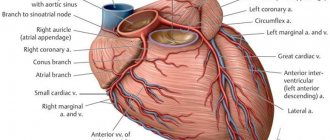
The myocardium is a muscle that controls the contractions of the heart and regulates blood supply to the entire body. For uninterrupted operation, it needs regular nutrition and oxygen, supplied through the coronary arteries.
If for some reason the breathing and nutrition of the myocardium are disrupted, muscle cells begin to die. Necrosis of one or another part of the heart muscle is called myocardial infarction .
Myocardial infarction often entails complete or partial disability, and this is not the worst thing. In 10-12% of cases it threatens the patient’s very life!
17.5 million - according to statistics, this is how many people die every year in the world from heart and vascular diseases. And by 2030, according to WHO experts, this figure will reach even more terrible figures - 23.6 million deaths from CVDs per year.
Causes of myocardial infarction
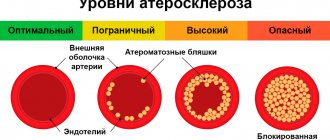
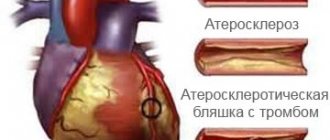
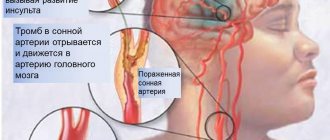
In most cases, necrosis of myocardial tissue occurs due to thrombosis of the coronary artery, which is provoked by atherosclerosis - atherosclerotic plaques clog the artery, disrupting the blood supply.
Other common causes of heart attack are coronary vasospasm and coronary thrombosis.
1 Ultrasound of the heart during a heart attack
2 Diagnosis of heart attack
3 Diagnosis when there is a threat of a heart attack
The rehabilitation program after a heart attack at the Almadeya clinic takes place in several stages:
Finding out the causes of a heart attack and selecting medications
The doctor will check the tests and conduct research, determine the cause of the disease and tell you which medications should definitely be taken for a safe life and upcoming rehabilitation.
Assessing the patient's problems that interfere with normal life after a heart attack
The rehabilitation team checks all the basic functions and vital activities that may be affected by a heart attack. The patient tells how he lived before the heart attack and what he wants to restore.
This information allows specialists to select an individual recovery program. Members of the rehabilitation team evaluate not only the symptoms of the heart attack, but also the symptoms of associated diseases. For example, the patient may have arthrosis of the joints, memory impairment, a history of stroke, hearing impairment, or the consequences of a fracture. The team takes everything into account and selects rehabilitation not only for a heart attack, but also to solve other problems that prevent a person from living a healthy life.
Setting rehabilitation goals and drawing up a rehabilitation plan
The rehabilitation team, together with the patient, formulate the goal of rehabilitation - what the patient will achieve at the end of the course. Typically, the goals are those life activities that the patient wants to restore.
Typically, the goals are those life activities that the patient wants to restore.
Examples of goals for different patients: after 3 weeks the patient will be able to speak freely; after 1 month the patient will return to work; after 3 weeks the patient will be able to independently walk around the apartment without restrictions to do cleaning.
The Almadeya Clinic provides:
— rehabilitation after coronary artery bypass surgery;
— rehabilitation after angioplasty and coronary artery stenting;
— rehabilitation after ACS (acute coronary syndrome);
— rehabilitation for angina pectoris and other heart diseases.
Sign up for a consultation
Who is at risk of myocardial infarction
Risk factors are:
- hypertonic disease;
- previous heart attack;
- smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hereditary predisposition;
- increased levels of “bad” cholesterol in the blood;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- elderly age;
- postmenopausal state (in women);
- regular stress;
- excessive stress (physical and emotional);
- bleeding disorders.
Types of myocardial infarction
Since areas of muscle tissue of different sizes can undergo necrosis, cardiologists distinguish between small-focal and large-focal myocardial infarction.
Also, heart attacks are divided, depending on the depth of damage to the heart wall, into:
- transmural - pathological changes cover the entire thickness of the muscle layer;
- intramural - necrosis lies deep in the heart muscle;
- subepicardial - areas of the myocardium close to the epicardium are affected;
- subendocardial - the necrotic process is concentrated in the area of contact between the myocardium and the endocardium.
