Many people who have suffered a brain stroke are afraid whether they will be allowed to drive again or work as drivers. Indeed, even after full rehabilitation, many patients remain with various disorders of greater or lesser severity. Let’s figure out whether it’s possible to drive a car after a stroke, what restrictions and risks exist.
Possible consequences of a stroke
During a brain stroke, a certain area of the brain dies. For the patient, this means the loss of nerve functions for which this area of nervous tissue was responsible:
- weakness or loss of mobility in one or all four limbs;
- impaired coordination and fine motor skills;
- double vision;
- loss of visual fields (a person sees only 25-50% of the “picture”);
- hearing loss;
- memory disorders;
- difficulties with decision making, concentration, attention;
- problems with speech perception/production;
- loss of temporal and spatial orientation;
- depression, mental disorders.
These disturbances may be temporary or permanent.
Types of circulatory disorders
Normal blood circulation in humans
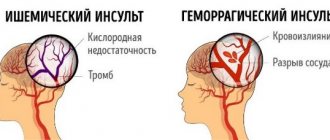
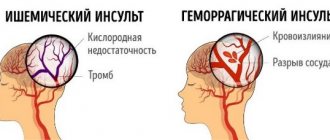
In medicine, there are two types of stroke. Each of them has its own causes and characteristic features.
The ischemic (cardioembolic) type occurs due to the closure of the lumen of blood vessels by a thrombus or blood clots. As a result, a certain area of the brain ceases to receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and microelements supplied through the bloodstream. This entails dysfunction and death of tissue cells.
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to rupture of blood vessels in the brain. The result is a large amount of blood, which negatively affects the functioning of the nerve fibers. This provokes their dysfunction.
As a result of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, tissue cell death and impaired blood circulation to the brain are observed. Against the backdrop of ongoing changes, systems and organs cease to function normally.
Return to driving: is it possible?
Having a stroke is not a contraindication to driving. Only violations that persist after the end of the rehabilitation period are significant. If they do not affect a person’s ability to drive a vehicle, then after passing a medical examination you can get behind the wheel.
Absolute contraindications to driving (1):
- mental disorders: delirium, mood swings, neuroses, personality disorders, mental retardation, hallucinations;
- post-stroke epilepsy;
- double-sided blindness;
- double vision as a result of strabismus;
- trembling of the pupil (nystagmus);
- limiting the field of view to more than 200;
- deformation of both hands;
- chronic dizziness.
There are a number of cases when driving a car is not contraindicated for a person, provided he chooses a vehicle that compensates for the deficiency of certain functions:
- in case of foot deformity, paralysis, leg paresis, the machine must be equipped with manual control;
- people with deformation of one hand, immobility of 2 or more fingers of the right hand, 3 or more fingers of the left hand, inability to fully adduct at least one finger, or hemiplegia are allowed to drive a car exclusively with an automatic transmission.
Problems that the patient may encounter
If the rehabilitation course is successful, the patient may not always be able to drive a car again.
This is hindered by the following problems:
- difficulty in assessing the situation on the road;
- lack of clarity of thinking;
- difficulties with timely braking;
- complications of actions and poor reactions;
- narrowed visual field.
Relevant factors negatively affect human behavior while driving. Such a driver poses a risk to other motorists. He himself may get injured.
Important! Categorical indicators for resumption of driving are cognitive impairment and poor visual abilities.
Statistical information suggests that after a stroke, cognitive impairments make themselves known in 70% of cases. We are talking about deterioration:
- attention;
- memory;
- orientation.
It is these violations that cause concern among specialists, so they cannot issue a permit to drive a vehicle.
How long should you abstain from driving?
According to Russian legislation, you can drive a car after a stroke after 3-6 months, if there are no medical contraindications. The decision on admission is made by a special medical commission that evaluates the person’s general health.
Unfortunately, such verification is not mandatory. Therefore, the patient often decides independently when he can drive. However, this approach is wrong. The patient himself may inadequately assess his condition and deny obvious problems. It is primarily in his interests to undergo a medical examination. If the decision of the medical commission seems biased, it is wise to seek advice from an independent expert.
