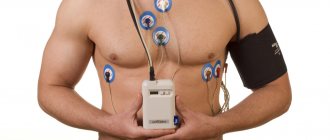
Hypertension and ABPM
Heart attacks and strokes are considered the scourge of modern society; the fast pace of life and numerous stresses make themselves felt by difficulties with the cardiovascular system. Cardiology of the 21st century has modern methods for identifying and treating these diseases. But such large numbers of sad statistics are caused by the fact that patients wait until the last minute to see a doctor. Many who did not choose to visit medical facilities in time are later transported by ambulance in serious condition.
One of the common reasons for emergency placement on the surgical table is hypertension, or rather its terrible consequences. Hypertension cannot be ignored; it needs control and treatment. ABPM helps diagnose diseases and promptly prevent the development of life-threatening conditions.
Few young people know what ABPM is, mistakenly considering hypertension and circulatory disorders to be the lot of older people. However, unfortunately, hypertension has become “younger” and can pose a danger even for 30-year-olds. But at this age it is not customary to think about blood pressure and problems with its fluctuations, which can be fraught with consequences. After all, hypertension can develop asymptomatically for a long time and can only be detected through regular tests. Therefore, it is useful for people of all ages to know about ABPM and what it is.
When is ABPM prescribed?
ABPM is carried out in the following cases:
- Arterial hypertension (identified elevated blood pressure numbers: 135/85 mmHg and above when measured at home; 140/90 mmHg and above when measured at a doctor’s appointment);
- arterial hypertension during pregnancy;
- assessment of the effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy;
- suspicion of “white coat hypertension”, when high blood pressure is recorded only when measured by medical staff;
- detection of increased blood pressure during sleep (high risk of acute cerebrovascular accident - stroke);
- arterial hypotension (blood pressure 90/60 mmHg and below);
- detection of orthostatic arterial hypotension.
Contraindications for the study:
- Exacerbation of skin diseases in the area of the cuff on the shoulder;
- disorders in the blood coagulation system with a tendency to bleeding (exacerbation stage);
- injuries of the upper extremities, contraindications to squeezing the shoulder with a cuff;
- obstruction of the patency of the brachial arteries identified during studies;
- significant heart rhythm disturbances;
- patient refusal.
Diagnosis of arterial hypotension using ABPM is irreplaceable due to the multifactorial nature of the development of this condition. For each individual patient, hypotension can be both a physiological norm and an independent illness; or may accompany another serious illness. Therefore, before prescribing medication or other treatment, it is necessary to understand the cause of low blood pressure in a person.
ABPM is also recommended for the following symptoms:
- constant fatigue or fatigue;
- frequent headaches, dizziness;
- blurred vision, spots before the eyes;
- noise, ringing, feeling of congestion in the ears.
ABPM: what is it and who is it prescribed for?
One of the important diagnostic tools in cardiology is ABPM, what kind of examination this is becomes clear from the transcript - daily blood pressure monitoring. This is a safe procedure. Over the course of a day or longer, if the doctor deems it necessary, a special device is painlessly attached to the patient’s body, which measures blood pressure at specified intervals. The device itself records data that will subsequently help to objectively assess the patient’s health status.
One of the misconceptions regarding ABPM is that this procedure is performed exclusively in a hospital. But no, daily blood pressure monitoring can be done without interrupting your usual lifestyle. Actually, this is its meaning - to monitor changes in a person’s pressure in his daily life.
ABPM is what will allow you to confirm hypertension, find out how much it threatens the patient’s life and prescribe adequate treatment. Or, on the contrary, refute the presence of hypertension, which will help avoid a false diagnosis and saturating the body with unnecessary medications.
Indications for ABPM:
- uncontrollable fear affecting some patients in medical settings, causing false research readings;
- borderline arterial hypertension (to clarify the numbers);
- high blood pressure;
- unfavorable genetics, a tendency to hypertension in young people;
- in case of fainting, to exclude low blood pressure;
- to monitor the effectiveness of treatment;
- in patients with already damaged vessels who have survived dangerous conditions, to determine critical blood pressure indicators.
