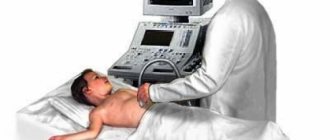
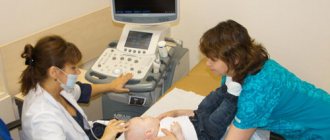
Ultrasound of a child’s heart (Echocardiography, ECHO CG for a child), standard pediatric echocardiography is the most modern research method in cardiology. During an ECHO CG, the doctor observes the work of the heart in real time and can examine all the structures of the child’s heart during operation. It is ultrasound of the heart that confirms or excludes the presence of many diseases of the cardiovascular system. It is often very important not to miss precious time for treatment, so that a minor pathology does not have time to develop into a serious disease. Promptly and competently performed echocardiography allows you to detect the problem in time and preserve the health of your baby.
What is cardiac ultrasound?
Echocardiograms, also known as cardiac ultrasounds, are used to study a baby's or fetus's heart as it functions. This is a simple and painless procedure, performed according to the same principles as the ultrasound examination of the fetus in the womb of a pregnant woman, which is familiar to all mothers. Echocardiography uses sound waves (ultrasound) to create images of the heart. The Doppler test uses sound waves to measure the speed and direction of blood flow. By combining these tests, the pediatric cardiologist obtains useful information about the anatomy and function of the heart. Echocardiography is the most common test used in children to diagnose or rule out heart disease, and to monitor children who have already been diagnosed with heart problems. This test can be done on children of all ages, even newborns or unborn children.
Causes of development of heart pathologies in children
Cardiovascular diseases in children can be either congenital or acquired. If we talk about congenital diseases, they occur in the fetus in the first half of pregnancy - these are congenital heart defects. There are many reasons for their development. This includes hereditary predisposition, ecology, exposure to intrauterine infections, frequent stress, and emotional overload to which pregnant women are exposed. As for acquired cardiovascular diseases, they occur in children, as a rule, due to infections that could not be completely cured.
Why is heart ultrasound done in children?
A cardiologist, pediatrician, or obstetrician may order an echocardiogram of the baby or fetus to see how well the heart muscle is working and to check for heart abnormalities. An echocardiogram can evaluate a heart murmur or a number of other conditions. This test allows doctors to very accurately diagnose disorders of the structure and function of the heart and assess blood flow in the heart and blood vessels. This is very informative and one of the most common types of studies in cardiology.
Ultrasound can help identify the causes of many heart problems, including:
- Noises
- Chest pain
- Aneurysm
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart defect
- Chronic heart failure
- Pericarditis
- Acquired heart defects
Pathologies that can be detected using cardiac ultrasound
After performing an ultrasound of the heart, a cardiologist analyzes the results, which helps to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. Most often, cardiac ultrasound helps identify the presence of the following cardiac pathologies in children:
- the presence of a hole (incomplete fusion) in the septum between the ventricles of the heart;
- the presence of a defect in the form of a hole in the interatrial septum;
- valve defects;
- narrowing of the aorta, etc.
If a child is diagnosed with any inflammatory processes in the heart, then the ejection function will be impaired, decreasing against the norm, and also during diagnosis, changes in the size of all cardiac cavities will be noticeable (they will be enlarged).
What are the types of cardiac ultrasound?
There are four special types of echocardiography:
- Echocardiography in M-mode
This is the simplest type of echocardiography and produces an image that looks like a slice rather than the actual structure of the heart. M-mode echo is useful for measuring structures of the heart, such as the chambers of the heart, the size of the heart itself, and the thickness of the heart walls.
- Doppler echocardiography
The Doppler method is used to measure and evaluate blood flow through the chambers and valves of the heart. The amount of blood pumped out with each beat is an indicator of the heart's performance. In addition, Doppler ultrasound can detect abnormal blood flow in the heart, which may indicate problems such as a hole between the chambers of the heart, a problem with one or more of the four heart valves, or a problem with the walls of the heart.
- Color Doppler
Color Doppler is an advanced form of Doppler echocardiography. Color Doppler uses different colors to indicate the direction of blood flow. This simplifies the interpretation of the Doppler method.
- 3-D (3-dimensional) echocardiography
This method is used to see the actual structures and movement of the heart structures. The 3D echo image appears cone-shaped on the monitor, and the movement of heart structures can be observed in real time. This allows the doctor to see the functioning of various structures of the heart and evaluate them.
ULTRASOUND SCREENING OF NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN UP TO 1 YEAR OF AGE
at the EVO Specialized Medical Center.
WHAT IS A BABY ULTRASOUND SCREENING?
