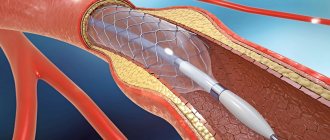
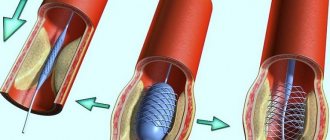
Stenting of cardiac vessels is an expensive operation that helps normalize blood circulation, restore arterial patency and prevent the development of serious complications. The intervention involves the introduction of a special balloon with a metal shell into the affected vessel, which expands the lumen of the vascular bed, eliminates atherosclerotic plaques and promotes the proper functioning of the cardiovascular system. However, one operation is not enough for the treatment result to be stable and long-lasting. It is important to strictly follow all doctor’s recommendations, including nutrition. Otherwise, stenting will not give the desired result, and atherosclerosis will progress. This can lead to a number of undesirable consequences - coronary heart disease, acute cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction.
Figures and facts
People who have had a heart attack have a higher risk of new cardiovascular events than those who have a healthy heart. Lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk. According to statistics, effective prevention of recurrent cardiovascular events through lifestyle changes saves 80,000 lives per year in the United States alone!
According to research, quitting smoking, regular physical activity and diet correction reduce mortality by 20-35%. However, despite such a powerful preventive effect, not all people are in a hurry to switch to a special diet after a myocardial infarction. It is known that only 43.4% of patients with cardiovascular diseases in high-income countries and 25.8% in low-income countries adhere to the principles of a healthy diet. Even after receiving full information about the importance of diet correction and the basic requirements for changing it, many patients simply reduce the caloric content of foods and continue to eat incorrectly. At the same time, the principles of healthy eating are simple both to understand and to implement.
What is a heart attack
A heart attack is damage or destruction of the heart muscle resulting from insufficient blood supply. The main risk factors are high blood pressure, high cholesterol and smoking.
Modern medicine makes it possible to save patients after a heart attack, returning them to their previous state. However, damage to the heart muscle significantly affects the heart rhythm and its functions. Therefore, it is extremely important to control all risk factors to prevent another heart attack. And diet plays a major role in this.
Principles of nutrition
Basic principles of a healthy diet:
- Eating vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts and seeds daily
- Predominance of healthy fats in the diet
- Eating fish or seafood two to three times a week
- Limiting consumption of fried and baked foods, especially chips, biscuits, cakes and other baked goods made from white flour
- Limiting salt intake.
An approximate diagram of a healthy diet, built in accordance with the fundamental principles of diet selection for cardiovascular diseases:
- At least five servings of vegetables and two servings of fruit per day. Let us remind you that a serving is approximately as much as fits in the palm of your hand (about 80 g)
- The presence of whole grain bread, durum wheat pasta, and rice in the diet
- Lean meat is preferred (fat should be trimmed and skin removed from poultry). Limiting the consumption of processed meats - sausages, sausages and other deli meats
- The presence of two to three servings of fish and seafood per week in the diet. They can be fresh, canned or frozen
- Presence of legumes in the diet. The menu should include lentils, peas, dried or canned beans, etc. at least twice a week.
- Eating about six eggs per week
- Limiting the consumption of pickled, fatty foods, baked goods, and sweets to a minimum
- Preference for skim milk and lactic acid products over full-fat dairy products
- The presence of unsaturated fats in the diet for cooking. Instead of spread, mayonnaise, margarine, use sunflower, olive, soybean, sesame oil
- Limiting the consumption of sugary drinks and tea, replacing coffee with caffeinated drinks.
What foods should you exclude?
Dishes high in salt, saturated fats and fast carbohydrates are unacceptable. The following are excluded: baked goods (rolls, pancakes, donuts, pastries, rolls, cakes, pies), fatty meat products (lard, boiled pork, brain, kidneys), fish (salted, smoked), broths (based on meat, mushrooms), chocolate , coffee, tomato juice.
In the early period, foods that promote gas formation are prohibited: tomatoes, cabbage, legumes.
