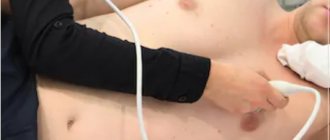
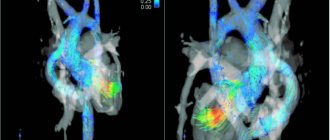
Echocardiography is considered one of the safest research methods, therefore it is often prescribed to children. Usually, a child is sent for an ultrasound of the heart after an ECG
, the results of which remained mixed. Modern ultrasound examination of the heart has many advantages over other types of diagnostics.
When is a child's heart ultrasound performed?
Doctors prescribe cardiac ultrasound for every child in the second month of life. Also, periodic ultrasound sessions of the heart are needed for children if there have been cases of defects of any internal organs, including the heart, and hypertension in their family. An ultrasound of the heart of a newborn baby is sometimes performed earlier than 1-1.5 months, if there is reason to suspect a defect or other problems with the organ. At a later age, direct indications for examination are murmurs, the nasolabial triangle turning blue when crying, as well as bluishness of the skin.
Indications for Echo-CG
Echocardiography, or Echo-CG, may be prescribed to a child if the following symptoms are present:
- pale or bluish skin, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle;
- shortness of breath, difficulty breathing;
- irregular heart rhythm, heart rate abnormalities;
- complaints of discomfort in the heart area;
- changes in blood pressure;
- increased sweating;
- fatigue, weakness;
- decreased tolerance to physical activity, etc.
In addition, if noises or abnormal tones are detected during listening during the initial appointment, the doctor may also refer for this study. Changes in the ECG or unsatisfactory results of other diagnostic methods are reasons to perform an urgent ultrasound of the heart.
There are other indications for diagnosis: Echo-CG is performed on infants if pathologies were detected during an intrauterine examination. After heart surgery, this diagnostic tool will help you monitor your condition and make sure everything is in order.
Children's Echo-CG is included in the complex of mandatory routine examinations for heart defects. Medical examination at 3 years, 7 and 14 years may also include this diagnostic method.
The doctor may refer you for an unscheduled ultrasound even in the absence of unpleasant symptoms. This is true for cases of past infections. The latter can affect the function of the heart. Thus, a history of infectious mononucleosis or severe acute tonsillitis are all grounds for such a prescription: you need to make sure that there are no complications on the child’s cardiovascular system.
How to prepare a child?
In addition to medical documents, you will need to bring to the ultrasound diagnostic room the diaper on which the baby is placed, and napkins to wipe off the gel from the skin after the procedure (or they will be given on the spot). To prevent the child from having the desire to “rebel” during an ultrasound of the heart, stock up on a bottle of milk or liquid porridge - this will make it easier to calm the baby. It will be useful to update information about the child’s height and weight to more accurately interpret the results. If this is not the first time a child has had a heart ultrasound, be sure to take the results of past studies with you.
Order of conduct
Echo-CG is performed absolutely painlessly and does not pose any risks to the child’s health, so the study can be repeated as often as the clinical case requires. There are also no age restrictions - the procedure can be carried out from the first days of life.
An ultrasound takes no more than 20 minutes. The child sits on the couch, the doctor applies a special gel to the skin of the chest and a special sensor to improve the conductivity of ultrasound. Then he applies the sensor and moves it across the chest, at which time an image of the heart appears on the monitor. The condition of the organ is assessed visually in real time, and with the help of the program, the necessary changes are made and blood flow is assessed. During the procedure, you may need to change your body position. As a rule, you should lie on your left side or back most of the time. The examination does not cause any discomfort, but for the baby’s peace of mind, the parent can be nearby.
Interpretation of the results and norms of ultrasound of the heart in children
Interpretation of the results of a cardiac ultrasound in a child begins during the examination itself and takes its final form from the specialist who ordered the examination. Much depends on age. Gender, age and weight are taken into account. A table with normal parameters helps the doctor navigate.
Norms for a newborn baby
Interpretation of heart ultrasound in a newborn is based on the parameters specified for boys and girls. As a rule, girls' heart sizes are smaller than boys'. The diameter of the right ventricle of the heart in girls is 0.5-1.3 cm, in boys - 0.4-1.4 cm. In girls, in normal condition, the right atrium should be 1.1-1.6 cm, in boys - 1 .2-1.7 cm. The thickness of the interventricular septum is 0.2-0.6 mm. It is difficult to judge the diameter of the aorta at such an early age.
Norms for an infant from 1 month
Interpretation of heart ultrasound for a child 1 month of age and older is carried out using the following parameters. The normal diameter of the left ventricle is 0.5-1.3 cm in girls and 0.6-1.4 cm in boys. A similar parameter for the left atrium is 1.2-1.7 cm in boys and 1-1.8 cm in girls. The thickness of the interventricular septum is 0.3-0.6 cm. The diameter of the aorta is 0.7-1.3 cm.
Norms for a child from 1 year
For a child over 1 year of age, the following indicators are normal: the diameter of the right ventricle is 0.2-1.3 cm, the left atrium is 1-1.9 cm. The optimal thickness of the interventricular septum is 0.2-0.6 cm. The diameter of the aorta is 0.9-1.5 cm.
