Violent feelings and pragmatism in life are incompatible things: when two loving people meet, it is not customary to be interested in their blood type. As practice shows, unfortunately. The ideal psychological and sexual compatibility of people in love can be overshadowed by incompatibility in blood type and Rh factor.
The latest research on the role of blood type on conception, published by Turkish scientists, states that men with blood type O are four times less likely to develop impotence compared to guys with other blood types. Experts from Ordu University in Turkey noted that blood type is as important a risk factor as smoking, excess weight, and high blood pressure. The reason is not clear, but scientists have stated that in people with the second blood type, the penis has a large number of veins, the lining of which can be damaged, which leads to erectile dysfunction.
Blood type also affects female fertility. Girls with the second group are more likely to bear a healthy child for a long time than with the first. Studies have shown that women in the first group quickly deplete their egg reserves early in life. But at the same time, women with the first group have a lower risk of developing preeclampsia - high blood pressure during pregnancy, which can be dangerous for the mother and child.
Be that as it may, life does not always happen “according to science,” which is why our article was written.
Story
The fourth blood group is the youngest and rarest. There are less than 10% of people with such indicators on Earth. People with AB indicators appeared on our planet about 1000 years ago. Today, there are several versions of why the blood suddenly changed its usual indicators.
Theory one. According to some scientists, the mixed group appeared as a result of interethnic marriages. It is believed that the first children with such indicators were born in marriages of Europeans and Mongols. Such unions were not possible before, and therefore the mixing of blood that gave such a group was not observed.
Theory two. Blood group AB is a protective reaction of the body. According to this theory, during times of widespread incidence of various viral infections, nature launched a protective mechanism by combining antigens A and B on the red blood cells of one person. Thus, the immune system was significantly strengthened, which made it possible to resist diseases such as measles, rubella, influenza, rabies and pneumonia.
However, this theory does not explain why there are so few people with these indicators.
Theory three. Diet. According to this theory, changes in blood composition are similar to mutations. Some geneticists argue that it was the emergence of new foods that provoked this mutation. In their opinion, chemically processed foods are to blame for the appearance of people with blood group 4. However, the fact of the small number of such people also does not fit into this hypothesis.
Blood group compatibility
In the 20th century, the idea of transfusion arose. Blood transfusion is a useful procedure that restores the total volume of blood cells; plasma proteins and red blood cells are replaced. The compatibility of the blood groups of the donor and recipient during transfusion is important, affecting the success of the blood transfusion. Otherwise, agglutination will occur - a fatal gluing of red blood cells, resulting in the formation of a blood clot, which leads to death. Blood compatibility for transfusion:
| Blood type | Recipients | Which ones can you transfuse from? |
| 0(I) | I, II, III, IV | I |
| A (II) | II, IV | I, II |
| B(III) | III, IV | I, III |
| AB(IV) | IV | I, II, III, IV |
First
The first blood group is considered to be the foundation of human civilization. Our ancestors developed the habits of excellent hunters, brave and persistent. They are ready to spend all their strength to achieve their intended goal. Modern first-bloods need to be able to plan their actions in order to avoid rash actions.
Main character traits:
- natural leadership;
- extroversion;
- better organizational skills.
Strengths:
- strong digestive system;
- physical endurance;
- increased ability to survive.
Weaknesses are considered:
- Types of arthrosis and their degrees for which a disability group is given
- increased acidity (risk of peptic ulcer);
- predisposition to allergies, arthritis;
- poor clotting;
Second
City dwellers. Evolution moved forward and people began to engage in agriculture. When plant protein became the source of human energy, the vegetarian second blood group arose. Fruits and vegetables began to be used as food - the human digestive system began to adapt to changing environmental conditions. People began to understand that following the rules increases their chances of survival.
Main character traits:
- communication skills;
- constancy;
- composure.
Strengths:
- good metabolism;
- excellent adaptation to change.
Weak sides:
- sensitive digestive system;
- weak immune system.
Third
People with the third blood group are called nomads. It is difficult for them to experience an imbalance within themselves, in the team. It is better to live in mountainous areas or near water bodies. They suffer from a lack of motivation because their bodies produce large amounts of cortisol when they are stressed.
Main character traits:
- flexibility in decisions;
- openness to people;
- versatility.
Strengths:
- strong immunity;
- tolerate changes in diet well;
- creative.
Weak sides:
- Is disability allowed for arthrosis of the knee and other joints?
- susceptible to autoimmune diseases;
- lack of motivation and self-confidence.
Fourth
Holders of the rarest, fourth blood group occurred as a result of the symbiosis of the second and third. A bohemian, easy life is what characterizes its representatives. They were tired of everyday decisions and devoted themselves to creativity. The total number of people with such a group is only 6% on the planet.