In our country, a microstroke is not considered a condition requiring removal from driving. However, throughout the world, survivors of a transient ischemic attack (TIA) are advised to refrain from driving for 2-4 weeks. This precaution is associated with a high risk of developing a recurrent micro-stroke or a full-blown stroke some time after a TIA.
Rehabilitation activities
People who have suffered from a stroke quite often ignore the ban on driving if they feel “healthy”. It is difficult to give up the habit of using your own rather than public transport. And the patient gets behind the wheel of a car without prior rehabilitation and passing tests, without thinking about his own safety and the risk to others.
The general ban on driving after a stroke is three to six months. During this period, the body will be able to recover to a satisfactory state. Types of rehabilitation measures:
To restore muscle performance, sessions with a physiotherapist are prescribed.
Exercises with a speech therapist aimed at restoring correct speech and swallowing function.
Massage to tone muscles. Prescribed by a specialist depending on the severity of the disease.
Adaptation to everyday life and complex drug therapy.
Vision diagnostics. Contacting an ophthalmologist is mandatory if the question arises about whether you can drive a car.
Psychological help. Patients who often become depressed, sad and cry need sessions with a qualified psychotherapist.
All of these procedures are aimed at speedy recovery of the patient. Even with minor brain damage, it is necessary to undergo a rehabilitation course to prevent a relapse, especially in a driving situation.
How is a person's ability to drive a car assessed?
The most common type of testing is a training trip with an instructor. It can take place on a real car or a computer simulator. During the 45-minute ride, the instructor assesses the number of errors, violations, and the adequacy of the decisions made. Based on the results of the race, he draws up his conclusion.
An alternative option is a test proposed by Belgian scientists. It takes much less time (15 minutes) and is performed in the doctor's office. During testing, the patient is offered tasks to:
- recognition of road signs, markings. Helps assess knowledge of traffic rules, correctness of reaction in specific road conditions;
- orientation, speed of perception, decision making;
- route planning;
- visual assessment of space;
- visuomotor tracking.
The test results allow us to weed out 80-85% of unreliable drivers.
How is it prohibited to drive a car if you are sick?
The most important thing you need to know is your personal sense of responsibility for the lives of other road users, including many children and pregnant women. We are writing about this because formally, until the next medical examination in order to obtain a certificate for the traffic police, no one may find out that a person has a dangerous disease with which driving is not only prohibited, but also very risky and unwise. And the main problem of interaction between departments in 2021 is that the doctor does not automatically transmit information to the traffic police about the emerging disease.
That is, in fact, if a driver developed, for example, epileptic seizures a year after he first received or changed his license, then he can drive for another 9 years with this dangerous disease. Yes, an inspector can detect a disease randomly and earlier. Or the motorist will be subject to deprivation of his license, which requires a medical examination as a condition for the return of his driver's license.
But legally, only a court can take away your right to drive. In general, there are 3 options when you do not have such a right:
- if you have never received a license,
- if you have been deprived of your rights,
- if the court decided to terminate such a right due to a medical contraindication to driving (Article 28 of the Federal Law on Road Safety).
Why in the latter case can only the court take away such a right, but it does not terminate automatically? Because this is exactly what the Supreme Court pointed out in one of its recent Plenum Resolutions:
A person who does not have the right to drive vehicles is a person who, at the time of committing an administrative offense, did not receive such a right in the manner prescribed by law, a person whose relevant license has expired, as well as a person whose right to drive vehicles was terminated by a court due to with medical contraindications or medical restrictions.
You will also be interested in:
- How to change rights after 10 years through State Services and MFC?
- New law on automatic deprivation of rights due to illness: when will it come into force?
- Is a medical certificate required when replacing a license after loss or damage?
What are the dangers of driving after suffering a brain stroke?
People who have had a stroke are at risk of relapse. Stressful situations, which cannot be avoided on the road, can provoke a second blow. If an attack occurs while driving, it will be difficult to avoid an accident. Not only you, but also passengers, drivers of neighboring cars, and pedestrians can get hurt.
