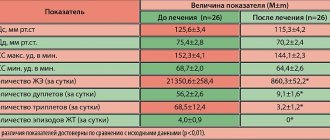
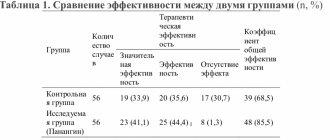
Concor and Concor Cor are medications belonging to the group of adrenergic blockers. The drugs in this group are used for treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate hypertension, angina attacks, ischemia and congestive insufficiency.
Concor and Concor Cor are medications belonging to the group of adrenergic blockers.
The drugs are analogues of each other and have not only similar names, but also chemical composition. For this reason, it is difficult for the patient to determine on his own which is better: Concor or Concor Cor. This question can only be answered by the attending physician treating the patient.
Compound similarities
Both products have the same composition, so they can be considered different forms of the same medication. In both versions of the drug, the active ingredient is bisoprolol fumarate.
In addition to the main component, the tablets of both types of medicine contain the following compounds that play an auxiliary role:
- calcium hydrogen phosphate;
- corn starch;
- colloidal form of silicon dioxide;
- MCC;
- magnesium stearate;
- crospovidone.
The tablet shells of both drugs also have a similar composition, with the exception of a set of dyes that give the drugs their color. Concor tablets have a light orange color due to the content of yellow iron oxide tablets in the shell, which is absent in the Concor Cora shell.
The drugs have antiarrhythmic, hypotensive, and antianginal properties.
The characteristic difference between the drugs Concor and Concor Cor
Dosage forms of the pharmaceutical product are distinguished by the appearance of tablets, which are stylized in shape to resemble a heart. The design of drug packaging is different.
The main difference is the difference in the dosage of the main component: Concor Cora contains 2.5 mg, while Concor is produced in dosages of 5 and 10 mg.
The difference between the drugs is in the form of the package and the number of tablets in it. A drug with a concentration of 2.5 mg of the active ingredient is sold in blisters containing 10 tablets, and the package can have 10, 5 or 3 such blisters. Concor is packaged in packs of 30-50 and 90 tablets.
The high-dose form of Concor is used in the treatment of hypertension and angina pectoris.
Medicines differ in cost: the high-dose form has a higher price compared to the low-dose form of the drug.
A high-dose form of the drug is used in the treatment of hypertension and angina. Bisoprolol in high concentrations can relieve symptoms characteristic of pathologies in the heart without harm to the human body. The dosage of the drug in the treatment of hypertension and coronary artery disease is determined by the attending physician separately for each person.
We recommend reading: Broken shield: is it possible to fix the thyroid gland with reflexology?
A low-dose form of the drug is prescribed for detected heart failure. When treating this pathological phenomenon in the heart, the initial dosage of the drug is 1.25 mg. During further therapy, if necessary, the patient can be switched by the doctor to take medication with a concentration of the active ingredient of 5 or 10 mg.
A large dosage can pose a danger to the patient’s body in the presence of CHF.
Concor Cor has limited indications for use. The drug is recommended for use in elderly people who suffer from heart failure to relieve the negative processes that occur in patients with this disease.
Concor Cor 2.5 mg No. 30 tablet p.o.
