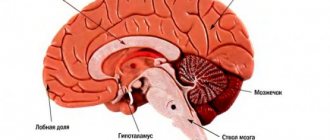
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a progressive disease. This means that the system designed to keep your body healthy is mistakenly attacking parts of the body that are vital to daily functioning. The protective covering of nerve cells is damaged, leading to decreased function of the brain and spinal cord.
The first signs of sclerosis in young people appear between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Usually they go down, but then come back again. The patient may be bothered by one symptom, and then months or years pass without any manifestations of the disease. The problem can also happen only once, but then go away and never return. For some people, the condition worsens over weeks or months.
A timely visit to a doctor will allow you to control the disease and help the specialist understand how effective your treatment is.
The first signs of multiple sclerosis in young people
The first indicators are varied and unpredictable, depending on which part of the central nervous system is affected and to what extent.
The most common disorders in young people are vision, sensitivity, emotional disorders, cerebellar functioning, and pelvic organs. Virtually any neurological symptom can be caused by multiple sclerosis. Some are immediately obvious. Others, such as fatigue, numbness and cognitive fog, may not be noticeable. This condition is quite difficult for the patient to describe to others, which makes it difficult for family and friends to understand the alarming signs.
Although there is no specific cure for MS, existing treatment approaches can help manage the disease and slow its progression. Early intervention offers the best chance against long-term disability. Therefore, it is very important to recognize the initial signs and consult a doctor immediately. Read on to learn more about the indicators of multiple sclerosis.
Expert opinion
Author: Olga Vladimirovna Boyko
Neurologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Multiple sclerosis is a progressive disease characterized by a malfunction of the central nervous system. The immune system, which is essential to keeping the body healthy, mistakenly begins to attack vital organs and body parts needed to function properly. As a result of the disease, the protective covering of nerve cells is affected, which entails a deterioration in the functioning of the spinal cord and brain.
The first symptoms of the disease in young people appear between the ages of 20 and 45 years. Sometimes they disappear, but then return with increasing force. The patient may be bothered by just one of the possible symptoms, and then years will pass without any manifestations of the disease.
The first signs of multiple sclerosis are unpredictable and varied, depending on which part of the nervous system is damaged and how damaged it is. These may be vision problems, emotional disorders, poor coordination, etc. Any of the neurological symptoms can occur due to multiple sclerosis. Some of them can be detected immediately, but signs such as increased fatigue and numbness may go unnoticed.
There is no cure for multiple sclerosis, but specific treatment approaches have already been developed to help curb the progression of the disease. The earlier therapy is started, the greater the chance of coping with the negative manifestations of the disease. Doctors at the Yusupov Clinic will conduct a full examination of the patient to select the optimal treatment.
Possible causes of sclerosis
Since the causes of sclerosis have not yet been identified, there are some assumptions about this disease. These are internal and unfavorable factors that contribute to the appearance of this disease.
Unfavorable factors contributing to the occurrence of sclerosis:
- caused by viral and bacterial diseases;
- poisoning of the body (intoxication);
- poor quality nutrition;
- psychological trauma in childhood;
- physical injuries;
- constant experience of stress.
Internal factors contributing to the appearance of sclerosis include the following reasons:
- human gene pool;
- disruptions in the functioning of the human immune and lymphatic system.
All of the above factors alone will not lead to the development of this pathology; only if the general symptoms listed above occur, this is possible. In this regard, it is necessary to monitor your condition from early childhood, but this should be done by the child’s parents.
Optic nerve damage
A common vision problem called optic neuritis is considered an early indicator of MS. It is considered a more “specific” sign compared to “vague” neurological symptoms such as tingling or numbness.
Optic neuritis is characterized by:
- temporary loss of vision;
- color blindness;
- Pain in the eyes;
- double vision.
In addition to the optic neuritis that accompanies MS, involuntary eye movements are added.
Sensory impairment
A unique aspect of the symptoms of multiple sclerosis is the extremely common temperature sensitivity of patients whose neurological symptoms are temporarily aggravated by an increase (or decrease) in body temperature.
Heat sensitivity, or Uthoff's phenomenon, occurs in 60–80% of patients with this disease. An increase in body temperature may cause temporary deterioration, usually associated with exposure to a warm environment or exercise, and lasts until core temperature returns to baseline. However, a decrease in body temperature as a result of taking cold baths or exposure to low ambient temperatures can also provoke a worsening of the clinical picture of the pathology.