Secrets of cooking healthy food3
A healthy diet is not just about lots of fruits, vegetables, fish and whole grains. This is also the correct heat treatment of dishes, which allows you to preserve the beneficial properties of the products.
How to fry correctly?
- Instead of frying the meat in a pan, it is better to wrap the meat in foil and bake in the oven or grill. It is better to do the same with fish and poultry.
- For frying, you should use sunflower and olive oil. To reduce the amount of oil soaked in food, use a non-stick frying pan.
- It is important to trim the fat from meat before cooking.
How to stew correctly?
- Use minimal salt.
- Refrigerate food immediately after cooking. The fat will harden on the surface, after which it can be removed.
What products are better to choose?
- Use low-fat lactic acid products and natural sugar-free yogurt
- Replace sour cream or mayonnaise with reduced-fat cottage cheese or natural low-fat yogurt
- Give preference to low-fat cheeses
- Use olive and other vegetable oils instead of cooking fats
- Choose lean meat and poultry without skin.
Harm from coffee
Coffee after a heart attack or coronary stenting should not be abused. To get a boost of energy, a small cup of coffee in the morning or before lunch will be enough. Before going to bed, the drink should be avoided.
If a person who has experienced an acute violation of cardiac circulation, after drinking coffee, feels an increased heart rate and slight dizziness, even such a portion of the invigorating drink should be completely avoided.
If the disease progresses calmly, there is no heart failure, or tachycardia, moderate consumption of coffee (preferably ground) will not cause harm. The patient must monitor his well-being, control the absence of shortness of breath, swelling in the abdominal area and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system.
Three enemies of the heart: fats...
Consumption of large amounts of saturated fat leads to increased cholesterol levels, mainly due to an increase in the content of the low-density lipoprotein fraction - the so-called bad cholesterol. Research shows that replacing saturated fats in the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are found in vegetable oils, can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events by 17%.
Sources of saturated fats in the diet are animal fats found in meat, poultry, and dairy products. They are also included in some vegetable oils, in particular palm and coconut. Saturated fat reserves are found in prepared foods - cookies, pastries, semi-finished products with cheese and meat.
Another very important risk factor for the development of heart and vascular pathology is trans fats. They increase your risk of coronary heart disease more than any other nutrient. Cardiovascular risk doubles for every 2% increase in calories consumed from trans fats.
Trans fats increase the level of total and “bad” cholesterol in the blood, and also reduce the level of “good” cholesterol - high-density lipoproteins. Trans fats are found in small amounts in dairy products, beef, veal, and lamb. But a much larger share in the diet can be occupied by industrial, artificial trans fats. They are used in baking, so cookies, cakes, buns and other delicacies are rich in trans fats. It should be taken into account that trans fats are also contained in butter: it contains 50% saturated and 4% trans fats. According to World Health Organization recommendations, the amount of saturated fat in the diet should be less than 10% of total energy intake, and the amount of trans fat should be less than 1%. Unsaturated fats should be used as a replacement.
Basic diet rules
The goal of the diet for myocardial infarction is to activate recovery processes in the heart muscle, create favorable conditions for normal blood circulation and metabolism, and ensure normal intestinal motor function.
According to the table of treatment tables according to Pevzner, the diet for myocardial infarction corresponds to table No. 10I.
General characteristics of the diet:
- a pronounced reduction in the calorie content of food due to all nutrients, but especially fats, a decrease in the amount of food, as well as salt and liquid.
The diet for myocardial infarction includes 3 diets, which are prescribed sequentially depending on the stage of the disease:
Diet 1
Such nutrition is prescribed in the first week of illness (acute period).
During this period, all dishes should be pureed, and the diet should be 6 times a day.
- Proteins should be 50g.
- fat 30-40g.,
- carbohydrates 150-200g.,
- free liquid 0.7-0.8 l per day.
The total calorie content of the diet is 1100 – 1300 kcal. Salt is not used.
Diet 2
This food is prescribed in the second or third week (subacute period). The food can be crushed, the diet corresponds to 6 times a day.
