When expecting the birth of an heir in the family, future parents wonder who he will take the height from, whether he will be born blond or brunette. But, perhaps, the main question is what blood type is and how the Rh factor is transmitted to the child. Some families will not pay attention to this. But its negative meaning in the future life of the baby can turn into a problem.
Therefore, the following issues need to be taken seriously:
- general concepts about the Rh factor;
- how it is formed;
- what does it depend on;
- How is the Rh factor inherited?
- about its danger during pregnancy of the expectant mother;
- how is a hereditary disease inherited with the Rh factor;
The importance of these issues is identified with the importance of other blood characteristics in general.
Preface about the Rh factor
{banner_banstat0}
The concepts of blood group and Rh factor appeared recently. When mixing erythrocytes from different samples, the scientist Landsteiner K. in 1940 noticed that in some cases clots formed.
Based on this, when further studying the properties of red blood cells, he divided them into 2 groups, calling them A and B.
His students have already identified a group containing both A and B.
This is how the ABO system was born, which divides blood into groups as follows:
- if antigens A and B are absent, then this group is designated I (0), which corresponds to the first blood group;
- if only A antigens are present, then this is designated II (A) - this is the second group;
- if only B antigens are present, then this group is designated III (B) - third group;
- if antigens A and B are present, then this is IV (AB) - the fourth group;
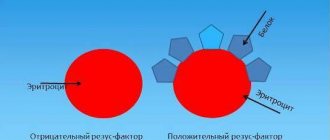
Further research revealed that protein may be present on the surface of red blood cells. This property is called a positive Rh factor; if the protein is absent in the blood, then it is a negative Rh factor.
All this formed the basis of the so-called Rh classification system.
Thus, there are 4 types of blood groups: I, II, II, IV (or 0, A, B, AB) and two Rh factors: Rh(+) - positive and Rh(-) - negative.
People with negative Rh may be only 15% of the entire population.
The indicators of blood group and Rh factor are in no way related to each other, but when determining a blood group, they always talk about its Rh factor, for example, II Rh(+). These two values are equally important during blood transfusions and during pregnancy.
Rhesus must be inherited from parents, not change throughout a person’s life, and when asked whether hereditary diseases are transmitted with the Rh factor and whether it depends on its positive or negative value, we can say for sure that it is not.
Now geneticists are studying the properties of blood. They established that the inheritance of Rh factors and blood groups is subject to the laws of Mendel, discovered by him in the 19th century. From the school curriculum there are well-known experiments with peas that confirm this law. How the gene for its negative value is inherited in the Rh factor is very well explained by this law.
Dietary recommendations
These people have a slow metabolism, and this results in a tendency to gain weight quickly. The situation is aggravated by poor nutrition.
Since representatives of this blood type are descended from hunters, they are recommended to include more meat in their diet - but with some nuances.
More detailed recommendations are given in the table.
| Product group | What is necessary? |
| Meat | Red meat and poultry, offal |
| Fish | Fatty varieties rich in omega-3 fatty acids: salmon, sturgeon, mackerel, horse mackerel, herring |
| Vegetables | Salads, legumes, greens, broccoli, radish |
| Cereals | Buckwheat |
| fruits | Almost anything except citrus fruits |
| Milk products | Cottage cheese and butter, low-fat kefir, if there is no intolerance |
| Beverages | Teas, especially herbal, unsweetened juices. |
Fatty foods are the first to be banned - they lead to problems in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. What foods are not recommended to eat?
It is worth limiting your consumption, or better yet, giving up altogether:
- Fat - due to the tendency to be overweight and have problems with blood vessels.
- Rice and lentils - can cause bloating.
- Ice cream and milk in its pure form . Often these people have poor digestibility of milk protein.
- Coffee and too strong tea, alcohol - contributes to the accumulation of tension, stress, excess energy, and leads to hypertension.
- Peanuts and their oils, soybeans.
- Salty and smoked food, excess spices.
- Fried foods , especially with a lot of oil. The best option is boiled, stewed or baked foods.
To spend calories rationally and not gain weight, you need to exercise. For those who hate sports, regular walking is suitable - but at least 40-60 minutes a day.