Transesophageal ultrasound
The transesophageal echocardiography procedure is more complex and has a number of limitations. An ultrasound sensor is inserted through the esophagus, which makes it possible to see the condition of the organ from all sides. The examination may be indicated for severe heart defects, chest deformities and lung diseases, inflammation of the aorta after prosthetics, etc. Preparation includes abstaining from food at least 6 hours before the examination, and during the procedure special medications may be required to improve the tolerability of the examination. Thus, it is sometimes advisable to perform intravenous anesthesia if a pronounced gag reflex is observed.
Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography)
This is a rather unusual study, which can be carried out in an extremely limited period of time - until the fontanelles on the baby’s head close. Fontanas are acoustic windows that, unlike bone tissue, do not interfere with the passage of ultrasonic waves. The large fontanelle usually closes by the end of the first year of life, but in some children this happens earlier - already at the 3-4th month of life. Neurosonography is performed on all children at the age of 1 month. Early ultrasound of the brain makes it possible to study its structure, diagnose possible structural changes (ischemic lesions, cysts, neoplasms, hemorrhages, pathological widening of structures), identify many pathological conditions of the central nervous system before their clinical manifestations, make a diagnosis in time and prescribe adequate treatment, which , in turn, leads to a significant improvement in the prognosis for the life and health of the child.
Preparing for the study. No special preparation is required for neurosonography. It is advisable that the child be active during the study.
Ultrasound of the hip joints
It should be performed on all children in the first month of life, regardless of the presence or absence of indications. Ultrasound allows you to identify pathology of the hip joints (delayed development of the joint, dislocation, subluxation, dysplasia - underdevelopment of one or both joints) and begin treatment even before the appearance of clinical signs. Starting treatment at a later date significantly worsens the child’s quality of life and leads to the need for surgical intervention.
Unlike X-ray examination, which shows only bone tissue and joint spaces, ultrasound of joints allows you to examine ligaments, tendons, joint capsule, cartilage, and synovium. It is extremely important for early diagnosis, because it records the initial changes in the joints.
Preparing for the study. No special preparation is required for ultrasound of the hip joints. The procedure takes about 5 minutes and is completely painless for the child.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract
Performed on all babies at the age of 1 month. Additionally, a study is prescribed for suspected inflammation (usually changes in urine analysis - detection of leukocytes, red blood cells, mucus), injuries to the back and abdomen, pain, and suspected congenital malformations. This study allows us to draw a conclusion about the functioning of the infant’s urinary system, evaluate the structure, shape, location of the kidneys and ureters, as well as the shape, size, volume of the bladder, the condition of its walls, and the volume of residual urine after urination. During the examination, it is possible to draw a conclusion about the functional state of the kidneys and bladder, and find the cause of urination disorders.
Preparing for the study. Preparing for an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder also requires meeting certain conditions. A full bladder is required for a full examination. Therefore, you need to take a bottle of water with you or prepare for breastfeeding before the test. It is quite difficult for a baby to catch the moment of urination, but just in case you should have a “strategic supply” of liquid with you. The approximate amount of liquid is at least 100 ml.
What is cardiac ultrasound?
Echocardiograms, also known as cardiac ultrasounds, are used to study a baby's or fetus's heart as it functions. This is a simple and painless procedure, performed according to the same principles as the ultrasound examination of the fetus in the womb of a pregnant woman, which is familiar to all mothers. Echocardiography uses sound waves (ultrasound) to create images of the heart. The Doppler test uses sound waves to measure the speed and direction of blood flow. By combining these tests, the pediatric cardiologist obtains useful information about the anatomy and function of the heart. Echocardiography is the most common test used in children to diagnose or rule out heart disease, and to monitor children who have already been diagnosed with heart problems. This test can be done on children of all ages, even newborns or unborn children.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Conducted for all children at the age of 1 month at the first full examination in a children's clinic.
The study evaluates the size of the abdominal organs, their structure and relative position, as well as the presence of additional formations, inflammatory changes, and traumatic injuries. Based on the results of an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, damage to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and pancreas can be detected. The most often excluded are:
- inflammatory diseases (hepatitis - inflammation of the liver, cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder, pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas);
- congenital developmental anomalies;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- parasitic infestations (infection with worms);
- cholelithiasis (formation of stones in the gall bladder and bile ducts).
Preparing for the study. Preparation for an abdominal ultrasound is very important. The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach! You cannot eat, drink, or take medications. This is the main condition for high-quality implementation of the procedure. The baby’s gastrointestinal tract must be absolutely calm, since gases, peristalsis, and digestion change the image and distort the result of the study, and also simply mechanically block part of the organs being examined.
Pediatric cardiology in Saratov: what should be done if a child has heart problems?
If you notice that your child is exhibiting certain symptoms characteristic of heart pathologies, we recommend making an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist. A pediatric cardiologist is a doctor involved in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system and connective tissue. The First Children's Medical Center employs highly qualified and competent specialists - pediatricians and cardiologists, with sufficient experience, who are able to establish the true cause of the dysfunction of the heart and blood vessels, and who are also able to find an approach to a child of any age - from infants to adolescents.