- The amount of proteins increases to 60-70g. per day,
- fat 50-60g.,
- 230-250 carbohydrates,
- free liquid 0.9-1.0 l,
- salt is allowed up to 3g. in a day.
The total calorie content of the table is 1600 – 1800 kcal.
Diet 3
This diet is prescribed during the scarring period, in the 4th week. Food is served chopped or in pieces. Diet 5 times a day.
- The amount of proteins increases to 85-90g.,
- fat up to 70g,
- 300-320g. carbohydrates,
- salt is allowed up to 5-6g. per day,
- free liquid up to 1-1.1 l.
Total calorie content 2100-2300 kcal.,
Food temperature
Food should not be too cold or hot, the optimal temperature is 15-50°C.
Diet
Food is taken often, but in small portions, to reduce the load on the cardiovascular system and digestive tract. The number of meals is increased by 2, the last meal should be eaten no later than three hours before bedtime.
Fortification of food
Food should be enriched with vitamins, especially A, C, D.
Water-soluble vitamins enter the body from fresh vegetables and fruits (their amount in the diet is increased), and fat-soluble vitamins from vegetable oils.
Limiting salt
Salt in the food of a patient with a myocardial infarction and after it is significantly reduced. Firstly, salt causes fluid retention and swelling, and secondly, it thickens the blood and impairs blood circulation.
Alcohol
All patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction are strictly prohibited from drinking alcohol. Alcohol has a stimulating effect on the nervous system, and also forces the cardiovascular system to work at an increased rate, which is very unfavorable in case of myocardial infarction. In addition, alcohol causes swelling and forces the kidneys to work double duty, which aggravates the disease.
… salt
Much attention should be paid to monitoring salt intake. It is known that excessive consumption of salty foods leads to the development of arterial hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases. When consuming more than 5 g of salt per day, the risk of heart disease and blood vessels increases by 17%, and the risk of stroke by 23%.
After a myocardial infarction, as well as after stenting, salt intake should be carefully monitored, given that it is contained in many prepared foods, including biscuits, processed and deli meats, sauces, pizza, hamburgers, etc. The World Health Organization recommends consuming no more than 5 g of salt per day.
What is recommended to enrich the diet with?
You can and should eat foods that promote rehabilitation after a heart attack:
- Fatty sea fish (omega-3 fatty acids reduce the risk of recurrent necrosis of the heart muscle).
- Yellow, red, green vegetables (antioxidants prevent the accumulation of toxic under-oxidized metabolic products in the body).
- Dried apricots, raisins, dates (a source of potassium - a heart rate stabilizer).
- Seafood (contains microelements that stabilize the rheological characteristics of the blood).
...and alcohol
A close connection has also been proven between excessive alcohol consumption and the development of cardiovascular diseases, in particular cardiomyopathy, arterial hypertension, arrhythmia, hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke. “Excessive” refers to drinking three or more units of alcohol per day.
One alcoholic unit is contained in 100 ml of wine or 285 ml of beer or 30 ml of spirits. There are no specific standards for alcohol consumption for a healthy diet. Obviously, one should strive to eliminate alcoholic beverages from the diet or at least minimize their consumption.
Infusion therapy
Drug drips are an integral part of treatment for symptoms of myocardial infarction. In particular, with this disease, ventricular tachycardia may occur, for which infusion solutions are indicated. In some cases, the Bezold-Jarisch reflex occurs in the myocardium, which is also suppressed by drugs administered through IVs. Anticoagulants and antiarrhythmic drugs are also administered. The method allows drugs to be distributed throughout the vascular system in the shortest possible time.
How is stenting performed?
Stenting is a minimally invasive operation that is performed under local anesthesia in the cath lab.
Through puncture of the radial artery in the arm (in most cases) or the femoral artery, the coronary artery is catheterized with a special guiding catheter.
Then a stent is delivered to the area of the coronary artery narrowed by the atherosclerotic plaque through a guidewire. A stent is a metal frame in the form of a compressed tube, placed on a balloon. The balloon is inflated and removed, and the stent remains in the artery as a scaffold, thereby leaving the artery lumen free for blood flow.