Main character traits:
- mysterious;
- individual.
Strengths:
- resistant to autoimmune diseases;
- resist allergic manifestations.
Weak sides:
- fanatics, capable of going to extremes;
- Drugs and alcohol should be avoided.
Little known facts
Many people believe that there are only four blood types on our planet. However, numerous studies have proven that there are many more. In different countries and on different continents, completely different groups that do not fit into the usual system are increasingly being discovered. There are only a few such people and there is no point in putting them into separate groups, which is why the AB0 system is still used all over the world.
Some parents do not think about what blood parameters their baby will be born with. But geneticists have long learned to calculate which group a baby will have. It’s interesting, but children of blood type 4 can appear in a family where the parents and their relatives never had it. Mixing groups 2 and 3 among parents can bring such surprises. Also, if one of the partners has the fourth AB group, the child can inherit it. For this reason, fathers do not need to worry and harass their wives with statements “The child is not from me.” Every father should know how the child gets his blood type, then there may be much less conflict in families of pathological jealous people.
In case of emergency, people with AB (IV) can receive a transfusion of any blood with the appropriate rh. This is due to the presence of antigens A and B, so that no blood can cause a negative reaction in them. However, given that this blood is the rarest, and especially if a person has a negative Rh factor, it is better to know in advance which of your relatives has the same indicators. Transfusion of different plasmas is carried out only in the most extreme cases. In our country, planned blood transfusions are performed only in groups.
INHERITANCE OF BLOOD TYPE BY A CHILD
Often in the maternity hospital, mothers are asked the question: “What cut group does my child have?” And then they think long and painfully: “Why did they say that my baby has the first blood type, if my husband and I have the second?”
To answer this question, let us remember what blood groups are and what laws of nature they “obey”.
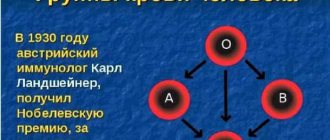
At the beginning of the last century, scientists proved the existence of 4 blood groups.
The Austrian scientist Karl Landsteiner, mixing the blood serum of some people with red blood cells taken from the blood of others, discovered that with some combinations of red blood cells and serum, “gluing” occurs - red blood cells stick together and form clots, but with others - not.
While studying the structure of red blood cells, Landsteiner discovered special substances. He divided them into two categories, A and B, highlighting a third, where he included cells that did not contain them. Later, his students - A. von Decastello and A. Sturli - discovered red blood cells containing A- and B-type markers simultaneously.
As a result of research, a system of dividing blood groups emerged, which was called ABO. We still use this system today.
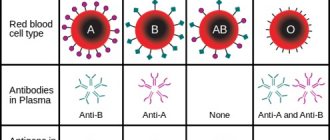
- I (0) – blood group is characterized by the absence of antigens A and B;
- II (A) – established in the presence of antigen A;
- III (AB) – B antigens;
- IV(AB) – antigens A and B.
The AB0 system has revolutionized scientists' understanding of the properties of blood. Genetic scientists began to study them further. They proved that the principles of inheritance of a child's blood type are the same as for other characteristics. These laws were formulated in the second half of the 19th century by Mendel, based on experiments with peas, familiar to all of us from school biology textbooks.
So how are blood groups inherited by a child according to Mendel’s law?
- According to Mendel's laws, parents with blood group I will give birth to children who lack A- and B-type antigens.
- Spouses with I and II have children with the corresponding blood groups. The same situation is typical for groups I and III.
- People with group IV can have children with any blood group, with the exception of I, regardless of what type of antigens are present in their partner.
- The inheritance of a blood group by a child is most unpredictable when the union of owners with groups II and III occurs. Their children are equally likely to have any of the four blood types.
- The exception to the rule is the so-called “Bombay phenomenon”. Some people have A and B antigens in their phenotype, but do not manifest themselves phenotypically. True, this is extremely rare and mainly among Indians, which is why it got its name.
TABLE OF INHERITANCE OF BLOOD TYPE BY A CHILD DEPENDING ON THE BLOOD GROUPS OF THE FATHER AND MOTHER
| MOM + DAD | CHILD'S BLOOD TYPE : POSSIBLE OPTIONS (%) | |||
| I+I | I (100%) | — | — | — |
| I+II | I (50%) | II (50%) | — | — |
| I+III | I (50%) | — | III (50%) | — |
| I+IV | — | II (50%) | III (50%) | — |
| II+II | I (25%) | II (75%) | — | — |
| II + III | I (25%) | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| II + IV | — | II (50%) | III (25%) | IV (25%) |
| III+III | I (25%) | — | III (75%) | — |
| III + IV | — | I (25%) | III (50%) | IV (25%) |
| IV + IV | — | II (25%) | III (25%) | IV (50%) |
INHERITANCE OF RH FACTOR
The birth of a child with a negative Rh factor in a family of Rh-positive parents causes deep bewilderment at best, and mistrust at worst. Reproaches and doubts about the fidelity of the spouse. Oddly enough, there is nothing exceptional in this situation. There is a simple explanation for such a delicate problem, which is based on the same laws of genetics.