What you should know about 24-hour Holter monitoring
Note Lakhta Clinics. We do not know from whose difficult hand such a clumsy and cumbersome word “monitoring” appeared in the Russian language instead of the long-established and intuitive term “monitoring” (from the English “observation, control”) in relation to Norman Holter’s methodology. In this material, we adhere to common sense and translate the name of the method as it is written and sounded in the original: monitoring.
What is Holter monitoring?
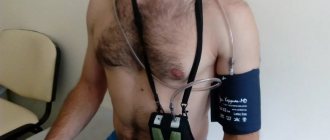
A portable, battery-powered, self-contained electrocardiograph is used, which is attached to the body and records the main indicators of heart function during a person’s daily activities.
When a patient comes to an appointment with complaints of heart problems, the doctor usually suggests an ECG (electrocardiography) to clarify the diagnosis. A standard stationary electrocardiograph provides a “snapshot” of the overall electrical activity of the heart. If such a snapshot is not informative enough, daily Holter monitoring is prescribed. The technology is almost the same as with a standard ECG: thin wires extend from a compact device mounted on the body, which are connected through electrodes to several points on the chest.
Depending on the nature of the symptoms present and the approximate frequency of their occurrence, the doctor may prescribe Holter monitoring for 12, 24 or 48 hours.
The most common indications for monitoring:
- fast or slow heart rate;
- dizziness (including when using a pacemaker);
- weakness and/or fatigue;
- feeling of lack of air;
- chest pain;
- feeling of “fluttering heart”;
- interruptions, uneven heartbeat;
- feeling of “missed heartbeats”.
Many heart problems occur sporadically throughout the day, and it is very unlikely that a person would end up in a doctor's office at that time. This is one of the most important advantages of Holter monitoring: the device will register pathological abnormalities whenever they occur, which will allow us to establish the root cause of such disorders. In addition, the Holter device allows you to monitor the condition of a person with already diagnosed cardiovascular disease. Most people feel much more comfortable with such a discreet device, preferring it to a long hospital stay.
Finally, the doctor may order 24-hour Holter monitoring to assess the effectiveness of the patient's medications.
How to use it
The Holter monitor is very easy to use, even if out of habit the technique looks complicated. The recorder is small enough to fit in the palm of your hand; it is usually worn around the neck or waist. The technical assistant attaches the electrodes to the skin, using a special adhesive (sticky, sticky) gel to fix them in the desired location and ensure the correct reading of electrical potentials. If there is heavy hair growth in this area, it may be necessary to shave it off before attaching the electrodes.
The metal in the electrodes picks up the contractile activity of the heart as electrical signals, which are then transmitted through wires to the monitor and recorded there.
At some point, the electrodes may lose reliable adhesion to the skin or fall off completely, and it is very important to return them to their place. The doctor will explain how this is done.
What to look for and what to expect
The attending physician will answer these questions in detail; he will also explain the nuances of using a specific monitor model. The general recommendations below will help prevent incorrect registration and avoid repeat testing. Avoid swimming, showering and bathing during the day you wear the Holter monitor. You can use wet wipes or a soapy washcloth for hygiene of the face, armpits, buttocks, and groin area. However, it is very important to ensure that no water gets on the device, wires or electrodes.
On the other hand, most patients are asked to go about their day as usual during a 24-hour Holter test, including doing any regular exercise - as long as it does not involve excessive sweating or staying in areas where the device might get wet.
During the study, the patient attends an educational institution or goes to work as usual. In some cases, your doctor may ask you to limit your alcohol or caffeine intake.
The patient should write down, in chronological order, all of their daily activities, as well as any symptoms they experience during the day. Marking the time of occurrence of paroxysmal pain in the chest, for example, will help the doctor, when deciphering the results, decide where to first look for the cause.
A person undergoing a Holter test records the following information about the circumstances surrounding the symptoms:
- what he was doing at that moment;
- what foods did you consume before?
- whether you drank alcohol;
- what was the level of stress (emotional tension);
- whether he was in a state of activity or rest.