Instructions for medical use of the drug Concor® Cor Trade name Concor® Cor International nonproprietary name Bisoprolol Dosage form Film-coated tablets 2.5 mg Composition One tablet contains the active substance: bisoprolol fumarate - 2.5 mg excipients: Core: calcium anhydrous hydrogen phosphate, corn starch, anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, magnesium stearate Coating composition: hypromellose 2910/15, macrogol 400, dimethicone 100, titanium dioxide (E 171) Description Heart-shaped, biconvex, white film-coated tablets , with a risk on both sides. Pharmacotherapeutic group Beta-blockers. Beta-blockers are selective. Bisoprolol. ATC code C 07AB07 Pharmacological properties Pharmacokinetics After oral administration, the bioavailability of bisoprolol is 90%. Volume of distribution: 3.5 l/kg. Plasma protein binding reaches approximately 30%. Bisoprolol is excreted from the body in two ways. About 50% is metabolized in the liver to form inactive metabolites, which are then excreted by the kidneys. The remaining 50% is excreted unchanged in the urine. The total clearance is approximately 15 l/hour. The plasma half-life of 10-12 hours provides a 24-hour effect following once daily dosing. The kinetics of bisoprolol is linear and does not depend on age. Special groups of patients Pharmacokinetics in patients with stable chronic heart failure (CHF) and impaired renal or hepatic function have not been studied. In patients with chronic heart failure (functional class III according to the New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification), the plasma concentration of bisoprolol and the half-life are longer compared to those in healthy volunteers. Pharmacodynamics Bisoprolol, the active ingredient of the drug Concor®Cor, is a highly selective beta1-blocker, without its own sympathomimetic activity, and does not have a clinically significant membrane-stabilizing effect. Bisoprolol has low affinity for beta2 receptors of the smooth muscles of the bronchi and blood vessels, as well as beta2 receptors related to the regulation of metabolism. Therefore, bisoprolol generally does not cause airway resistance and beta2-mediated metabolic effects. The selective effect of the drug on beta1 receptors extends beyond the therapeutic dose. Indications for use are the treatment of stable chronic heart failure with reduced left ventricular systolic function, in addition to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and diuretics, and optionally cardiac glycosides. Method of administration and dosage Standard treatment of CHF consists of an ACE inhibitor (or, in case of intolerance to an ACE inhibitor, an angiotensin receptor blocker), a beta blocker, diuretics, and, if necessary, cardiac glycosides. Patients must be stable (without acute heart failure) when treatment with bisoprolol is initiated. It is advisable that the attending physician has experience in treating patients with CHF. Directions for use Concor®Cor should be taken in the morning, regardless of meals. The tablets should be taken with a small amount of liquid. The tablets should not be chewed. Doses Initiation of treatment of persistent chronic heart failure with the drug Concor®Cor requires a special titration phase. Treatment of chronic heart failure with Concor®Cor begins in accordance with the following gradual dose titration scheme. Individual adaptation may be required depending on how well the patient tolerates the prescribed dose, e.g. The dose can be increased only if the previous dose was well tolerated. 1 week 1.25 mg bisoprolol fumarate (1/2 tablet Concor®Cor 2.5 mg) daily once a day 2 week 2.5 mg bisoprolol fumarate (1 tablet Concor®Cor 2.5 mg) daily once a day Week 3 3.75 mg bisoprolol fumarate (1.5 tablets Concor®Cor 2.5 mg) daily once a day Week 4-7 5 mg bisoprolol fumarate daily once a day* Week 8-11 7.5 mg bisoprolol fumarate daily once a day* Week 12 and after 10 mg bisoprolol fumarate daily once a day as maintenance therapy* * Concor®Cor 2.5 mg is suitable for the initial treatment of stable chronic heart failure. Higher dosages are suitable for maintenance therapy. The maximum recommended dose of bisoprolol fumarate is 10 mg once daily. During and after the titration phase, transient worsening of heart failure, hypotension, or bradycardia may occur. Therefore, careful monitoring of vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate) and symptoms of progression of heart failure is required. Modification of treatment If, during or after the titration phase, there is a temporary worsening of heart failure, hypotension or bradycardia develops, a dosage review of the concomitant drug is recommended. A temporary reduction in bisoprolol dosage or interruption of treatment may also be necessary. Once the patient's condition has stabilized, re-titration should be performed or treatment should be continued. Duration of treatment for all indications Therapy with Concor®Cor is usually long-term. Do not abruptly interrupt treatment or change the recommended dose without consulting your doctor, as this may cause temporary worsening of your heart condition. In particular, therapy should not be abruptly interrupted in patients with coronary artery disease. If interruption of treatment is necessary, the dose should be reduced gradually. Patients should be regularly monitored when initiating treatment and when discontinuing Concor®Cor. Special groups of patients Impaired renal or hepatic function Due to approximately equal excretion of bisoprolol by the kidneys and liver, patients with