To timely identify a possible pathology of the cardiovascular system in a child, the Clinic carries out the necessary examinations using modern equipment (such as ECG, ultrasound of the heart, exercise tests, daily ECG Holter monitoring, as well as daily blood pressure monitoring). Also in the arsenal of the First Children's Medical Center there are the necessary methods for laboratory diagnosis of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
The First Children's Medical Center has programs for long-term monitoring of your child, here you can get advice from other specialists. For your convenience, the clinic has a day hospital.
What is a transesophageal echocardiogram?
Sometimes a regular echocardiogram does not provide all the images needed. Your doctor may recommend a test that uses special echocardiography probes to take pictures from inside the esophagus. This procedure is called a transesophageal echocardiogram. In this test, a tube with an ultrasound probe is passed down the throat into the esophagus. The esophagus is located directly behind the heart, and images taken there can give a very clear picture of the heart and its structures. This procedure requires anesthesia and takes about 20 minutes.
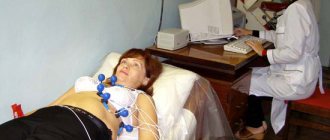
What is a stress echocardiogram?
Stress echocardiography is performed while the heart is beating normally and then again after exercise. In this test, the child is asked to run on a treadmill or pedal an exercise bike to increase their heart rate and the amount of blood and oxygen the heart needs to function.
If your child is too young or unable to run on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike, the doctor may use a medicine called dobutamine to increase the heart rate. A stress echocardiogram may be a more effective way to evaluate arterial stenosis or thrombosis.
Preparing for echocardiography
No special preparation is required before performing echocardiography. Experts do not recommend engaging in sports training before the procedure. If your child is taking any sedative or stimulant medications, you should consult your doctor. Some medications may need to be stopped for 1-2 days before the ultrasound so that they do not affect the picture of the heart muscle. Immediately before the test, you should try to calm the child so that his pulse is within normal values.
What heart pathologies are diagnosed using ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the heart is a fundamental method for diagnosing the following cardiovascular pathologies:
- various congenital and acquired heart defects (ventricular and atrial septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, mitral stenosis and mitral insufficiency, tricuspid and aortic valve defects, etc.);
- aortic aneurysm;
- hypertrophy of the myocardium of the ventricles or atria (often develops secondary to defects);
- various types of cardiomyopathy (hypertrophic, dilated);
- blood clots in the chambers of the heart;
- myocarditis (inflammation of the middle layer of the heart muscle);
- endocarditis (inflammation of the inner layer of the heart muscle);
- changes in the myocardium (presence of scars, sclerotic processes);
- additional chords in the chambers of the heart;
- ischemic disease, etc.
Timely diagnosis of these heart diseases is necessary for proper treatment. If any heart defect is detected in a small child, the issue of the need for surgical intervention is decided. Early stages of diseases that can be detected by ultrasound of the heart are more treatable than advanced forms. In addition, the examination is necessary to determine the child’s physical fitness group. If you have any cardiac pathology, some sports may be contraindicated.
Therefore, before enrolling in the sports section, it is better to conduct an ultrasound of the heart.
When performing an ultrasound of the heart, a small child is often diagnosed with a patent foramen ovale. This is a small opening that connects the right and left atria. Normally, it heals after some time, so there is no need to worry if your baby is found to have an atrial septal defect. In this case, you need to consult a cardiologist and come for a repeat echocardiogram after some time. It is believed that the interatrial window closes normally before the age of 5 years. If after this moment it remains, then they already talk about congenital heart disease and decide on the choice of optimal treatment.
Cost of services
| Name of service | Price |
| Ultrasound of the heart (Echo-CG) with Doppler | 2,600 rub. |
Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart is an informative, fast and safe method of studying the condition of a child’s heart, which allows you to accurately establish a diagnosis and carry out the required treatment with maximum efficiency, or get rid of worries and doubts about the state of your baby’s health.
You can get additional information about cardiac ultrasound and make an appointment for diagnostics at a medical center by phone.
Question answer
— Why is it worth choosing cardiac ultrasound as a diagnostic method?
This diagnostic method allows you to identify the presence of pathology at an early stage of development, which allows the doctor to prescribe timely treatment and monitor its progress and results. In addition, ultrasound diagnostics is a safe and absolutely painless research method.
— At what age can a child have an ultrasound of the heart?
An ultrasound of a child’s heart can be done even in the first days of life. Ultrasound does not cause any harm to both adults and children, so the frequency of this procedure is not limited.
— We need a good pediatric cardiologist in Saratov. Is it possible to make an appointment and undergo an examination at your center?
Of course, in our Center, a cardiologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, Elena Nikolaevna Shulgina, conducts consultations. You can make an appointment for a consultation and, if necessary, sign up for an examination. You can make an appointment for a consultation from 8.00 to 20.00 by calling (8452) 244-000. Reception is by appointment only.
Make an appointment with a cardiologist
Choose a doctor