The decision to travel by plane after a heart attack or stroke is a serious step that requires some preparation and a comprehensive analysis of the specific situation. Flying on an airplane after a stroke or heart attack is not prohibited, but in each specific case only the attending physician can give an accurate answer, having assessed the risks and the general condition of the patient. To make the right decision, you need to understand the dangers of flying in such cases, when it is safe to travel after illness and stenting operations, and how to help yourself if your condition worsens.
Important! Flights after such cardiovascular diseases can cost a person’s life, so the decision must be balanced, and the need for a flight must be justified.
What are the dangers of flying after a heart attack or stroke?
At high altitudes, atmospheric pressure decreases, the air is thinner, and the amount of oxygen is reduced. All this causes pressure surges in the body, which poses the main danger. To provide the body with sufficient oxygen supply, the heart is forced to work faster, and this causes additional stress on the blood vessels.
What is myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is damage to an area of the heart muscle due to circulatory problems. If pathologies occur in certain vessels that feed the heart muscle (blockage with a blood clot, narrowing), it does not receive oxygen. This leads to cell death. As a result, the heart cannot fully perform its functions and pump blood throughout the body.
The lesion can be small-focal or large-focal. After such violations, patients undergo rehabilitation aimed at strengthening blood vessels and reducing the load on them. Depending on the type of heart attack (broad classification), the rehabilitation period ranges from two weeks to six months.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to fly on airplanes until the end of the rehabilitation period prescribed by the doctor.
What is a stroke
Stroke is the second most deadly disease. It develops suddenly and leads to either death or paralysis and disability. The success of treatment depends on how quickly help was provided to the patient.
A stroke is the death of brain cells. The outcome largely depends on the site of the lesion, its extent and cause:
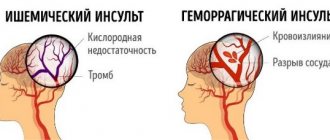
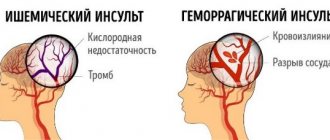
- Ischemic stroke occurs due to blockage of blood vessels, as a result of which blood does not flow to brain cells, and they quickly die.
- Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to bleeding in the brain due to rupture of blood vessels in the head. In this case, edema occurs, which blocks the access of oxygen to the brain cells, and necrosis occurs, that is, they die.
The rehabilitation period is much longer than for myocardial infarction. Often, after suffering a stroke, people learn to walk, write, and talk again. The patient returns to a more or less usual way of life after two months (depending on the severity of the disease). And the rehabilitation and recovery itself can take six months or even several years. People who have suffered micro-strokes and cerebral hemorrhages are most often interested in the possibility of flying after such an illness, since in a severe form of the disease there can be no talk of traveling.
Risks of flying after a heart attack or stroke
Myocardial infarction often causes complications, which imposes certain restrictions on flights. The heart attack itself can be successfully treated, but the consequences do not go unnoticed. The following complications may occur:
- Acute aneurysms (protrusion of arterial walls due to their thinning and overstretching, as a result of which the lumen of the vessel expands, the elasticity of the walls decreases, and the vessels cannot contract fully to ensure normal blood supply).
- Conduction disorders of the nerve bundles of the heart (nerve impulses do not reach the heart muscle, but they give a signal to contract. As a result, the heart muscles contract incorrectly and cannot push blood into the aorta for its further movement through the vessels).
- Acute heart failure or cardiogenic shock (requires immediate resuscitation).
- Myocardial rupture.
- Heart failure.
Even if you have successfully completed the rehabilitation course, the risk of such complications always remains. Therefore, you need to carefully weigh the risks and the need for travel.
Important! The more time has passed after rehabilitation, the higher the chance of a successful plane flight.
