© Author: Sazykina Oksana Yuryevna, cardiologist, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Repolarization of the myocardium, or cardiac muscle, is one of many biochemical processes that occur in the cells of the heart to ensure myocardial contractility. So, in order for a cell (cardiomyocyte) to begin to contract, it must receive electrical stimulation. This is ensured by the flow of positively charged ions into the cell through the cell membrane. Then the membrane will change charge, and the energy necessary for contraction will be released. A kind of electrical “restart” of the cell occurs, as a result of which it contracts. This mechanism is called depolarization . And repolarization occurs after the cell returns to its original state, that is, the cell “rests” after the work done. In this way, any muscle cell in the body contracts.
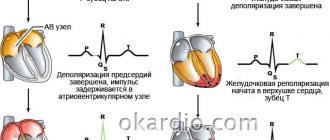
The processes of depolarization and repolarization alternate strictly and regularly, ensuring the systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation) phases of the heart. The repolarization phase is a kind of resting phase, during which it is almost impossible to excite the cell. This phase on the electrocardiogram corresponds to the QT interval.
stages of depolarization and repolarization in the myocardium and their reflection on the ECG (depolarization is shown in yellow, repolarization in red)
With heart disease, or in the absence of cardiac pathology, but with a violation of the regulatory effect on the cardiovascular system in humans, the processes of myocardial repolarization may be disrupted. Sometimes this manifests itself with certain symptoms and requires treatment, and sometimes regular examination by a cardiologist is sufficient.
Causes of disturbances in ventricular repolarization processes
As a rule, repolarization disorders are diagnosed in people over 50 years of age, but in recent years their prevalence among patients under forty years of age has increased. These processes in the heart muscle in adults can be caused by both completely harmless reasons and serious diseases of the heart or other organs. So, in the latter case, when pathological processes occur in the myocardium of one location or another, the cells lose the ability to exchange ions between the intracellular and extracellular environments. For example, if inflammatory, ischemic processes or necrosis occur in the heart muscle, followed by the replacement of normal tissue with connective tissue scars, then the normal cycle of de- and repolarization phases is disrupted.
The main causative factors that can provoke disruption of chemical-electrical processes in the myocardium include the following:
- Myocarditis,
- Myocardial ischemia,
- Previous myocardial infarction with the formation of a post-infarction scar, atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis,
- Arterial hypertension with the formation of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,
- Cardiomyopathy of a restrictive, dilated or hypertrophic nature of any origin,
- The so-called “athlete’s heart”, when professional athletes have an enlargement of the left chambers of the heart with myocardial hypertrophy,
- Congenital defects of genes encoding the transport of ions into the cell cause long and short QT interval syndromes, as well as early ventricular repolarization syndrome (EVRS),
- Taking certain medications - atropine, cardiac glycosides, adrenaline, etc.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia (neurocirculatory).
Also, disturbances in repolarization processes in the myocardium are characteristic of changes in neuro-regulatory influences on the heart, in particular from the vagus nerve and sympathetic nervous system, or from the adrenal glands, when the latter produce excess amounts of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the blood. Disturbances in the normal functioning of the heart muscle often occur due to pathology of the thyroid gland, because the hormones released into the blood by the gland have a direct effect on the heart.
As a rule, widespread processes in the myocardium (ischemia, cardiosclerosis, cardiomyopathy) cause the occurrence of diffuse disturbances in repolarization processes, and limited ones cause local disturbances. For example, with neurocirculatory dystonia, repolarization disturbances occur in the anteroseptal region of the left ventricle, after a heart attack of the lateral and high-lateral sections - along the lateral wall, and after a myocardial infarction along the posterior wall of the LV - repolarization disturbances in the lower or upper wall of the LV.
depolarization and repolarization of the myocardium is normal
depolarization and repolarization of the myocardium during ischemia
In the case where no visible causes can be identified in a patient, but disturbances in repolarization processes are detected, they are called nonspecific.