Ultrasound screening of newborns and children in the first year of life includes:
- examination of the abdominal organs and kidneys (deviations from the norm in shape, size, structure and location of organs) ;
- examination of the hip joints for orthopedic deformities (dislocation, dysplasia) ;
- examination of the brain for developmental defects.
WHY DO AN ULTRASOUND OF YOUR BABY?
For every mother and every father of a newborn son or daughter, the main issue is the health of the child. And the first year of a child’s life is the most critical stage for future health, during which a number of diseases and problems can be excluded. Modern parents have probably heard a lot about screening studies. For example, all expectant mothers in our country must undergo prenatal (antenatal) screening diagnostics during pregnancy. These studies are aimed at timely detection of abnormalities in the fetus. And the earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chance of a positive pregnancy outcome and the health of the newborn. Screening to identify hidden defects (congenital and acquired), hereditary pathologies, deviations from the norm in the structure and location of the internal organs of a newborn child allows you to calm the worried hearts of young parents or, if necessary, not to miss precious time to begin treatment for the baby.
WHAT DIAGNOSTICS DOES A BABY NEED?
Various disorders in the child’s body can occur both during intrauterine development and during childbirth. Diseases of newborns can be caused by hereditary chromosomal abnormalities, the influence of a number of negative factors during pregnancy, and birth injuries.
Diagnostics includes collecting patient complaints, assessing the presence of disease symptoms identified during an external examination + results of laboratory and instrumental studies. However, newborn children do not complain. Symptoms of the disease are often mild and sometimes completely absent. Laboratory tests and instrumental studies remain in our arsenal.
Currently, there is practically no problem with laboratory tests; in well-equipped child care institutions, any indicator in the blood or urine can be determined. Instrumental studies have some limitations, because screening of the baby must be carried out in the first 3 months of life, and it is during this period that the child’s body is extremely sensitive to any external influences.
The slightest carelessness during diagnosis can lead to serious and even irreparable consequences. The screening method for newborns should not only be highly informative, but also convenient and safe. Today, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is the best diagnostic method for newborns and children under 1 year of age.
BENEFITS OF ULTRASOUND FOR CHILDREN UNDER 1 YEAR OF AGE:
- There are no harmful external influences on the child.
- Ultrasound is absolutely harmless even for a child’s body.
- Possibility of repeated research.
- Harmlessness will remain with repeated diagnostic procedures.
- Non-invasiveness of the method (ultrasound is not associated with damage to the skin, mucous membranes, or penetration into the internal environment of the body).
- The short duration of the study.
- There is no preliminary preparation for the study, in particular, ultrasound can be performed immediately after feeding, and not just on an empty stomach; there is no need for a cleansing enema, intravenous administration, ingestion of a contrast agent, etc.
- The method is completely painless. The child experiences absolutely no pain or discomfort, so there is no need for anesthesia.
IS ULTRASOUND HARMFUL FOR A NEWBORN?
Ultrasound waves, unlike X-rays, are completely safe - for both adults and children, even for the smallest inhabitants of the planet and the most precious people for you personally. Over several decades of ultrasound use, no side effects or negative effects on the body have been recorded. During an ultrasound examination, a special sensor comes into contact with parts of the child’s body. The ultrasonic wave emanating from it passes through the tissues without causing any harm or pain to the child’s body. The reflected signal is transmitted to the computer monitor in the form of an image.
WHY SHOULD CHILDREN BE PERFORMED IN EVO?
- Specialists. Diagnosis is carried out only by experienced and qualified doctors who can easily detect even the slightest deviation in the initial stage.
- Equipment. Our ultrasound machines meet all modern requirements and maximum resolution.
- Medical consultations. Upon completion of the diagnosis, if certain deviations from the norm are detected, you can immediately obtain advice from an appropriate specialist and recommendations for treatment and/or prevention. Find out more here.
- Time. Ultrasound is performed only at a time convenient for you, which can be agreed upon in advance with the administrators; queues and unwanted contacts are excluded.
NEURSONOGRAPHY in EVO.
Ultrasound of the child's brain through the large fontanel. It is performed on children in the 2nd month of life, whose head bones have not yet fused, and between them there are “fontanelles” - canals with softer tissue. The presence of this natural bone defect will allow ultrasonic waves to easily penetrate deep into the brain structures, which means to qualitatively examine the internal structure of the brain, identify congenital anomalies, as well as pathology acquired during the prenatal period or during labor. As the “fontanelles” harden, this becomes difficult. Brain ultrasound can detect:
- brain tumors, cystic formations of the meninges, areas of hemorrhage in the medulla (intracranial hemorrhage);
- increased intracranial pressure;
- hydrocephalus due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles of the brain.