A stroke also has certain consequences for the entire body. But depending on the cause, the risk of recurrence may be lower. For example, if the blockage of a vessel was caused by a foreign body, then the chance of a recurrence of this situation is small. Or in the case of a hemorrhagic stroke, when the rupture of healthy vessels occurred due to injury during an impact, the possibility of a recurrence of such a situation is also minimized. But if the cause of the blockage was a detached blood clot, it is not worth the risk, since the slightest load on the vessels may cause the situation to recur. In each specific case, they consult a doctor who will or will not give permission to fly.
How does flying affect the human body?
The most unfavorable moments during a flight, even for healthy people, are takeoff, landing and turbulence. But the flight itself is a certain burden on the body, since the conditions in an airplane located at a high altitude are different from the usual ones, and they are not famous for comfort. Plus, added to the stress and anxiety that many people experience. If a healthy body tolerates changes in the physical parameters of the air, discomfort and stress quite normally, then for those who have suffered serious illnesses, air travel turns into a problem:
- Due to the air conditioning and crowds of people, the atmosphere in the aircraft cabin is not the most favorable. Dry air leads to rapid dehydration of the body, which in turn leads to blood thickening, and this is dangerous for people with cardiovascular diseases.
- Staying in a stationary position for a long time causes swelling, poor circulation and can lead to blood clots, which is also harmful for people who have suffered strokes and heart attacks.
- Due to excitement, the heartbeat increases, the load on the heart and blood vessels increases. And if a healthy person goes through this unnoticed, then people with heart pathologies can get complications.
- During takeoff and landing, atmospheric pressure changes rapidly, the amount of oxygen decreases, which also adversely affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system and causes unnecessary stress on the body.
- In areas of turbulence, invisible vibrations occur that affect the rhythm of the heart, and this leads to circulatory disorders, as a result of which the heart muscle and brain cannot be fully supplied with oxygen.
We, healthy people, endure all these phenomena almost unnoticed, sometimes experiencing only slight dizziness, blocked ears and discomfort. For people after a stroke or heart attack, such phenomena affect them more openly and negatively, so they have a harder time with flying.
Is it possible to drive a car after a stroke?
Many patients suffering from acute cerebrovascular accident are drivers. Feeling a little better, they are eager to get behind the wheel again. But isn't it dangerous to drive a car in this condition?
Experts categorically prohibit driving during the first 3-6 months after a stroke. Despite ongoing rehabilitation measures, patients may still have problems with:
- clarity of thinking;
- assessment of the road situation;
- timely response;
- fields of view.
These factors have a negative impact on driving style, making it unpredictable and dangerous for other road users.
After the end of the driving ban period, the patient must undergo special tests proposed by the medical commission. They allow you to evaluate not only motor skills, but also thinking. Even after passing the tests positively, you need to think: is it worth driving a car or is it better to refrain from unnecessary stress?
What determines permission to fly after a heart attack or stroke?
Having suffered a myocardial infarction or stroke is not a death sentence or a reason to give up air travel forever. But before planning a flight, you should definitely consult your doctor and get his permission. You will receive such permission if:
- Enough time has passed since the illness (the doctor will determine this period himself, since only he knows your anamnesis and medical history). It is not recommended to board a plane before 2 months. On average, doctors give permission to fly on an airplane after 6 months.
- The rehabilitation was successful: you strictly followed the doctors’ recommendations, completed a course of massage, physical therapy, and other physiotherapeutic procedures, and are currently healthy.
- Your blood pressure is stable. The highest indicator should not exceed 140/90. You do not experience surges and there are no complications (hypertension is a complication that occurs in 90% of cases after cardiovascular diseases).
- You are not stressed and are not afraid to fly. One of the negative factors that provoke complications and increase the risk of relapse is fear of flying, which causes pressure surges due to fear and panic. If you do not have aerophobia, you will be allowed to fly.
- You have been examined. Before a flight after a heart attack or stroke, it is necessary to undergo an ECG or ultrasound of the cerebral vessels to exclude the possibility of manifestations of the consequences of an aneurysm.