renal or hepatic impairment do not need to adjust the dose of Concor®Cor. Dose titration in these patient groups should be carried out with extreme caution. Elderly patients: No dose adjustment is required. Side effects The frequency of side effects of the drug is assessed as follows: very common (≥ 1/10); frequent (≥ 1/100, < 1/10); uncommon (≥ 1/1000, < 1/100); rare (≥ 1/10,000, < 1/1000); very rare (< 1/10,000), frequency unknown (cannot be determined from available data). Mental disorders: Uncommon: sleep disturbance, depression. Rarely: nightmares, hallucinations. Nervous system disorders: Common: dizziness, headache. Rarely: fainting. Visual disturbances: Rarely: decreased tear production (which should be taken into account when using contact lenses). Very rare: conjunctivitis. Hearing and balance disorders: Rare: hearing impairment. Cardiac disorders: Very common: bradycardia. Common: worsening heart failure. Uncommon: atrioventricular conduction disorders. Vascular disorders: Common: feeling of coldness or numbness in the extremities, hypotension. Uncommon: orthostatic hypotension. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Uncommon: bronchospasm in patients with a history of bronchial asthma or obstructive airway disease. Rarely: allergic rhinitis. Gastrointestinal disorders: Common: gastrointestinal disorders such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation. Disorders of the liver and biliary tract: Rarely: hepatitis. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rare: hypersensitivity reactions (itching, redness, rash). Very rare: alopecia. Beta blockers may trigger or worsen psoriasis or cause the characteristic rashes of psoriasis. Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Uncommon: muscle weakness and cramps. Disorders of the reproductive system and mammary gland: Rarely: impaired potency. General disorders: Often: weakness, fatigue. Laboratory indicators: Rarely: increased triglyceride levels, increased levels of liver enzymes (AST, ALT). Tell your doctor if you experience any of these side effects, or any other unwanted or unexpected effects. Reporting Suspected Side Effects It is very important to report any suspected side effects. This allows for continuous monitoring of the benefit/risk profile of a given drug. Contraindications The drug Concor®Cor should not be used in patients with the following diseases: - acute heart failure or during episodes of decompensated heart failure requiring intravenous inotropic therapy - cardiogenic shock - second or third degree atrioventricular block - sick sinus syndrome - sinoatrial block - symptomatic bradycardia - symptomatic hypotension - severe bronchial asthma - severe forms of peripheral occlusive arterial disease or Raynaud's syndrome - untreated pheochromocytoma - metabolic acidosis - hypersensitivity to bisoprolol or to any of the excipients - children and adolescents under 18 years of age With caution - bronchospasm (bronchial asthma , obstructive airway diseases) - diabetes mellitus with significant fluctuations in blood glucose levels; symptoms of hypoglycemia may be masked - strict diet - ongoing desensitizing therapy. Like other beta blockers, bisoprolol may increase sensitivity to allergens and increase the severity of anaphylactic reactions. Treatment with epinephrine does not always provide the expected therapeutic effect. - first degree AV block - Prinzmetal's angina - peripheral occlusive arterial lesions (symptoms may worsen after initiation of therapy) - general anesthesia Drug interactions Concomitant use of other drugs may affect the effect and tolerability of the drug. These interactions can also occur if too little time has passed since you took the other drug. Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medications, even if they were not prescribed to you by your doctor. Concomitant use is not recommended. Calcium antagonists such as verapamil and, to a lesser extent, diltiazem, when used simultaneously with the drug Concor®Cor, can lead to a decrease in the contractility of the heart muscle and delay the conduction of atrioventricular impulses. In particular, intravenous administration of verapamil to patients receiving beta-blocker therapy can lead to profound hypotension and atrioventricular block. Class 1 antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, quinidine, disopyramide, lidocaine, phenytoin; flecainide, propafenone) may enhance the inhibitory effect of Concor®Cor on atrioventricular conduction and contractility of the heart muscle. Concomitant use of centrally acting antihypertensive drugs (such as clonidine, methyldopa, moxonidine, rilmenidine) with bisoprolol may worsen heart failure as a result of a decrease in central sympathetic tone (decreased heart rate and cardiac output, vasodilation). Abrupt withdrawal, especially before stopping beta blockers, may increase the risk of developing rebound hypertension. Caution is required during simultaneous use. Calcium antagonists of the dihydropyridine type (for example, felodipine, amlodipine) when used simultaneously with Concor®Cor may increase the risk of hypotension. In patients with heart failure, the risk of subsequent deterioration of ventricular pumping function cannot be excluded. Class III antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, amiodarone) may enhance the suppressive effect of Concor®Cor on the conduction of atrioventricular impulses. The effects of local beta-blockers (for example, eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma) may be additive with the systemic effects of Concor®Cor. Parasympathomimetic drugs, when used simultaneously with the drug Concor®Cor, can enhance the suppressive effect on the conduction of atrioventricular impulses and increase the risk of developing bradycardia. The hypoglycemic effect of insulin or oral antidiabetic drugs may be enhanced. Signs of low blood glucose (hypoglycemia) may be masked or suppressed. Anesthetic drugs may increase the risk of the suppressive effect of Concor®Cor on the heart and lead to hypotension. Cardiac glycosides (digitalis), when used simultaneously with the drug Concor®Cor, can lead to an increase in impulse conduction time, and thus to a decrease in heart rate. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may reduce the hypotensive effect of Concor®Cor. The simultaneous use of Concor®Cor and beta-sympathomimetics (for example, isoprenaline, dobutamine) may lead to a decrease in the effect of both drugs. The combination of Concor®Cor with sympathomimetics that activate both beta and alpha adrenergic receptors (for example, norepinephrine, epinephrine) may enhance the alpha-adrenergic receptor-mediated vasoconstrictor effects of these drugs, leading to an increase in blood pressure. Such interactions are more likely with non-selective beta blockers. Antihypertensive drugs, as well as other drugs with a possible antihypertensive effect (for example, tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, phenothiazines) may enhance the hypotensive effect of Concor®Cor. Combinations to be discussed Mefloquine when used concomitantly with Concor®Cor may increase the risk of bradycardia. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (except monoamine oxidase B inhibitors) may enhance the hypotensive effect of beta blockers. Concomitant use may also lead to the development of a hypertensive crisis. Special instructions Special groups of patients: at the moment there is not enough therapeutic experience with the use of the drug Concor®Cor in patients with heart failure and concomitant insulin-dependent diabetes type I, severe renal impairment, severe liver dysfunction, restrictive cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease or organic valve defects heart, disrupting hemodynamics. There is also no sufficient therapeutic experience with the use of Concor®Cor in patients with heart failure and myocardial infarction during the first 3 months. General anesthesia: In patients under general anesthesia, beta-adrenergic receptor blockade reduces the incidence of arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia during induction of anesthesia and intubation, as well as during the postoperative period. It is currently recommended to continue maintenance beta-adrenergic blockade perioperatively. The anesthesiologist should be warned about taking beta-adrenergic receptor blockers due to the possibility of interaction with other drugs, which can lead to the development of bradyarrhythmias, a weakening of reflex tachycardia and a decrease in the reflex ability to compensate for blood loss. If it is necessary to discontinue beta-blocker therapy before surgery, this should be done gradually and completed 48 hours before anesthesia. Respiratory System: Although cardioselective (β1) beta blockers may have less effect on pulmonary function compared with non-selective beta blockers, like all beta blockers they should not be used in patients with obstructive airway disease unless there is a compelling reason for their use . If such reasons exist, Concor®Cor can be used with caution. In patients with obstructive airway diseases, treatment with Concor®Cor should be started with the lowest possible dose. In addition, patients should be closely monitored for the development of new symptoms (eg, shortness of breath, exercise intolerance, cough). For asthma or other chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases that may cause symptoms, bronchodilator medications should be prescribed concomitantly. In patients with asthma, increased airway resistance may occur, so increased dosage of beta2-stimulants may be necessary. Psoriasis: Patients with psoriasis or a history of psoriasis should only take beta blockers (eg, bisoprolol) after carefully weighing the benefits and risks. Feochromocytoma: In patients, Feochromocytoma Concor®cort can only be prescribed after the previous blockade of alpha receptors. Tyrotoxicosis: in the treatment of Concor®cord, symptoms of thyroid hyperfunction (thyrotoxicosis) can be disguised. Pregnancy and lactation period Pregnancy The pharmacological effect of bisoprolol can have a harmful effect on pregnancy and/or fetus/newborn. As a rule, beta-adrenergic receptors blockers reduce placental blood flow, which is associated with a deceleration of growth, intrauterine death, miscarriages or premature births. Unwanted effects (for example, hypoglycemia and bradycardia) can occur in the fetus and a newborn. If the treatment with beta-adrenergic receptors is necessary, it is preferable to take selective Beta1 adrenergic receptor blockers. The use of Concor®corte is possible only with unambiguous necessity. If treatment with Concor® Coron is necessary, utero-placental blood flow and fetal growth should be controlled. In the case of adverse effects on pregnancy or fetus, the possibility of alternative treatment methods should be considered. Carefully observe the newborn after childbirth. Symptoms of hypoglycemia and bradycardia should usually be expected in the first three days of life. There is no lactation of data on the release of