In addition to pathological causes, moderate disturbances in the processes of repolarization of the left ventricle can also occur in a completely healthy person. This is detected when a patient with repolarization disorders diagnosed by ECG after further examination does not reveal any problems with the heart or other organs. In this case, repolarization disorders practically do not pose a threat to the patient’s life.
How are phase changes monitored on a cardiogram?
Pathological disturbances of repolarization provoke changes in the ECG curve of the height of the T wave. However, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis - this phenomenon is observed not only in heart diseases, but also in any metabolic disorders. If a shift in the ST segment is also observed, this indicates an imbalance in the electrolyte balance in the cells. The repolarization process can be disrupted by a serious pathology - hypersympathicotonia, accompanied by an increase in the level of adrenaline in the blood.
Many people have pathological changes in the lower wall of the heart muscle, completely unaware of it - such processes are caused by heavy physical labor, constant stressful situations, hormonal disorders and aging of the body
This condition is caused by an increase in the tone of the sympathetic department of the autonomic system and causes:
- decreased sweating, secretion of saliva and mucus;
- dry skin;
- tachycardia;
- painful sensations in the heart;
- noticeable change in mood;
- increased blood pressure.
Are disturbances in repolarization processes manifested clinically?
Chemical-electrical disorders themselves do not have strictly specific symptoms, therefore, a violation of repolarization processes is an ECG syndrome. Patients with such disorders may experience increased fatigue, reduced tolerance to normal physical activity due to fatigue, discomfort or pain in the chest, dizziness or shortness of breath on exertion.
However, if repolarization disorders in a patient are caused by one or another pathology, its corresponding signs become the leading symptoms. Thus, in the presence of ischemic changes in the myocardium, attacks of angina pectoris occur; in heart failure due to post-infarction scar changes or cardiomyopathy - shortness of breath during exercise or at rest along with edema, etc.
In the case when disturbances in repolarization processes are complicated by the development of arrhythmia or ventricular tachycardia, the patient experiences interruptions in heart function, a feeling of rapid heartbeat, sweating, dizziness, fainting and other signs of arrhythmia, up to arrhythmogenic shock or clinical death. The latter conditions are caused by the occurrence of complications due to short or long QT syndrome. Thus, when QT is shortened, rhythm disturbances of the re-entry type, for example, atrial fibrillation, are more common, and when QT is lengthened, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia occurs.
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms are observed only in the form of the disease that is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system:
- loss of consciousness, fainting ;
- rhythm disturbances ( tachyarrhythmia , extrasystole , ventricular fibrillation );
- vagotonic, hyperamphotonic, tachycardial, dystrophic are formed under the influence of humoral factors on the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- systolic and diastolic dysfunction of the heart caused by its hemodynamic disorders ( pulmonary edema , hypertensive crisis , shortness of breath , cardiogenic shock ).
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that the patient does not have any strictly specific complaints characteristic of repolarization disorders, the diagnosis is made on the basis of an electrocardiogram. Therefore, the main diagnostic method is the ECG and its variations - daily ECG monitoring, ECG after exercise, and sometimes transesophageal ECG.
The main criteria on the cardiogram are the following signs:
- The presence of a small R wave in the ventricular QRST complex,
- Presence of oblique elevation (ST segment elevation),
- Changes in the T wave - it becomes narrow, asymmetrical and even negative, as with ischemic changes.
Such changes are most typical of early ventricular repolarization syndrome (EVRS), which often occurs in children, adolescents, young adults and athletes. This syndrome is one of the variants of disruption of repolarization processes.
classic variant of changes in SRGC
Other variants of repolarization disorder are short QT syndrome and long QT syndrome. The last two syndromes should not be confused with short PQ syndrome, as they are completely different types of heart rhythm disorders. Short QT syndrome is manifested on the cardiogram by a decrease in the duration of the QT interval of less than 0.33-0.35 s, and long QT syndrome is manifested by an increase in the duration of the interval of more than 0.47-0.48 s.
If the patient has an underlying pathology that could serve as a causative factor for the repolarization disorder, the patient is prescribed additional examination. Standard methods usually include echocardioscopy, blood testing for thyroid or adrenal hormones, chest radiography, and in case of heart attacks or ischemic changes according to ECG, coronary angiography.