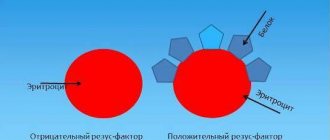
The Rh factor is a lipoprotein located on the membranes of red blood cells in 85% of people (they are considered Rh positive). If it is absent, they speak of Rh-negative blood. These indicators are denoted by the Latin letters Rh with a plus or minus sign, respectively.
The gene for a positive Rh factor is designated D, it is a dominant trait (always appears). The Rh negative gene is recessive and is designated d (appears only in the absence of D). Therefore, people with a set of DD or Dd chromosomes will have Rh positive blood, and only those with a dd chromosome set will have Rh negative blood.
Consequently, parents with a homozygous absence of the Rh factor (dd) can only give birth to children with Rh negative blood.
Parents with homozygous Rh positive factor (DD) will only give birth to children with Rh positive blood.
But in the union of people with Rh positive blood with heterozygous presence of Rh (Dd), their children will have Rh positive in 75% of cases and negative in the remaining 25%.
So, parents: Dd x Dd. Children: DD, Dd, dd – these are Rh negative children of Rh positive parents! .
Inheritance of the blood type of the Rh system, possible in a child, depending on the blood groups of his parents.
| Mother's blood type | Father's blood type | |
| Rh(+) | rh(-) | |
| Child's blood type | ||
| Rh(+) | Any | Any |
| rh(-) | Any | Rh negative |
And some more interesting things from geneticists...
INHERITANCE OF CHARACTERISTICS
For centuries, parents have only wondered what their child would be like. Today is an opportunity to look into the future. Thanks to ultrasound, you can find out the gender and some features of the anatomy and physiology of the baby.
Genetics will make it possible to determine the likely color of the eyes and hair, and even whether the baby has an ear for music. All these characteristics are inherited according to Mendelian laws and are divided into dominant and recessive.
Brown eye color, hair with small curls, and the ability to roll the tongue into a tube are dominant signs. Most likely, the child will inherit them. Unfortunately, dominant signs also include a tendency to early baldness and graying, myopia and gaps between the front teeth.
Gray and blue eyes, straight hair, fair skin, and a mediocre ear for music are considered recessive. These signs are less likely to occur.
BOY OR...
For many centuries, the blame for the lack of an heir in the family was placed on the woman. To achieve the goal of having a boy, women resorted to diets and calculated favorable days for conception. But let's look at the problem from a scientific point of view. Human sex cells (eggs and sperm) have half the set of chromosomes (that is, there are 23 of them). 22 of them are the same for men and women. Only the last pair is different. In women these are XX chromosomes, and in men they are XY.
So the probability of having a child of one sex or another depends entirely on the chromosome set of the sperm that managed to fertilize the egg. To put it simply, the father is entirely responsible for the gender of the child!
Head of the department for newborn children Ilkevich N.G.
Neonatologist of the department for newborn children Valentyukevich T.S.
Rh negative
Advertising:
If we consider that there are only about 20% of people on Earth with RH-, and there are even fewer citizens with the fourth blood group, we can conclude that the 4th negative blood type is the rarest of the four recognized ones. Some sources claim that the Rh factor can change in representatives of the fourth negative blood group.
However, official medicine refutes such facts.
Sometimes patients with blood type AB can actually say that they were Rh positive and became Rh negative. Such cases have been recorded, but they are explained by laboratory errors. Some people with negative blood have a special variant of the KEL protein. It is he who can imitate antigens on the surface of red blood cells. Previously, this protein was not always detected due to imperfect equipment. It is for this reason that Rh was set incorrectly.
It is worth noting that owners of this protein cannot be donors. And if there is a need to transfuse them with plasma, only negative biomaterial will be suitable for them. Today, genotyping is used to establish the exact rhesus and group. This is a modern study that excludes errors.
Compatibility tests when planning pregnancy
It should be noted that the Rh factor does not affect the course of the first pregnancy, but it must be determined in order to protect the woman and give her a chance to give birth to a second and subsequent children.