bisoprolol with breast milk. Consequently, during lactation, the use of Concor® Corocal is not recommended. Features of the effect of the drug on the ability to drive a vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms in a study in patients suffering from diseases of the coronary vessels of the heart, bisoprolol did not affect the ability to drive. However, depending on the patient’s individual reaction to treatment, the ability to drive and control mechanisms can be disturbed. This should be paid special attention before the start of treatment, when changing drugs, as well as with the simultaneous use of alcohol. An overdose symptoms: with an overdose (for example, with a daily dose of 15 mg instead of 7.5 mg), an atrioventricular blockade of the third degree, bradycardia and dizziness were observed. Basically, the most common symptoms of an overdose of beta-blockers are bradycardia, hypotension, bronchospasm, acute heart failure and hypoglycemia. Today, several cases of an overdose of bisoprolol (maximum dose: 2000 mg) are known in patients with hypertension and/or coronary heart disease with signs of bradycardia and/or hypertension; All patients recovered after an overdose. There is a large individual variability of sensitivity to a single high dose of bisoprolol, and patients with heart failure probably have very high sensitivity. Therefore, the treatment of these patients with the drug Concor®cort must begin with a gradual increase in the dose in accordance with the scheme provided in the section “Method of application and dose”. Treatment: In the case of an overdose, it is necessary to stop treatment with Concor® Coron and conduct supportive and symptomatic treatment. There are limited data that Bisoprolol is almost not displayed using dialysis. Based on the alleged pharmacological actions and recommendations for other beta-blockers, it is necessary to consider the following general measures with appropriate clinical indications. Bradycardia: intravenous administration of atropine. If the reaction to treatment is insufficient, with caution, isoprenaline or another drug with positive chronotropic properties can be administered. In some circumstances, an installation of a transvenous pacemaker may be needed. Arterial hypotension: intravenous administration of solutions and vasoconstrictive substances should be used. Intravenous introduction of the glucagon can also be useful. Atrioventricular blockade (second or third degree): it is necessary to carry out thorough monitoring and treatment of patients with infusion administration of isoprenaline or by installing a transvenous pacemaker. Deterioration of heart failure (acute): intravenous administration of diuretics, inotropic drugs, vasodilators. Bronchospasm: therapy with bronchodilators using drugs such as isoprenaline, beta2-sympatomymetics and/or aminophylline. Hypoglycemia: intravenous introduction of glucose. The form of release and packaging of 30 tablets in the contour cell package made of polyvinyl chloride film and aluminum foil. 1 contour cell package, along with instructions for use in the state and Russian languages, are placed in a cardboard pack. Storage conditions Store at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children! The term of storage of 3 years does not use the drug after the expiration of the shelf life of the vacation condition from pharmacies according to the recipe manufacturer Merk KGAA, Germany Packer Merk KGAA, Germany, the owner of the registration certificate Merk KGAA, Germany, the organization address of the organization that accepts in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on the quality of products (goods ) Representation (Austria) in Kazakhstan of Almaty, st. Shashkin 44 phone number (727) 2444004, fax number (727) 2444005 Email address
Contraindications
Both varieties have similar contraindications for use, which should be taken into account when prescribing the drug for drug therapy.
In accordance with the instructions for use, contraindications to treatment with the drug are:
- acute heart failure;
- decompensated heart failure in chronic form;
- AV blockade 2-3 degrees;
- cardiogenic shock;
- sinoatrial block;
- bradycardia;
- decreased blood pressure;
- presence of bronchial asthma and COPD;
- metabolic acidosis;
- changes in peripheral arterial circulation;
- age less than 18 years;
- allergy to components.
During pregnancy, drug treatment is possible only if it is required to maintain the health of the mother. Bisoprolol has the ability to reduce the speed of blood flow in the placenta, which provokes malnutrition of the fetus, and this can cause problems with its development. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, when using medications, strict monitoring of the condition of the mother and child is necessary.
Concor during pregnancy
Figure 3 - Taking Concor during pregnancy
Expectant mothers should be extremely careful when choosing certain medications. In the case of Concor, you can take it only if the benefit to the mother’s body is greater than the damage. Concor should not be taken during lactation, since the baby receives bisoprolol and auxiliary components through breast milk. If discontinuation of the drug is not possible, then breastfeeding should be discontinued.
How to take Concor and Concor Cor?
According to the instructions, the tablets should be taken orally, the drug should be taken once - in the morning. The intake should be accompanied by washing down the tablet with a small amount of water; The tablets cannot be chewed.