Untimely detection of circulatory pathology and brain disorders will not allow timely initiation of treatment and can lead to irreversible consequences such as brain dysfunction and neurological disorders.
Ultrasound of internal organs in EVO.
Allows you to identify congenital diseases, anomalies in the structure and location of organs, congenital neoplasms (cysts, tumors) in the abdominal cavity.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract is used to diagnose changes in the shape and size of the kidneys, underdevelopment of the kidneys, as well as various anomalies in the structure of the bladder and muscle valves (sphincters).
- Ultrasound of the liver, pancreas and gall bladder is performed to diagnose various structural and degenerative changes in the liver, pancreas and biliary tract.
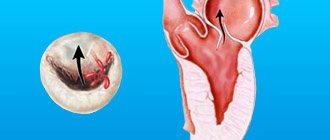
Ultrasound of the hip joints at EVO.
This study will allow timely recognition of congenital hip dysplasia and its complication – congenital hip dislocation. Screening is carried out on infants aged 1 to 2 months and makes it possible to detect abnormalities that were not previously noticeable, which gives a high chance of complete normalization of the child’s musculoskeletal system. Early detection of orthopedic pathology allows immediate correction to begin, thanks to which the baby can be completely healthy within six months.
How much does ultrasound screening of a newborn and a child up to one year cost at EVO?
Currently, the EVO Specialized Medical Center is running a promotion: the total cost of systemic screening ultrasound examinations is 3,000 rubles instead of 5,050 rubles. Your savings are 2,050 rubles!!! And this is much lower than in other clinics!
FAQ:
My baby was born premature. Will an ultrasound harm him?
Ultrasound is harmless even for premature babies. Moreover, prematurity often entails an increased risk of a number of congenital diseases. Therefore, screening ultrasound is not only desirable for premature babies, but also indicated.
I did all the tests for the child. Everything is fine there. Why do I need an ultrasound?
Normal clinical indicators of a newborn’s tests do not at all exclude abnormalities in the internal organs, musculoskeletal system, and brain. Therefore, during screening studies, laboratory diagnostics are carried out only in combination with ultrasound.
Is it possible to limit yourself to one study (to look at the head or kidneys) and at the same time save additional money, and postpone the rest for later?
Yes, you can. But it's not necessary. The essence of screening diagnostics lies, firstly, in its timeliness, and secondly, in its complexity. “The miser pays twice” and, unfortunately, your savings today may cost you dearly in the future.
CT is a more informative method than ultrasound. Why don't you do it?
In terms of its diagnostic value, ultrasound is not inferior to computed tomography, and in some cases even surpasses it. It is worth noting that CT scanning is not safe for a child, since the baby is exposed to x-ray radiation and must lie still for a certain time, which entails anesthesia. In our opinion, without any specific evidence for this, such risks for a newborn and a child in the first year of life are unjustifiably unnecessary.
You can get answers to other questions, as well as sign up for an ultrasound scan, by calling the EVO Medical Center (8) 812 701 03 30.
Remember that “nature knows no stop in its movement and punishes all inactivity” (Johann Wolfgang von Goethe).
What happens during an ultrasound of the heart?
This is a harmless and painless test, the same as an ultrasound for a pregnant woman. Mom and baby enter a darkened exam room where your baby can lie down on a regular bed. It is important that your child remains silent and still during the test, so an entertaining video may be shown to help keep him occupied and calm. Young children may be bottle fed during the study.
An ultrasound technician with special training in working with babies and children will apply warm ultrasound gel to the baby's chest and heart area and then place a small probe on the chest to obtain images from multiple vantage points. A small amount of clear gel is applied between the sensor and the chest to ensure proper contact. The gel does not leave stains and is wiped off at the end of the test. Several stickers called electrodes will also be placed on your chest to track the ECG during the exam. The echocardiogram is recorded digitally, so the doctor can review it and compare it with echocardiograms done in the past or ones that will be done in the future. The doctor can select and show many images on the monitor screen. You will be able to see an image of a beating heart, and you will also be able to see and hear the flow of blood. The picture usually changes as the sensor moves. Loud sounds of blood flow may be heard. If your child has too much trouble relaxing for a routine echocardiogram, he or she may need to be sedated before the test. If sedation is required, the child will be asked not to eat or drink for several hours before the test. Before giving the medicine, the doctor or nurse will make sure there is no reason why the sedatives should not be given (such as a bad cold), and then explain the procedure to the parent.