- You have been trained to take preventive medications. It is advisable to take a course of blood pressure stabilizing, sedative and blood thinning medications.
- You have your own first aid kit with medications recommended by your doctor, and you clearly know what to take and when.
Important! It will be a big plus if no serious complications have arisen during the entire period after the illness.
Compliance with all these conditions is the key to your safety and a smooth flight without complications. It is important to understand that heart attack and stroke are pathologies that, in case of recurrence, require immediate qualified assistance, which is not available on board the aircraft. Therefore, in order to minimize risks, you need to carefully prepare in advance and take care of your safety.
Important! If emergency transportation of a person with a stroke or heart attack is required, transportation is carried out accompanied by a team of qualified doctors who are provided with all the necessary equipment and medications.
Preparing and facilitating the flight
It is advisable for the patient to prepare himself for the future flight. To do this, the following activities are carried out:
- The blood vessels of the brain are strengthened, medications prescribed by doctors are taken;
- Diagnostic screening is done to identify a possible aneurysm;
- It is imperative to take the prescribed medications; you will definitely need medications against blood pressure and motion sickness;
- A pillow is taken on board to ensure that the passenger is comfortable in the seat. As a result, the load on the cervical spine is reduced.
Air carrier employees must provide official permission to provide an oxygen bag. You can also take antidepressants if your doctor approves.
Often people who have suffered from an illness need blood thinning. For this purpose, special medications are taken.
Attention! It is necessary to avoid drinking drinks with a high content of caffeine and alcohol; it is better to give preference to plain still water; it is recommended to drink a lot of it.
Before the flight, experts advise first putting on compression garments for the comfort of the body. Sometimes the passenger must walk between the rows.
The patient must try to treat his own health with great care and take care of it. When a person feels normal, the doctor cannot prohibit flights. It is important to remember that if you managed to fully recover once, it is unlikely that this will happen again a second time.
Contraindications for air travel
There are cases that serve as a categorical contraindication to air travel after a heart attack or stroke. These include:
- Rehabilitation period (until the period set by the doctor has ended, flying is prohibited).
- A complication in the form of arterial hypertension, which is common.
- Heart rhythm disturbances that arose as a complication (atrial fibrillation, atrioventricular block, etc.).
- Untreatable cardiovascular failure.
- Angina at rest or unstable angina on exertion.
Introduction
Acupuncture has been recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) as an alternative and complementary treatment for stroke patients and as a way to improve rehabilitation [1].
The frequency of use of acupuncture for stroke is increasing every year both in the countries that are the founders of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), and in Europe and North America [2]. The mechanism underlying the therapeutic effect remains unknown. The influence of acupuncture on the restoration of other impaired functions, except motor, and its role in the treatment of stroke complications and secondary prevention have not been sufficiently studied. The purpose of the study is to conduct an analysis of the scientific literature, on the basis of which to summarize the current known mechanisms of acupuncture and electroacupuncture, to summarize data on the effectiveness and specificity of the method in the prevention and treatment of stroke, the prevention of complications of the disease, the rehabilitation of post-stroke patients, to detail the most commonly used acupuncture points in acute brain disorders blood circulation
The search was performed without restrictions on the language of publication. Full-text and abstract databases were used as literature sources. The source search procedure included working in PubMed. The keywords for the search were words in English: “stroke and acupuncture”, “stroke and electroacupuncture”, “stroke and treatment and acupuncture”, “stroke and prevention and acupuncture”, “stroke and spasticity and acupuncture”, “stroke and dysphagia and acupuncture”, “stroke and cognitive impairment and acupuncture”. A filter was applied to search for articles published between 2013 and the present.
The mechanism of action of acupuncture for stroke
The mechanisms of action of acupuncture have been most studied in ischemic stroke. There is very little fundamental research into the effect of acupuncture in hemorrhagic stroke.