Depending on the location of the lesion, there are 2 types of myocardial infarction:
- right ventricular;
- left ventricular.
Based on clinical manifestations, cardiologists distinguish between typical and atypical myocardial infarction.
1 ECG for heart attack
2 IVF-KG for heart attack
3 Blood test for markers of heart attack
Symptoms of myocardial infarction
The severity of signs of a heart attack depends on the stage of the disease.
The pre-infarction period is not observed in all patients; it occurs in the form of exacerbation and increased frequency of angina attacks and can last hours and days, or several weeks.
The most acute period is accompanied by the development of myocardial ischemia and the formation of an area of necrosis, lasting from 20 minutes to 3 hours. The main symptom is burning or pressing pain, which often appears due to physical activity or severe stress. The pain may radiate to the left arm, shoulder, neck, shoulder blade or lower jaw.
Painful sensations vary in duration (more than 30 minutes) and are not relieved even by repeated administration of nitroglycerin.
Other symptoms of myocardial infarction:
- cold sweat;
- fear of death, severe weakness;
- shortness of breath, suffocation;
- sometimes vomiting.
First aid for myocardial infarction: if you detect at least a few of the listed symptoms, you must immediately call an ambulance! The patient must be put down and have access to fresh air. Before the arrival of the medical team, it is possible to take 1 tablet of nitroglycerin (or 1 dose of isoket) under the tongue.
The acute period of myocardial infarction begins from the moment of formation of a focus of necrosis on the myocardium and lasts from 2 to 14 days.
During this period, a person may not experience pain. Due to the formation of an area of necrosis and inflammation of the heart tissue, body temperature rises. The patient's symptoms of cardiovascular failure persist and increase. Blood pressure is low or normal.
First aid is the same: immediately go to an ambulance.
The subacute period is accompanied by the formation of scar tissue and lasts 4-8 weeks. This period of myocardial infarction is not characterized by heart pain and fever.
The patient's condition is normalized, blood pressure and pulse rate are gradually approaching normal, and manifestations of cardiovascular failure are weakening.
Post-infarction period - all symptoms disappear, laboratory parameters gradually return to normal. The body adapts to the consequences of changes in the structure of the heart muscle.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction in atypical forms of the disease:
Abdominal - symptoms are masked as signs of abdominal diseases: pain and bloating in the abdomen, nausea. Asthmatic - the patient experiences shortness of breath and attacks of suffocation. Cerebral - manifestations of brain disorders: headache, dizziness, confusion. Arrhythmic - a person complains of rapid heartbeat or irregular heartbeat. Edema form - there is pronounced peripheral edema of soft tissues.
1 Diagnosis of heart attack in MedikCity
2 Diagnosis of heart attack in “MedicCity”
3 Diagnosis of heart attack in MedikCity
Life after stenting
Doctor - cardiologist of the cardiology department (for patients with myocardial infarction) No. 1 Artemyeva A. I.
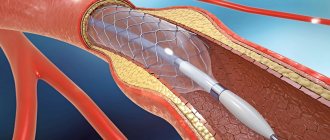
Coronary stenting is a method of intravascular prosthetics of the heart arteries for various pathological changes in the structure of their wall. Stents are used to reconstruct the corneal arteries.
A stent is a metal frame, which is a small metal tube made of wire cells (Fig. 1). A stent is inserted into the artery after it has widened and is placed at the site of the artery lesion. The stent supports the walls of the artery.
Figure 1 – Stent in a coronary vessel
Stents are placed on balloons, which allows them to have very small dimensions when unexpanded, and after the balloon is inflated inside the coronary artery, they expand, remaining in this position forever. Currently, a variety of stent models are used in interventional cardiology, differing from each other in certain design features. All of them are absolutely compatible with human organs and tissues, have a flexible structure and are elastic enough to support the artery wall. In addition, they are all made from radiopaque materials, which is a prerequisite for subsequent monitoring of their condition.