Episodes of temperature sensitivity among patients with sclerosis are also known as pseudoexacerbations or pseudorelapses. Although the increase in symptoms may be similar in nature to those that occur during an exacerbation, the worsening of the condition is not associated with the active progression of the disease and is temporary. Moreover, the symptoms return to normal when the internal temperature is restored. Therefore, the patient experiences significant difficulties in maintaining an appropriate level of physical activity
Therapy at home
When treating and caring at home, the patient requires professional help and constant diagnosis of the disease. This will make it possible to monitor the patient’s condition and not miss the need for urgent therapeutic intervention. Therefore, high-quality treatment and care at home will not work. What can be offered in such a situation is only care without treatment or special measures.
Our boarding house with a medical focus invites you to leave useless activities and turn to us for help. Our specialists will conduct a full diagnosis of the ward and talk about his condition at this hour, advise the correct measures of care or full service in our boarding house.
Cerebellar disorders
Coordination problems are common in multiple sclerosis and arise mainly from pathology in the cerebellum itself or when brain connections are disrupted. Patients may have either acute dysfunction associated with an acute exacerbation or chronic cerebellar problems with progressive disease.
Involvement of the cerebellar and brainstem connections occurs quite often during an exacerbation. Relapse of the cerebellum early in the development of the disease is associated with an increased risk of cerebellar damage during the subsequent course of MS. Experience shows that cerebellar involvement early in the disease worsens the prognosis. In a recent database study of approximately 15,000 patients who experienced a total of 50,000 exacerbations, cerebellar relapses accounted for approximately 10% of the total. They were more common in younger men and those with longer duration of progression.
It is estimated that 80% of patients with established MS experience tremors, which are especially common in patients with advanced disease. This is a consequence of unstable functioning of the cerebellum. Tremor can affect the limbs, trunk, vocal cords and head, but such a severe form is a relatively rare consequence of sclerosis.
Thus, cerebellar dysfunction may be a clear indicator of progressive MS. In general, this entails increased disability and poor prognosis.
Treatment
Treatment of multiple sclerosis is aimed at solving several problems:
- stopping the active immunoinflammatory process,
- decreased activity of the immune system to nerve fiber sheaths,
- slowing down the development of the disease, stopping the appearance of new “plaques”,
- combating symptoms that significantly impair the quality of life.
To solve problems, medications and physiotherapy are used.
Complex drug therapy
During treatment, it is important to take immunomodulators and anti-inflammatory drugs. The following drugs are especially well known:
- Interferons beta. The drugs have an immunomodulatory effect on the main components of immune reactions.
- Medicines based on glatiramer acetate. Medicines in this group are capable of replacing myelin antigens and triggering the process of inhibition of T1 lymphocytes. In this case, T2 lymphocytes, on the contrary, are activated. Due to this, the drug has a neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Fingolimod. Modulator of sphingosine-phosphate receptors on lymphocyte membranes. Significantly reduces the number of “autoaggressive” T cells circulating in the blood.
- Natalizum. Slows down penetration through the blood-brain barrier and reduces the activity of T-lymphocytes in areas of axonal damage. The inflammatory process is significantly slowed down.
During exacerbations, when the disease is accompanied by obvious attacks, adrenocorticotropic hormone and corticosteroids (methylprednisolone) are used. Thanks to these drugs, it is possible to quickly reduce the movement of immune cells to the spinal cord and brain. But these drugs are only good as short-term therapy. They are not suitable for long-term use, as they can cause addiction.
If the disease is accompanied by signs of depression, the doctor may prescribe amitriptyline or melipramine. However, the prescription of these drugs is done extremely carefully - only after a detailed examination. Unfortunately, many patients already have urinary retention, and amitriptyline and melipramine can significantly aggravate the situation. An alternative for such patients can be all kinds of selective inhibitors without anticholinergic properties, but with an excellent ability to reuptake serotonin. These drugs include trazadone, sertraline, fluoxetine, and paroxetine.
Also, in the presence of depression, agomelatine has been widely used in recent years. This is a drug with a melatonergic mechanism of action. It normalizes circadian rhythms (oscillations).
If you have problems with urination, targeted therapy is needed to solve this problem.