Taking into account the published L. Chavez et al. [3] in 2017, a meta-analysis of basic research and other data, the following main components of the mechanism of action of acupuncture in stroke can be identified:
1) stimulation of neurogenesis and cell proliferation in the central nervous system (CNS);
2) regulation of cerebral blood flow in the ischemic area;
3) anti-apoptosis in the ischemic zone;
4) regulation of the exchange of neurotransmitters, mediators of inflammation and oxidative stress;
5) improving the function of neuronal synapses, stimulating long-term potentiation (LTP);
6) stimulation of neuroplasticity;
7) decreased permeability of the blood-brain barrier.
Cell proliferation in the CNS
Acupuncture triggers 2 different mechanisms.
Firstly, neurogenesis is stimulated in neurogenic areas of the brain (subventricular zone of the lateral ventricle, dentate gyrus of the hippocampus). Electroacupuncture during cerebral ischemia in mice improved stem cell division by increasing the expression of GSK-3β/PP2A proteins, which control protein synthesis, proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of cells; increased the content of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [4], promoted the expression of retinoic acid, which enhances neurogenesis in the subventricular zone and hippocampus [5].
Secondly, acupuncture caused cell proliferation in the ischemic focus and adjacent zones (ischemic penumbra zone). After ischemia caused by middle cerebral artery occlusion and subsequent reperfusion in laboratory mice, electroacupuncture activated a cascade of Wnt and β-catenin signaling proteins, stimulating the proliferation of reactive astrocytes and neural progenitor cells [6]. Electroacupuncture increased stem cell activity [7], brain cell proliferation by stimulating Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK1/2) and cyclin expression [8, 9]. In the experiment, electroacupuncture promoted the proliferation of glial astrocytes in the peri-infarct cortex, striatum, ischemic tissue and neurogenic areas by increasing the expression of BDNF [4, 10]. This is undoubtedly important because BDNF is one of the most potent growth factors associated with recovery from stroke.
Regulation of cerebral blood flow in the ischemic area
Endothelial damage during stroke contributes to impaired nitric oxide production and increased endothelin-1 production, leading to vasospasm, which increases ischemia. The vasoactive modulating effect of electroacupuncture in mice at the points of the posteromedian meridian GV14 (note: hereinafter the names of acupuncture points are indicated according to the International Acupuncture Nomenclature, see Tables 1 and 2 ), GV20, GV26, through cholinergic activation and release of nitric oxide, increased perfusion on the affected side [eleven]. Electroacupuncture in laboratory rats decreased the expression of angiotensin II and its receptor type 1 (AT1R), promoting vasodilation and increasing cerebral blood flow [12]. It is of interest to study the effect of acupuncture on cerebral blood flow during ischemia in clinical studies that have already begun (protocols have been published, results are awaited).
Table 1. Designations of classical channels according to the International Acupuncture Nomenclature
Table 2. Designations of extra-meridian points according to the International Acupuncture Nomenclature
Antiapoptosis
Inhibition of apoptosis may reduce ischemic injury. It was shown that electroacupuncture during cerebral ischemia in rats at points GV20, GV26, CV6 increased the level of anti-apoptotic factors Akt, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL and cIAP 1/2, inhibited apoptotic mediators DR5 and the caspase family - caspase 3, 8 and 9 [ 13]. Electroacupuncture stimulation of points ST36, LI4, LI11, GV14, GV16, GV20, GV24, GV26, CV24, LU5, SP6 in rats with the ischemia-reperfusion model activated cascades of anti-apoptotic protein kinases (Bcl-2/Bax, PI3K/Akt, ERK1 /2, mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAPK) [14-17], suppressed neurotoxicity and inhibited the activation of the nuclear factor kappa-bi (nuclear factor - NF-kB) [18, 19]. Important factors in apoptosis are activation of large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (BKCa) and expression of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) [20]. Electroacupuncture at the GV26 point suppressed the expression of BKCa and mRNA at the site of injury, reduced neuronal apoptosis in rats (ischemia-reperfusion model), and improved motor function [21].