Recently, in order to prevent restenosis, specialists have begun to actively use drug-eluting stents, from which, after implantation into the coronary vessel, a pharmacological drug is released within several weeks, preventing excessive growth of the intima (inner lining) of the artery and an increase in atherosclerotic plaque. Taking into account modern capabilities, successful results of stenting are observed in 95% of patients who have undergone it. The feasibility of performing this operation and the choice of a specific type of stent is determined by a cardiac surgeon based on diagnostic data obtained during a preliminary examination of the patient.
Stenting can be either planned or emergency. It is carried out under the control of X-ray equipment, under local anesthesia, through a skin puncture on the wrist, forearm or thigh, without the need for large incisions, anesthesia and connection to a heart-lung machine. This intervention does not require strict bed rest and is quite well tolerated by patients.
During the intervention, a stent attached to a balloon catheter is inserted into the artery and advanced directly to the site of narrowing of the vessel. The balloon is then inflated under high pressure and the stent is deployed. The correct installation of the stent is monitored on the monitor screen.
Usually the results of the operation are good, it is relatively safe and the risk of complications after it is minimal. Sometimes an allergic reaction of the body to a substance introduced during the operation for x-ray observation is possible. There is also a hematoma or bleeding at the site of arterial puncture. To prevent complications, the patient remains in the intensive care unit with bed rest. Within a few days, after the wound at the puncture site has healed, the operated patient is discharged from the hospital. After this, restrictions are usually lifted, the person returns to normal life, and observation is carried out periodically by a doctor at his place of residence.
The bloodlessness and apparent simplicity of the operation, the short postoperative period and the effectiveness of coronary stenting make it a modern and popular solution to the problem of many cardiovascular diseases. Unlike surgery, which is performed using artificial blood circulation, the stenting procedure lasts 30-40 minutes and has virtually no complications.
Stenting is not completely effective; in approximately 15-20% of cases the reverse process occurs, and the vessel narrows again. One of the reasons for this process is excessive growth of muscle tissue, and, as a result, narrowing of the vessel wall. However, research by cardiologists does not stop, improving the technology of coronary stenting and achieving increasingly stable positive results statistics.
Currently, about 400 different models of stents have been developed, and the development of the method leads to their constant modernization. These stents differ in the alloy from which they are made, length, shape of the holes, coating of the surface in contact with the blood, and delivery system to the coronary vessels. So, in addition to balloon-expandable stents, there are self-expanding stents, etc.
However, it is worth remembering that even the most advanced methods of cardiac surgery do not replace the need for prevention and careful attention to your health and the health of your heart. Regular physical activity, commensurate with age and physical capabilities, fresh air, a balanced diet, enriched with vitamins and excluding weight gain, limiting the consumption of foods containing cholesterol - these are concepts that never lose their relevance.
The apparent simplicity of stenting, the absence of the need for long recovery after it, as well as the noticeable therapeutic effect of the operation often create in patients the illusion of a complete recovery. However, stenting is aimed only at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. The cause of coronary heart disease - atherosclerosis - continues to exist and progress, creating a threat of recurrence of angina, the development of myocardial infarction, heart failure and other very serious problems.
For this reason, a person who has undergone surgery must be fully aware of all the possible dangers of his situation and the need for further treatment.
Physical activity is one of the most important lifestyle requirements after stenting. Regular exercise slows down the development of atherosclerosis, trains the heart muscle, helps stabilize blood pressure, and has a general health effect on the body. It is important that sport helps the body burn fat, which means maintaining normal weight and blood cholesterol levels.
There are no sets of exercises that would suit every single patient after stenting. The training regimen and intensity are tailored individually, depending on the person’s condition, the list of his diseases, and exercise tolerance. All this is determined by a cardiologist.
The patient who has undergone this operation should be prepared for the fact that from now on he will play sports at least 4-5 times a week. Among specific types of loads, special physical therapy exercises, walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging are recommended. Sports that are accompanied by “explosive” loads, require significant physical effort and potentially pose a risk of injury (weight lifting, boxing) are not recommended.
Speaking about physical activity, it is important to mention sexual activity after stenting. Sexual activity can be carried out as usual; it can be resumed at any time as soon as the patient feels the need for it. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can take nitroglycerin before sexual intercourse, as well as before any other type of exercise. However, this is not always required.
