of the damaged area with connective tissue, increasing the rigidity of the vessel and aggravating the disease.
- Production of active enzymes (renin, angiotensin, nitric oxide, etc.). Their effect on the vascular wall in conditions of disease leads to an increase in pressure and forms a pathological circle.
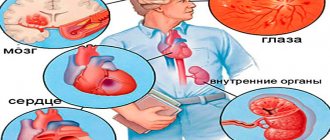
Why is this dangerous? High blood pressure is the cause of insufficient blood flow in target organs:
| Organ | Pathology |
| Heart | Chronic failure does not allow one to fully cope with simple physical activities (climbing stairs, cleaning the house, etc.). Acute failure (heart attack) with extensive damage leads to rapid death, and if treated, it leads to chronic failure of the heart muscle. |
| Brain | Chronic deficiency is the cause of a gradual decline in mental abilities (intelligence, memory, etc.) Acute deficiency (stroke) can lead to death or severe disability with loss of the ability to care for oneself |
| Kidneys | Chronic failure leads to the proliferation of connective tissue with a gradual decrease in function. The acute form is erased, provided that both kidneys are functional |
| Retina | The chronic form is characterized by a gradual decrease in visual acuity. The acute form is the cause of complete blindness within a short period of time. |
In hypertension, when the upper pressure is increased and the lower pressure is normal, the risk of severe or fatal complications is 2–5 times higher compared to the form where both indicators are increased. But any type of arterial hypertension without treatment in 83% of cases leads to acute damage to the heart and brain - the main causes of death in adults around the world.
Considering the mechanism of development of ISAH, there is no complete cure for the disease, but with constant therapy, with good blood pressure control, the risk of death from complications is reduced by 25%.
The diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of patients with arterial hypertension are carried out by therapists and cardiologists. The development of complications requires the intervention of neurologists, nephrologists and ophthalmologists.
Causes of pathology
Secondary form of ISAH
Secondary ISAH is a complication of a number of pathologies:
| Group of diseases | Specific diseases |
| Hereditary and congenital disorders | Coarctation (narrowing) of the aorta Patent ductus arteriosus Polycythemia (increased red blood cell count) |
| Cardiac and vascular disorders | Complete atrioventricular block (impaired heart contraction) Aortic valve insufficiency Atherosclerosis of the renal arteries Aortoarteritis (inflammation of the vascular lining) |
| Other violations | Anemia Fever Thyrotoxicosis (high level of thyroid activity) |
Primary form of ISAH
Primary, or essential, ISAH develops through the interaction of two or more risk factors (these risk factors are the same for any form of arterial hypertension):
- genetic defect;
- age-related changes in the vascular wall (decreased elasticity) and metabolic disorders (increased activity of pressure-stimulating hormones);
- atherosclerosis;
- smoking;
- excess weight with impaired fat metabolism;
- diabetes;
- female gender (incidence is twice as high).
Prevention
To prevent problems from arising, you need to prevent the occurrence of isolated systolic hypertension:
- get rid of excess weight;
- reduce the amount of salt in the diet;
- eat foods containing calcium, potassium and magnesium;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- carry out anti-stress therapy;
- control the course of diabetes mellitus in the presence of such pathology;
- Use any medications only under medical supervision.
An increase in upper blood pressure against the background of normal lower blood pressure may indicate dangerous disorders. To cope with the pathology, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination and strictly adhere to the doctor’s recommendations.
Did you like the article? Save it!
Still have questions? Ask them in the comments! Cardiologist Mariam Harutyunyan will answer them.
Ivan Grekhov
Graduated from the Ural State Medical University with a degree in General Medicine. General practitioner
Classification
| Classification according to changes in diastolic pressure levels | Classification by stream |
| Type 1 (60%) – no increase. Type 2 (40%), or “burnt-out hypertension” - a gradual transition of the form with increased numbers of upper and lower pressure into ISAH. | Stable – fluctuations in upper pressure are insignificant, a crisis increase is extremely rare. Labile or crisis - pronounced fluctuations in systolic pressure with frequent hypertensive crises. |
What do the indicators depend on?
Despite the fact that upper blood pressure is called cardiac blood pressure, the numbers are influenced by several factors, namely
Hypertensive crisis - what is it?
- heart rate;
- blood ejection rate;
- left ventricular stroke volume;
- distensibility of the aortic walls.
Thus, the upper blood pressure is affected not only by the heart, but also by the blood vessels (large).