Regulation of the exchange of neurotransmitters, inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress
Ischemic damage is accompanied by an imbalance of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. Acupuncture can normalize neurotransmitter metabolism. It was shown that stimulation of extrameridian acupuncture points of the back EX-B2 on 2 sides along the spine in rats with cerebral ischemia promoted an increase in the expression of GABA-Aγ2 and GABA-BR2 receptors in the striatum and spinal cord, as well as the level of β-endorphins, and reduced the volume of infarction [ 22].
The inflammatory response during the development of cerebral ischemia is mainly mediated through the innate immune response by microglial cells, astrocytes, macrophages, cytokines: interleukins (IL-1, IL-6 and IL-10) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). The inflammatory response induced gene expression and activation of transcription factors that regulate the ischemic cascade [23]. In models of ischemia-reperfusion in rats, it was revealed that electroacupuncture at points ST36, GV20, LI11 has an anti-inflammatory effect, inhibiting the local release of cytokines, including TNF-α, inhibits heat shock proteins (HSP70), and inhibits cell turnover -like receptor 4 (Toll-like receptor 4). This inhibits the activation of NF-kB and reduces the expression of immune response genes [24, 25]. Evidence of the anti-inflammatory effect of acupuncture in ischemia is a decrease in the level of adrenocorticotropic hormone and HSP70 in the blood and brain tissue after electroacupuncture at the GV20 point [26]. Thus, electroacupuncture can reduce inflammation in ischemic stroke.
The antioxidant effects of acupuncture were observed in rats with multi-infarct injury modeled by occlusion of two cerebral arteries. As a result of acupuncture at points CV17, CV12, CV6, ST36, SP10, GV20, inhibition of oxidative stress mediated by NAPDH oxidase was observed [27]. Laser puncture at the GV20 point in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion contributed to a decrease in the level of malondialdehyde, an increase in the activity of glutathione peroxidase, catalase and superoxide dismutase in mitochondria, and led to a decrease in the volume of the ischemic focus [28].
Stimulation of long-term potentiation (LTP) of neuronal synapses
Animal models have shown that cerebral ischemia affects the CA-1 region of the hippocampus, which is responsible for learning and memory formation. The cellular model of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus is the phenomenon of LTP, realized through intracellular signaling cascades. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP (cAMP) activates protein kinases and CREB, a cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB-protein), which plays an important role in memory formation [29]. A two-week course of acupuncture at ST36 points in rats with multi-infarct injury activated the cAMP/PKA/CREB cascade, promoted the modulation of LTP in CA-1 and improved cognitive function [30].
Another cascade that activates CREB is the microRNA (mRNA) pathway and LIM kinase 1 (LIMK1), a key enzyme in long-term memory. LIMK1 regulates actin remodeling, causing dendritic restructuring, axon modification, ensures synaptic plasticity, and promotes CREB protein synthesis. Electroacupuncture at points GV20 and GV24 facilitated the expression of mRNA and increased the content of LIMK1 in the hippocampal CA-1 region [31]. Electroacupuncture of GV20 and GV24 points in rats (an ischemia-reperfusion model) stimulated the CREB activation pathway through the calmodulin (CaM) and calmodulin-dependent kinase IV (CaMKIV) system, promoting improved cognitive behavior and a reduction in infarct volume on histological examination [32].
Stimulation of neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity consists in the functional compensation of intact neurons, which determines the restoration of impaired functions after a stroke. Studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have shown that brain plasticity after stroke is manifested in changes in cortical thickness, gray matter volume, white matter conducting fibers, and activation of functional connections [33, 34]. Functional connections of the brain formed neural networks that were significant both during load and at rest (“resting networks”). According to functional MRI of the brain, it was found that acupuncture at the GB34 point in patients with ischemic stroke and hemiplegia improves the functioning of cognitive, motor and perceptual resting networks [35], promotes neuroplasticity and functional reorganization of neurons.