Also, even specialists may miss some residual disorders left after a stroke. Signs of unsafe driving:
- driving too fast/slow for specific road conditions;
- ignoring road signs, traffic lights, signals of other road users;
- incorrect/slow selection of distance;
- loss of orientation in familiar places;
- non-compliance with lanes (driving between lanes, shifting into adjacent lanes unnecessarily);
- the driver cannot drive the car independently, asks for help, tips from passengers, and reacts excessively emotionally to what is happening.
If you notice one of the listed signs in yourself or the driver, the best thing is to stop, change or leave the car, call a taxi or use public transport. Before you get behind the wheel again, you need to weigh the pros and cons, putting safety first.
At the first signs of a stroke: headache, dizziness, ringing in the ear, you must immediately park the car. Further driving is contraindicated, even if the condition improves.
Kinds
The consequences of a stroke are several types of amnesia. Based on what type of injury the attending physician diagnoses, individual treatment and rehabilitation measures are prescribed.
Types of amnesia:
- Damage to verbal memory;
- Visual glitches;
- Motor skills disorders;
- Damage to emotional-figurative memory.
- Vascular dementia.
Verbal
Verbal memory is the ability to remember, retain and reproduce verbal information.
If the part of the brain responsible for storing information received verbally is damaged, then the patient cannot remember the names of relatives and friends, forgets the names of objects, and loses vocabulary. Communication with others becomes extremely difficult, and the victim has difficulty remembering new information.
Visual memory impairment
A person’s ability to fix, store and use various information that is received in the form of a visual image is called visual memory.
After a stroke, a patient whose area that stores visual information is damaged may not recognize everything around him: his home, family, friends, objects, etc.
Loss of motor skills
Motor skills are a person’s ability to confidently perform complex movements. Patients forget the simplest actions: how to use cutlery, walk, squat, write, grasp objects with their hands, go up and down stairs, etc.
Loss of emotional-figurative memory
Emotional-visual memory is responsible for the ability to record and store feelings and emotions that are associated with any object, person, event or phenomenon. If it is violated, the patient ceases to recognize the images and emotions that are associated with them. He does not remember the taste of dishes that he previously considered favorite, changes his musical tastes, and does not recognize the voices of loved ones and acquaintances.
Vascular dementia
The most complex type of brain disorder, which is difficult to recover, is vascular dementia. The adequacy of a person’s perception of what surrounds him disappears almost completely over time.
A person does not recognize objects that he used to constantly use, does not remember their names and purposes. When communicating with other people, the patient cannot remember their names and where he knows them from. This applies not only to distant acquaintances or strangers, but also to close relatives, friends and colleagues.
However, if you choose the right intensive rehabilitation measures and constantly monitor the patient’s condition, you can slow down the process of dementia and adapt the person to real life.
When can you return to work after a stroke?
Many patients want to return to work as quickly as possible. However, after a stroke, stamina often decreases and sudden fatigue occurs in situations that were previously easy. Even with preserved physical capabilities, concentration may decrease after a stroke. Therefore, they recommend returning to work part-time and gradually increasing working hours. A psychologist will help you choose a comfortable duration of work.
The ability to go to work and the time required for this depend on:
- consequences of a stroke (lost and retained abilities);
- the work the patient performed before the stroke;
- the amount of support that the employer is willing to provide.
It is important to stay in touch with your employer. This will help the patient feel less isolated and ease concerns about returning to work. When a person decides that he is ready to return to work after a stroke, he will need to determine what changes the employer can make to help the patient. Regardless of whether a patient plans to return to work or not, it is necessary to find out what financial support they are entitled to. Many patients can count on benefits from the state.
What to do if a person cannot return to his previous position after a stroke?
If it is not possible to return to the job that the patient was engaged in before the stroke, it is often possible to find another activity (paid work or volunteering) or undergo training for a new type of employment. In such cases, you can contact the labor exchange. There are employment consultants for people with disabilities. They help you gain new skills and highlight employers who work with patients with special needs.
Social workers should also be contacted for available support . They will, for example, tell you about services or funds that can help pay for taxi fare to work if the patient is unable to use public transport, or pay for training for the patient's colleagues on disability issues.
Write to us what difficulty you encountered, and we will suggest further steps for rehabilitation or provide the missing information.