If the main problem is urgency, tolterodine oxybutynin, amitriptyline, nifedipine are used.
If concerns are associated with emptying the bladder, the blocker terazosin helps. But it is important that when taking the drug there is careful monitoring to ensure that orthostatic hypotension does not develop.
Some patients may also be additionally prescribed medications aimed at reducing external sphincter tension. Among them are diazepam, tizanidine.
The above drugs are used in tablet and injection forms.
Hypobaric oxygenation
Oxygen saturation is a big help for patients with multiple sclerosis. This is possible through the hypobaric oxygenation procedure.
Hypobaric oxygenation is especially relevant for patients in whom multiple sclerosis is accompanied by cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Hypobaric oxygenation is carried out in a pressure chamber. Oxygen is supplied under high pressure. During the process of hypobaric oxygenation, adaptation and regeneration mechanisms are activated.
Massage
An excellent way to reduce discomfort and pain in patients with different types and stages of sclerosis is massage. Massage is especially useful for solving the following problems:
- Relaxes muscles and relieves spasticity.
- Activation of blood circulation.
- Preventing bedsores. Relevant for people who have to spend most of their time in bed.
Diet therapy for multiple sclerosis
- A common principle for all patients with multiple sclerosis is to limit sources of fast carbohydrates in the diet. The main ones are sugar and baked goods made from refined flour.
- The remaining principles of nutrition largely depend on what specific problems the patient has in each particular case.
- If chewing is difficult, it is recommended to eat pureed foods.
If you have constipation, you should use more liquid foods (if there are no problems with the urinary system at the same time) and products with bifidobacteria.
Disorders in the functioning of the pelvic organs
Sixty-eight percent of people with MS experience one or more types of pelvic floor abnormalities. Symptoms include loss or absence of bladder or bowel control: urinary incontinence, urinary frequency and urgency, bowel incontinence, sexual dysfunction, pelvic organ prolapse, and pelvic pain associated with a “spastic” pelvic floor.
The most common diagnosis among MS patients is a spastic (overactive) bladder. The organ is unable to hold a normal amount of urine in the bladder, which does not empty properly.
A spastic bladder is characterized by:
- private urination;
- hesitancy to start urinating;
- frequent night urination;
- urinary incontinence;
- inability to completely empty the bladder.
Healthy bladder function is important for long-term kidney health, infection prevention, personal independence, self-confidence and improved quality of life. Untreated bladder problems can cause:
- increasing weakness;
- Bladder and urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney stones, which cause serious pain and compromise your overall health;
- problems with work, home and social activities;
- loss of independence, self-esteem and self-confidence.
Early medical evaluation is important to determine the cause of bladder dysfunction and select appropriate treatments. More serious urinary problems can lead to blood and skin infections.
Professional care at the Vesna boarding house
Caring for a patient with multiple sclerosis is a difficult task. We understand the relatives of such a patient, therefore, we offer high-quality services for this event. Since the patient is in a helpless state, our staff will do everything to make him feel comfortable and undergo all the treatment measures prescribed by our doctors.
Why is it difficult to care for a person diagnosed with multiple sclerosis? The whole point is that:
- the patient constantly experiences chronic fatigue;
- constantly forgets everything he knows or has learned in a day;
- confuses the sequence of his actions;
- violates the use of medication doses and the time of taking them.
A patient in such a situation requires constant help and moral support. Our employees will give everything your relative needs and brighten up his loneliness.
Providing patronage services
When providing care services, there are standard types of responsibilities:
- when moving, the patient is provided with the necessary special medical equipment;
- exercising full control over the use of medications;
- constant change of linen;
- Clothing repair;
- daily walks;
- accompanying the ward to physical procedures;
- assistance with eating;
- haircut and other hygiene services.
In addition, there are additional services, but this is discussed with the boarding house management.
Emotional disorders
Emotional disturbances are often common in MS and include mood changes and affective states. Important mood disorders include major depression, panic attacks, and anxiety. Their relationship to disease is multifactorial and complex, and the extent to which they are direct consequences of disease remains unclear.
Symptoms of mood disorders in young people with MS do not differ from those in healthy people and respond just as well to standard treatment. Affect disorders include euphoria, pathological laughter and crying, and other symptoms. These abnormalities are the result of a lack of myelin and are one of the most characteristic indicators of multiple sclerosis.