Reduced permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB)
Increased permeability of the BBB is one of the reasons for the development of complications of stroke (hemorrhagic transformation of the ischemic focus, enlargement of the hematoma during hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral edema, dislocation syndrome). Factors that increase BBB permeability are the microvascular endothelial cell membrane protein caveolin-1 and matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 [36]. Electroacupuncture at point GV20 in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage contributed to a decrease in the passage of Evans Blue dye into the brain tissue 30 minutes after intravenous administration, according to spectrofluorimetry, a decrease in the expression of caveolin-1 and matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9, which indicates a decrease in the permeability of the BBB [37] . This mechanism holds promise for research into the role of acupuncture in preventing complications of severe stroke.
Acupuncture in restoring impaired functions in stroke
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are used to demonstrate the therapeutic effects of acupuncture. CONSORT (CONsolidated Standards of Reporting Trials, CONSORT) and STRICTA (STandards for Reporting Interventions in Controlled Trials of Acupuncture, STRICTA) standards are used to reduce bias and improve methodological quality. , developed in 2001 and revised in 2010 [38]. In this regard, it is a common practice to publish protocols of RCTs, planned or recently initiated, without reporting the results.
We present data from completed studies.
Motor disorders. One of the priority goals of medical rehabilitation of patients after a stroke is to improve motor skills and reduce spasticity. Movement disorders impair mobility, limit daily activities, reduce the chances of returning to professional activities and reduce the patient’s quality of life. The results of a large number of studies on the restoration of motor deficits using acupuncture have been published.
Data from a 2021 meta-analysis demonstrate the effectiveness of acupuncture in achieving functional balance, increasing muscle strength, and improving overall well-being in stroke patients [39]. A meta-analysis of 5 RCTs (2015) showed that acupuncture significantly reduces spasticity after stroke (according to the Fugl-Meyer assessment of physical performance - FMA) [40]. Different acupuncture points are used. Thus, acupuncture GV20, GB20, GB39, LI11, LI4, ST36, SP6 in combination with antiplatelet agents led to better restoration of tone on the FMA scale in comparison with antiplatelet therapy alone. However, the dynamics of restoration of the white matter microstructure, according to MRI diffusion data, did not depend on the use of acupuncture [41].
We describe a case of successful 3-month acupuncture treatment of paresis and spasticity in the arm of a patient after an ischemic stroke. Acupuncture at points GV20, PC7, SI3, EX-UE9 was combined with kinesiotherapy using the CIMT (Constraint-induced movement therapy) method. A sustained improvement was achieved in the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS), FMA, Action Research Arm Test (ARAT), and Motor Activity Log (MAL) [42].
There are reports of proven effectiveness of scalp therapy in the treatment of movement disorders after stroke. The therapeutic effect can be either delayed or immediate. A single acupuncture in the motor area of the scalp on both sides for 30 minutes in patients with ischemic stroke and hemiplegia helps to immediately improve motor skills in the distal upper limb and proximal lower limb (according to the FMA scale), normalizes the tone of the biceps brachii and rectus femoris muscles , according to electromyography data [43].
In 2021, the results of a multicenter RCT conducted in China were published, which included 241 patients with hemiplegia due to ischemic stroke. Scalp therapy was used in the motor and sensory areas, acupuncture: for the upper extremities - points LI10, TE5, LI4, electroacupuncture LI15 and LI11; for the lower extremities - ST34, GB34, ST40, ST41, LR3, electroacupuncture SP6 and ST36. As a result, the acupuncture group showed more pronounced changes in neurological status (according to the NIHSS scale) and better recovery of lower limb function (according to the FMA scale) [44].
Recovery of motor deficits correlates with improvement in the functional state of the cerebral cortex. Thus, acupuncture at points GV20, GB20, GB39, LI11, LI4, ST36, SP6 in patients with stroke promotes a more pronounced restoration of resting motor networks (according to functional MRI of the brain) and a decrease in neurological deficit (according to the Neurological Deficit Score - NDS) than in patients without acupuncture [45].