Most often, surges in systolic blood pressure are encountered by elderly people, whose vascular elasticity decreases due to age-related changes. But today, hypertension is also diagnosed in young people. The reasons causing the violation may be the following:
- unhealthy diet, replete with fatty, salty, spicy foods;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol;
- sedentary lifestyle);
- increased physical or mental stress;
- stressful situations;
- chronic fatigue;
- sleep disorders;
- weather;
- some medicines and traditional medicine.
Obese people suffer from hypertension in 90% of cases
Characteristic symptoms
ISAH in 50% of cases is asymptomatic until signs of blood flow disturbances in the heart and brain appear. Manifestations are the same for all forms of hypertension:
- headaches of varying localization and intensity;
- discomfort, pain in the projection of the heart;
- nonspecific symptoms of chronic insufficiency of cerebral blood flow: fatigue, mood changes, memory problems, etc.;
- decreased vision, “spots” and darkening in the eyes.
During a crisis at high pressure levels, severe headaches, vision changes, nosebleeds, and dizziness may occur. But more than half of the patients do not have specific clinical manifestations. High blood pressure – an accidental discovery at a doctor’s appointment or at home; Often, general health does not suffer, allowing you to perform normal activities.
Secondary changes in blood flow in the main organs gradually reduce the ability to perform usual activities and lead to disability.
Diagnostics
Have you suspected or discovered that you have high blood pressure?
Make an appointment with your GP as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct an initial examination, which will allow you to establish an accurate diagnosis and select adequate treatment. In most cases, the diagnosis of systolic hypertension includes:
- Anamnesis collection . The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient regarding the existing symptoms of the disease, lifestyle, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies. All this allows the specialist to make an assumption regarding the possible causes of the increase in upper pressure.
- Physical examination . It involves the doctor listening to the heart using a phonendoscope, during which the specialist has the opportunity to determine the presence of a murmur in the heart, disturbances in its sounds, and other associated abnormalities.
- ECG . The most popular diagnostic method for high systolic pressure, which allows you to confirm the diagnosis of “systolic hypertension”, as well as identify heart rhythm disturbances.
In some cases, the patient may be prescribed Holter monitoring (daily cardiogram).
- Ultrasound of the heart . An auxiliary diagnostic method, during which disturbances in the functioning and structure of the heart valves, and serious defects in the structure of the heart muscle are detected.
- Doppleography . _ A diagnostic method that allows you to assess the condition of the vascular system. With systolic hypertension, it is important to monitor the condition of the arteries leading from the heart to other organs and their systems.
- Laboratory research methods . Most often we are talking about a general analysis of urine, blood, and a blood biochemistry test that determines cholesterol and sugar levels.
If necessary, the therapist can refer the patient for consultation to specialized doctors - a cardiologist and an endocrinologist.
Treatment methods
In cases of secondary ISAH, the disease that causes the high blood pressure is treated.
Therapy of the primary form is carried out with a combination of drugs from several groups:
| Group of drugs | Examples |
| Diuretics | Indapamide Hypothiazide |
| Beta blockers | Atenolol Bisoprolol |
| Calcium antagonists | Amlodipine Verapamil |
| Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors | Enalapril Lisinopril |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers | Losartan Valsartan |
In the case of the primary form, treatment is long-term (sometimes lifelong).
How to lower upper pressure
This can be done with medications or non-drug home remedies. The main thing is to understand the cause of hypertension.
When it comes to medications, doctors most often recommend Papazol and Metoprolol, which combine the properties of a diuretic and an antispasmodic. They act softly, slowly. In case of crisis levels of hypertension, a combination of drugs from different groups is prescribed, the combination is selected by the doctor. Furosemide is used in combination with Cinnarizine or Nebivator, Zofenopril, Blocktran. Or Lasix with Amlodipine, Quinapril, Candesartan. You can take Nifedipine.
You can quickly reduce upper pressure by using Capoten and Corvalol. Medication intake is monitored by tonometry. If there is no effect within an hour, the medications are repeated. The maximum dose of Capoten is 4 tablets, Corvalol is up to 100 drops. This reduction in blood pressure is safe.
An active lifestyle, walks in the fresh air - ways that do not require much effort improve the condition of the vascular wall.
You shouldn’t get carried away with folk recipes; ISAH is a serious disease. But you can still make steam baths for your feet and hands at home with a contrasting transition to cold water (a few minutes). Pharmacy tinctures of peony, hawthorn, and lemon balm are popular at home and are found in every hypertensive medicine cabinet.
Viburnum compote reduces the systolic rate. Beetroot juice, tincture of calendula (30 drops per dose), rose hips, stevia (drug of choice for diabetes).