Mood and affective disorders can cause enormous pain and distress to the patient and lead to disruption of family, career and social life. Doctors who can effectively diagnose and treat this can have a significant impact on patients' quality of life.
How to help loved ones cope with illness
Chronic pathology becomes more and more severe over time. Attacks occur suddenly, at least 2 times a year. Often people lose the ability to move, care for themselves, and become helpless. The boarding house “Quiet House” has created all the conditions so that patients with multiple sclerosis from Voronezh feel as comfortable as possible:
constant supervision of doctors and health workers;
- comfortable beds and anti-decubitus mattresses;
- full sleep - the patient is not distracted by the hustle and bustle of the home;
- balanced feeding and drinking regime;
- if necessary, assistance with feeding and personal care;
- caring and understanding attitude.
Diagnosis of early multiple sclerosis
The doctor must perform all the necessary neurological examinations, take a medical history and conduct a number of other tests to determine the presence of sclerosis in a young patient.
Diagnostic testing may include the following procedures:
- MRI scan. The use of contrast dye with MRI allows the doctor to identify active and inactive lesions in the brain and spinal cord;
- visual evoked potential test—requires stimulation of nerve pathways to analyze electrical activity in the brain. In the past, auditory potential tests have also been used to diagnose the disease;
- spinal studies - a study of the spinal cord is performed to identify abnormalities in the cerebrospinal fluid. This may help eliminate the possibility of infections;
- blood tests are carried out to exclude the possibility of other pathologies with similar indicators.
Making a diagnosis requires evidence that demyelination (the immune system's destruction of myelin) occurs at different times in more than one area of your brain, spinal cord, or optic nerves.
The diagnostic process also requires excluding other diseases that have similar symptoms. Lyme disease, lupus, and Sjögren's syndrome are just a few examples.
Belarus is in a high-risk zone for the incidence of multiple sclerosis - more than 50 cases per 100 thousand people are registered in the country.
- in 2016, 51.9 cases per 100 thousand population were registered;
- in 2017 - 54.9 per 100 thousand;
- in 2018 - 56.7 per 100 thousand.
Experts attribute this prevalence to the geographical location of the country (there is an opinion that the further the country is from the equator, the higher the incidence), with a lack of sunlight and vitamin D. There are many factors that influence the likelihood of developing multiple sclerosis. Heredity plays a role. In addition, an increase in the number of cases may be associated with improved diagnosis of the disease.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, progressive autoimmune disease in which a person's own immune cells destroy the myelin sheath of nerve fibers. As a result, the speed of nerve impulse transmission and, accordingly, the function of the muscle fiber decreases. As the disease progresses, aggressive immune cells not only damage the myelin sheath of neurons, but also lead to the death of nerve cells.
Ekaterina Mazurenko, Associate Professor of the Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery of BelMAPO, Candidate of Medical Sciences. Science Ekaterina Mazurenko:
“Approaches to diagnosing the disease have changed. Previously, after the first clinical episode, the patient was given an amorphous diagnosis of “demyelinating disease of the central nervous system,” which did not allow timely administration of adequate therapy for multiple sclerosis. The modern approach involves early detection of the disease and the prescription of preventive treatment, which allows our patients to remain active and able to work for a long time. Today, a new term “clinically isolated syndrome” is used to denote the first clinical attack of the disease. In some cases, after the first clinical episode and in the presence of changes on MRI of the brain that are typical for multiple sclerosis, we can prescribe preventive treatment.”
The modern classification of multiple sclerosis is based on the type of disease, since it is these differences that determine the treatment tactics for patients.
Three types of multiple sclerosis
- relapsing-remitting MS;
- secondary progressive type of MS;
- primary progressive type of MS.
Relapsing- remitting MS. Exacerbations with the appearance of new clinical symptoms alternate with remissions. There is a complete or partial restoration of functions after an exacerbation. The cardinal feature is the absence of an increase in symptoms during periods of remission. Over time, in more than half of patients, this type of course transforms into secondary progressive MS.
Secondary progressive type of MS (SPMS). It usually develops 5–10 years from the onset of the disease. The deterioration of the patient's condition is associated with an increase in clinical symptoms during periods of remission, which is the main diagnostic sign of this form. In some cases, there is a slow progression of the disease without periods of improvement and exacerbations, in others, exacerbations persist, but become more erased against the background of a steady slow deterioration of neurological symptoms.