The second extremely important component of therapy is diet.
"Food is medicine." These words are attributed to Hippocrates, and even today we can still attest to their authenticity. Special nutrition after stenting is not just a prevention of heart problems that may or may not arise in the future. This is treatment.
It’s sad, but not all patients adhere to the recommended nutritional rules. And we can say without a doubt that this plays a big role in the high incidence of recurrent angina and repeated stenting.
Diet therapy after stenting of coronary vessels should be based on the following principles.
- restriction in the diet of animal fats. This means reducing the consumption of foods such as fatty meats (lamb, pork), lard, processed foods, margarine. You should not eat butter, cheeses, sour cream, or cream in large quantities. It is also worth limiting your egg consumption to 3-4 eggs per week. All fatty foods are future cholesterol plaques that will resume the symptoms of IHD after stenting.
- limiting refined carbohydrates and sweets. From the foods that are often on your table, you will have to cross out sweets (it is better to replace them with dried fruits), excess sugar, pastries, carbonated drinks, etc. In the body, carbohydrates are converted into fats, which is why you should avoid sweets as much as possible.
- salt restriction. It causes fluid retention and increased blood pressure. Many patients with coronary artery disease who undergo stenting have hypertension. They should pay particular attention to this recommendation. The amount of salt should be reduced to 3-4 g per day (half a teaspoon). Be careful: many prepared foods (canned food, bread, etc.) contain salt, so you should limit its consumption more or less depending on what foods are present in your diet.
- limiting the consumption of coffee and other drinks and products containing caffeine (strong tea, chocolate, cocoa). Caffeine causes vasospasm and increased heart function, which creates increased stress on the cardiovascular system and harms patients with coronary artery disease and stenting. However, it is worth understanding: the diet does not require a complete abstinence from coffee; with controlled blood pressure and the absence of severe symptoms, it can be consumed in small quantities. It is better to choose natural Arabica beans - they have less caffeine than robusta and, especially, than instant coffee.
- adding vegetable oils, fresh vegetables and fruits, fish to the diet (consume at least 2 times a week). All this prevents the development of atherosclerosis. Dietary fiber from plant foods binds and removes cholesterol from the intestines, omega-polyunsaturated fatty acids from fish and vegetable oils reduce the content of harmful lipids (low-density lipoproteins, triglycerides) in the blood and increase the content of beneficial ones (high-density lipoproteins).
If your cardiologist recommends taking medications, you must follow this advice. The volume of drug therapy after surgery will decrease, but it is impossible to completely abandon medications for IHD. Follow the treatment regimen and do not forget: your good health after surgery is largely maintained due to the fact that you follow the therapy regimen.
If any complaints appear or the condition worsens, you should definitely consult a doctor for examination and treatment correction.
After undergoing stenting, it is recommended to quit smoking. Actually, this should be done before the operation, and it is best to never start smoking at all. However, if you have undergone surgery and still smoke, you can be given advice that will definitely help: quit cigarettes immediately!
Some patients console themselves with the thought that two or three cigarettes a day is quite a bit, and there will be no harm from them. This is wrong. Any type of smoking (active or passive) with any number of cigarettes smoked negatively affects the heart and blood vessels. It increases blood pressure, has a cardiotoxic effect, accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis, increases the likelihood of developing arrhythmias and the risk of heart attack. The pleasure derived from smoking is in no way justified by the enormous harm it causes.
Now about alcohol. It is a known fact that dry red wine has a healing effect on the heart. In some places you can even find information that it protects against atherosclerosis and almost causes the resorption of cholesterol plaques in the vessels. Indeed, small amounts of such wine have a beneficial effect on the course of atherosclerosis. However:
- we are talking about small quantities of the drink, no more than 1 glass of wine per day.
- only high-quality, expensive alcohol provides benefits, and not those types of alcohol that can be bought in any supermarket
— the benefits of red wine are not so obvious that it is mandatory to drink it regularly. The notorious cessation of smoking will bring many times greater benefits.
After the stenting operation, the patient will be able to return to normal work. The specific time frame for restoration of working capacity may vary; it depends on the person’s condition (the severity of coronary artery disease, the presence of a recent heart attack, etc.) and his profession. Intellectual workers can start working almost immediately after stenting, and those whose specialty is related to physical activity are allowed to start working later.