Children usually fall asleep within 30 minutes and sleep for about an hour. Although sedated echocardiograms are very safe, careful monitoring of heart rate, blood pressure and oxygen is performed while the child is sleeping. When the child wakes up, he or she may have poor balance (may last more than an hour) and should be monitored closely. The doctor and nurse will continue to monitor you closely until your baby is fully awake and drinking juice or milk.
Older children and teenagers usually do not need sedatives and may enjoy watching a monitor. To avoid anxiety, make sure your child knows that the exploration is fun, that it won't hurt, and that mom will be there.
Except in cases of sedation, no special preparations need to be made. It will help if your child wears a shirt or blouse with buttons down the front. The child may also eat normally before the examination. Bring a bottle of milk for a baby or a smartphone with a cartoon for an older child.
Ultrasound of a child’s heart - how is the procedure performed?
An ultrasound of the child's heart is performed in the supine position (on his back). The child's chest is exposed, the doctor applies a hypoallergenic gel, which ensures the sliding of the sensor. When performing ultrasound diagnostics, the device records the reflected waves and the specialist receives the dimensions of the chambers and ventricles of the heart, blood vessels, as well as a complete understanding of the current state of the organ.
If a cardiac ultrasound is scheduled for an infant, it is necessary to ensure that he is not hungry - this is necessary so that the child behaves more calmly during the procedure. Ultrasound diagnostics does not cause any discomfort to the child. No special preparation is required for an ultrasound of a child's heart.
What is a transesophageal echocardiogram?
Sometimes a regular echocardiogram does not provide all the images needed. Your doctor may recommend a test that uses special echocardiography probes to take pictures from inside the esophagus. This procedure is called a transesophageal echocardiogram. In this test, a tube with an ultrasound probe is passed down the throat into the esophagus. The esophagus is located directly behind the heart, and images taken there can give a very clear picture of the heart and its structures. This procedure requires anesthesia and takes about 20 minutes.
Is cardiac echocardiography safe?
During this study, there is no radiation or other load on the organ. Therefore, if necessary, it can be prescribed even several times a week.
This study is characterized by the absence of complications and side effects.
EchoCG does not harm either the expectant mother or the fetus during pregnancy.
Limitations for the procedure may include inflammatory diseases of the skin of the chest, chest deformities and some other reasons.
What is a stress echocardiogram?
Stress echocardiography is performed while the heart is beating normally and then again after exercise. In this test, the child is asked to run on a treadmill or pedal an exercise bike to increase their heart rate and the amount of blood and oxygen the heart needs to function.
If your child is too young or unable to run on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike, the doctor may use a medicine called dobutamine to increase the heart rate. A stress echocardiogram may be a more effective way to evaluate arterial stenosis or thrombosis.
Scheduled ultrasound for a child at three months
Neurosonography. Even if the first study does not reveal any pathology, ultrasound of the brain is repeated at the age of three months, because it is by this time that all the consequences of the hypoxia suffered by the child are visualized.
Ultrasound of the hip joints. At three months of age, it is recommended to re-perform an ultrasound of the hip joints; at this time, in addition to assessing the angles, attention is paid to the process of formation of ossification nuclei.
Ultrasound of the thymus. Vaccinations begin at the same time. In addition to tests, when preparing for vaccination, it is advisable to conduct an ultrasound of the thymus gland (thymus). Together with a blood test, this study provides the pediatrician with information about the state of the immune system, and can prevent a number of complications and make the vaccination campaign more effective.
Cost of services
| Name of service | Price |
| Ultrasound of the heart (Echo-CG) with Doppler | 2,600 rub. |
Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart is an informative, fast and safe method of studying the condition of a child’s heart, which allows you to accurately establish a diagnosis and carry out the required treatment with maximum efficiency, or get rid of worries and doubts about the state of your baby’s health.
You can get additional information about cardiac ultrasound and make an appointment for diagnostics at a medical center by phone.
Ultrasound of the hip joints (HJ) in newborns
This type of study is carried out on all children of one month of age in order to diagnose dysplasia and congenital dislocation of the hip joint. It is of great importance to carry out the research in a timely manner no later than three months after the baby is born.
pixabay.com/
“Even such a severe pathology of the hip joint as congenital hip dislocation, detected at an early age, is treated conservatively (massage, wide swaddling). With late diagnosis of dislocation/subluxation of the hip joint, surgical treatment may be necessary, and left unattended dysplasia can cause lameness and poor posture in the child in the future,” notes the FAN interlocutor.
Modern equipment and qualified doctors make it possible to identify many common pathologies at an early stage. No special preparation is required for the procedure. The ultrasound diagnostic method itself is absolutely safe and does not cause discomfort to the baby. A comprehensive examination will take parents no more than half an hour. Don’t forget to see all the specialists on time to once again make sure that your baby is healthy.