Data from studies of the dynamics of motor function in stroke patients using acupuncture are presented in Table. 3 . It is obvious that the clinical effect is based on the above-described cellular and biochemical mechanisms of action of acupuncture.
Table 3. Results of studies of the effectiveness of acupuncture in restoring motor function in patients with stroke
Dysphagia. The positive effect of acupuncture on swallowing function after stroke is confirmed by meta-analysis data. Thus, published in 2021 by Q. Ye et al. [46] a systematic review of 71 RCTs (6010 patients, 2991 acupuncture group, 3019 control group) demonstrated that the therapeutic effectiveness of acupuncture (as monotherapy or in combination with medications and rehabilitation) was higher than in control groups. In 2021, L. Li et al. [47] prepared an updated meta-analysis of 29 RCTs (2190 patients with post-stroke dysphagia) confirming the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of swallowing disorders.
Different points are used to treat dysphagia. Acupuncture at the GV16 point, electroacupuncture at the trilingual points and at the GB20 points on both sides contributed to a more pronounced improvement in the video-fluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS), standardized swallowing assessment (SSA) scale, and normalization of the position of the thyroid cartilage larynx (according to ultrasound) in comparison with low-frequency electrical stimulation in the supraglottic region. Trilingual points include the extrameridian Shanglianquan (Extra) point 1 cun below the middle of the mandible and two points 0.8 cun from it [48].
Acupuncture at points GB20, EX-HN14, BL10, GV16, Gongxue point (1 cun below VB20), CV23 in patients with post-stroke dysphagia led to improved swallowing according to VFSS [44]. The results of studies on the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of dysphagia are presented in table. 4 . Many studies have not yet been completed. Further search for points that are effective for dysphagia and research into the combination of acupuncture with other techniques is necessary.
Table 4. Results of studies on the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of dysphagia in patients with stroke
Cognitive impairment . Treatment of cognitive dysfunction after stroke with acupuncture is a pressing issue, as improved cognition is associated with quality of daily life.
In 2014, F. Liu et al. [49] published a meta-analysis of 21 RCTs on the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of post-stroke cognitive impairment, involving 1421 patients. A meta-analysis confirmed the positive effects of acupuncture on the recovery of cognitive deficits. Acupuncture at points GV20, GV24, GB13, EX-HN-1 contributed to better recovery of cognitive functions (according to the MMSE, MOCA scales) than in the control group that did not receive acupuncture [44].
For cognitive deficits, acupuncture improves the effectiveness of drug therapy. Acupuncture at points GV20, EX-HN-1, ST2, GB20, GB12, BL10, GV26, HT7, PC6, ST40, SP6, LR3 in combination with nimodipine (30 mg orally 3 times a day) in patients after ischemic stroke contributes to a more pronounced improvement in MOCA test scores compared to monotherapy with both nimodipine and acupuncture [50]. Information on the results of studies of the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of cognitive impairment is presented in table. 5 .
Table 5. Results of studies on the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of cognitive impairment in patients with stroke
In general, restoration of impaired functions using acupuncture is of great clinical and scientific interest. Research into the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of neurological disorders other than those listed is needed, including patients with hemorrhagic stroke in the studies.
The place of acupuncture in the treatment of stroke complications
There is limited data on the effectiveness of acupuncture in treating stroke complications. This indicates the need to study the possibilities of acupuncture in the prevention and treatment of conditions such as cerebral edema, malnutrition and hypercatabolic syndrome, thrombosis, infectious and other complications.