Classification and risk groups
There is the following classification of early repolarization syndrome:
- with damage to the heart muscle and blood vessels;
- there is no lesion.
The syndrome is also classified according to the degree of severity on the electrocardiogram into 3 classes:
- Minimal (observed in a small number of leads, from 2 to 3).
- Moderate (the number of leads increases from 4 to 5).
- Maximum (6 or more leads).
According to statistics, abnormalities in the functioning of the heart are detected 3 times more often in males.
However, most often the disease appears during pregnancy or menopause in women, since at this time the sensitivity of the body increases significantly and the general hormonal background changes. The disease is detected, as a rule, during routine examinations, in case of any complaints about well-being.
Professional athletes who experience constant physical activity and people who have suffered from hypothermia are also at risk. And some doctors even claim that the disease is hereditary.
tonometra.net
When is treatment required?
The question of the need to treat disorders of repolarization processes should be resolved as soon as possible after they are detected on the cardiogram and further examination of the patient. In the absence of a causative cardiac pathology, the patient is prescribed medications or a pacemaker is installed, based on the presence or absence of clinical manifestations of tachyarrhythmias (fainting, tachycardia, heart failure).
Thus, due to the fact that short QT interval syndrome often leads to life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias, all patients with this syndrome need to determine the indications for implantation of an electrical pacemaker (pacemaker) (cardioverter-defibrillator).
Patients with long QT syndrome require pacemaker implantation if they have a history of life-threatening arrhythmias or a high risk of sudden cardiac death (for example, there is a family history of sudden cardiac death at a young age for no apparent reason and without the presence of obvious cardiac pathology). If the risk is not great, it is enough for the patient to take a drug from the group of beta-blockers (BAB), for example, Concor, Egilok, Coronal, etc.
In case of early repolarization syndrome without other cardiac pathology (isolated ERR, for example, in athletes), it is enough for the patient to limit participation in sports events and competitions. If there is organic damage to the myocardium, a complex of necessary drugs is prescribed (nitrates for ischemic changes and angina pectoris, diuretics for heart failure, antihypertensives for hypertension, etc.).
Thus, short QT syndrome requires treatment in any case , and early repolarization syndrome and long QT syndrome require treatment when there are clinical manifestations of tachyarrhythmias in the form of fainting and/or a high risk of sudden cardiac death has been identified and/or there is any other heart pathology. But in any case, the treatment is completely selected by the attending physician, since self-medication can cause irreparable harm to health.
Disturbances in the process of cardiac repolarization in children
In children, any of the described repolarization disorders may occur. Most often, long and short QT syndromes (QT interval syndrome and QT interval syndrome, respectively) are caused by genetic defects. Therefore, when such syndromes are detected in a child, special attention is paid to the following data:
- Clinical data - fainting (with or without stress), congenital deafness,
- Family history data (established diagnosis of QT SUDD or QT QT, sudden cardiac death in close relatives before the age of 30).
If congenital syndromes are suspected, a genetic study is performed to identify mutant genes. However, the study often produces false positive and false negative results. Apart from congenital genetic defects, other common causes of the syndromes are congenital and acquired heart defects, as well as cardiomyopathies.
Unlike QT SIDS and QT SIDS, which are almost always caused by genetics or heart disease, SRCC most often occurs in isolation, that is, without any other pathology. Such a child only requires regular monitoring by a cardiologist with an ECG performed twice a year, as well as adherence to a correct lifestyle with limiting excessive physical activity.
Forecast
The prognosis for isolated early ventricular repolarization syndrome is completely favorable. The prognosis in the presence of any of the repolarization disorders caused by other diseases is determined by the nature and severity of this disease. For example, the prognosis for a heart defect that was not promptly corrected surgically is unfavorable, while after surgery the duration and quality of life increase significantly. Again, cases of sudden cardiac death among young relatives in the family significantly worsen the prognosis for the patient, and the absence of family history and clinical manifestations have a more favorable prognostic value.