Primary progressive type of MS. From the moment of the first episode of the disease, there is a gradual, steady increase in neurological symptoms for at least 1 year, without clear periods of exacerbation and remission.
Ekaterina Mazurenko:
“Multiple sclerosis is always two parts: inflammation and neurodegeneration. Inflammation is characterized by the appearance of new clinical symptoms and the formation of active foci of demyelination on MRI. Neurodegeneration is observed already in the earliest stages of the disease and is manifested by damage to neuron axons and brain atrophy. When axonal damage accumulates in any functional system, the patient experiences irreversible disability. That is why early detection of the disease, adequate treatment of exacerbations and timely administration of preventive treatment are so important, which helps to avoid an increase in severe physical limitations and disability in the patient.”
In what cases should a patient be referred to a neurologist?
To a general practitioner (therapist):
The patient complains of the appearance of symptoms in various functional areas. For example, unsteadiness and uncertainty when walking, awkwardness or weakness of one or both arms, legs, transient tingling and numbness of the limbs, double vision, difficulty swallowing. Quite characteristic of the initial stages of the disease is the periodic appearance and disappearance of symptoms. In any case when a patient develops neurological symptoms, the general practitioner should refer the patient to a neurologist.
To the ophthalmologist:
The patient complains of significant blurred vision, double vision, or the appearance of a “blurry spot” before the eyes. If a diagnosis of “retrobulbar neuritis” is made, especially in young people, such a patient should definitely be referred for a consultation with a neurologist.
To the urologist:
Multiple sclerosis may begin with urological problems (urinary urgency or incontinence, urinary retention).
Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by a variety of symptoms affecting various functional systems.
The visual sphere is affected: there is a decrease in vision, which is not corrected by glasses, patients may complain of pain behind the eye, and visual fields fall out. Over time, vision may be restored partially or completely.
Sometimes the disease can debut with damage to the pyramidal system: the patient experiences a decrease in muscle strength, changes in the reflex sphere (decreased skin reflexes, increased tendon-periosteal reflexes, as well as the appearance of pathological signs).
The coordination system may be affected : walking and coordination of movements are impaired.
may be affected : Patients with MS experience limb numbness and paresthesia.
Brainstem symptoms often : blurred speech (dysarthria) or impaired swallowing, choking when eating (dysphagia), impaired conjugal eye movements (internuclear ophthalmoplegia).
Currently, diagnosis of the disease is carried out according to the 2021 Macdonald criteria , which are used throughout the world. Their goal is to simplify and speed up diagnosis.
Main diagnostic criteria:
- the presence of clinical manifestations (at least two clinical attacks and damage to two systems) according to the patient’s neurological status;
- the presence of characteristic foci of demyelination according to the results of magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and/or spinal cord.
Features of the course and diagnosis of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis
The secondary progressive type of MS (SPMS) is characterized by the predominance of the neurodegenerative process over the inflammatory process, which means that the patient will experience increased brain atrophy, axonal damage and associated disability.
Ekaterina Mazurenko:
“The majority of patients are with the relapsing-remitting type of multiple sclerosis. Unfortunately, over time they develop a secondary progressive form. The risk of transition varies and depends on a number of factors. Time plays a role: the longer the patient is sick, the higher the likelihood. This development of events may be influenced by inadequate treatment of exacerbations. It is very important to remove them in time with pulse therapy using hormones (methylprednisolone). An internationally recognized regimen: 1000 mg intravenously daily for 3–5 days. Adequate treatment of exacerbations allows you to quickly relieve inflammation and prevent axonal degeneration, and therefore avoid the accumulation of residual neurological deficits in the patient.”
The key point in the course and diagnosis of the secondary progressive type of multiple sclerosis is the increase in neurological symptoms in the period between exacerbations. The main criterion for progression is the increase in EDSS score over 6 months. The EDSS scale allows you to very clearly and effectively assess the degree of disability of the patient and track the deterioration of the neurological status.
Unfortunately, the secondary progressive type of MS is difficult to treat. This is due, among other things, to the fact that most drugs that modify the course of multiple sclerosis affect inflammation, while in SPMS neurodegenerative processes predominate. However, drugs for the treatment of SPMS have already been registered around the world.