Results from retrospective cohort studies suggest that acupuncture treatment reduces the risk of epilepsy in patients with stroke [51], as well as the risk of acute myocardial infarction [52]. Acupuncture in the acute period of stroke reduces the risk of developing depression by 30.6% [53]. Complications of stroke include sleep disorders, the lack of treatment of which worsens the results of rehabilitation and increases the risk of developing a recurrent acute cerebrovascular accident [54–56]. A systematic review of 13 RCTs (2016) found that acupuncture was effective in treating insomnia after stroke compared with drug therapy and placebo acupuncture. The placebo acupuncture technique involves a tube and a blunt needle that does not pierce the skin; All patients cover their eyes with a dark bandage during treatment. Points HT7 and EX-HN1 were used [57]. The mechanism of action of acupuncture in the treatment of insomnia is mediated by neurotransmitters (norepinephrine, melatonin, gamma-aminobutyric acid, beta-endorphin) [58].
The role of acupuncture in stroke prevention
There are also very few studies on the effectiveness of acupuncture in preventing recurrent stroke. A published retrospective cohort study of 30,058 patients reported that groups using acupuncture had a lower risk of recurrent stroke [59]. Given the paucity of studies, there is a need for further randomized, placebo-controlled trials with sham acupuncture in a blinded control group to delineate the role of acupuncture in secondary and primary stroke prevention.
When can you fly after a heart attack?
The answer to this question directly depends on the rehabilitation period that the doctor has determined for you. If you followed all the recommendations and successfully completed the course, then in the absence of complications and other circumstances, you will be allowed to fly. The recovery period depends on the type of illness suffered, the extent of the affected area, the causes of the pathology, stenting operations undergone, etc. To give an approximate idea of how long it takes to fly, below are approximate rehabilitation periods for some cases:
- Small focal myocardial infarction – 2 weeks.
- Large focal myocardial infarction – 6 months.
- Stroke – at least 2 months, on average – 6 months under favorable circumstances.
- Vascular stenting surgery – 2 weeks.
Important! The data provided is for informational purposes only. Your doctor will tell you the exact timing.
Even after rehabilitation, there is no need to rush to fly by plane unless absolutely necessary. The more time has passed since the illness, the better. Remember that it is your life, not just your health, that is at stake. Cardiovascular diseases are very insidious, a relapse can occur at any time, and without qualified help a person’s life cannot be saved.
Bath after a stroke
The bathhouse is traditionally considered a source of health. High air temperature reflexively increases blood circulation and sweating, has a detrimental effect on pathogenic skin microflora, reduces muscle pain, calms and relieves stress. But is it possible to go to the bathhouse after a stroke?
It is difficult to give a definite answer to this question:
- On the one hand, high temperatures increase the load on the cardiovascular system. In the bathhouse, the heart rate increases and blood pressure rises, which can cause repeated cerebrovascular accidents.
- On the other hand, heat helps to relax smooth muscles and improve trophic processes in tissues, including the brain. This effect can be used in an integrated approach to rehabilitation.
Of course, in the first year after an acute cerebral circulation disorder, it is worth excluding exposure to high temperatures, but in the future this can be a good way to support health. It is worth remembering that visiting a bathhouse after a stroke is only possible with the permission of the attending physician.
To summarize, we can note what you absolutely cannot do after a stroke - smoking and drinking alcohol. The restriction on driving a car can be lifted after passing a medical examination, and flying on an airplane is allowed after a comprehensive examination. Visiting a bathhouse is a great way to relieve stress, but it must be coordinated with your doctor. And by the way, drinking coffee after a stroke is undesirable; it is better to choose caffeine-free drinks.
Rules for flying after a heart attack or stroke
Patients with health problems impose a certain responsibility on the air carrier. The company does not want situations that would entail certain checks and have a negative impact on its reputation. Therefore, you must follow the rules and take maximum care of your own safety.
Air travel conditions
A person who has suffered a heart attack or stroke is obliged to inform the air carrier about the state of his health. You must notify the airline when you book your tickets or when you purchase them at the ticket office. You may be required to provide a doctor's certificate or written permission from the air carrier to fly. This is necessary to ensure your safety on board by providing the necessary medications or assistance from qualified professionals.
You must carry necessary medications with you, which must be declared before boarding. Not all medications are allowed to be carried in hand luggage, so you need to make sure in advance that you are allowed to take what you need.