The stenting operation eliminates the symptoms of coronary artery disease, the person’s condition improves after it, therefore, it is quite rare to talk about registering disability for patients who have undergone it.
In the event that stenting does not lead to improvement, the patient’s angina returns early, or a heart attack occurs after the operation, assigning a disability group to the person is possible. However, this operation is not performed on people at risk of deterioration and complications, so usually stenting still gives a positive result and contributes to the restoration of a person’s performance, and not its final loss.
When a person’s condition stabilizes after surgery, he is allowed to travel by any means and without restrictions. The main thing is that a person regularly takes medications and follows other doctor’s recommendations. Among all types of recreation, it is better to choose an active one, taking into account your tolerance to physical activity. Patients are most often not contraindicated from visiting baths and saunas, although a more specific opinion on this matter should be given by a cardiologist.
A cardiologist is a doctor who often sees and observes his patients for years. Coronary heart disease is a chronic phenomenon, so this is not surprising.
Sometimes you come across such stories: a person develops hypertension, angina, then suffers a heart attack and undergoes stenting. However, even after this, the “adventures” do not end: periodically the patient is hospitalized with hypertensive crises, after some time his angina pectoris returns, he again undergoes stenting or even coronary bypass surgery... Repeated heart attacks and heart failure are not uncommon phenomena even after repeated operations. As a result, a person feels much worse than he could, and his life expectancy is reduced.
Why does this happen? The reason is not only the insidiousness and danger of the disease, although, undoubtedly, both are fully inherent in coronary heart disease. Most often, an unfavorable outcome of the disease is determined by the fact that a person makes insufficient efforts to improve his condition and prolong his life.
If you have had stent surgery and you are not following all the lifestyle recommendations, it is time to consider changing your attitude towards treatment. All the tips listed above are clear, simple and doable; you just need to follow them, constantly and conscientiously.
After stenting, hemodynamics change in the heart and throughout the body, so the body needs time to adapt to this. In addition, with stenting, a foreign body is actually installed in the coronary vessel. This causes a reaction from the immune system and blood clotting, creating an increased readiness in the body to accelerate the development of coronary atherosclerosis, the formation of blood clots in blood vessels, etc.
The period of hospital treatment is not enough for the body to fully recover, so cardiac rehabilitation is recommended for patients after stenting.
A set of health procedures will consolidate the results of therapy and improve a person’s condition. A special training program will help the patient get used to the new lifestyle.
Complications of myocardial infarction
The overwhelming majority of deaths from heart attack occur in the first hours and days and are associated with complications of myocardial infarction:
- Life-threatening arrhythmias - ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest;
- Cardiogenic shock is a condition that develops with extensive damage to the left ventricular myocardium and is characterized by a progressive decrease in blood pressure and impaired blood supply to vital organs;
- A cardiac aneurysm and its rupture are thinning of the heart wall and its protrusion under the pressure of blood in the ventricles. If an aneurysm ruptures, tamponade and cardiac arrest occur;
- Cardiac tamponade is a deadly complication of a cardiac aneurysm in which blood leaks into the pericardial cavity after the aneurysm ruptures. As a result of the rapid filling of the pericardium with blood, the heart can no longer carry out its pumping function and stops;
- Rupture of the interventricular septum;
- Acute heart failure (pulmonary edema);
- The occurrence of complete atrioventricular block and a decrease in heart rate to 20-30 per minute.
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction
First, the doctor examines the patient and collects information from the patient or his relatives about the nature and duration of pain, the strength and frequency of attacks, medications taken, and their effect on well-being.
Next, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics of myocardial infarction are carried out:
- general and biochemical blood tests (usually in a hospital setting);
- study of cardiac-specific enzymes and markers of damage to the heart muscle (usually in a hospital setting);
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart);
- coronary angiography (in a hospital setting).