If a patient is diagnosed with arterial hypertension and angina pectoris, the dosage of the drug is determined by the doctor individually, taking into account the clinical course of the pathology and the individual physiology of the patient’s body. The recommended initial dosage of Concor is 5 mg once a day. If necessary, the doctor can increase the dose by 5 mg per day. For drug treatment of hypertension and angina pectoris, the maximum permissible dosage of the drug is no more than 20 mg per day.
We recommend reading: Cavinton and Vinpocetine: which is better?
In case of heart failure, the medication regimen involves the appointment of:
- ACE inhibitors or angiotensin blockers.
- Diuretics.
- Beta blockers.
- Cardiac glycosides.
High dosage medication should not be prescribed to patients under 18 years of age.
Treatment of chronic insufficiency using the low-dose version of Concor Cora requires preliminary titration and constant monitoring by a physician.
The duration of the course is determined by the doctor supervising the treatment process.
Treatment of chronic insufficiency using a low-dose version of the drug requires preliminary titration and constant monitoring by a physician. The maximum permissible dosage of the drug for chronic insufficiency is 10 mg per day.
After the initial dose of the medicine, the patient should be observed by a doctor for 4 hours. During this period, the doctor needs to monitor pulse, blood pressure and conductivity indicators.
Drugs should be prescribed with caution when:
- hypoglycemia due to the development of diabetes mellitus;
- pathologies in the thyroid gland;
- Prinzmetal's angina;
- strict diet;
- mild to moderate arterial circulatory disorders;
- AV blockade of the first degree;
- psoriasis.
In addition, caution is necessary when following a strict diet and when carrying out desensitizing treatment.
The regimen for taking Concor Cora and the dose are determined by the doctor in accordance with the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Side effects of Concor and Concor Cora
Common undesirable body reactions may include slow heartbeat, hypotension, nausea, and poor health.
In addition, the following side effects may occur during therapy:
- bradycardia, worsening of chronic heart failure, numbness, severe decrease in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension;
- dizziness, loss of consciousness, headache, depression, insomnia, nightmares;
- attacks of bronchial asthma;
- cramps, muscle weakness;
- hearing damage, conjunctivitis;
- diarrhea, vomiting;
- increased levels of liver enzymes in the blood;
- decreased potency;
- alopecia;
- itching, rash, redness of the skin, allergic rhinitis.
A product with a minimal amount of active ingredient has a similar list of side effects that occur when using it.
Side effects
Side effects are rare, but they are not excluded:
- cramps, muscle weakness;
- bronchial asthma (exacerbation);
- sleep disorders;
- depressive states;
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- rarely – loss of consciousness;
- conjunctivitis;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- problems with potency;
- allergic reactions (itching, rashes, rhinitis of allergic origin).
Reviews from doctors
Chamorovsky A. N., cardiologist, work experience 9 years
Concor is a gold standard selective beta blocker that is effective for use in patients with coronary artery disease. Has an effect aimed at reducing the number of heart contractions. Used in patients with heart failure. The drug has an affordable price, which allows it to be used in the treatment of different groups of the population.
We recommend reading: Treatment of thyroid cancer with folk remedies
Zafiraki V.K., cardiologist, 18 years of experience
Concor is an original drug, but it is not much more expensive than generics. At the same time, the original drug is the standard of therapeutic effect and safety, and generics can only come close to the original. Well tolerated, side effects typical of beta blockers are rare. Concor is one of the safest in its class.
Sometimes a drug's reputation is damaged if it is used for other purposes. Then there will be no result, and the patient will remain disappointed. Not every pain in the chest, even if on the left, in the region of the heart, is angina. Accordingly, Concor, although it has angina therapy among its indications, will not help if the pain is of a different origin. Only a doctor can figure out what kind of pain it is.
Interaction with other drugs and alcohol
Figure 4 - Combination of Concor with other medications
The instructions for the drug Concor describe in some detail the compatibility with other drugs, because there is a list of drugs with which the Concor tandem is prohibited. Concor can be used in conjunction with analogues and generics, but such a combination must be discussed with your doctor so that an overdose does not occur and the blood pressure does not drop below normal levels.
Concor and Amlodipine
Amplodipine is an antihypertensive drug used for high blood pressure. The attending physician may prescribe a similar tandem if he believes that Concor will be ineffective. It is worth remembering that patients with heart failure cannot take Amplodipine and Concor together.
Concor and Arifon
Arifon - a diuretic indapamide - in combination with the beta blocker Concor is an effective complex in the treatment of hypertension. Concor lowers blood pressure, and Arifon reduces the volume of circulating blood, thus protecting the patient from signs of heart failure.