Upper high blood pressure is corrected with a balanced diet: nuts, vegetables, fruits, eggs, milk, cheese, parsley, spinach, seafood. Be sure to exclude smoked meats, spices, and limit salt to 5 g/day. Anything that retains fluid in the body is taboo. The entire diet is agreed upon with the doctor. Self-medication for hypertension is death-like.
Forecast
Arterial hypertension, when the upper pressure is high and the lower pressure is normal in 68%, is combined with diabetes, pathology of lipid metabolism and ischemic disease, which significantly increases the risk of developing vascular and cardiac complications.
75% of people in the older age group are diagnosed with increased blood pressure, of which 52–87% have ISAH. 84% of the population dies every year from vascular pathology due to a constant form of high blood pressure.
Treatment of hypertension reduces mortality by 17%, and the risk of fatal complications (sudden death, stroke, heart attack) by 32%.
There is no complete cure for the disease - hypertension requires constant, lifelong therapy, but its implementation is the key to extending the quality and duration of life.
Norms
For each person, these indicators may be different. The norm depends on age, gender, weight, race, state of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems. Some people feel healthy with a constant blood pressure of 150/100, others feel unwell at 130/90 mmHg. Art.
We are accustomed to considering 120/80 mm Hg as the standard. Art. But this is far from true. It is better to focus on age, since it depends on it what kind of pressure may cause concern. For example, the upper limits of normal:
- up to 20 years - 100/70, 120/80 mm Hg. Art.;
- up to 40 years - 120/80, 130/80 mm Hg. Art.;
- up to 60 years - 130/80, 140/90 mm Hg. Art.;
- over 60 - 150/90 mm Hg. Art.
The average numbers on the tonometer display, which cause concern for the patient’s health, are 140/90 mm Hg. Art. But this is only relevant for a healthy person. For example, in diabetes mellitus, such blood pressure is normal and does not require special correction with medications.
High blood pressure with normal lower pressure is called isolated hypertension, requiring special examination and treatment
Pressure below 100/60 mm Hg. Art. refers to reduced. But for athletes or people constantly exposed to stress, it becomes normal over time. This is how the body adapts to the situation and regulates the person’s condition.
Important! Not only increased, but also decreased upper pressure indicates problems in the body. Low blood pressure is not as dangerous, but can lead to decreased gas exchange in the tissues and lungs. Hypoxia, in turn, in some cases ends in collapse (coma or even death).
How is isolated arterial hypertension with high systolic values treated?
The set of measures is generally identical to those for classical hypertension. Etiological treatment is necessary to eliminate the underlying disease that caused the pathological condition.
Symptomatic therapy consists of the use of combination drugs or the use of narrowly targeted medications:
- ACE inhibitors.
- Diuretics of various types.
- Calcium channel blockers and beta blockers.
This, however, is not enough. The use of medications is a half-measure. It is necessary to radically change your lifestyle. Quit smoking and alcohol, even in the smallest doses.
It is necessary to optimize the regime of physical activity, no physical inactivity, but you should not bother. Drinking regimen (2 liters of water per day), amount of salt consumed per day (less than one teaspoon).
The diet should contain fresh vegetables and fruits, protein. You need to worry less; stress is one of the risk factors. Although this is not so easy to do.
These methods are quite sufficient to normalize the health of the cardiovascular system.
Is it possible to develop isolated hypertension during pregnancy?
Yes, such a scenario is quite possible. The mother's body optimizes its activity, devoting all its strength to the benefit of the fetus.
Depending on the initial parameters, such as general health, endocrine status, the presence or absence of bad habits, the nature of professional activity, physical activity, normal blood pressure before pregnancy, we can talk about certain conditions during gestation.
Women more often have arterial hypotension, that is, low blood pressure. But everyone cannot be assessed by one criterion. ISAH also occurs. As a rule, the condition returns to normal after childbirth and stabilizes within the first month.
In any case, it is recommended to be observed by a cardiologist, especially if childbirth does not improve the situation.
Preventive measures
Primary and secondary prevention measures do not present any difficulties. It is enough to follow simple recommendations and follow common sense:
- Quit cigarettes and tobacco products altogether.
- Avoid alcoholic beverages.
- Normalize your diet. As many fortified foods as possible, as little fatty, fried, smoked and sweet foods as possible.
- Move more, but don't overexert yourself. This is fraught with a stroke.
- Consume less table salt.
- Regularly undergo examinations by doctors of the profile described above to monitor the state of the cardiovascular system.
- When prescribing therapy, take the prescribed medications in a timely manner.
A set of measures will prevent the development of hypertension in the future.