If there are no contraindications, you can and even need to work out in the gym. Outdoor sports include running, skiing, and team sports. It would be a good idea to sign up for a swimming pool to relieve excess tension from your back muscles.
The most basic thing about the concept of blood group
{banner_banstat1}
The child’s blood depends on the parents and is inherited with the so-called ABO gene, which is located on chromosome 9. The following table will show how likely it is that a group will be taken from its parents.
| Parents' blood types | Heritable blood type in a child as a percentage | ||||
| I | II | III | IV | ||
| I and I | 100% | — | — | — | — |
| I and II | 50% | 50% | — | — | |
| I and III | 50% | — | 50% | — | |
| I and IV | — | 50% | — | 50% | |
| II and II | 25% | 75% | — | — | |
| II and III | 25% | 25% | 25% | 25% | |
| II and IV | — | 50% | 25% | 25% | |
| III and III | 25% | — | 75% | — | |
| III and IV | — | 25% | 50% | 25% | |
| IV and IV | — | 25% | 25% | 50% | |
With 100 percent probability we can say which blood type will be passed on to the baby if they both have the first.
What is special about the third group?
Peter D'Adamo states that the food a person eats reacts chemically with their blood type. And if you follow a diet designed for a specific blood type, food will be digested more efficiently. With the help of such proper nutrition, you can not only get rid of excess weight, but also get more energy and prevent many diseases.
For people with blood type O, D'Adamo recommends avoiding corn, wheat, buckwheat, lentils, tomatoes, peanuts and sesame seeds. It is better to replace chicken meat with rabbit, goat and lamb meat. The majority of the diet should consist of eggs, low-fat dairy products, fish - salmon, sardines, cod, halibut, mackerel, sea trout, flounder. In addition, green vegetables are very healthy - broccoli, Brussels sprouts, various greens, beets, sweet potatoes, carrots, red and white cabbage, eggplant, parsnips and all types of peppers.
The mysteries of the third blood group include interesting facts for which scientists have not found an explanation. For example, this blood type predominates in our time among Finno-Ugrians, Hungarians, Czechs and Serbs. People with the third blood group most easily adapt to changing climate conditions. It is impossible not to note the interesting character traits of carriers of this blood group - they are viable, active, mobile, and quickly master new technologies. More than 40 percent of American millionaires and billionaires have a third blood type - perhaps this ability to successfully run a business was formed largely due to centuries of honed ability to adapt to new living conditions and competition. It is these qualities that are most often found in people with the third blood group.
The influence of genetics on the Rh factor
{banner_banstat2}
It is now reliably known that the Rh factor in humans is determined by genetics. A pair of genes is considered: D positive and d negative. They can be the same type of components DD or dd (the so-called homozygous pair of genes) and different components, for example Dd (heterozygous), where D is dominant in this case and whether the Rh factor is positive depends on it. It is these genes that are inherited. They are the reason for the birth of a baby with Rh negative from parents who have Rh positive.
The inheritance table below shows all possible predictions of a child's Rh factor, depending on what the parents' Rh factor is:
| Rh factors of parents | Rh factor of the child | ||
| mothers | father | (Rh+) | (Rh-) |
| Rh+ | Rh+ | 50% | 50% |
| Rh+ | Rh- | 50% | 50% |
| Rh- | Rh+ | 50% | 50% |
| Rh- | Rh- | — | 100% |
As can be seen from the table, if two parents are Rh negative, then the child will be born with a negative Rh factor; in other cases, it all depends on how the genes are inherited.
General principles of inheritance of characters.
Simply put, every trait in the body (hair color, eye color, blood type, Rh factor) is encoded by two genes.