But Arifon has a side effect - it flushes potassium from the body, which can cause hypokalemia.
Concor and Lozap
The active substance of the drug Lozap, losartan potassium, is intended for the treatment of arterial hypertension. That is, it does not allow peripheral vessels to spasm and thereby does not allow blood pressure to rise. Concor and Lozap enhance each other's effects. Concor works to reduce cardiac output, while Lozap dilates arterioles and reduces peripheral pressure. As a result, blood pressure returns to normal.
The combination of drugs Concor and Lozap is most effective when the degree of arterial hypertension is quite high, and treatment with one drug is not so effective.
Concor and Enap
The simultaneous use of Concor and Enap or Enalapril, which are based on the same active ingredient - enalapril, should be prescribed with caution, since the drugs can enhance the effect of each other. So, the instructions say: with the simultaneous use of beta-blockers, methyldopa, nitrates, calcium channel blockers, hydralazine, prazosin, the antihypertensive effect may be enhanced. That is, blood pressure that is already lowered with the help of Concor can decrease further.
Enap is good for kidney disease, excess weight and a history of diabetes. Concor is indicated for use in patients with heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia, and frequent attacks of angina. But if the resting heart rate is 50 - 60 beats/min, and there are conduction blockades, then you should take Enap, since Concor will only worsen these conditions.
The combined use of Concor and Enalapril lowers blood pressure and slows the progression of complications from the heart and kidneys. If you experience constant weakness, dizziness and fatigue during use, you should immediately inform your doctor.
Concor and Prestarium
Like all other ACE inhibitors, Prestarium goes well with the β1-blocker Concor. They are prescribed in tandem for high blood pressure, when the use of one drug is ineffective, reducing the risk of fatal complications for people with heart failure, obesity, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease.
But the decision to prescribe the combination Concor + Prestarium is made by the attending physician.
Prestarium itself is not as effective a medicine as Concor. If the pressure is 180/105 mmHg. Art., then it must be taken in combination with other drugs for hypertension.
Concor and Moxonidine
Concomitant use of Moxonidine with β-blockers such as Concor is not recommended. This can lead to a decrease in myocardial contractility and increased bradycardia
Concor and Lorista
Lorista is a generic version of the drug Lozap. That is, it contains the same active ingredient as the original drug, but it has not passed all stages of clinical trials. Generic status makes medicines cheaper without losing their properties. Lorista contains valsartan, a drug belonging to the group of sartans, which are prescribed for the development of a dry cough due to ACE inhibitors. The combination of Concor and Lorista is inferior in strength to the combination of Concor and any ACE inhibitor, since Lorista does not reduce the risk of complications of coronary artery disease.
Concor and alcohol
Figure 5 - Drinking alcohol with the drug Concor
It is known that when drinking alcohol, blood vessels dilate for a short time, that is, the heartbeat accelerates. True, after a short amount of time the opposite happens - vasospasm. And a sharp rise in blood pressure is not the most pleasant, but also not the most dangerous, thing that can await a patient taking Concor. The instructions directly state that Concor and alcohol are incompatible. The central nervous system is depressed, and the patient’s psychomotor abilities deteriorate. Also, do not forget that the medicine and alcohol will be excreted through one excretory system - the kidneys. This can lead to organ damage, and in some cases functional impairment may develop. Internal bleeding may begin, a hypertensive crisis, pulmonary edema, and vascular collapse may begin. But the worst result of taking Concor and alcohol together is death.
Therefore, doctors strongly recommend that you stop drinking alcohol while taking Concor.
Patient reviews
Vadim, Stavropol
I have heart arrhythmia and have attacks of tachycardia. I can recommend the drug as a fast-acting remedy for arrhythmia; you can forget about attacks of tachycardia.
The advantages of the drug are underestimated. Side effects that arise when taking it: increased fatigue, poor attention, headache, slight dizziness, and most importantly, dry eye syndrome - severe pain in the eyes appears, and it’s simply impossible to work at the computer!
You should be careful with a weak pulse at night, how many times have you woken up from acute lack of air.
Olga B., Krasnodar
Concor is an effective drug for high blood pressure. The advantage of its use is its positive effect on both the heart and blood vessels. The cost of this drug is low. The only inconvenience is that you have to take the pills constantly. If I forget to drink, my blood pressure rises again.