It is also very useful to note whether the electrodes have been securely attached throughout the day. Loose or disconnected electrodes may make results unreliable and incomplete. Avoid being near high voltage sources while wearing the monitor as strong electromagnetic fields can distort the recorded signals. For the same reason, avoid going near powerful magnets that are part of a structure, such as metal detectors or an MRI scanner.
Some electronic devices can also interact and affect the functioning of the Holter monitor. You should listen to your doctor's advice if he or she asks you to refrain from using, for example, an electric toothbrush, electric razor, microwave oven, or cell phone while wearing the monitor.
Daily Holter monitoring is a completely non-invasive study. Some may find it inconvenient, but it does not pose any serious risk.
The only possible complication may be some irritation of the skin where the electrodes are attached to the body. Therefore, it is imperative to warn your doctor about a possible allergic reaction to adhesive and adhesive substances, if such reactions have already been noted in the past. In this case, it will be possible to select another, individually neutral auxiliary substance for fixing the electrodes.
Understanding the Results
At the end of the test period, the person returns to the doctor, the monitor is unfastened and removed, and all historical records and special notes are provided to the doctor for review. Objective indicators stored in the device’s memory are compared with the patient’s records and are necessarily taken into account when making a diagnosis.
Holter monitoring can reveal a latent cardiac anomaly or pathology, identify symptoms and potential triggers that have escaped attention, and detect a connection between existing problems and taking any medications.
As a rule, you have to wait for detailed research results (about a week or a little more).
Next steps
After the doctor identifies the reasons underlying the existing symptoms, it will be possible to discuss the strategy and tactics of further treatment. If the patient is already taking a previously prescribed course of therapy, it may be necessary to make adjustments to the dosage or replace any drug.
In some cases, the diagnosis remains unclear even after studying the results of 24-hour Holter monitoring. For example, on that day, the existing problem may not have manifested itself in tangible symptoms, or the monitor could not pick up abnormal heart activity.
In these cases, other diagnostic tests are additionally prescribed, or longer monitoring is recommended. Wireless models of monitors and ECG on adhesive patches allow you to record heart rhythms for a period longer than one day.
In general, Holter monitoring can cause short-term and completely negligible discomfort, but in some cases this method turns out to be a source of vital information about hidden myocardial pathology.
Based on materials from Medical News Today
What is important to know when examining ABPM
ABPM is an examination that can and should be carried out without interrupting your usual work. Early detection of the prestage of hypertension and correction of the activity and rest regime can prevent the formation of stable hypertension.
ABPM is a simple procedure that does not require special preparation. But when carrying it out, it is better to adhere to certain rules and doctor’s recommendations.
Patients undergoing ABPM are given recommendations:
- if the cuff has moved down the arm, return it to its place - there should be a distance of 1-2 cm between the lower edge and the elbow bend;
- try not to move after the sound signal indicates the start of the measurement; a repeated signal will signal the end;
- make sure that the tube leading from the cuff to the monitor does not become compressed;
- Do not shower during the ABPM examination and try to avoid getting water on the device;
- do not be exposed to intense stress, or write down the exact time when this happened;
- don’t get hung up on the research, don’t constantly look at the monitor data, try to sleep at night and not worry too much about the device;
- do not linger for a long time near sources of electromagnetic waves;
- If you have any concerns regarding the serviceability of the device, do not attempt to repair or disassemble it, notify your doctor.
ABPM results and their interpretation will be based on the average daily blood pressure, episodes of maximum high blood pressure, daily index of systolic and diastolic pressure, how quickly and high the blood pressure rises in the morning. Indicators of excessive or insufficient reduction in blood pressure during night sleep are very important for diagnosis and risk assessment.
Indications for the 24-hour blood pressure monitoring procedure
As noted above, the ABPM procedure is often indicated for working people, without specifying age. The purpose of such an examination is to detect the slightest changes in blood pressure during the day. Patients are even recommended to keep diaries where they should record the events of the day: from waking up to going to bed. This allows the doctor to further determine what exactly - what stress or emotional experiences - is associated with an increase or decrease in pressure.