Therefore, future parents need to find out the compatibility of their Rhesus in advance. To check blood compatibility, both spouses must undergo tests at the planning stage.
Women who are Rh negative and planning a pregnancy with a Rh positive man should have a blood test done to check for antibodies. You can donate blood for antibodies even if you are already pregnant. In the latter case, this should be done as early as possible in order to prevent miscarriage and fetal diseases.
Risks during pregnancy
Advertising:
Unlike representatives of other groups, those women who have fourth positive blood may not worry about blood group conflicts during pregnancy. The only recommendation for these women is to check Rh compatibility. If a woman has a positive blood type 4, there is no risk of conflict. If, on the contrary, the risks for such patients are no higher than for representatives of other blood groups. It must be remembered that a Rh conflict can only arise when women have negative blood, and men have Rh positive blood and the child is Rh positive.
Rh factor
During scientific research in 1940, an antigen was found in the blood of macaques, which later received the name Rh factor. It is hereditary and depends on race. Those people who have this antigen in their blood are Rh positive, and if it is absent, they are Rh negative.
Transfusion compatibility:
- Rh negative is suitable for transfusion to people with Rh negative;
- Rh positive is compatible with any Rh blood.
If you use Rh-positive blood for a patient with a Rh-negative category, then special anti-Rhesus agglutinins will be produced in his blood, and with another manipulation, red blood cells will stick together. Accordingly, such a transfusion cannot be carried out.
Any transfusion is stressful for the human body. Whole blood is transfused only if the loss of this biological fluid reaches 25% or higher. If less volume is lost, blood substitutes are used. In other cases, transfusion of certain components, for example, only red blood cells, is indicated, depending on the type of lesion.
How to avoid problems
If incompatibility is detected, the doctor organizes several blood tests for the still pregnant woman to monitor the level of antibodies. After birth, the baby's blood is also tested. If the baby is “Rh+”, then the mother is offered an injection of anti-D (immunoglobulin) within a few days after birth. Anti-D prophylaxis is taking a drug that prevents a woman’s body from producing antibodies against Rh+ cells. Today, Rh sensitization during pregnancy and after childbirth can be largely prevented. This is achieved through prophylaxis with anti-D immunoglobulin.
Advertising:
All Rh-negative expectant mothers are offered anti-D immunoglobulin injections. This procedure prevents harm from Rh incompatibility
.
Typically, all pregnant women who are Rh-negative and do not have antibodies to the D antigen are recommended prophylaxis with anti-D immunoglobulin. This is either one injection between 28-30 weeks of pregnancy, or two - at 28-34 weeks. This kind of prevention is called ongoing prenatal (antenatal).
The process by which the mother's body begins to produce antibodies against antigen D is called potentially sensitizing. Sometimes, after such circumstances arise, additional injections of anti-D immunoglobulin are necessary. Such situations include the following:
- threatened miscarriage or miscarriage;
- ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy;
- abortion;
- vaginal bleeding;
- obstetric intervention;
- abdominal trauma, such as after a fall or car accident.
Any event, be it vaginal bleeding or abdominal trauma, should be reported to your midwife or doctor as soon as possible.
A timely consultation with your doctor is the right step towards a trouble-free pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby.
Incompatibility problem
The Rh factor is checked using a blood test. “Rh−” poses a threat to the mother in labor if her Rh does not coincide with the baby’s Rh. Research has shown that some problems are related to blood type incompatibility between mother and fetus or between parents. As written above, markers (antigens) protect the body from external pests such as bacteria and viruses. When an antigen encounters a foreign object, it creates antibodies against it. The same thing can happen when trying to get pregnant. The body will react by producing antibodies to the appearance of sperm or a fetus, which will prevent conception.
Many migraine medications help manage the symptoms but do not cure the pathology. Triptans are a group of medications that are intended specifically for the treatment of the disease. Read more in the article: “triptans for migraines.”
The problem appears when the Rh of the mother's blood does not match the Rh of the fetus, and the body begins to produce antibodies against proteins on the baby's red blood cells. An Rh-negative mother does not always pose a threat to fetal development:
- if both parents are Rh-negative and the child also receives “Rh−”, then no complications arise;
- if the mother has “Rh−” and the father “Rh+”, and the fetus receives Rh negative, then there is no threat of conflict;
- if the woman in labor has “Rh+” and the child has Rh negative, protein incompatibility will not occur.
The chance of a child inheriting Rh and the probability of conflict in the table.
Rh factor
Advertising:
| Father | Mother | Child | Probability of conflict |
| + | + | 75% + 25% — | No |
| + | — | 50% + 50% — | 50% |
| — | + | 50% + 50% — | No |
| — | — | — | No |