Methodologies we use
Once the goal is set, the rehabilitation team creates a rehabilitation plan. He is very individual. At the Almadea Clinic we can offer many techniques. It is best to get an idea of all the options at your first meeting with the rehabilitation team. However, most often we use:
- Occupational therapy – restoration of everyday skills and self-care, learning to walk long distances without fatigue, training in dressing when shortness of breath and fatigue, selection of adaptive devices that help to live.
- Classes with a psychologist to restore memory, attention, to get rid of stress, to treat depression without medications.
- Sessions with a physical therapist to learn how to stand up, walk, climb stairs and walk.
- Training to restore endurance and reduce fatigue after a heart attack is carried out on a treadmill or on an exercise bike.
- A rehabilitation nurse can teach how to care for a critically ill patient.
- And also: physiotherapy, intravenous drips and injections, massage and more.
The duration of the course depends on the severity of the heart attack, the patient’s willingness to do homework, and the help of relatives. For some, a few small sessions will be enough. For others, recovery may take several months. The rehabilitation program is discussed with the patient and his relatives. We explain what and why we are doing.
Treatment of myocardial infarction
Intensive care measures for acute myocardial infarction may include:
- administration of thrombolytic agents to dissolve the blood clot and restore blood flow in the myocardium;
- pain relief (narcotic analgesics are often used);
- stabilization of blood pressure;
- the use of antianginal, antiarrhythmic drugs, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, etc.
Surgical techniques are often used in the treatment of myocardial infarction:
- angioplasty (expansion of a narrowed vessel using a balloon catheter);
- coronary stenting (installation of a stent at the site of narrowing of the coronary artery, after its expansion with a balloon);
- shunting (suturing a shunt that bypasses the narrowed area).
Post-hospital treatment of myocardial infarction (outpatient management after discharge from hospital) also includes a number of activities:
- observation by a cardiologist;
- pharmacotherapy;
- blood pressure and heart rate control;
- diet;
- avoiding stress, overwork and strain;
- recommended physical activity;
- rejection of bad habits.
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction and treatment of patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction at MedikCity
At the MedicCity clinic, the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and treatment of patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction, as well as those suffering from other cardiac diseases, are carried out at the highest professional level.
Our cardiologists are armed with the best expert-level equipment, extensive scientific knowledge and the latest developments!
We have reasonable prices and an individual approach. You can find out the schedule of specialists and the cost of services by calling: +7 (495) 604-12-12.
"MedicCity" is the right choice!
Rehabilitation options at the Almadeya Clinic
Outpatient rehabilitation
You come to our clinic, and our specialists will work on the equipment that we have. The clinic has an ergo-apartment - a training ground for everyday skills and self-care. In the exercise therapy room we have an exercise bike and a treadmill to restore walking and exercise tolerance. Using suspension systems, you can train muscles that don’t obey. The clinic has a variety of physical therapy techniques that will help restore impaired functions.
Rehabilitation at home
Our team comes to your home, you don't need to travel anywhere. You receive rehabilitation in a familiar environment, surrounded by family and friends. Our specialists even work with seriously ill patients who were refused admission to a rehabilitation hospital.
Rehabilitation online
Telerehabilitation is convenient when the patient is in another city or is afraid of contact with people due to an epidemic or for another reason.
We usually combine all these forms of rehabilitation. In this way, at-home rehabilitation can transition to outpatient or online rehabilitation.
Questions that concern patients with cardiovascular pathology and after myocardial infarction:
- What complications can there be?
- How is rehabilitation carried out for cardiovascular pathology and rehabilitation for a heart attack?
- What are the consequences of a heart attack?
- Is recovery possible after a myocardial infarction?
- How to live after myocardial infarction?
- What can and cannot be done after a myocardial infarction?
- How to have sex after myocardial infarction?
- How to work after a myocardial infarction, when can you go to work after a myocardial infarction?
- How is walking restored after myocardial infarction?
- How to evaluate the heart after a heart attack?
- What medications should I take after myocardial infarction?
- Why, after a heart attack, do I have shortness of breath, weakness, my head doesn’t work well, and I don’t want to do anything?
- In what cases is disability necessary after a heart attack?
- What exercises for the heart and what kind of gymnastics are needed after a heart attack?
Write to us what difficulty you encountered, and we will suggest further steps for rehabilitation or provide the missing information.