There are many objective reasons for monitoring:
- blood pressure control in patients suffering from hypertension;
- initial analysis of the condition of a patient who has consulted a doctor;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- frequent stress, depression;
- taking medications to lower blood pressure;
- sleep apnea syndrome (short-term cessation of breathing during sleep);
- the presence of pathologies of the autonomic system;
- complaints of increased blood pressure during certain periods of daily activity;
- suspicion of severe late toxicosis during pregnancy (preeclampsia);
- choosing the optimal type of delivery for a pregnant woman with severe hypertension;
- preventive monitoring of the health of the working population;
- examination of conscripts.
"Latum" - a modern clinic
The fast pace of life and workload make you give up on your health and put off taking care of it until later. What if “later” doesn’t come? When prescribing ABPM, the cost of delay may be life. Hypertension does not tolerate neglect.
Despite the importance of ABPM research, its cost is low. Both students with cardiovascular problems and pensioners can afford it. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of ABPM; for daily blood pressure monitoring, the price is significantly lower than the value of your life. There are a lot of people who want to undergo the necessary procedure, so waiting in line in public hospitals can take a long time, and time is against the patient.
An excellent solution to the problem is to go to a private clinic on Korovinskoye Highway, where you can immediately make an appointment at a convenient time and undergo a study. “Latum” is a clinic with an individual approach to each patient. The clean and comfortable clinic, located in the Northern Administrative District, offers patients consultations and appointments from highly qualified professionals. We are located near the Seligerskaya metro station. This metro line is laid along the street. 800th anniversary of Moscow. Our doctors and laboratory technicians have a wide range of modern research methods and the latest equipment.
Experienced medical cardiologists will determine whether the patient needs ABPM, and if necessary, an examination will be carried out as soon as possible. Also, those who wish can undergo ABPM on their own initiative; the price of the examination in the clinic is low and will pleasantly please patients. Upon completion of the study, our specialists will not silently fill out your card and, without explanation, hand over a list for purchasing medications, as sometimes happens. Our doctors will give you a breakdown of ABPM, then give you extended recommendations and prescriptions.
In the private clinic “Latum” near Dmitrovskoye Highway, you can undergo a comprehensive examination, establish a diagnosis and treatment method. Call us at +7 (495) 150-17-78 and make an appointment so as not to waste time in line. You can also sign up through our website. Take the first step towards restoring your health.
Carrying out the ABPM procedure
Blood pressure monitoring can be performed in a hospital or clinic. For this purpose, the patient is invited to come early in the morning. After the traditional blood pressure measurement, the patient is put on a device for daily monitoring of readings. For right-handed people, the cuff from the device is attached to the left hand, for left-handed people - vice versa. The device itself can be attached to a belt or shoulder. If it is necessary to simultaneously record a cardiogram, appropriate electrodes are attached to the chest.
Equipment for ABPM is configured in a special way. It independently pumps air after a certain time, usually once every half hour during the day and once per hour at night. During these periods, patients need to relax, lower their hand down and wait until the end of the measurement. If unpleasant symptoms appear, the patient can press a button on the device outside of the specified schedule, and the measurement will take place unscheduled.
During the procedure, the patient keeps a diary. There he should record the time of eating, the slightest stress, and unpleasant symptoms. The entries might look something like this: “I went up to the second floor, ate an apple, felt pain in my heart.” The time is shown next to it.
The next morning, the device is removed, the information is transferred to a computer for data decoding and analysis by a doctor.
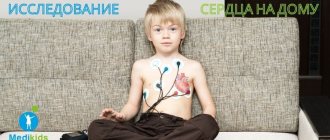
Can the procedure be performed on children?
In childhood, blood pressure monitoring is carried out from the age of 7 years. Often the procedure is done in conjunction with round-the-clock ECG recording. Indications for ABPM in childhood:
- hypertension;
- hypotension;
- periodic cases of loss of consciousness;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
The ABPM examination method for children is not fundamentally different from that used for adults. The only difference is that the details should be explained to the child in more detail, emphasizing the need to wear the device all day and night.
Determining the limits of normal blood pressure for children is quite difficult. Indicators may differ depending on age, height, physical activity, and somatic type. During the period of hormonal changes, blood pressure levels may fluctuate. In particular, for a tall child the norm can be considered a pressure of 120/80; for a short child this is too high.