In reality, the number of genes that determine the trait is much greater. For each trait, the child receives one gene from the mother, another from the father. In genetics, dominant and recessive genes are distinguished. The dominant gene is designated by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet, and in its presence the recessive gene, as a rule, does not manifest its properties. A recessive gene is indicated by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet. If for some trait an organism contains two identical genes (two recessive or two dominant), then it is called homozygous for this trait. If an organism contains one dominant and one recessive gene, then it is called heterozygous for this trait, and at the same time those properties of the trait that are encoded by the dominant gene are manifested. For example: A is a dominant gene that determines brown eye color and A is a recessive gene that determines blue eye color
Possible genotype options: AA - homozygote, brown eyes Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes aa - homozygote, blue eyes
Example 1:
wife AA - homozygous, brown eyes, both genes are dominant; husband AA - homozygous, blue eyes, both genes are recessive
When germ cells (egg and sperm) are formed, one gene goes into each germ cell (gamete), i.e. in this case, the female body forms two gametes containing one dominant gene each, and the male body forms two gametes containing one recessive gene each. When germ cells merge, the embryo receives one maternal and one paternal gene for this trait.
wife AA + husband aa Gametes: A A a a Child: Aa Aa Aa Aa
Thus, in this situation, 100% of the children will have brown eyes and be heterozygotes for this trait.
Example 2:
wife Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes husband Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes wife Aa + husband Aa gametes: A a A a child: AA, Aa, Aa, aa
In this case, the probability of having children with brown eyes (homozygotes) is 25%, heterozygotes are 50% with brown eyes, and blue eyes (homozygotes) are 25%.
Example 3:
wife Aa - heterozygote, brown eyes husband aa - homozygote, blue eyes Wife Aa + husband aa Gametes: A a a a Child: Aa, Aa, aa, aa
In this case, 50% of children have brown eyes and are heterozygotes and 50% have blue eyes (homozygotes)
How many of its carriers are there on the planet?
As mentioned above, the first positive blood type is the most common. According to statistics, this is 42-45% of the world's population. The “national characteristics” of this group are also noteworthy. For example, among Russians and Belarusians the number of I(0) speakers is more than 90%.
It is noteworthy that it is one of the most common on the planet. What else? Find out from the article:
One for all: universal donor
The first positive group has always been considered universal due to the absence of antigens. It contains alpha and beta antibodies and has no foreign elements, which is why people with the first (zero) group are called universal donors. This blood is suitable for all people. However, there is one feature that cannot be ignored: blood of group zero is prone to coagulation disorders. This is true when the carrier purchases medications without a doctor’s prescription.
Compatibility table for blood transfusion
The third group is compatibility during donation
A person with group 3 will not be a universal recipient. In other words, his blood for transfusion is not suitable for everyone. Blood of the first group is universal. But for those with the 4th category, blood of all groups is suitable - 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Here's what concerns the third blood category in this vein:
- A person with group 3 can become a donor for people with blood categories 3 and 4.
- It is permissible for a person with blood group 3 to receive blood transfusions of the first and third categories.
- The 3rd positive and the 3rd negative are incompatible! Rejection can even be fatal for the patient.
If it is not possible to transfuse suitable blood to a person in need, then specialists use serum or blood substitutes (“artificial blood”) - special sterile liquids that can replace it itself, as well as plasma. Such compositions are not a complete alternative, but are capable of supporting human life.
General information
Blood is a biological fluid that circulates throughout the body of every person in a volume of 5-6 liters (approximately 7% of body weight). Researcher K. Landsteiner discovered four of its categories:
- The first one is O.
- The second is A.
- Third - V.
- The fourth is AB.
The most common option is the first, the rarest is the fourth. The third negative will be in honorable second place in terms of non-prevalence.
Question 3:
What dose of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin and in what time frame is administered to a woman with Rh-negative blood after childbirth? Is it true that the administered dose of the drug should be increased after a caesarean section?
Answer
: Women with Rh-negative blood after childbirth are given anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin in an amount of 1-1.5 ml (200-300 µg) no later than 24-48 hours after birth for prophylactic purposes. During surgical interventions, transplacental bleeding may increase, and therefore the administered dose of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is increased by 1.5 times.
Compatibility of father and mother
We now know that the discrepancy between the blood characteristics of a pregnant woman and the embryo has serious consequences. They are especially severe in the case when the child has a third negative blood group, and the mother has the first or second. But let us note once again that the danger is real only for problematic pregnancy.
But now let’s move on to the Rh harmony of father and mother. Let's look at the compatibility of parents who have blood group 3:
- The third is negative in a woman. A suitable father is with blood types 1 and 3.
- The third is negative in a man. A suitable mother is with the 3rd and 4th blood groups.
What threatens the incompatibility of mother and father by Rhesus?