Why is it so important to get a diagnosis early?
The later treatment is prescribed, the sooner the patient will reach an EDSS score of 6 (which means he has become disabled). Therapy is considered most effective when assessed on the EDSS scale from 0 to 3 points. It is important to make a timely diagnosis and prescribe preventive treatment to reduce the frequency and severity of exacerbations and make the course of multiple sclerosis manageable.
The route of a patient with multiple sclerosis
If multiple sclerosis is suspected, to confirm the diagnosis and decide whether to prescribe DMT, the neurologist issues a referral:
Minsk and Minsk region:
- Minsk City Consultative and Diagnostic Center (it is the main institution);
- 5 city clinical hospital;
- Minsk Scientific and Practical Center for Surgery, Transplantology and Hematology (formerly 9th City Clinical Hospital);
- Republican Scientific and Practical Center of Neurology and Neurosurgery;
- Minsk Regional Clinical Hospital.
Brest:
- Brest Regional Clinical Hospital.
Vitebsk:
- Vitebsk Regional Diagnostic Center;
- Vitebsk Regional Clinical Hospital;
- Vitebsk Regional Clinical Specialized Center.
Gomel
- Gomel Regional Clinical Hospital.
Grodno
- Grodno University Clinic.
Mogilev
- Mogilev Regional Clinical Hospital.
The appointment of PMTRS is determined by a medical council consisting of the chief freelance neurologist of the region, the head of the department, the attending physician, and an employee of the department of neurology of educational institutions. According to the order of the Ministry of Health dated February 20, 2020 No. 174, which regulates the prescription of DMT, treatment of multiple sclerosis begins from the moment the first episode appears, if there are foci of demyelination in the brain and/or spinal cord on MRI.
Ekaterina Mazurenko:
“When choosing a drug that modifies the course of multiple sclerosis, the risk and benefit for the patient are assessed in each individual case. It takes into account how aggressive the disease is and how often exacerbations are recorded.”
The effectiveness of treatment is assessed using three main indicators:
- presence of clinical manifestations;
- appearance of new lesions on MRI;
- increase in disability according to the EDSS scale.
Performing MRI with contrast allows you to assess the activity of the pathological process. This test identifies areas of demyelination in the brain and/or spinal cord that have a number of typical features. It will help identify acute foci of demyelination (they accumulate contrast) that have appeared relatively recently, for example, within a few weeks. In general, MRI evaluates both the appearance of new lesions and the increase in the size of old ones.
Additional training on MS
The BelMAPO website has a training module dedicated to the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis, which includes the main criteria for diagnosing the disease and detailed instructions for using the EDSS scale. In addition, in advanced training courses, part of the lectures are also devoted to the problem of MS.
This information is intended for medical and pharmaceutical professionals only. To be distributed at the venues of medical or pharmaceutical exhibitions, seminars, conferences and other similar events or directly transferred to medical and pharmaceutical workers. Dissemination of information by any other means that opens access to it to an indefinite number of persons is prohibited. The images used are not of actual patients. The article was created with the support of Novartis Pharma Services AG (Switzerland), representative office in the Republic of Belarus. BY/NEUR/11.2020/pdf/102662
Treatment of multiple sclerosis in young people
Treatment is divided into 3 categories:
- therapy for exacerbations;
- slowing progression using modification methods;
- symptomatic therapy.
Treatments are becoming increasingly complex as additional subtypes of the disease are being explored. This reduces the frequency and severity of exacerbations, as well as the accumulation of lesions detected by magnetic resonance imaging.
Initiating treatment to slow inflammatory lesions in the early stages is considered a way to prevent the development of disability. There is not yet enough comparative effectiveness data to guide health care providers in making optimal treatment choices.
Yusupov Hospital is one of the best centers for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in Moscow. Contact us for a consultation!
Benign MS
It proceeds with a favorable outcome. The disease begins rapidly, with frequent attacks and severe symptoms. Then the exacerbation is replaced by remission (attenuation). Subsequently, remissions become longer, and the myelin on the nerve fibers has time to fully recover. This is also facilitated by properly selected treatment and optimal motor mode. It is the benign variant that accounts for cases of healing from multiple sclerosis. Unfortunately, this happens infrequently, in only 20% of cases.